2022羊城杯密码wp
Crypto
3-1LRSA
给了P*P*Q,P*Q*Q,gcd()求出P*Q再分别除以它求出P,Q
给了t=(p*P-58*P+q)%Q,已知t,P,Q求p,q,其中t=44很小
所以有:
( p − 58 ) ∗ P = ( q − t ) % Q ( p − 58 ) ∗ P − k ∗ Q = ( q − t ) (p-58)*P=(q-t)\ \%\ Q\\ (p-58)*P-k*Q=(q-t) (p−58)∗P=(q−t) % Q(p−58)∗P−k∗Q=(q−t)
( p − 58 − k ) ∗ ( 1 P 0 Q ) = ( p − 58 q − t ) \begin{pmatrix} p-58 & -k \\ \end{pmatrix}\ *\begin{pmatrix} 1 & P \\ 0 & Q \end{pmatrix} = \begin{pmatrix} p-58 & q-t \end{pmatrix} (p−58−k) ∗(10PQ)=(p−58q−t)
( 1 P 0 Q ) \begin{pmatrix} 1 & P \\ 0 & Q \end{pmatrix} (10PQ)为我们所需的格子
from Crypto.Util.number import *
from gmpy2 import *
B = 1023
P2Q = 17550772391048142376662352375650397168226219900284185133945819378595084615279414529115194246625188015626268312188291451580718399491413731583962229337205180301248556893326419027312533686033888462669675100382278716791450615542537581657011200868911872550652311318486382920999726120813916439522474691195194557657267042628374572411645371485995174777885120394234154274071083542059010253657420242098856699109476857347677270860654429688935924519805555787949683144015873225388396740487817155358042797286990338440987035608851331840925854381286767024584195081004360635842976624747610461507795755042915965483135990495921912997789567020652729777216671481467049291624343256152446367091568361258918212012737611001009003078023715854575413979603297947011959023398306612437250872299406744778763429172689675430968886613391356192380152315042387148665654062576525633130546454743040442444227245763939134967515614637300940642555367668537324892890004459521919887178391559206373513466653484926149453481758790663522317898916616435463486824881406198956479504970446076256447830689197409184703931842169195650953917594642601134810084247402051464584676932882503143409428970896718980446185114397748313655630266379123438583315809104543663538494519415242569480492899140190587129956835218417371308642212037424611690324353109931657289337536406499314388951678319136343913551598851601805737870217800009086551022197432448461112330252097447894028786035069710260561955740514091976513928307284531381150606428802334767412638213776730300093872457594524254858721551285338651364457529927871215183857169772407595348187949014442596356406144157105062291018215254440382214000573515515859668018846789551567310531570458316720877172632139481792680258388798439064221051325274383331521717987420093245521230610073103811158660291643007279940393509663374960353315388446956868294358252276964954745551655711981
