07-ThreadLocal有哪些使用场景?【Java面试题总结】
ThreadLocal有哪些使用场景?
7.1 多线程场景下共享变量问题
ThreadLocal是线程本地变量,可以存储共享变量副本,每一个独立线程都有与共享变量一模一样的副本。ThreadLocal在当前线程下共享变量是全局共享的,各个线程之间是相互独立的。
ThreadLocal在多线程场景下解决共享变量问题代码案例:
public class SharedVariableExample {
private static ThreadLocal<Integer> sharedVariable = new ThreadLocal<>();
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
final int value = i; // 保存当前值,确保每个线程的值不同
executorService.submit(() -> {
sharedVariable.set(value); // 将值设置到ThreadLocal中
try {
processValue(); // 处理共享变量
} finally {
sharedVariable.remove(); // 在任务完成后清除ThreadLocal的值
}
});
}
executorService.shutdown();
}
private static void processValue() {
int value = sharedVariable.get(); // 从ThreadLocal中获取值
System.out.println("Thread " + Thread.currentThread().getName() + ": Value = " + value);
}
}
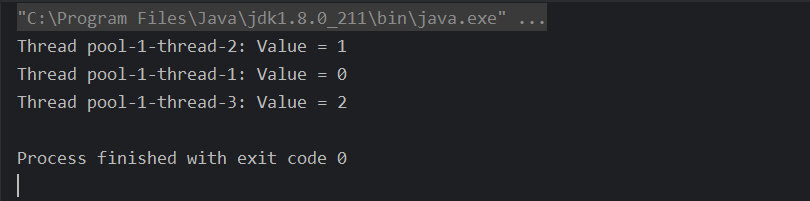
执行结果如下,每个线程都有自己独立的共享变量副本,并且在当前线程下任务一个地方值都是一样的(一个线程下,可能存在多个方法,多个方法即当前线程下共享变量全局共享)
7.2 保存系统上下文信息
在多线程环境中,有时需要在线程之间传递数据,但不希望通过方法参数或全局变量来传递。ThreadLocal可以在当前线程中存储数据,其他线程可以通过ThreadLocal获取该数据。
使用ThreadLocal实现保存上下文信息代码案例如下
新建User类
public class User {
private String username;
public User(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
}
新建RequestContext类,用于保存信息到ThreadLocal中
public class RequestContext {
private static ThreadLocal<RequestContext> contextHolder = new ThreadLocal<>();
private String requestId;
private User currentUser;
private RequestContext(String requestId, User currentUser) {
this.requestId = requestId;
this.currentUser = currentUser;
}
public static void setCurrentContext(String requestId, User currentUser) {
RequestContext context = new RequestContext(requestId, currentUser);
contextHolder.set(context);
}
public static RequestContext getCurrentContext() {
return contextHolder.get();
}
public String getRequestId() {
return requestId;
}
public User getCurrentUser() {
return currentUser;
}
}
新建UserService处理请求
public class UserService {
public void processRequest() {
RequestContext context = RequestContext.getCurrentContext();
String requestId = context.getRequestId();
User currentUser = context.getCurrentUser();
System.out.println("Processing request: " + requestId + " ,Current user: " + currentUser.getUsername());
}
}
模拟两个请求,分别由不同的两个用户发起的请求。UserService类和RequestContext类本身没有直接的关系,从程序运行结果来看,信息确实从RequestContext透传到了UserService中,说明ThreadLocal起到了中间作用,可以用来保存系统上下文信息。
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 模拟请求1
User user1 = new User("Alice");
RequestContext.setCurrentContext("request-1", user1);
UserService userService = new UserService();
userService.processRequest();
// 模拟请求2
User user2 = new User("Bob");
RequestContext.setCurrentContext("request-2", user2);
userService.processRequest();
}
}
7.3 管理数据库连接
public class ConnectionManager {
private static ThreadLocal<Connection> connectionHolder = new ThreadLocal<>();
public static Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
// 从ThreadLocal获取连接
Connection connection = connectionHolder.get();
// 如果连接不存在,则创建新连接并保存到ThreadLocal
if (connection == null || connection.isClosed()) {
connection = createConnection();
connectionHolder.set(connection);
}
return connection;
}
private static Connection createConnection() throws SQLException {
// 创建数据库连接
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/dev";
String username = "root";
String password = "root";
return DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password);
}
public static void closeConnection() throws SQLException {
// 关闭连接并从ThreadLocal中移除
Connection connection = connectionHolder.get();
if (connection != null && !connection.isClosed()) {
connection.close();
}
connectionHolder.remove();
}
}
public class DatabaseService {
public void performDatabaseOperation() throws SQLException {
Connection connection = ConnectionManager.getConnection();
// 使用连接执行数据库操作
// ...
