vuex详解
vuex
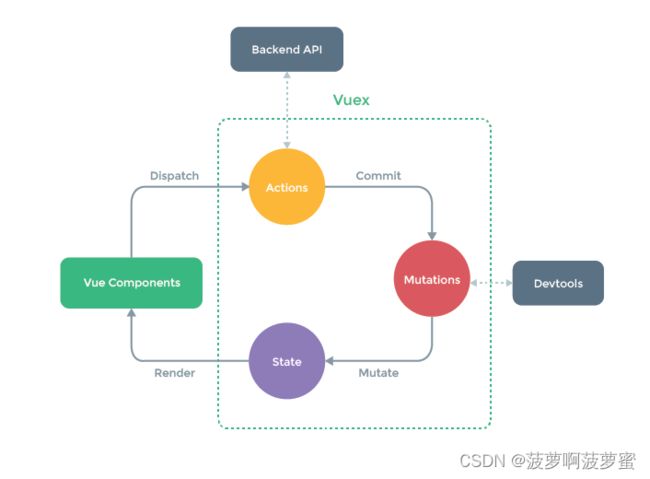
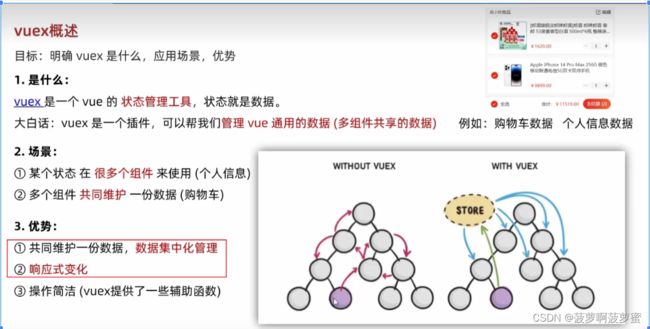
集中式状态(数据)管理工具, 管理共享的数据,这个数据是响应式的,单向数据流的,多组件数据共享;
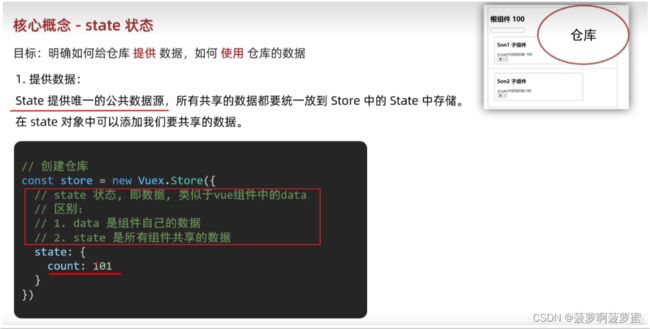
sate可以写成一个对象,也可以写成一个state函数返回一个对象;
mutation中的方法, 第一个形参永远是state对象, 第二个参数是传递过来的参数;
action中的方法,第一个形参是context对象, 第二个参数是传递过来的参数;
action函数接受一个与 store 实例具有相同方法和属性的 context 对象, 通常解构context对象{ }来使用;
getter函数第一个参数是state, 第二个参数是getters, 可以调用其他getters的方法;
actions、mutations、getters中的方法可以互相调用,在各自内也可以互相调用;
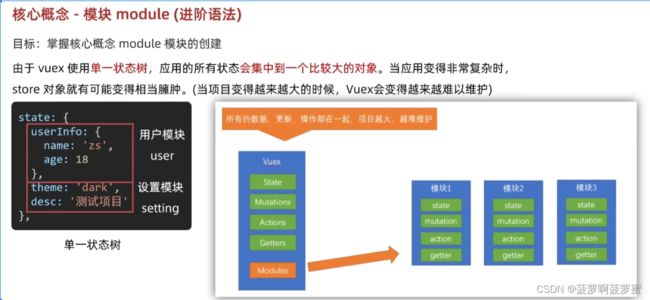
state getters mutations actions modules;
mapState mapGetters mapMutions mapAction;
…mapState …mapGetters在computed中映射解构出来, 然后直接使用值;
…mapMutations …mapActions在methdos中映射解构出来,然后调用执行对应的函数;
state getters 在computed中; mutation action在methdos中;
同步代码只能通过mutation;异步代码(如发送请求)通过action;
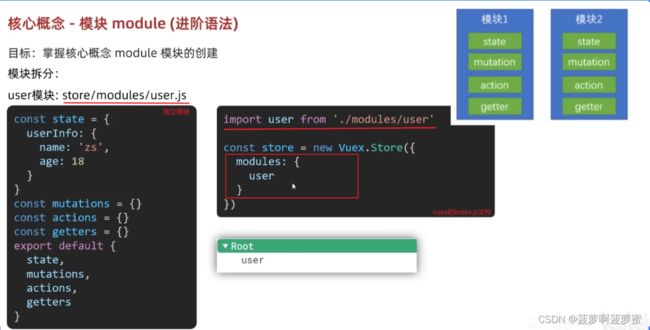
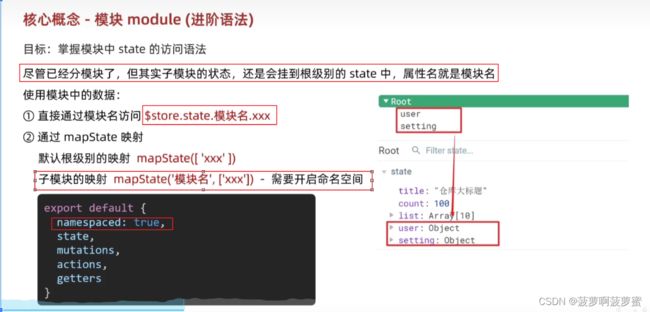
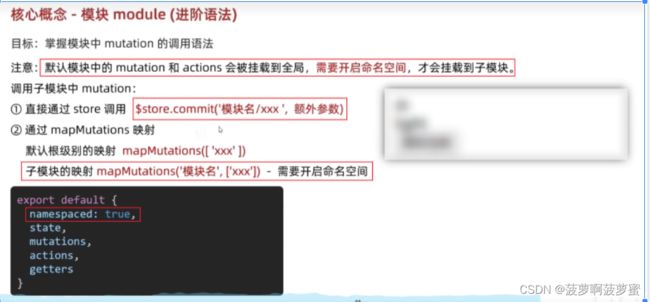
模块化的vuex需要开启命名空间, namespaced: true;
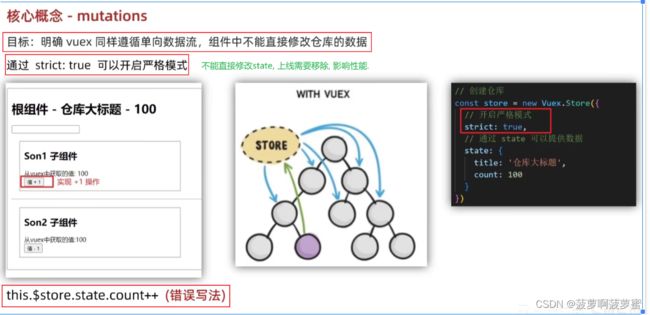
修改state中的值, 只能通过mutation; (可以检测到修改)
this.$store.commit( " xxx" )通过commit方法调用mutation中的方法;
this.$store.dispatch( ""xxx )通过dispatch方法调用action中的方法;
action中的方法通过context.commit(“xxx”)调用mutation中的方法;