PQ2 = 17632503734712698604217167790453868045296303200715867263641257955056721075502316035280716025016839471684329988600978978424661087892466132185482035374940487837109552684763339574491378951189521258328752145077889261805000262141719400516584216130899437363088936913664419705248701787497332582188063869114908628807937049986360525010012039863210179017248132893824655341728382780250878156526086594253092249935304259986328308203344932540888448163430113818706295806406535364433801544858874357459282988110371175948011077595778123265914357153104206808258347815853145593128831233094769191889153762451880396333921190835200889266000562699392602082643298040136498839726733129090381507278582253125509943696419087708429546384313035073010683709744463087794325058122495375333875728593383803489271258323466068830034394348582326189840226236821974979834541554188673335151333713605570214286605391522582123096490317734786072061052604324131559447145448500381240146742679889154145555389449773359530020107821711994953950072547113428811855524572017820861579995449831880269151834230607863568992929328355995768974532894288752369127771516710199600449849031992434777962666440682129817924824151147427747882725858977273856311911431085373396551436319200582072164015150896425482384248479071434032953021738952688256364397405939276917210952583838731888536160866721278250628482428975748118973182256529453045184370543766401320261730361611365906347736001225775255350554164449014831203472238042057456969218316231699556466298168668958678855382462970622819417830000343573014265235688391542452769592096406400900187933156352226983897249981036555748543606676736274049188713348408983072484516372145496924391146241282884948724825393087105077360952770212959517318021248639012476095670769959011548699960423508352158455979906789927951812368185987838359200354730654103428077770839008773864604836807261909
t = 44
c = 4364802217291010807437827526073499188746160856656033054696031258814848127341094853323797303333741617649819892633013549917144139975939225893749114460910089509552261297408649636515368831194227006310835137628421405558641056278574098849091436284763725120659865442243245486345692476515256604820175726649516152356765363753262839864657243662645981385763738120585801720865252694204286145009527172990713740098977714337038793323846801300955225503801654258983911473974238212956519721447805792992654110642511482243273775873164502478594971816554268730722314333969932527553109979814408613177186842539860073028659812891580301154746
e = 0x10001
PQ = gcd(PQ2, P2Q)
P = P2Q // PQ
Q = PQ2 // PQ
M = matrix(ZZ, [[1, P], [0, Q]])
lll = M.LLL()[0]
p = int(-lll[0]) + 58
q = int(lll[1]) + t
phi = (p - 1) * (q - 1)
d = inverse(e, phi)
n = p * q
print(long_to_bytes(int(pow(c, d, n))))
# b'DASCTF{8f3djoj9wedj2_dkc903cwckckdk}
3-2EasyRsa
给了多组n,gcd()求出共同的素数p,然后解rsa
from Crypto.Util.number import *
from gmpy2 import *
m = 38127524839835864306737280818907796566475979451567460500065967565655632622992572530918601432256137666695102199970580936307755091109351218835095309766358063857260088937006810056236871014903809290530667071255731805071115169201705265663551734892827553733293929057918850738362888383312352624299108382366714432727
