python求遍历、最短路径、最小生成树、旅行商问题并绘图展示
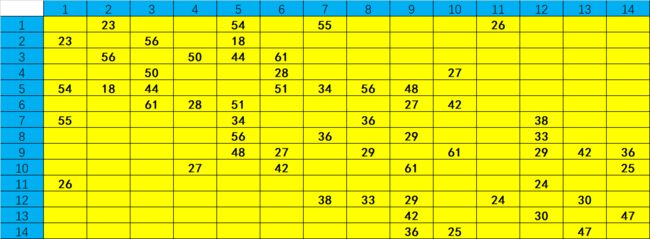
一、源数据
二、python程序
(1) 数据预处理
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from scipy.sparse import coo_matrix
import networkx as nx
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 避免图片无法显示中文
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif']=['SimHei']
# 显示所有列
pd.set_option('display.max_columns', None)
pd.set_option('display.width', 1000)
# 读取数据
data=pd.read_excel('data.xlsx',sheet_name='Sheet1',index_col=0)
data=data.fillna(0)
print('矩阵的空值以0填充:\n',data)
coo=coo_matrix(np.array(data))
# 矩阵行列的索引默认从0开始改成从1开始
coo.row+=1
coo.col+=1
data=[int(i) for i in coo.data]
coo_tuple=list(zip(coo.row,coo.col,data))
coo_list=[]
for i in coo_tuple:
coo_list.append(list(i))
# 出发点
start_node=1
# 目的地
target_node=14
# 设置各顶点坐标(只是方便绘图,并不是实际位置)
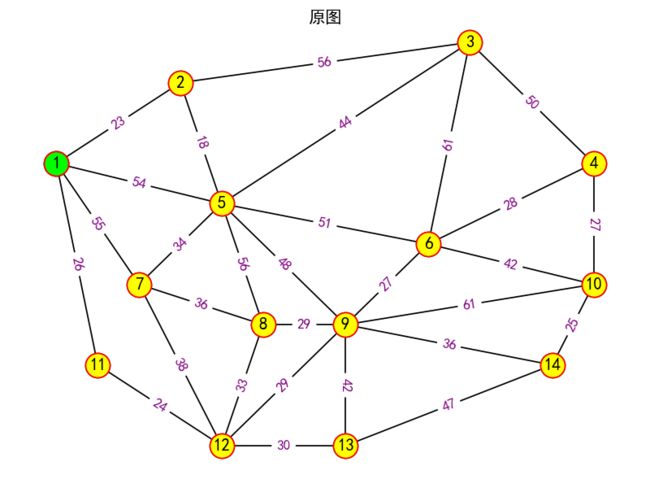
pos={1:(1,8),2:(4,10),3:(11,11),4:(14,8),5:(5,7),6:(10,6),7:(3,5),8:(6,4),9:(8,4),10:(14,5),11:(2,3),12:(5,1),13:(8,1),14:(13,3)}
输出结果如下:
矩阵的空值以0填充:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14
1 0.0 23.0 0.0 0.0 54.0 0.0 55.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 26.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
2 23.0 0.0 56.0 0.0 18.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
3 0.0 56.0 0.0 50.0 44.0 61.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
4 0.0 0.0 50.0 0.0 0.0 28.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 27.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
5 54.0 18.0 44.0 0.0 0.0 51.0 34.0 56.0 48.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
6 0.0 0.0 61.0 28.0 51.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 27.0 42.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
7 55.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 34.0 0.0 0.0 36.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 38.0 0.0 0.0
8 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 56.0 0.0 36.0 0.0 29.0 0.0 0.0 33.0 0.0 0.0
9 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 48.0 27.0 0.0 29.0 0.0 61.0 0.0 29.0 42.0 36.0
10 0.0 0.0 0.0 27.0 0.0 42.0 0.0 0.0 61.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 25.0
11 26.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 24.0 0.0 0.0
12 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 38.0 33.0 29.0 0.0 24.0 0.0 30.0 0.0
