0基础速成Java环境下JDBC编程(细节超全,保姆级教程)
Java环境下的JDBC编程
JDBC编程优点:可以重复执行固定操作
使用JDBC必备条件
1.编程语言:Java
2.数据库:MySQL
3.数据库驱动包:mysql-connector-Java
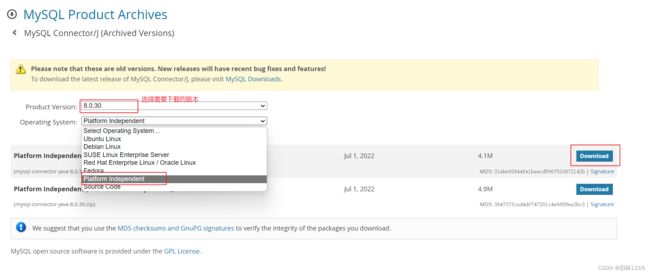
驱动包链接: https://downloads.mysql.com/archives/c-j/
驱动包安装步骤:
1.选择自己需要下载的版本(一般下载与自己电脑的MySQL版本相近的)
2.新建一个项目
3.新建一个lib目录:
项目名称处右键选择新建

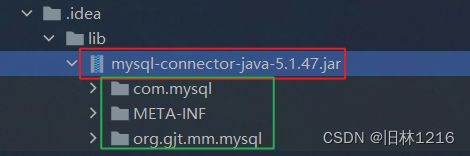
4.将数据库驱动包复制到根目录下:
红色框框的jar包为粘贴上的
5.粘贴成功后右键点击jar包选择Add and Library自动出现以下文件夹,如出现则表示导入成功
6.导入成功后则可直接在src中新建Java程序连接数据库了
JDBC编码步骤
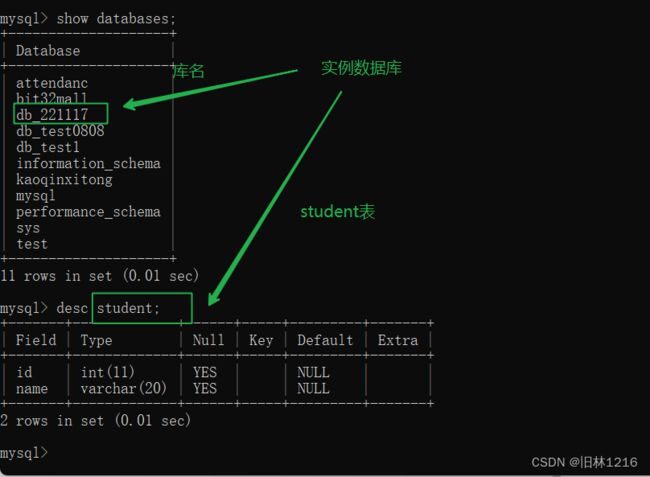
1.准备一个数据库表:
如图所示此次示例用的数据库名为db_221117,新建了一个表名字为student
2.简单的示例代码:
import com.mysql.jdbc.jdbc2.optional.MysqlDataSource;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.SQLOutput;
public class JDBC测试1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
DataSource dataSource = new MysqlDataSource();
((MysqlDataSource)dataSource).setURL("jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/db_221117?characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=false");
((MysqlDataSource)dataSource).setUser("root");
((MysqlDataSource)dataSource).setPassword("123456");
Connection connection = dataSource.getConnection();
String sql = "insert into student values (1,'张三')";
PreparedStatement statement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
int ret = statement.executeUpdate();
System.out.println("ret = " + ret);
statement.close();
connection.close();
}
}
上述代码详解:
1.URL:
URL:是统一资源定位符, 互联网上的每个文件都有一个唯一的URL,它包含的信息指出文件的位置以及浏览器应该怎么处理它
一般使用MySQL的URL都为:(数据库名字需改变)若报异常则在后面拼上&serverTimezone=UTC
jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/MySQL?characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=false
//加上时区版(东八区为例):
jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/MySQL?characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=false&serverTimezone=UTC
j d b c : m y s q l : / / \color{#228B22}{jdbc:mysql:// } jdbc:mysql://—是指JDBC连接方式
127.0.0.1 : \color{#228B22}{127.0.0.1: } 127.0.0.1:—是指你的本机地址;
3306 \color{#228B22}{3306 } 3306—SQL数据库的端口号,若安装数据库时没更改一般都为3306;
M y S Q L \color{#FF6A6A}{MySQL} MySQL—进行操作的数据库名字
c h a r a c t e r E n c o d i n g = u t f 8 \color{#228B22}{characterEncoding=utf8 } characterEncoding=utf8—描述请求字符编码方式,一般写为utf8
u s e S S L = f a l s e \color{#228B22}{useSSL=false} useSSL=false—关闭加密功能
2.创建DataSource
DataSource dataSource = new MysqlDataSource();
((MysqlDataSource)dataSource).setURL("jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/db_221117?characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=false");
((MysqlDataSource)dataSource).setUser("root");//用户名
((MysqlDataSource)dataSource).setPassword("123456");//密码
3.和数据库建立连接
Connection connection = dataSource.getConnection();
//连接
此处可能抛出异常,可直接在main后加入throws语句让JVM自行处理此异常
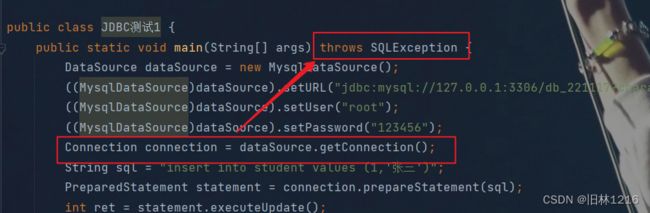
4.构造SQL语句:
String sql = "insert into student values (1,'张三')";
//sql 用来描述sql语句是啥样的,具体执行需要靠后面
PreparedStatement statement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
//PreparedStatement 与处理过的语句,每执行一次sql语句都需要重新构造一下
//statement 接口提供三种执行SQL语句的方法
5.执行语句
增删改使用:executeUpdate();来执行
查找使用:executeQuery();来执行
int ret = statement.executeUpdate();
//ret 用来记录此次操作影响了几行
System.out.println("ret = " + ret);
6.断开连接,释放资源
先创建先释放
statement.close();
connection.close();
3.从键盘读取数据进行操作
还是对同一个数据库操作
import com.mysql.jdbc.jdbc2.optional.MysqlDataSource;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.SQLOutput;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class JDBC测试1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
DataSource dataSource = new MysqlDataSource();
((MysqlDataSource)dataSource).setURL("jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/db_221117?characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=false");
((MysqlDataSource)dataSource).setUser("root");
((MysqlDataSource)dataSource).setPassword("123456");
Connection connection = dataSource.getConnection();
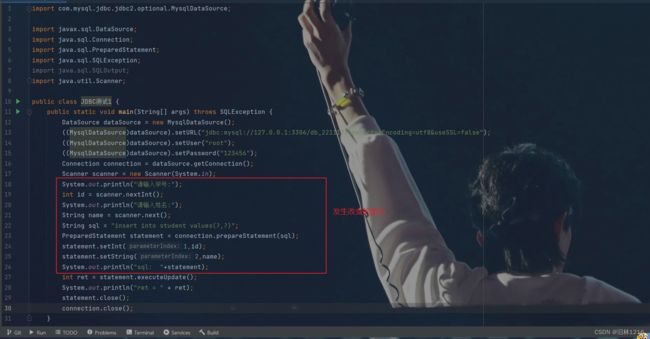
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入学号:");
int id = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.println("请输入姓名:");
String name = scanner.next();
String sql = "insert into student values(?,?)";
//占位符: 一个?代表一个变量
PreparedStatement statement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
statement.setInt(1,id);
statement.setString(2,name);
//1和2分别表示此处为第一个?和第二个?
System.out.println("sql: "+statement);
int ret = statement.executeUpdate();
System.out.println("ret = " + ret);
statement.close();
connection.close();
}
}
这里将操作改为从键盘输入信息插入到student表中
运行结果:
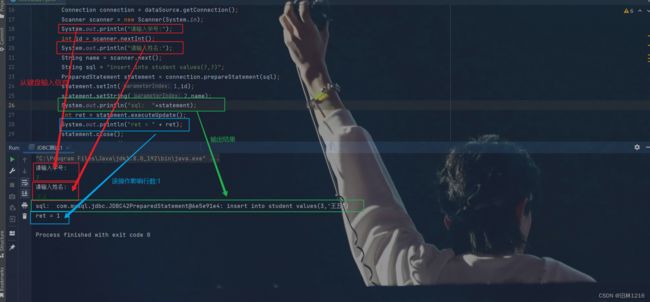
4.简单的查找操作
查询student表(无限制条件)
import com.mysql.jdbc.jdbc2.optional.MysqlDataSource;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import javax.xml.transform.Result;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class JDBC测试2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
DataSource dataSource = new MysqlDataSource();
((MysqlDataSource)dataSource).setURL("jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/db_221117?characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=false");
((MysqlDataSource)dataSource).setUser("root");
((MysqlDataSource)dataSource).setPassword("123456");
Connection connection = dataSource.getConnection();
String sql = "select * from student ";
//SQL查询语句
PreparedStatement statement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
//statement 接口提供三种执行SQL语句的方法
ResultSet resultSet = statement.executeQuery();
//执行了SQL语句
//ResultSet结果集:数据查询结果返回的一种对象
while (resultSet.next()) {
//resultSet.next()读取下一行,若不为空则继续
//第一次执行resultSet.next()后,此时光标指在表的第一行
int id = resultSet.getInt("id");
//获取读的结果
String name = resultSet.getString("name");
System.out.println(id + ": " + name);
}
System.out.println("sql: "+statement);
resultSet.close();
statement.close();
connection.close();
}
}
若将String sql = "select * from student ";变成:String sql = "select * from student where id = 3";
结果:
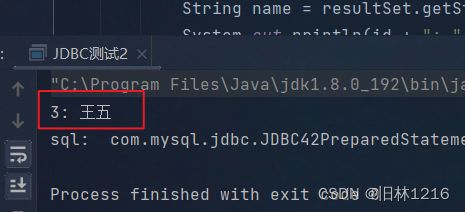
无论是如何查询都只用改变sql即可