前言
在报表数据处理中,Excel公式拥有强大而多样的功能,广泛应用于各个业务领域。无论是投资收益计算、财务报表编制还是保险收益估算,Excel公式都扮演着不可或缺的角色。传统的做法是直接依赖Excel来实现复杂的业务逻辑,并生成相应的Excel文件。因此只需在预设位置输入相应参数,Excel公式即可被激活,迅速计算并呈现结果。正因如此,在这类场景中,企业积累了大量用于计算的Excel文件,它们已经成为了无价的财富。
然而,传统的Excel文件方式存在难以管理和数据不安全的缺点。为了解决这些问题,可以采用B/S架构+Excel组件库的方式。
本文将以个人所得税的计算为例,使用React+Spring Boot+GcExcel来实现。首先准备好Excel文件,按照国家税务总局提供的个税计算页面进行创建。
个人所得税的收入类型有8种:
- 工资薪金所得
- 年终奖所得
- 劳务报酬所得
- 个体工商户、生产经营所得
- 酬劳所得
- 偶然所得
- 利息、股息、红利所得
- 财产转让所得
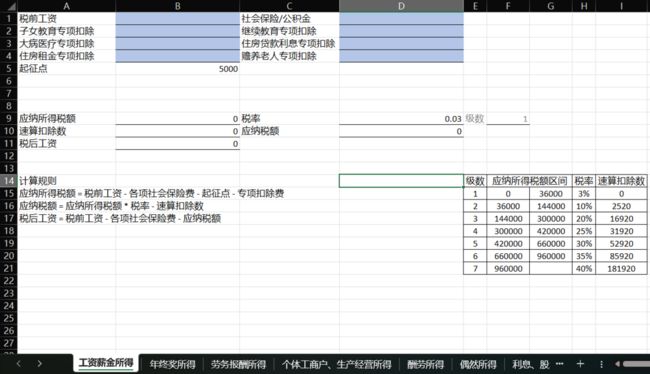
其中,工资薪金所得最为复杂,包括社会保险和专项扣除。每种类型的计税方式都不同,为了便于理解,我们为每个类型创建了一个工作表进行计算。
以下是准备好的Excel文件,其中蓝色部分为需要输入参数的单元格,其他单元格将自动计算。
完成准备工作后,下面开始前后端工程的搭建。
实践
前端 React
创建React工程
新建一个文件夹,如TaxCalculator,进入文件夹,在资源管理器的地址栏里输入cmd,然后回车,打开命令行窗口。使用下面的代码创建名为client-app的react app。
npx create-react-app salary-client进入刚创建的salary-client文件夹,使用IDE,比如VisualStudio Code打开文件夹。
界面部分
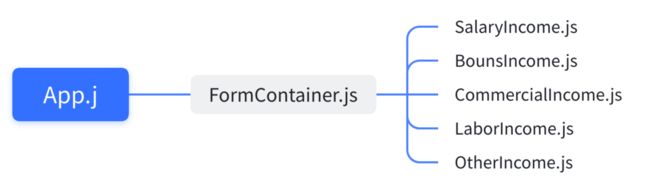
个人所得税涉及的收入类型一共有8种,其中(“酬劳所得”,“偶然所得”,“利息、股息、红利所得”,“财产转让所得”)四种的计算方式接近,UI布局相似,借助React的component特性,最终需要提供5种表单界面。
如下图所示:
为了让UI看起来更好看一些,可以先引入一个UI框架,这里我们使用了MUI。
npm install @mui/material @emotion/react @emotion/styled首先,更新Src/App.js的代码,其中添加了DarkMode的Theme, 代码如下:
import './App.css';
import { ThemeProvider } from '@emotion/react';
import { createTheme } from '@mui/material';
import { FormContainer } from './Component/FormContainer';
const darkTheme = createTheme({
palette: {
mode: 'dark',
},
});
function App() {
return (
个人所得税计算器
);
}
export default App;可以看到,App.js中引用了FormContainer,下来添加 ./Component/FormContainer.js。
FormContainer主要是提供一个Selector,让用户选择收入类型,根据选择的类型渲染不同的组件。
import React, { useState } from 'react';
import { SalaryIncome } from "./SalaryIncome"
import { NativeSelect, FormControl } from '@mui/material';
import { BounsIncome } from './BounsIncome';
import { CommercialIncome } from './CommercialIncome';
import { LaborIncome } from './LaborIncome';
import { OtherIncome } from './OtherIncome';
export const FormContainer = () => {
const [calcType, setCalcType] = useState("工资薪金所得");
const GetIncomeControl = () => {
switch (calcType) {
case "工资薪金所得":
return
setCalcType(e.target.value)} >
{GetIncomeControl()}
);
}例如:\
接下来,分别创建几个xxxIncome组件。
1.工资薪金所得 SalaryIncome.js
import React, { useState } from 'react';
import { TextField, Button, Stack } from '@mui/material';
import axios from 'axios';
export const SalaryIncome = (props) => {
const [income, setIncome] = useState("");
const [insurance, setInsurance] = useState("");
const [childEdu, setChildEdu] = useState("");
const [selfEdu, setSelfEdu] = useState("");
const [treatment, setTreatment] = useState("");
const [loans, setLoans] = useState("");
const [rent, setRent] = useState("");
const [elder, setElder] = useState("");
const [taxableIncome, setTaxableIncome] = useState("");
const [taxRate, setTaxRate] = useState("");
const [deduction, setDeduction] = useState("");
const [tax, setTax] = useState("");
const [takeHomeSalary, setTakeHomeSalary] = useState("");
async function calculateTax(event) {
event.preventDefault();
let res = await axios.post("api/calcPersonTax", {