13 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 42.0 0.0 0.0 30.0 0.0 47.0
14 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 36.0 25.0 0.0 0.0 47.0 0.0
(2) 遍历:深度优先和广度优先
# 创建空的无向图
G=nx.Graph()
# 给无向图的边赋予权值
G.add_weighted_edges_from(coo_list)
# dfs深度优先
print('\n深度优先遍历:')
# 从源头开始在深度优先搜索中生成边
print(list(nx.dfs_edges(G,source=start_node)))
# 返回从源头开始的深度优先搜索构造的定向树
T_dfs=nx.dfs_tree(G,source=start_node)
print(T_dfs.nodes)
# bfs广度优先
print('\n广度优先遍历:')
# 从源头开始在广度优先搜索中生成边
print(list(nx.bfs_edges(G,source=start_node)))
# 返回从源头开始的广度优先搜索构造的定向树
T_bfs=nx.bfs_tree(G,source=start_node)
print(T_bfs.nodes)
输出结果如下:
深度优先遍历:
[(1, 2), (2, 3), (3, 4), (4, 6), (6, 5), (5, 7), (7, 8), (8, 9), (9, 10), (10, 14), (14, 13), (13, 12), (12, 11)]
[1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 5, 7, 8, 9, 10, 14, 13, 12, 11]
广度优先遍历:
[(1, 2), (1, 5), (1, 7), (1, 11), (2, 3), (5, 6), (5, 8), (5, 9), (7, 12), (3, 4), (6, 10), (9, 13), (9, 14)]
[1, 2, 5, 7, 11, 3, 6, 8, 9, 12, 4, 10, 13, 14]
(3) 求最短路径:dijkstra算法和floyd算法
# 单源最短路径dijkstra迪杰斯特拉算法求最短路径和最短路程
min_path_dijkstra=nx.dijkstra_path(G,source=start_node,target=target_node)
min_path_length_dijkstra=nx.dijkstra_path_length(G,source=start_node,target=target_node)
print('\ndijkstra算法:顶点%d到顶点%d的最短路径:%s,最短路程:%d'%(start_node,target_node,min_path_dijkstra,min_path_length_dijkstra))
# 多源最短路径floyd弗洛伊德算法求最短路径和最短路程
index_floyd=list(nx.floyd_warshall(G,weight='weight'))
min_path_length_floyd=nx.floyd_warshall_numpy(G,weight='weight')
min_path_length_floyd=pd.DataFrame(data=min_path_length_floyd,index=index_floyd,columns=index_floyd)
print('\nfloyd算法:各顶点之间的最短路程矩阵:\n',min_path_length_floyd)
输出结果如下:
dijkstra算法:顶点1到顶点14的最短路径:[1, 11, 12, 9, 14],最短路程:115
floyd算法:各顶点之间的最短路程矩阵:
1 2 5 7 11 3 4 6 10 8 9 12 13 14
1 0.0 23.0 41.0 55.0 26.0 79.0 120.0 92.0 134.0 83.0 79.0 50.0 80.0 115.0
2 23.0 0.0 18.0 52.0 49.0 56.0 97.0 69.0 111.0 74.0 66.0 73.0 103.0 102.0
5 41.0 18.0 0.0 34.0 67.0 44.0 79.0 51.0 93.0 56.0 48.0 72.0 90.0 84.0
7 55.0 52.0 34.0 0.0 62.0 78.0 113.0 85.0 126.0 36.0 65.0 38.0 68.0 101.0
11 26.0 49.0 67.0 62.0 0.0 105.0 108.0 80.0 114.0 57.0 53.0 24.0 54.0 89.0
3 79.0 56.0 44.0 78.0 105.0 0.0 50.0 61.0 77.0 100.0 88.0 116.0 130.0 102.0
4 120.0 97.0 79.0 113.0 108.0 50.0 0.0 28.0 27.0 84.0 55.0 84.0 97.0 52.0
6 92.0 69.0 51.0 85.0 80.0 61.0 28.0 0.0 42.0 56.0 27.0 56.0 69.0 63.0
10 134.0 111.0 93.0 126.0 114.0 77.0 27.0 42.0 0.0 90.0 61.0 90.0 72.0 25.0
8 83.0 74.0 56.0 36.0 57.0 100.0 84.0 56.0 90.0 0.0 29.0 33.0 63.0 65.0
9 79.0 66.0 48.0 65.0 53.0 88.0 55.0 27.0 61.0 29.0 0.0 29.0 42.0 36.0
12 50.0 73.0 72.0 38.0 24.0 116.0 84.0 56.0 90.0 33.0 29.0 0.0 30.0 65.0
13 80.0 103.0 90.0 68.0 54.0 130.0 97.0 69.0 72.0 63.0 42.0 30.0 0.0 47.0
14 115.0 102.0 84.0 101.0 89.0 102.0 52.0 63.0 25.0 65.0 36.0 65.0 47.0 0.0
(4) 绘制原图
plt.figure()
plt.suptitle('原图')
# 绘制无向加权图
nx.draw(G,pos,with_labels=True)
# 显示无向加权图的边的权值
labels=nx.get_edge_attributes(G,'weight')
# 设置顶点颜色
nx.draw_networkx_nodes(G,pos,node_color='yellow',edgecolors='red')
# 显示边的权值
nx.draw_networkx_edge_labels(G,pos,edge_labels=labels,font_color='purple',font_size=10)
nx.draw_networkx_nodes(G,pos,nodelist=[start_node],node_color='#00ff00',edgecolors='red')
(5) 求最小生成树:kruskal算法和prim算法
plt.figure()
plt.suptitle('kruskal算法或prim算法:最小生成树')
T=nx.minimum_spanning_tree(G,algorithm='kruskal')
# T=nx.minimum_spanning_tree(G,algorithm='prim')
# T=nx.minimum_spanning_tree(G,algorithm='boruvka')
# 绘制无向加权图
nx.draw(G,pos,with_labels=True)
# 设置最小生成树的顶点颜色
nx.draw_networkx_nodes(G,pos,nodelist=T.nodes,node_color='yellow',edgecolors='red')
# 设置最小生成树的边颜色和宽度
nx.draw_networkx_edges(G,pos,edgelist=T.edges,edge_color='blue',width=5)
# 显示无向加权图的边的权值
labels=nx.get_edge_attributes(G,'weight')
# 显示边的权值
nx.draw_networkx_edge_labels(G,pos,edge_labels=labels,font_color='purple',font_size=10)
nx.draw_networkx_nodes(G,pos,nodelist=[start_node],node_color='#00ff00',edgecolors='red')
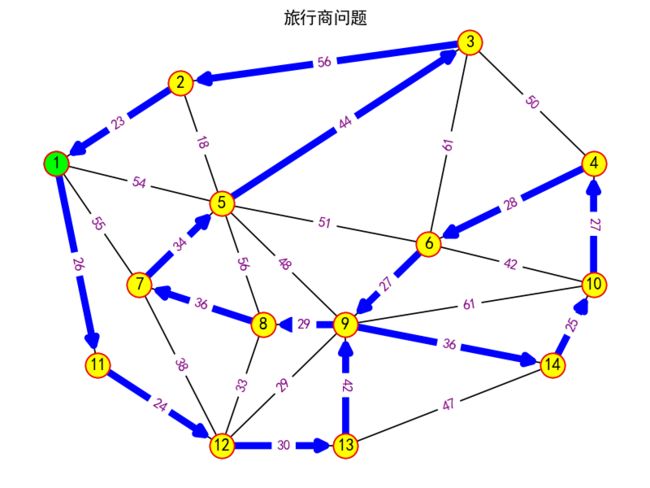
(6) 旅行商问题
plt.figure()
plt.suptitle('旅行商问题')
tsp=nx.approximation.traveling_salesman_problem(G,weight='weight')
tsp_edges=[]
tsp_length=0
for i in range(0,len(tsp)-1):
tsp_edges.append([tsp[i],tsp[i+1]])
print('\n旅行商问题:',tsp_edges)
# 绘制无向加权图
nx.draw(G,pos,with_labels=True)
# 显示无向加权图的边的权值
labels=nx.get_edge_attributes(G,'weight')
# 设置顶点颜色
nx.draw_networkx_nodes(G,pos,node_color='yellow',edgecolors='red')
nx.draw_networkx_nodes(G,pos,nodelist=[start_node],node_color='#00ff00',edgecolors='red')
# 设置边颜色和宽度
nx.draw_networkx_edges(G,pos,edgelist=tsp_edges,edge_color='blue',width=5,arrows=True,arrowstyle='->',arrowsize=15)
# 显示边的权值
nx.draw_networkx_edge_labels(G,pos,edge_labels=labels,font_color='purple',font_size=10)
plt.show()
旅行商问题: [[1, 11], [11, 12], [12, 13], [13, 9], [9, 14], [14, 10], [10, 4], [4, 6], [6, 9], [9, 8], [8, 7], [7, 5], [5, 3], [3, 2], [2, 1]]