vuex中的数据是单向数据流, 数据不能使用v-model双向绑定;
state
存放vuex管理的公共数据;
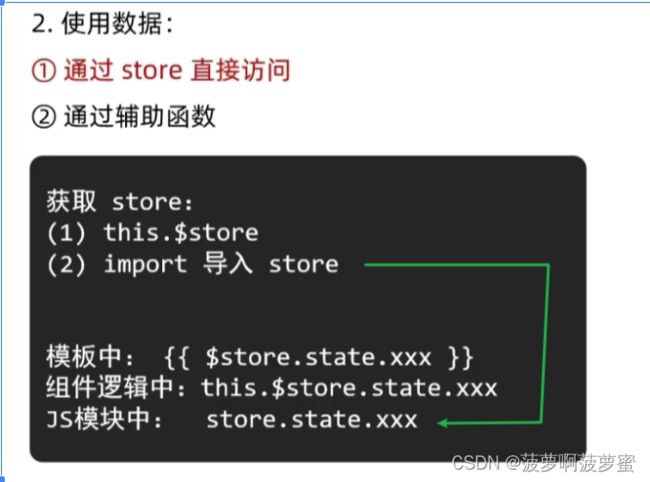
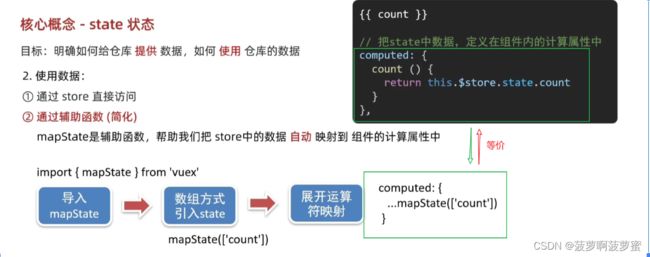
从全局vuex中获取数据
this.$store.state.xxx
...mapState( ['xxx' ] )
从模块化的vuex中获取数据
this.$store.state.模块名.属性名
...mapState( '模块名', [ '属性名' ] )
data中获取不到vuex中的数据;
state:{
"xxx":xxx,
}
使用state中的数据:
1.this.$store.state.xxx
2.通过导入的mapState函数将当前组件需要的数据,映射为当前组件的computed计算属性:
import {mapState} from "vuex";
computed:{
...mapState(["xxx"]) // 在computed中解构出来
}
在模板中直接使用 {{xxx}}
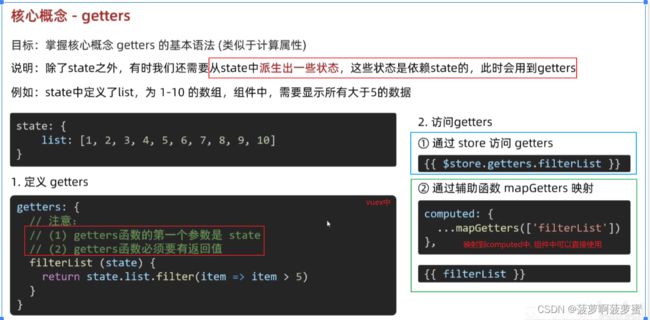
getters
对state中的数据加工, 不会修改state, 类似于就算属性, 不用加()调用, 有缓存机制;
state中的数据改变, getter的数据响应式同步改变;
全局vuex
this.$store.getters.xxx// 不同加( )调用
...mapGetters( [ 'xxx' ] )
模块化的vuex
this.$store.getters[ '模块名/属性名' ]
...mapmapGetters( '模块名', [ '属性名' ] )
可以获取state对象, 对state中的数据进行加工;
getters:{
show1(state) {
return state.count * 2
},
show2:state => state.count*2
}
使用getter中的数据
1.this.$store.getters.xxx
2.通过导入的mapGetters函数将当前组件需要的数据,映射为当前组件的computed计算属性:
import {mapGetters} from "vuex";
computed:{
...mapGetters(["xxx"]) // 在computed中解构出来
}
在模板中直接使用{{xxx}}
mutations
修改state中数据的的唯一方法;
mutations中的方法, 第一个参数是state对象, 第二个是传递过来的参数;
只能执行同步代码;
全局vuex
this.$store.commit( "方法名", 参数)
...mapMutations( [ '方法名' ] )
模块化的vuex
this.$store.commit( "模块名/方法名", 参数)
...mapMutations( '模块名', ['方法名' ] )
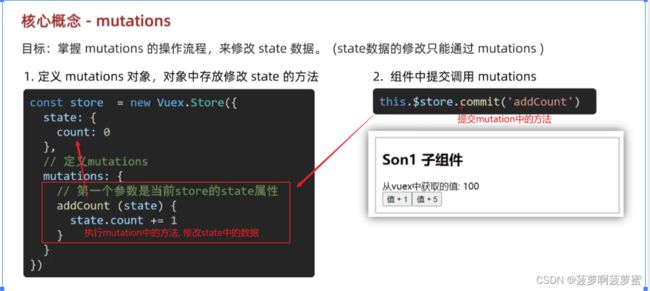
mutations:{
// state对象,payload传递的参数
demo(state,payload) {
state.count+=payload
}
}
使用mutation中的方法
1.在methods中调用this.$store.commit('方法名',payload)
methods: {
demoHandler(){
this.$store.commit('demo',5) //调用mutation中的方法,并传参;
}
}
2.1 <button @click="demoHandler">++</button>
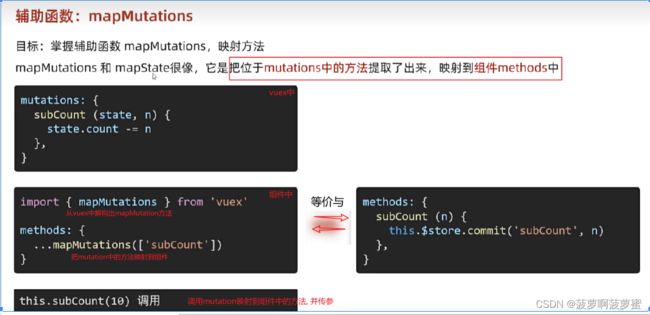
通过导入的mapMutations函数,将需要的mutations函数,映射为当前组件的methods方法:
import { mapMutations } from 'vuex'
methods: {
...mapMutations(["demo"]), // 在methods中解构出来demo方法, 在处理函数中调用并传参;
demoHandler() {
this.demo(5)
}
}
2.2 在模板中直接调用解构出来的方法并传参
<button @click="demo(5)">++</button>
import { mapMutations } from 'vuex'
methods: {
...mapMutations(["demo"]), // 在methods中解构出来demo方法
}
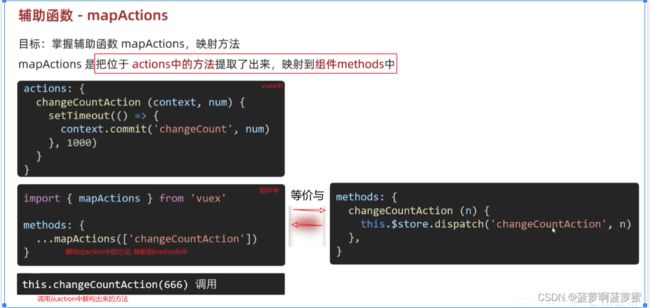
actions
处理异步代码, 例如发送网络请求;
action本质还是触发mutation中的方法来改变state中的数据;
context.commit(“方法”,payload)
action中的方法,第一个形参是context对象, 解构出来{ commit } 直接使用 ; 第二个形参是传递过来的参数;
context对象是一个mini的store对象;
全局vuex中
this.$store.dispatch( "方法名",payload)
...mapActions( [ '方法名' ] )
模块化的vuex
this.$store.dispatch( '模块名/方法名', 参数 )
...mapActions( '模块名', ['方法名' ])
action:{