e = 65537
f = open("output.txt", "r")
a = f.readlines()[::-1]
for i in a:
# print(gcd(65439077968397540989065489337415940784529269429684649365065378651353483030304843439003949649543376311871845618819107350646437252980144978447924976470943930075812834237368425374578215977641265884859875440799334807607478705932175148673160353577875890074101393042506714001617338265284910381849259298772642190619,86843235426823545017422014398916780909062053456790256392304973548517489132984667679637386416948409930796162377844525829968317585749956057149930523547463230147376192820753802868362225137830225967953826475779047454555958271846035526319036389127587352017149417549187850782892924691511398536178090031958365483499))
p = 7552850543392291177573335134779451826968284497191536051874894984844023350777357739533061306212635723884437778881981836095720474943879388731913801454095897
n = int(i)
q = n // p
assert n % p == 0
phi = (p-1)*(q-1)
d = inverse(e,phi)
c = pow(m, d, n)
m = c
f.close()
print(long_to_bytes(m))
3-3Solomen’s puzzle 1
考点:里德-所罗门码
里德-所罗门码可以纠错,首先看视频学习里德-所罗门码的编码方式和如何纠错
这里大致说一下纠错,根据视频所述及题目给出的信息:
假设mx为里德-所罗门码,mmx为出错以后的mx(错了2位)。(以多项式的形式表示)
原有 m x g x = 0 \frac{mx}{gx} = 0 gxmx=0即 m x = h x ∗ g x mx=hx*gx mx=hx∗gx,而 g x = ( x − a l p h a 0 ) ∗ ( x − a l p h a 1 ) ∗ ( x − a l p h a 2 ) ∗ ( x − a l p h a 3 ) gx = (x - alpha ^ 0) * (x - alpha ^ 1) * (x - alpha ^ 2) * (x - alpha ^ 3) gx=(x−alpha0)∗(x−alpha1)∗(x−alpha2)∗(x−alpha3)
这意味着 ( a l p h a 0 , a l p h a 1 , a l p h a 2 , a l p h a 3 ) ( alpha ^ 0, alpha ^ 1, alpha ^ 2, alpha ^ 3) (alpha0,alpha1,alpha2,alpha3)为 g x gx gx和 m x mx mx的根,即将根带入求得值都为0
如果令 m m x − m x = y 1 ∗ x e 1 + y 2 ∗ x e 2 mmx-mx=y1*x^{e_1}+y2*x^{e_2} mmx−mx=y1∗xe1+y2∗xe2,其中 e 1 , e 2 , y 1 , y 2 e1,e2,y1,y2 e1,e2,y1,y2分别为出错的位置和其对应的大小,则可以得到四组方程( m x ( a l p h a k ) = 0 mx(alpha^k)=0 mx(alphak)=0):
m m x ( a l p h a k ) = = y 1 ∗ a l p h a k ∗ e 1 + y 2 ∗ a l p h a k ∗ e 2 ( ∀ k ∈ { 0 , 1 , 2 , 3 } ) mmx(alpha^k)= =y1*alpha^{k*e_1}+y2*alpha^{k*e_2}({\forall}k\in\lbrace0,1,2,3\rbrace) mmx(alphak)==y1∗alphak∗e1+y2∗alphak∗e2(∀k∈{0,1,2,3})
然后解方程组求解 y 1 , y 2 , e 1 , e 2 y1,y2,e1,e2 y1,y2,e1,e2,不过我不会,但我选择爆破
每组出错的位子在[4,5,6,7]中,大小为0到256,完全可以爆破的
from Crypto.Util.number import *
import hashlib
m = 257
F = Zmod(m)
alpha = F(223)
PR.<x> = PolynomialRing(F)
gx = (x - alpha ^ 0) * (x - alpha ^ 1) * (x - alpha ^ 2) * (x - alpha ^ 3)