calcType: props.calcType,
income: income,
insurance: insurance,
childEdu: childEdu,
selfEdu: selfEdu,
treatment: treatment,
loans: loans,
rent: rent,
elder: elder,
});
if (res != null) {
let data = res.data;
setTaxableIncome(data.taxableIncome);
setTaxRate(data.taxRate);
setDeduction(data.deduction);
setTax(data.tax);
setTakeHomeSalary(data.takeHomeSalary);
}
}
function reset(event) {
event.preventDefault();
setIncome("");
setInsurance("");
setChildEdu("");
setSelfEdu("");
setTreatment("");
setLoans("");
setRent("");
setElder("");
setTaxableIncome("");
setTaxRate("");
setDeduction("");
setTax("");
setTakeHomeSalary("");
}
return (
setIncome(e.target.value)}
value={income} fullWidth required size="small"/>
setInsurance(e.target.value)}
value={insurance} fullWidth size="small"/>
setChildEdu(e.target.value)}
value={childEdu} fullWidth size="small"/>
setSelfEdu(e.target.value)}
value={selfEdu} fullWidth size="small"/>
setTreatment(e.target.value)}
value={treatment} fullWidth size="small"/>
setLoans(e.target.value)}
value={loans} fullWidth size="small"/>
setRent(e.target.value)}
value={rent} fullWidth size="small"/>
setElder(e.target.value)}
value={elder} fullWidth size="small"/>
)
}2.年终奖金所得 BounsIncome.js
import React, { useState } from 'react';
import { TextField, Button, Stack } from '@mui/material';
import axios from 'axios';
export const BounsIncome = (props) => {
const [income, setIncome] = useState("");
const [taxableIncome, setTaxableIncome] = useState("");
const [taxRate, setTaxRate] = useState("");
const [deduction, setDeduction] = useState("");
const [monthlyWage, setMonthlyWage] = useState("");
const [tax, setTax] = useState("");
const [takeHomeSalary, setTakeHomeSalary] = useState("");
async function calculateTax(event) {
event.preventDefault();
let res = await axios.post("api/calcPersonTax", {
calcType: props.calcType,
income: income,
});
if (res != null) {
let data = res.data;
setTaxableIncome(data.taxableIncome);
setTaxRate(data.taxRate);
setDeduction(data.deduction);
setMonthlyWage(data.monthlyWage);
setTax(data.tax);
setTakeHomeSalary(data.takeHomeSalary);
}
}
function reset(event) {
event.preventDefault();
setIncome("");
setTaxableIncome("");
setTaxRate("");
setDeduction("");
setMonthlyWage("");
setTax("");
setTakeHomeSalary("");
}
return (
setIncome(e.target.value)}
value={income} fullWidth required />
)
}3.劳务报酬所得 LaborIncome.js
import React, { useState } from 'react';
import { TextField, Button, Stack } from '@mui/material';
import axios from 'axios';
export const LaborIncome = (props) => {
const [income, setIncome] = useState("");
const [taxableIncome, setTaxableIncome] = useState("");
const [taxRate, setTaxRate] = useState("");
const [deduction, setDeduction] = useState("");
const [nonTaxablePart, setNonTaxablePart] = useState("");
const [tax, setTax] = useState("");
const [takeHomeSalary, setTakeHomeSalary] = useState("");
async function calculateTax(event) {
event.preventDefault();
let res = await axios.post("api/calcPersonTax", {