jiaAsync(context,paylod){
settimeout( ()=>{
commit("jia",payload) // 通过commit调用mutation中的方法并传参
}, 1500)
}
}
mutation:{
jia(state,num){
state.count+=num
}
}
使用action中的方法
1. methods: {
bigHandler() {
this.$store.dispatch("jiaAsync", 5) // 通过dispatch调用action中的方法, action中的方法通过commit再调用mutation 的方法, mutation中的方法再执行!
}
}
2.1 通过导入的mapActions 函数,将需要的actions 函数,映射为当前组件的methods方法:
methods: {
...mapActions(['sumAsync']), // 从action中解构出来sumAsync方法
bigHandler() {
this.sumAsync(5) // 在处理函数中调用sumAsync方法并传参
}
},
2.2 在模板中直接调用解构出来的方法并传参
<button @click="sumAsync(10)">bigSum变</button>
methods: {
...mapActions(['sumAsync']),
},
actions: {
// 解构context对象
increment ({ commit }) {
commit('increment')
}
}
context 是一个包含了多个属性和方法的对象;
1. context.state:等同于 store.state,可以通过 context.state 访问 Vuex store 的状态。
2. context.getters:等同于 store.getters,可以通过 context.getters 访问 Vuex store 的 getter 方法。
3. context.commit:用于触发一个 mutation 方法。可以通过 context.commit('mutationName') 来调用一个 mutation 方法来修改 Vuex store 的状态。
4. context.dispatch:用于触发一个 action 方法。可以通过 context.dispatch('actionName') 来调用另一个 action 方法。
5. context.rootState:等同于 store.state,但指向根级的 state 对象。
6. context.rootGetters:等同于 store.getters,但指向根级的 getters 对象。
Vuex概述
actions