code = b'\xb9$5.>\xff\xe3S\xc91\xb2\xeb\x1byR(\x12{\xc4\xbf\xa4wo|\xc5-;\xc9\xc9S[\xaeX\xad\xf0\xef@\x1c\x87]\x9a\xb9:\x8cu\xa5\xe3EA<"\xfd\x9a\xbfqB\x94\xc3R\x95\xd5\xbd\xd0\x10u\x10\xe3\xa5"S\xed\xd0\xf8\x02\xbf\x124A~1]\xceP\xdf\xf2Cr1\x93\xacw\x03\tQe\xcc2b\xbf\x0f\x92\xad\x19\x00\xab|\xf3\xc9\x9b&I%\xf5\x9b#\xf7\xa2\xcb\xb1\x0c\xee\xb56\xd5\xd2\xd5[?^\x9d\x8b\x93\xbe\x832\xee\xa9\xa5\x83$\xe9\xe5\x95\x01\xd6\x9f\xad\x1f\x90\xc3]aL\x10\x07{#4i^\xae\xdf|\x9f\x94\xf4\xaf\x06R\x86j&\xeb\x0b\x06\xcf\xb2\x8e\xb4\xb9s\x97[\xf1ip\x06\xf8\xfdFs\xf1`\xc6\x82\xd8\xce\xf6\x95{\xe3\x8cQ\xed\xef\xe9\xb9\'\x19\xdf^\xc8\x81\xde\x1fQ\x1e\x86\xda\xf8\xfd4M0#\xef\x8a\xe9\xe5\xfc\xe2\xe3\xe6\xd0e\xce\xe1\x0b\x9eM\x07\xc2Y\xf8B\xe1\xde\xfaP\xe9\x9d\xde\xc3\xe3C\xa5'
n = 94257413713770111563970534929325680923943690882102478219183863722026590313165304301118258536360712467357451726680293716779730218553691126214750969333228034756948476572806064756873382054384808713137658321644158757777088916851366208046581218865015163572359836440643828462291397248680038931998325006839692797347
flag = []
for k in range(32):
c = code[k*8:k*8+8]
c = [_ for _ in c]
mx = PR(c)
f = 0
for e1 in range(4, 8):
if f: break
for e2 in range(4, 8):
if f: break
if e1==e2:break
for y1 in range(0, m):
if f: break
for y2 in range(0, m):
if f: break
count = 0
for i in range(4):
if not int(mx(alpha ^ i)) == int(y1 * alpha ^ (i * e1) + y2 * alpha ^ (i * e2))%m:
break
count += 1
if count == 4:
mmx = mx - y1 * x ^ e1 - y2 * x ^ e2
flag += [_ for _ in list(mmx)[4:]]
f = 1
realflag = b''
for i in flag:
realflag+=long_to_bytes(int(i))
realflag = bytes_to_long(realflag)
e = 10632528934906371807995216845027219767890923967559690651733628659750564299493611010425615580946665632019547006685100876646048602773295571936276450835367591
realflag = realflag * inverse(e,n) % n
realflag = long_to_bytes(int(realflag))
# b'DASCTF{What_a_funny_rsa_question_posted_by_Reed_and_Solomen_LOL_HHHHHH}'
realflag = hashlib.md5(realflag).hexdigest()
print(realflag)
# 4e4fc02d88b0c8f66c924489e1bf58ea
3-4linearAlgebra
C = A ∗ M C=A*M C=A∗M,给了 C C C,而 M M M的第一行甚至第二行包含了 f l a g flag flag
A c = ( A , a s i z e , n ) Ac = (A, asize, n) Ac=(A,asize,n),给了 A c Ac Ac, c o r r u p t ( ) corrupt() corrupt()函数随机将 A A A中 32 32 32个元素改变,而 A A A也仅仅为 32 ∗ 32 32*32 32∗32的矩阵,这就有很大的可能 A A A中有两行及以上是没有发生变化的
如果我们将 C C C的每一个元素都看成是由背包加密得来的,那么我们就可以通过 A c Ac Ac中未发生变化的那一行配合背包来解出 M M M的每一列
先看看哪些行没变
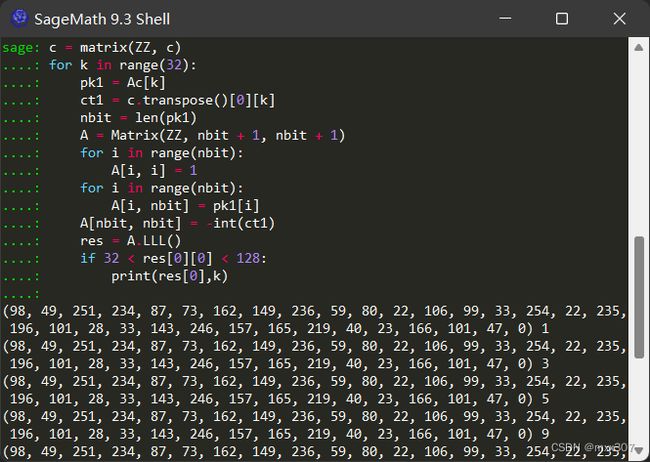
c = matrix(ZZ, c)
for k in range(32):
pk1 = Ac[k] #某一行
ct1 = c.transpose()[0][k] #对原c而言,固定某一列,对应某一行
nbit = len(pk1)
A = Matrix(ZZ, nbit + 1, nbit + 1)
for i in range(nbit):
A[i, i] = 1
for i in range(nbit):
A[i, nbit] = pk1[i]
A[nbit, nbit] = -int(ct1)
res = A.LLL()
if 32 < res[0][0] < 128:
print(res[0],k) # 求出M对应的固定某一列,因为固定某一列,所以如果求出结果相同,则表明该行的Ac没变
找到好多行(1,3,5,9,…)没有变化,取其中一行,恢复 M M M
f = open('out', 'r')
f.readline()
c = []
for i in range(32):
C = f.readline().strip('\n').replace(' ', ' ').replace(' ', ' ').replace(' ', ',').replace('[,','[')[1:][:-1]
C = list(map(int, C.split(',')))
c.append(C)
f.readline()
Ac = []
for i in range(32):
AC = f.readline().strip('\n').replace(' ', ' ').replace(' ', ' ').replace(' ', ',').replace('[,','[')[1:][:-1]
AC = list(map(int,AC.split(',')))
Ac.append(AC)
c = matrix(ZZ, c)
# for k in range(32):
# pk1 = Ac[k]
# ct1 = c.transpose()[0][k]
# nbit = len(pk1)
# A = Matrix(ZZ, nbit + 1, nbit + 1)
# for i in range(nbit):
# A[i, i] = 1
# for i in range(nbit):
# A[i, nbit] = pk1[i]
# A[nbit, nbit] = -int(ct1)
# res = A.LLL()
# if 32 < res[0][0] < 128:
# print(res[0],k)
flag1 = ''
flag2 = ''
for k in range(32):
pk1 = Ac[1] # 取了第1行
ct1 = c.transpose()[k][1] # 对应c转置后中的第1列
nbit = len(pk1)
A = Matrix(ZZ, nbit + 1, nbit + 1)
for i in range(nbit):
A[i, i] = 1
for i in range(nbit):
A[i, nbit] = pk1[i]
A[nbit, nbit] = -int(ct1)
res = A.LLL()
# if 32 < res[0][0] < 128:
# print(res[0],k)
flag1 += chr(int(res[0][0]))
if k < 4: #flag为uuid4的形式,长36
flag2 += chr(int(res[0][1]))
print(flag1+flag2)
# b5932c2c-e210-4c39-9fb5-a7f35e861d32
3-5NovelSystem2
关键看到 s e l f . p s i = ( s e l f . p ∗ ∗ 2 + s e l f . p + 1 ) ∗ ( s e l f . q ∗ ∗ 2 + s e l f . q + 1 ) self.psi = (self.p ** 2 + self.p + 1) * (self.q ** 2 + self.q + 1) self.psi=(self.p∗∗2+self.p+1)∗(self.q∗∗2+self.q+1),眼熟得很
和 p b c t f 2021 Y e t A n o t h e r R S A pbctf2021\ Yet\ Another\ RSA pbctf2021 Yet Another RSA像得很,找了一下别人的wp1和wp2和论文参考
直接拿了wp1中的脚本~~(我是脚本小子)~~,解出来 p + q p+q p+q,然后就可以分解 N N N啦
最后把数据放进类里面,直接decrypt即可
from Crypto.Util.number import *
from gmpy2 import *
import time
class NovelSystem:
def __init__(self, p, q, e):
self.p = mpz(p)
self.q = mpz(q)
self.N = self.p * self.q
self.beta = 0.397
self.psi = (self.p ** 2 + self.p + 1) * (self.q ** 2 + self.q + 1)
self.e = mpz(e)
self.d = invert(mpz(self.e), mpz(self.psi))
self.r = 3
def add_(self, a, b):
m, n = a
k, l = b
if a[1] == 0:
a, b = b, a
m, n, k, l = k, l, m, n
if l == 0:
if n == 0:
return (m * k, m + k)
if (n + k) % self.N == 0:
if (m - n ** 2) % self.N == 0:
return (0, 0)
return ((m * k + self.r) * invert(m - n * n) % self.N, 0)
return ((m * k + self.r) * invert(n + k, self.N) % self.N, (m + n * k) * invert(n + k, self.N) % self.N)
if (m + k + n * l) % self.N != 0:
return ((m * k + (n + l) * self.r) * invert(m + k + n * l, self.N) % self.N,
(n * k + m * l + self.r) * invert(m + k + n * l, self.N) % self.N)
if (n * k + m * l + self.r) % self.N == 0:
return (0, 0)
return ((m * k + (n + l) * self.r) * invert(n * k + m * l + self.r, self.N) % self.N, 0)
def mul_(self, a, n):
ans = (0, 0)
while n > 0:
if n & 1 == 1:
ans = self.add_(ans, a)
a = self.add_(a, a)
n //= 2
return ans
def encrypt(self, m):
return self.mul_(m, self.e)
def decrypt(self, c):
return self.mul_(c, self.d)
############################################
# Config
##########################################
"""
Setting debug to true will display more informations
about the lattice, the bounds, the vectors...
