【JUC基础】JUC入门基础(二)
目录
-
- 异步回调
- JMM 理解
-
- 对 volatile 的理解
-
- 1、保证可见性
- 2、不保证原子性
- 3、禁止指令重排
- 对 JMM 的理解
- 详解单例模式
-
- 饿汉式
- 懒汉式
- DCL懒汉式:双重检测锁模式的懒汉式单例
- 静态内部类实现单例
- 通过反射破坏单例,修改后的DCL饿汉式
- 枚举实现单例防止反射破坏
- 理解 CAS(compareAndSwap)
- CAS 出现的 ABA 问题
-
- 理解 ABA 问题
- 解决 ABA 问题(带版本号的原子操作、乐观锁思想)
- 公平锁,非公平锁
- 可重入锁(递归锁)
- 自旋锁
- 排除死锁
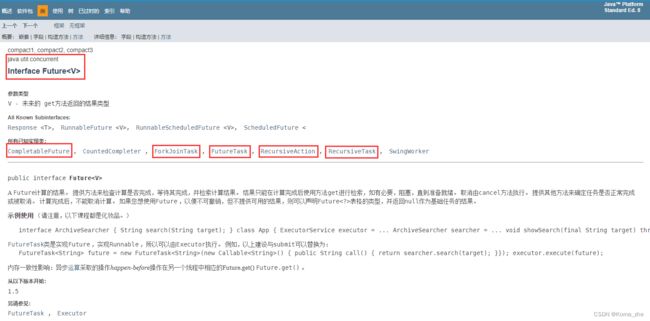
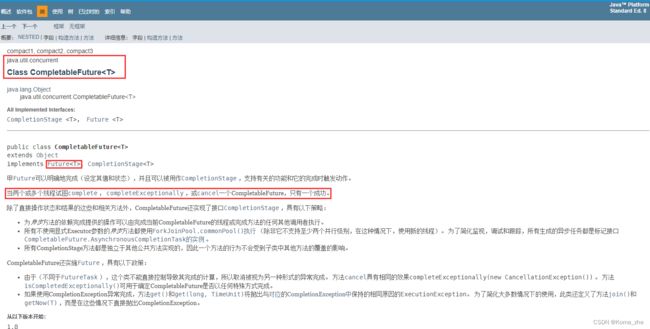
异步回调
- 没有返回值的 runAsync 异步回调
import java.util.concurrent.*;
/**
* 异步调用: CompletableFuture
* 异步执行
* 成功回调
* 失败回调
*/
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
//发起一个请求 void
// 没有返回值的 runAsync 异步回调
CompletableFuture<Void> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "runAsync=>void");
});
System.out.println("11111111");
completableFuture.get();//获取执行结果
}
}
- 有返回值的异步回调 supplyAsync
import java.util.concurrent.*;
/**
* 异步调用: CompletableFuture
* 异步执行
* 成功回调
* 失败回调
*/
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
// completableFuture.get(); // 获取阻塞执行结果
// 有返回值的 supplyAsync 异步回调
// ajax,成功和失败的回调
// 失败返回的是错误信息;
CompletableFuture<Integer> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "supplyAsync=>Integer");
//int i = 10 / 0;
return 1024;
});
//whenComplete: 参数BiConsumerJMM 理解
对 volatile 的理解
1、保证可见性
import java.util.concurrent.*;
public class test {
// 如果不加volatile 程序会死循环
// 加了volatile是可以保证可见性的
private volatile static Integer number = 0;
//main线程
public static void main(String[] args) {
//子线程1
new Thread(()->{
while (number==0){
}
}).start();
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//子线程2
new Thread(()->{
while (number==0){
}
}).start();
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
number=1;