calcType: props.calcType,
income: income,
});
if (res != null) {
let data = res.data;
setTaxableIncome(data.taxableIncome);
setTaxRate(data.taxRate);
setDeduction(data.deduction);
setNonTaxablePart(data.nonTaxablePart);
setTax(data.tax);
setTakeHomeSalary(data.takeHomeSalary);
}
}
function reset(event) {
event.preventDefault();
setIncome("");
setTaxableIncome("");
setTaxRate("");
setDeduction("");
setNonTaxablePart("");
setTax("");
setTakeHomeSalary("");
}
return (
setIncome(e.target.value)}
value={income} fullWidth required />
)
}4.个体工商户、生产经营所得 CommercialIncome.js
import React, { useState } from 'react';
import { TextField, Button, Stack } from '@mui/material';
import axios from 'axios';
export const CommercialIncome = (props) => {
const [income, setIncome] = useState("");
const [taxableIncome, setTaxableIncome] = useState("");
const [taxRate, setTaxRate] = useState("");
const [deduction, setDeduction] = useState("");
const [tax, setTax] = useState("");
const [takeHomeSalary, setTakeHomeSalary] = useState("");
async function calculateTax(event) {
event.preventDefault();
let res = await axios.post("api/calcPersonTax", {
calcType: props.calcType,
income: income,
});
if (res != null) {
let data = res.data;
setTaxableIncome(data.taxableIncome);
setTaxRate(data.taxRate);
setDeduction(data.deduction);
setTax(data.tax);
setTakeHomeSalary(data.takeHomeSalary);
}
}
function reset(event) {
event.preventDefault();
setIncome("");
setTaxableIncome("");
setTaxRate("");
setDeduction("");
setTax("");
setTakeHomeSalary("");
}
return (
setIncome(e.target.value)}
value={income} fullWidth required />
)
}5.余下四种类型 OtherIncome.js
import React, { useState } from 'react';
import { TextField, Button, Stack } from '@mui/material';
import axios from 'axios';
export const OtherIncome = (props) => {
const [income, setIncome] = useState("");
const [taxableIncome, setTaxableIncome] = useState("");
const [taxRate, setTaxRate] = useState("");
const [tax, setTax] = useState("");
const [takeHomeSalary, setTakeHomeSalary] = useState("");
async function calculateTax(event) {
event.preventDefault();
let res = await axios.post("api/calcPersonTax", {
calcType: props.calcType,
income: income,
});
if (res != null) {
let data = res.data;
setTaxableIncome(data.taxableIncome);
setTaxRate(data.taxRate);
setTax(data.tax);
setTakeHomeSalary(data.takeHomeSalary);
}
}
function reset(event) {
event.preventDefault();
setIncome("");
setTaxableIncome("");
setTaxRate("");
setTax("");
setTakeHomeSalary("");
}
return (
setIncome(e.target.value)}
value={income} fullWidth required />
)
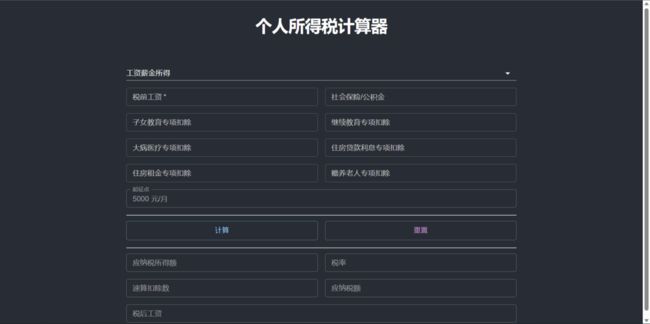
}此时,完成UI部分后,可以尝试运行起来,效果如下:
//通过代码运行React app
npm start可以试着填一些数据,但是当我们点击计算时会报错,这是因为服务端还没有准备好。
前端请求部分
熟悉Axios的同学可以跳过这部分,前面的代码里,已经给出了Axois发送请求的代码。
可以看到无论是哪一种类型的组件,请求都发送到了相同的url("api/calcPersonTax"),以SalaryIncome为例,代码如下:
async function calculateTax(event) {
event.preventDefault();
let res = await axios.post("api/calcPersonTax", {
calcType: props.calcType,
income: income,