"""
debug = True
"""
Setting strict to true will stop the algorithm (and
return (-1, -1)) if we don't have a correct
upperbound on the determinant. Note that this
doesn't necesseraly mean that no solutions
will be found since the theoretical upperbound is
usualy far away from actual results. That is why
you should probably use `strict = False`
"""
strict = False
"""
This is experimental, but has provided remarkable results
so far. It tries to reduce the lattice as much as it can
while keeping its efficiency. I see no reason not to use
this option, but if things don't work, you should try
disabling it
"""
helpful_only = True
dimension_min = 7 # stop removing if lattice reaches that dimension
############################################
# Functions
##########################################
# display stats on helpful vectors
def helpful_vectors(BB, modulus):
nothelpful = 0
for ii in range(BB.dimensions()[0]):
if BB[ii, ii] >= modulus:
nothelpful += 1
print(nothelpful, "/", BB.dimensions()[0], " vectors are not helpful")
# display matrix picture with 0 and X
def matrix_overview(BB, bound):
for ii in range(BB.dimensions()[0]):
a = ('%02d ' % ii)
for jj in range(BB.dimensions()[1]):
a += '0' if BB[ii, jj] == 0 else 'X'
if BB.dimensions()[0] < 60:
a += ' '
if BB[ii, ii] >= bound:
a += '~'
print(a)
# tries to remove unhelpful vectors
# we start at current = n-1 (last vector)
def remove_unhelpful(BB, monomials, bound, current):
# end of our recursive function
if current == -1 or BB.dimensions()[0] <= dimension_min:
return BB
# we start by checking from the end
for ii in range(current, -1, -1):
# if it is unhelpful:
if BB[ii, ii] >= bound:
affected_vectors = 0
affected_vector_index = 0
# let's check if it affects other vectors
for jj in range(ii + 1, BB.dimensions()[0]):
# if another vector is affected:
# we increase the count
if BB[jj, ii] != 0:
affected_vectors += 1
affected_vector_index = jj
# level:0
# if no other vectors end up affected
# we remove it
if affected_vectors == 0:
print("* removing unhelpful vector", ii)
BB = BB.delete_columns([ii])
BB = BB.delete_rows([ii])
monomials.pop(ii)
BB = remove_unhelpful(BB, monomials, bound, ii - 1)
return BB
# level:1
# if just one was affected we check
# if it is affecting someone else
elif affected_vectors == 1:
affected_deeper = True
for kk in range(affected_vector_index + 1, BB.dimensions()[0]):
# if it is affecting even one vector
# we give up on this one
if BB[kk, affected_vector_index] != 0:
affected_deeper = False
# remove both it if no other vector was affected and
# this helpful vector is not helpful enough
# compared to our unhelpful one
if affected_deeper and abs(bound - BB[affected_vector_index, affected_vector_index]) < abs(
bound - BB[ii, ii]):
print("* removing unhelpful vectors", ii, "and", affected_vector_index)
BB = BB.delete_columns([affected_vector_index, ii])
BB = BB.delete_rows([affected_vector_index, ii])
monomials.pop(affected_vector_index)
monomials.pop(ii)
BB = remove_unhelpful(BB, monomials, bound, ii - 1)
return BB
# nothing happened
return BB
def attack(N, e, m, t, X, Y):
modulus = e
PR.< x, y > = PolynomialRing(ZZ)
a = N + 1
b = N * N - N + 1
f = x * (y * y + a * y + b) + 1
gg = []
for k in range(0, m + 1):
for i in range(k, m + 1):
for j in range(2 * k, 2 * k + 2):
gg.append(x ^ (i - k) * y ^ (j - 2 * k) * f ^ k * e ^ (m - k))
for k in range(0, m + 1):
for i in range(k, k + 1):
for j in range(2 * k + 2, 2 * i + t + 1):
gg.append(x ^ (i - k) * y ^ (j - 2 * k) * f ^ k * e ^ (m - k))
def order_gg(idx, gg, monomials):
if idx == len(gg):
return gg, monomials
for i in range(idx, len(gg)):
polynomial = gg[i]
non = []
for monomial in polynomial.monomials():
if monomial not in monomials:
non.append(monomial)
if len(non) == 1:
new_gg = gg[:]
new_gg[i], new_gg[idx] = new_gg[idx], new_gg[i]
return order_gg(idx + 1, new_gg, monomials + non)
gg, monomials = order_gg(0, gg, [])
# construct lattice B
nn = len(monomials)
BB = Matrix(ZZ, nn)
for ii in range(nn):
BB[ii, 0] = gg[ii](0, 0)
for jj in range(1, nn):
if monomials[jj] in gg[ii].monomials():
BB[ii, jj] = gg[ii].monomial_coefficient(monomials[jj]) * monomials[jj](X, Y)
# Prototype to reduce the lattice
if helpful_only:
# automatically remove
BB = remove_unhelpful(BB, monomials, modulus ^ m, nn - 1)
# reset dimension
nn = BB.dimensions()[0]
if nn == 0:
print("failure")
return 0, 0
# check if vectors are helpful
if debug:
helpful_vectors(BB, modulus ^ m)
# check if determinant is correctly bounded
det = BB.det()
bound = modulus ^ (m * nn)
if det >= bound:
print("We do not have det < bound. Solutions might not be found.")