System.out.println(number);
}
}
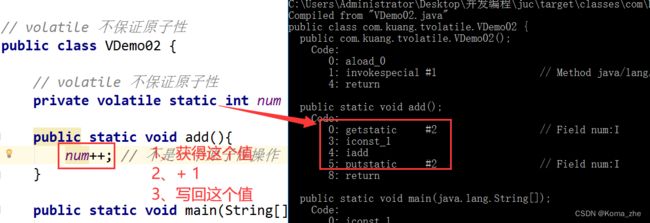
2、不保证原子性
public class test {
private static volatile int number = 0;
public static void add() {
number++;//++ 不是一个原子性操作,是 2~3 个操作
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//理论上number == 20000
for (int i = 1; i <= 20; i++) {
new Thread(() -> {
for (int j = 1; j <= 1000; j++) {
add();
}
}).start();
}
//main gc
while (Thread.activeCount() > 2) {
Thread.yield(); //yield让出计算资源并重新竞争资源
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ",num=" + number);//每次都不一样
}
}
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
public class test {
// 这些类的底层都直接和操作系统挂钩,是在内存中修改值。
private static volatile AtomicInteger number = new AtomicInteger();
public static void add(){
//number++;
number.incrementAndGet(); //底层是 CAS 保证的原子性
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//理论上number=20000
for (int i = 1; i <= 20; i++) {
new Thread(()->{
for (int j = 1; j <= 1000 ; j++) {
add();
}
}).start();
}
//main gc
while (Thread.activeCount()>2){
Thread.yield();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+",num="+number);
}
}
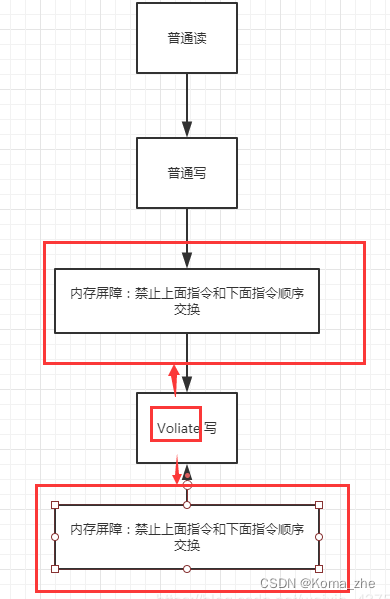
3、禁止指令重排
源代码 –> 编译器优化重排 –> 指令并行也可能会重排 –> 内存系统也会重排 –> 执行
int x=1; //1
int y=2; //2
x=x+5; //3
y=x*x; //4
//期望的执行顺序是 1_2_3_4 可能执行的顺序会变成2134 1324
volatile 可以避免指令重排:volatile 中会加一道内存的屏障,这个内存屏障可以保证在这个屏障中的指令顺序。
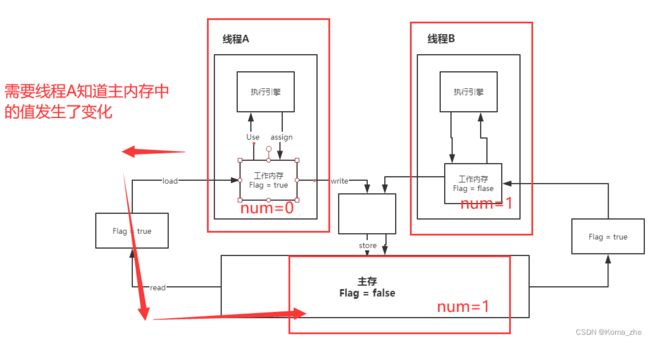
对 JMM 的理解
JMM:Java内存模型,不存在的东西,是一个概念,也是一个约定。
关于 JMM 的一些同步的约定:
- 1、线程解锁前,必须把共享变量立刻刷回主存
- 2、线程加锁前,必须读取主存中的最新值到工作内存中
- 3、加锁和解锁是同一把锁
线程中分为工作内存、主内存。
8种操作:(读read,加载load)(使用use,赋值assign)(写write,存储store)(加锁lock,解锁unlock)
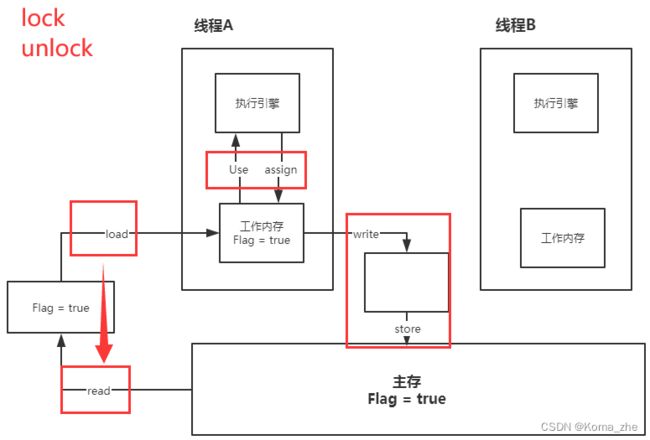
内存交互操作有8种,虚拟机实现必须保证每一个操作都是原子的,不可在分的(对于 double 和 long 类型的变量来说,load、store、read 和 write 操作在某些平台上允许例外)
- read(读取):作用于主内存变量,它把一个变量的值从主内存传输到线程的工作内存中,以便随后的load动作使用;
- load(载入):作用于工作内存的变量,它把read操作从主存中变量放入工作内存中;
- use(使用):作用于工作内存中的变量,它把工作内存中的变量传输给执行引擎,每当虚拟机遇到一个需要使用到变量的值,就会使用到这个指令;
- assign(赋值):作用于工作内存中的变量,它把一个从执行引擎中接受到的值放入工作内存的变量副本中;
- store(存储):作用于主内存中的变量,它把一个从工作内存中一个变量的值传送到主内存中,以便后续的write使用;
- write(写入):作用于主内存中的变量,它把store操作从工作内存中得到的变量的值放入主内存的变量中;
- lock(锁定):作用于主内存的变量,把一个变量标识为线程独占状态;
- unlock(解锁):作用于主内存的变量,它把一个处于锁定状态的变量释放出来,释放后的变量才可以被其他线程锁定;
JMM对这八种指令的使用,制定了如下规则:
- 不允许 read 和 load、store 和 write 操作之一单独出现,必须成对使用。即使用了 read 必须 load,使用了store 必须 write
- 不允许线程丢弃他最近的 assign 操作,即工作变量的数据改变了之后,必须告知主存
- 不允许一个线程将没有 assign 的数据从工作内存同步回主内存
一个新的变量必须在主内存中诞生,不允许工作内存直接使用一个未被初始化的变量。就是怼变量实施 use、store操作之前,必须经过 assign 和 load 操作 - 一个变量同一时间只有一个线程能对其进行 lock。多次 lock 后,必须执行相同次数的 unlock 才能解锁
- 如果对一个变量进行 lock 操作,会清空所有工作内存中此变量的值,在执行引擎使用这个变量前,必须重新 load 或 assign 操作初始化变量的值
- 如果一个变量没有被 lock,就不能对其进行 unlock 操作。也不能unlock一个被其他线程锁住的变量对一个变量进行 unlock 操作之前,必须把此变量同步回主内存
详解单例模式
饿汉式
//饿汉式单例
public class Hungry {
//一上来就实例化,可能会浪费空间
private byte[] data1 =new byte[1024*1024];
private byte[] data2 =new byte[1024*1024];
private byte[] data3 =new byte[1024*1024];
private byte[] data4 =new byte[1024*1024];
//私有化构造器
private Hungry() {
}
private final static Hungry HUNGRY = new Hungry();
public Hungry getInstance() {
return HUNGRY;
}
}
懒汉式
// 懒汉式单例
public class LazyMan {
//构造器私有化
private LazyMan() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"OK");
}
private static LazyMan lazyMan;
public static LazyMan getInstance() {
if (lazyMan == null) {
lazyMan = new LazyMan();
}
return lazyMan;
}
//多线程并,会有隐患!
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
new Thread(()->{
lazyMan.getInstance();
}).start();
}
}
}
DCL懒汉式:双重检测锁模式的懒汉式单例
// 懒汉式 DCL单例
public class LazyMan {
// 构造器私有化
private LazyMan() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "OK");
}
// 加volatile,防止指令重排
private volatile static LazyMan lazyMan;
// 双重检测锁模式的 懒汉式单例 DCL懒汉式
public static LazyMan getInstance() {
// 第一次检查
if (lazyMan == null) {
synchronized (LazyMan.class) {
// 第二次检查
if (lazyMan == null) {
lazyMan = new LazyMan();
/**
* 1. 分配内存空间
* 2、执行构造方法,初始化对象
* 3、把这个对象指向这个空间
* 执行顺序123,132都有可能
* A:123 B:132
* B把这个对象指向这个空间,发现不为空执行return
* 但是此时在线程A中,lazyMan还没有完成构造,lazyMan要加volatile,防止指令重排
*/
}
}
}
return lazyMan;
}
//多线程并发
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
new Thread(() -> {
lazyMan.getInstance();
}).start();
}
}
}
静态内部类实现单例
public class Singleton {
private static class SingletonHolder {
private static final Singleton INSTANCE = new Singleton();
}
private Singleton() {
}
public static Singleton getInstance() {
return SingletonHolder.INSTANCE;
}
}
通过反射破坏单例,修改后的DCL饿汉式
// 懒汉式单例
public class LazyMan {
private volatile static LazyMan lazyMan;
//私有化构造器
private LazyMan() {
synchronized (LazyMan.class) {
if (lazyMan != null) {
throw new RuntimeException("不要试图使用反射破坏异常");
}
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "OK");
}
// 双重检测锁模式的 懒汉式单例 DCL懒汉式
public static LazyMan getInstance() {
if (lazyMan == null) {
synchronized (LazyMan.class) {
if (lazyMan == null) {
lazyMan = new LazyMan();// 不是一个原子性操作
}
}
}
return lazyMan;
}
//多线程并发
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
LazyMan instance = LazyMan.getInstance();
Constructor<LazyMan> declaredConstructor = LazyMan.class.getDeclaredConstructor(null);
declaredConstructor.setAccessible(true);//无视私有
LazyMan instance2 = declaredConstructor.newInstance();
System.out.println(instance);
System.out.println(instance2);
}
}
//可以继续破坏
枚举实现单例防止反射破坏
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
// enum 本身也是一个 Class 类
public enum EnumSingle {
INSTANCE;
public EnumSingle getInstance(){
return INSTANCE;
}
}
class Test{
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
EnumSingle instance1 = EnumSingle.INSTANCE;
//java.lang.NoSuchMethodException: com.zzy.single.EnumSingle.() 没有空参构造方法
//Constructor declaredConstructor = EnumSingle.class.getDeclaredConstructor(null);
//反编译中,只有有参构造方法 EnumSingle(String s, int i)
//java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: Cannot reflectively create enum objects
Constructor<EnumSingle> declaredConstructor = EnumSingle.class.getDeclaredConstructor(String.class,int.class);
declaredConstructor.setAccessible(true);
EnumSingle instance2 = declaredConstructor.newInstance();
System.out.println(instance1);
System.out.println(instance2);
}
}
理解 CAS(compareAndSwap)
CAS : compareAndSet 比较并交换
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
public class test {
//CAS : compareAndSet 比较并交换
public static void main(String[] args) {
AtomicInteger atomicInteger = new AtomicInteger(2020);
//boolean compareAndSet(int expect, int update)
//期望值、更新值
//如果实际值 和 期望值相同,那么就更新
//如果实际值 和 期望值不同,那么就不更新
System.out.println(atomicInteger.compareAndSet(2020, 2021));
System.out.println(atomicInteger.get());
//因为期望值是2020 实际值却变成了2021 所以会修改失败
//CAS 是CPU的并发原语
atomicInteger.getAndIncrement(); //++操作
System.out.println(atomicInteger.compareAndSet(2020, 2021));
System.out.println(atomicInteger.get());
}
}
CAS : compareAndSet 比较并交换源码:
public class AtomicInteger extends Number implements java.io.Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 6214790243416807050L;
// Java无法操作内存,C++可以,Java通过native方法调用C++
// Java通过Unsafe类操作内存
private static final Unsafe unsafe = Unsafe.getUnsafe();
private static final long valueOffset;
static {
try {
// 获取内存地址的偏移值
valueOffset = unsafe.objectFieldOffset
(AtomicInteger.class.getDeclaredField("value"));
} catch (Exception ex) { throw new Error(ex); }
}
private volatile int value;
...
public final boolean compareAndSet(int expect, int update) {
return unsafe.compareAndSwapInt(this, valueOffset, expect, update);
}
public final int getAndIncrement() {
return unsafe.getAndAddInt(this, valueOffset, 1);
}
// 内存操作,效率很高
// 自旋锁
// Unsafe类 unsafe.getAndAddInt(this, valueOffset, 1)
// var1 = this; var2 = valueOffset; var4 = 1
public final int getAndAddInt(Object var1, long var2, int var4) {
int var5;
do {
// 获取内存地址valueOffset中的值
var5 = this.getIntVolatile(var1, var2);
} while(!this.compareAndSwapInt(var1, var2, var5, var5 + var4));
// while中:如果当前对象var1中的内存地址偏移值var2,这个值如果还等于var5,那么这个值等于var5+var4
return var5;
}
CAS 出现的 ABA 问题
CAS:比较当前工作内存中的值和主内存中的值,如果这个值是期望的,那么则执行操作,如果不是就一直循环,使用的是自旋锁。
缺点:
- 循环会耗时
- 一次性只能保证一个共享变量的原子性
- 存在ABA问题
理解 ABA 问题
狸猫换太子:
- 线程1:期望值是1,要变成2;
- 线程2:两个操作:
1、期望值是1,变成3
2、期望是3,变成1
所以对于线程1来说,A的值还是1,所以就出现了问题,骗过了线程1
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
public class test {
// CAS compareAndSet : 比较并交换
public static void main(String[] args) {
AtomicInteger atomicInteger = new AtomicInteger(2020);
//public final boolean compareAndSet(int expect, int update)
// 如果我期望的值达到了,那么就更新,否则,就不更新, CAS 是CPU的并发原语!
// ============== 捣乱的线程 ==================
System.out.println(atomicInteger.compareAndSet(2020, 2021));
System.out.println(atomicInteger.get());
System.out.println(atomicInteger.compareAndSet(2021, 2020));
System.out.println(atomicInteger.get());
// ============== 期望的线程 ==================
System.out.println(atomicInteger.compareAndSet(2020, 77777));
System.out.println(atomicInteger.get());
}
}
解决 ABA 问题(带版本号的原子操作、乐观锁思想)
解决 ABA 问题:引入原子引用,对应的思想:乐观锁。
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicStampedReference;
public class test {
//AtomicStampedReference 注意,如果泛型是一个包装类,注意对象的引用问题,正常在业务操作,这里面比较的都是一个个对象
static AtomicStampedReference<Integer> atomicStampedReference = new
AtomicStampedReference<>(1, 1);
// CAS compareAndSet : 比较并交换
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Thread(() -> {
// 获得版本号
int stamp = atomicStampedReference.getStamp();
System.out.println("a1版本号=>" + stamp);
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 修改操作时,版本号更新 + 1
atomicStampedReference.compareAndSet(1, 2,
atomicStampedReference.getStamp(),
atomicStampedReference.getStamp() + 1);
System.out.println("a2版本号=>" + atomicStampedReference.getStamp());
// 重新把值改回去, 版本号更新 + 1
System.out.println(atomicStampedReference.compareAndSet(2, 1,
atomicStampedReference.getStamp(),
atomicStampedReference.getStamp() + 1));
System.out.println("a3版本号=>" + atomicStampedReference.getStamp());
}, "a").start();
// 乐观锁的原理相同!
new Thread(() -> {
// 获得版本号
int stamp = atomicStampedReference.getStamp();
System.out.println("b1=>" + stamp);
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(atomicStampedReference.compareAndSet(1, 3,
stamp, stamp + 1));
System.out.println("b2=>" + atomicStampedReference.getStamp());
}, "b").start();
}
}
公平锁,非公平锁
- 公平锁: 非常公平, 不能够插队,必须先来后到
- 非公平锁:非常不公平,可以插队 (默认都是非公平)
// ReentrantLock 源码
public class ReentrantLock implements Lock, java.io.Serializable {
...
public ReentrantLock() {
sync = new NonfairSync();
}
public ReentrantLock(boolean fair) {
sync = fair ? new FairSync() : new NonfairSync();
}
...
}
可重入锁(递归锁)
拿到外面的锁之后,就可以自动获得拿到里面的锁
//Synchronized
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Phone phone = new Phone();
new Thread(() -> {
phone.sms();
}, "A").start();
new Thread(() -> {
phone.sms();
}, "B").start();
}
}
class Phone {
//外面一把锁
public synchronized void sms() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":sms");
//里面一把锁
call();
}
public synchronized void call() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":call");
}
}
//一定是
/*
A:sms
A:call
B:sms
B:call
*/
Lock 锁必须配对,相当于 lock 和 unlock 必须数量相同,在外面加的锁,也可以在里面解锁;在里面加的锁,在外面也可以解锁
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
//Lock
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Phone2 phone = new Phone2();
new Thread(() -> {
phone.sms();
}, "A").start();
new Thread(() -> {
phone.sms();
}, "B").start();
}
}
class Phone2 {
Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
public void sms() {
lock.lock();
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":sms");
//里面还有锁
call();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public void call() {
lock.lock();
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":call");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
自旋锁
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicReference;
//自旋锁
public class SpinlockDemo {
//初始: int -> 0; 引用类型 Thread -> null
AtomicReference<Thread> atomicReference = new AtomicReference<>();
// 加锁
public void myLock() {
Thread thread = Thread.currentThread();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "==> myLock");
//自旋锁
while (!atomicReference.compareAndSet(null, thread)) {
}
}
// 解锁
public void myUnlock() {
Thread thread = Thread.currentThread();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "==> myUnlock");
//自旋锁
atomicReference.compareAndSet(thread, null);
}
}
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class TestSpinLock {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//ReentrantLock
/* ReentrantLock reentrantLock = new ReentrantLock();
reentrantLock.lock();
reentrantLock.unlock();*/
// 底层使用的自旋锁 CAS
SpinlockDemo lock = new SpinlockDemo();
new Thread(()->{
lock.myLock();
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.myUnlock();
}
},"T1").start();
new Thread(()->{
lock.myLock();
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.myUnlock();
}
},"T2").start();
}
}
/*
T1==> myLock
T2==> myLock //必须等T1解锁,自旋
T1==> myUnlock
T2==> myUnlock
*/
排除死锁
A、B各持有锁,试图获取对方的锁,例如:
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String lockA = "lockA";
String lockB = "lockB";
new Thread(new MyThread(lockA, lockB), "T1").start();
new Thread(new MyThread(lockB, lockA), "T2").start();
}
}
class MyThread implements Runnable {
private String lockA;
private String lockB;
public MyThread(String lockA, String lockB) {
this.lockA = lockA;
this.lockB = lockB;
}
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (lockA) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "lock: " + lockA + "=> get: " + lockB);
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
synchronized (lockB) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "lock: " + lockB + "=>get: " + lockA);
}
}
}
}
使用 jstack 进程号,找到死锁问题,进程号由 jps -l 得到
...
"T2":
at JUC_learn.MyThread.run(test.java:36)
- waiting to lock <0x053bedc8> (a java.lang.String)
- locked <0x053bedf0> (a java.lang.String)
at java.lang.Thread.run(Thread.java:745)
"T1":
at JUC_learn.MyThread.run(test.java:36)
- waiting to lock <0x053bedf0> (a java.lang.String)
- locked <0x053bedc8> (a java.lang.String)
at java.lang.Thread.run(Thread.java:745)
Found 1 deadlock.