insurance: insurance,
childEdu: childEdu,
selfEdu: selfEdu,
treatment: treatment,
loans: loans,
rent: rent,
elder: elder,
});
if (res != null) {
let data = res.data;
setTaxableIncome(data.taxableIncome);
setTaxRate(data.taxRate);
setDeduction(data.deduction);
setTax(data.tax);
setTakeHomeSalary(data.takeHomeSalary);
}
}可以看到,整个请求变得非常简单,主要是把state的值取出来,通过post请求发送到服务端,然后根据返回值,把数据重新设给state,这样就完成UI数据的更新了。
配置请求转发中间件
我们在请求时访问的是相对地址,React本身有一个nodeJS,默认的端口是3000,而Spring Boot的默认端口是8080。前端直接访问会有跨域的问题,因此我们要做一个代理的配置。
在src文件夹下面添加文件,名为setupProxy.js,代码如下:
const { createProxyMiddleware } = require('http-proxy-middleware');
module.exports = function(app) {
app.use(
'/api',
createProxyMiddleware({
target: 'http://localhost:8080',
changeOrigin: true,
})
);
};服务端 Spring Boot
创建工程及添加依赖
使用IDEA创建一个Spring Boot工程,如果使用的是社区(community)版本,不能直接创建Spring Boot项目,那可以先创建一个空项目,idea创建project的过程,就跳过了,这里我们以创建了一个gradle项目为例。
plugins {
id 'org.springframework.boot' version '3.0.0'
id 'io.spring.dependency-management' version '1.1.0'
id 'java'
id 'war'
}
group = 'org.example'
version = '1.0-SNAPSHOT'
repositories {
mavenCentral()
}
dependencies {
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-web'
implementation 'com.grapecity.documents:gcexcel:6.2.0'
implementation 'javax.json:javax.json-api:1.1.4'
providedRuntime 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-tomcat'
testImplementation('org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-test')
}
test {
useJUnitPlatform()
}在dependencies 中,我们除了依赖Spring Boot之外,还添加了GcExcel的依赖,后面导出时会用到GcExcel,目前的版本是6.2.0。
添加API
在Application类上,添加属性 @RequestMapping("/api").,并添加 calcPersonTax API。
@Spring BootApplication
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api")
public class SalaryTaxCalculator {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SalaryTaxCalculator.class, args);
}
@PostMapping("/calcPersonTax")
public CalcResult calcTax(@RequestBody CalcParameter par) {
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
workbook.open(GetResourcePath());
return CalcInternal(workbook, par);
}
private String GetResourcePath(){
return Objects.requireNonNull(SalaryTaxCalculator.class.getClassLoader().getResource("PersonalTaxCalcEngine.xlsx")).getPath();
}
private CalcResult CalcInternal(Workbook workbook, CalcParameter par) {
//todo
}
}可以看到在CalcInternal方法内,我们使用GcExcel,根据calcType来判断使用哪一个sheet来进行计算。对不同Sheet只需要通过GcExcel设值,并从特定的格子里取值即可。
同时,我们还需要创建两个类,CalcParameter和CalcResult。CalcParameter用于从request中把post的data解析出来,CalcResult用于在response中返回的数据。
CalcParameter:
public class CalcParameter {
public String calcType;
public double income;
public double insurance;
public double childEdu;
public double selfEdu;
public double treatment;
public double loans;
public double rent;
public double elder;
}CalcResult:
public class CalcResult {
public double taxableIncome;
public double taxRate;
public double deduction;
public double tax;
public double takeHomeSalary;
public double monthlyWage;
public double nonTaxablePart;
}使用GcExcel完成公式计算