print("Try with highers m and t.")
if debug:
diff = (log(det) - log(bound)) / log(2)
print("size det(L) - size e^(m*n) = ", floor(diff))
if strict:
return -1, -1
else:
print("det(L) < e^(m*n) (good! If a solution exists < N^delta, it will be found)")
# display the lattice basis
if debug:
matrix_overview(BB, modulus ^ m)
# LLL
if debug:
print("optimizing basis of the lattice via LLL, this can take a long time")
BB = BB.LLL()
if debug:
print("LLL is done!")
# transform vector i & j -> polynomials 1 & 2
if debug:
print("looking for independent vectors in the lattice")
found_polynomials = False
for pol1_idx in range(nn - 1):
for pol2_idx in range(pol1_idx + 1, nn):
# for i and j, create the two polynomials
PR.< a, b > = PolynomialRing(ZZ)
pol1 = pol2 = 0
for jj in range(nn):
pol1 += monomials[jj](a, b) * BB[pol1_idx, jj] / monomials[jj](X, Y)
pol2 += monomials[jj](a, b) * BB[pol2_idx, jj] / monomials[jj](X, Y)
# resultant
PR.< q > = PolynomialRing(ZZ)
rr = pol1.resultant(pol2)
# are these good polynomials?
if rr.is_zero() or rr.monomials() == [1]:
continue
else:
print("found them, using vectors", pol1_idx, "and", pol2_idx)
found_polynomials = True
break
if found_polynomials:
break
if not found_polynomials:
print("no independant vectors could be found. This should very rarely happen...")
return 0, 0
rr = rr(q, q)
# solutions
soly = rr.roots()
if len(soly) == 0:
print("Your prediction (delta) is too small")
return 0, 0
soly = soly[0][0]
ss = pol1(q, soly)
solx = ss.roots()[0][0]
return solx, soly
def inthroot(a, n):
return a.nth_root(n, truncate_mode=True)[0]
N, e, s = (69608791192421919283757675475568920773353852553984294535246714322217147926140334786382671447161809319059757926660104907264892471513691210713164936055575369238706600340586833164515933300246888063235136692968128246137215938114060492757345025435557818940819819146315427528432401269318798897677955790143951114837, 3569709831456961963983317856906282564247794656174883346551318455409781951821532194464316039706968856000098892463123452801581913760419867217744612993876726508565953876218527986879338419527071132882516845467078252901861510834762733680624403662683842157212966883670782784707420186939792539380416673702618954148609178781352393489552193742869735649479707631323667621294737562886946346783459713562739324444015141587968954791790724386091523034752910330271202144122827876441229219899077622471534860855412052877175120218922873300885113936346989198403927493848984768217738562507350427274074810257890679068944519650350540061773, 3)
X = 1 << 400
Y = 2 * inthroot(Integer(2 * N), 2)
res = attack(N, e, 4, 2, X, Y)
b, c = res[1], N
Dsqrt = inthroot(Integer(b^2-4*c),2)
p, q = (b + Dsqrt) // 2, (b - Dsqrt) // 2
assert p * q == N
c = (mpz(25277872308079622747549210576460613586229133947234593535200353386990766871354231190884983744062724190757790170095336476433339679661865115249940491581950905446714526508336734968117122923367321009658430492676221613955154012709104353264746945809594342072744903918483080444098810305069478604650812993367066108686), mpz(23837611977059204694294310415628596206205358541193793076161113947121055317488611201828968875769165810136018932772918536959013421962176622562932517080185242296377551991015543007194938521921909070483342042300905806379510158998331097627686209024554054114596970966269941945120227200103961459438854583220408434182))
enc = NovelSystem(p,q,e)
m = enc.decrypt(c)
print(long_to_bytes(int(m[0]))+long_to_bytes(int(m[1])))
# b'DASCTF{a1a4a518320a469088c64aa4fbc22438}'