// 操作完成后关闭连接
ConnectionManager.closeConnection();
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
// 创建多个线程模拟并发访问
Thread thread1 = new Thread(() -> {
try {
DatabaseService service = new DatabaseService();
service.performDatabaseOperation();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
Thread thread2 = new Thread(() -> {
try {
DatabaseService service = new DatabaseService();
service.performDatabaseOperation();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
// 启动线程
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
}
}
一个请求对应一个数据库连接,一个请求下的所有对数据库的操作都是基于该连接进行的。这样可以在一定程度上避免频繁的创建和销毁数据库连接,从而提高性能。
7.4 基于ThreadLocal实现事务功能
使用ThreadLocal实现事务注解的原理是通过在每个线程中维护一个事务上下文对象,将事务状态与当前线程绑定起来。当需要开启事务时,通过注解或编程方式将事务上下文对象与当前线程进行关联,以便在整个事务执行过程中使用相同的事务上下文对象。
首先,定义一个事务上下文对象,用于存储事务相关的信息,例如事务状态、连接对象等。
public class TransactionContext {
private Connection connection;
private boolean inTransaction;
// 省略构造方法和其他属性的访问方法
public Connection getConnection() {
return connection;
}
public void setConnection(Connection connection) {
this.connection = connection;
}
public boolean isInTransaction() {
return inTransaction;
}
public void setInTransaction(boolean inTransaction) {
this.inTransaction = inTransaction;
}
}
接下来,定义一个事务管理器类,使用ThreadLocal来存储和获取当前线程的事务上下文对象。
package com.spring6.learn.ThreadLocal.test6;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.SQLException;
public class TransactionManager {
private static ThreadLocal<TransactionContext> transactionContextHolder = new ThreadLocal<>();
public static void beginTransaction() {
TransactionContext context = new TransactionContext();
transactionContextHolder.set(context);
context.setInTransaction(true);
}
public static void commitTransaction() {
TransactionContext context = transactionContextHolder.get();
if (context != null && context.isInTransaction()) {
Connection connection = context.getConnection();
try {
connection.commit();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
context.setInTransaction(false);
closeConnection(connection);
}
}
public static void rollbackTransaction() {
TransactionContext context = transactionContextHolder.get();
if (context != null && context.isInTransaction()) {
Connection connection = context.getConnection();
try {
connection.rollback();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
context.setInTransaction(false);
closeConnection(connection);
}
}
public static Connection getCurrentConnection() {
TransactionContext context = transactionContextHolder.get();
if (context != null) {
return context.getConnection();
}
return null;
}
public static void setCurrentConnection(Connection connection) {
TransactionContext context = transactionContextHolder.get();
if (context == null) {
context = new TransactionContext();
transactionContextHolder.set(context);
}
context.setConnection(connection);
}
private static void closeConnection(Connection connection) {
try {
if (connection != null && !connection.isClosed()) {
connection.close();
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public class TransactionManagerTest {
private Connection connection;
@Before
public void setUp() throws SQLException {
connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mysql", "root", "root");
TransactionManager.setCurrentConnection(connection);
TransactionManager.beginTransaction();
}
@After
public void tearDown() throws SQLException {
TransactionManager.rollbackTransaction();
TransactionManager.setCurrentConnection(null);
if (connection != null && !connection.isClosed()) {
connection.close();
}
}
@Test
public void testTransaction() throws SQLException {
// 在事务中插入一条数据
String insertQuery = "INSERT INTO mytable (name) VALUES (?)";
try (PreparedStatement statement = connection.prepareStatement(insertQuery)) {
statement.setString(1, "John Doe");
statement.executeUpdate();
}
// 在事务中查询数据
String selectQuery = "SELECT COUNT(*) FROM mytable";
try (PreparedStatement statement = connection.prepareStatement(selectQuery)) {
ResultSet resultSet = statement.executeQuery();
if (resultSet.next()) {
int count = resultSet.getInt(1);
assertEquals(1, count); // 验证插入的数据是否存在
}
}
}
}
TransactionManager.beginTransaction();
}
@After
public void tearDown() throws SQLException {
TransactionManager.rollbackTransaction();
TransactionManager.setCurrentConnection(null);
if (connection != null && !connection.isClosed()) {
connection.close();
}
}
@Test
public void testTransaction() throws SQLException {
// 在事务中插入一条数据
String insertQuery = "INSERT INTO mytable (name) VALUES (?)";
try (PreparedStatement statement = connection.prepareStatement(insertQuery)) {
statement.setString(1, "John Doe");
statement.executeUpdate();
}
// 在事务中查询数据
String selectQuery = "SELECT COUNT(*) FROM mytable";
try (PreparedStatement statement = connection.prepareStatement(selectQuery)) {
ResultSet resultSet = statement.executeQuery();
if (resultSet.next()) {
int count = resultSet.getInt(1);
assertEquals(1, count); // 验证插入的数据是否存在
}
}
}
}