前面我们定义了 CalcInternal,在 CalcInternal 中,我们需要使用GcExcel来完成公式计算。
GcExcel的公式计算是自动完成的,我们使用workbook打开Excel文件后,只需要set相关的value。之后在取值时,GcExcel会自动计算响应公式的值。
private CalcResult CalcInternal(Workbook workbook, CalcParameter par) {
var result = new CalcResult();
var sheet = workbook.getWorksheets().get(par.calcType);
switch (par.calcType) {
case "工资薪金所得" -> {
sheet.getRange("B1").setValue(par.income);
sheet.getRange("D1").setValue(par.insurance);
sheet.getRange("B2").setValue(par.childEdu);
sheet.getRange("D2").setValue(par.selfEdu);
sheet.getRange("B3").setValue(par.treatment);
sheet.getRange("D3").setValue(par.loans);
sheet.getRange("B4").setValue(par.rent);
sheet.getRange("D4").setValue(par.elder);
result.taxableIncome = (double) sheet.getRange("B9").getValue();
result.taxRate = (double) sheet.getRange("D9").getValue();
result.deduction = (double) sheet.getRange("B10").getValue();
result.tax = (double) sheet.getRange("D10").getValue();
result.takeHomeSalary = (double) sheet.getRange("B11").getValue();
}
case "年终奖所得" -> {
sheet.getRange("B1").setValue(par.income);
result.taxableIncome = (double) sheet.getRange("B3").getValue();
result.taxRate = (double) sheet.getRange("D3").getValue();
result.deduction = (double) sheet.getRange("B4").getValue();
result.monthlyWage = (double) sheet.getRange("D4").getValue();
result.tax = (double) sheet.getRange("B5").getValue();
result.takeHomeSalary = (double) sheet.getRange("D5").getValue();
}
case "劳务报酬所得" -> {
sheet.getRange("B1").setValue(par.income);
result.taxableIncome = (double) sheet.getRange("B3").getValue();
result.taxRate = (double) sheet.getRange("D3").getValue();
result.deduction = (double) sheet.getRange("B4").getValue();
result.nonTaxablePart = (double) sheet.getRange("D4").getValue();
result.tax = (double) sheet.getRange("B5").getValue();
result.takeHomeSalary = (double) sheet.getRange("D5").getValue();
}
case "个体工商户、生产经营所得" -> {
sheet.getRange("B1").setValue(par.income);
result.taxableIncome = (double) sheet.getRange("B3").getValue();
result.taxRate = (double) sheet.getRange("D3").getValue();
result.deduction = (double) sheet.getRange("B4").getValue();
result.tax = (double) sheet.getRange("D4").getValue();
result.takeHomeSalary = (double) sheet.getRange("B5").getValue();
}
default -> {
sheet.getRange("B1").setValue(par.income);
result.taxableIncome = (double) sheet.getRange("B3").getValue();
result.taxRate = (double) sheet.getRange("D3").getValue();
result.tax = (double) sheet.getRange("B4").getValue();
result.takeHomeSalary = (double) sheet.getRange("D4").getValue();
}
}
return result;
}这样就完成了服务端的代码。
最终效果
我们可以使用工资薪金所得试验一下,可以看到数据被计算出来了。因为目的是为了分享服务端公式计算的方案,所以计算的结果是否正确,就不做细致考虑。
总结
个税计算的场景并不复杂,主要是通过Excel完成公式计算即可,在服务端使用GcExcel可以大幅度降低前后端的开发难度,系统的搭建过程可以完全不需要考虑计算的逻辑。
在实际的公式计算场景中,可能往往会比个税计算的场景复杂,借助GcExcel这样Excel组件库,可以很容易的把已有的Excel文件迁移到线上,提高工作效率。
另外,本文中分享的代码并不是最符合实际工作中的要求,读者还可以从以下角度去优化自己的代码。
- 收入类型可以抽成枚举,这样维护和使用起来更容易。
- 目前每一个react组件里的冗余度还不低,还可以继续抽象组件,避免重复写代码。
- 在服务端,因为公式计算的逻辑是不会变的,在实际场景中,也有可能同一时间要加载复数个Excel文件,可以考虑把workbook常驻内存,来提高性能。
扩展链接: