LINUX 路由子系统流程分析
title: LINUX 路由子系统流程分析
date: 2020-11-28
categories:
- Linux
tags: - Linux
- Routing-Subsystem
上次分析了Linux协议栈的收包过程。里面有一段是直接省略了过去,那就是linux路由子系统。本文还是提供一个大致的流程。对于详细的算法以后会慢慢补充完整。
上次说道经过么一个调用关系,收包流程就可以走到 ip_local_deliver() 函数之后在进行等等的操作。
ip_rcv_finish()
->ip_route_input_noref()
->ip_route_input_common()
->dst_input()
在实际的收报代码中,这个地方的代码就出现了一行 ip_route_input_noref()。就是这一行最终调用了这个 ip_route_input_common() 函数,其也就是linux路由子系统的关键部分(还有一部分就是手动添加路由表的处理)。
/* linux-3.4.11/net/ipv4/ip_input.c */
ip_route_input_noref(skb, iph->daddr, iph->saddr,iph->tos, skb->dev);
static inline int ip_route_input_noref(struct sk_buff *skb, __be32 dst, __be32 src,
u8 tos, struct net_device *devin)
{
return ip_route_input_common(skb, dst, src, tos, devin, true);
}
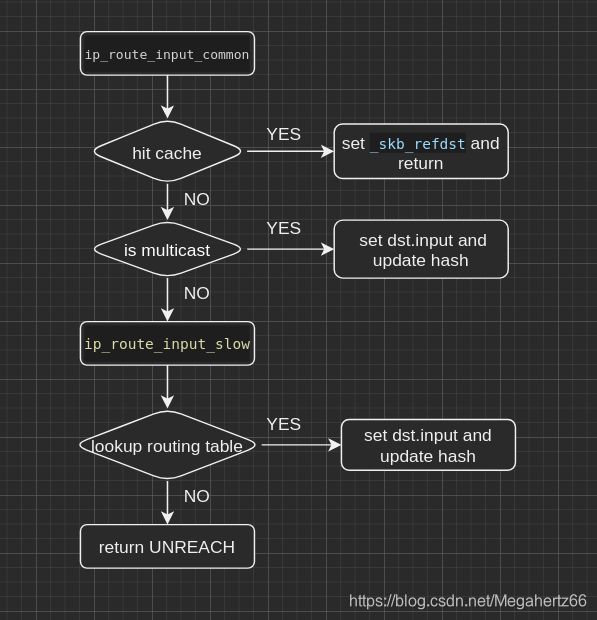
ip_route_input_common()(IPV4部分)位于linux-3.4.11/net/ipv4/route.c文件中。函数功能是将收到包进行路由。重点来看这个函数。
按照我粗浅的图上看来,这个地方可以大体分为三个部分,分别对应于能够 hit cache 和 多播 以及 其他。
Hit Cache
int ip_route_input_common(struct sk_buff *skb, __be32 daddr, __be32 saddr,
u8 tos, struct net_device *dev, bool noref)
{
...
hash = rt_hash(daddr, saddr, iif, rt_genid(net));
for (rth = rcu_dereference(rt_hash_table[hash].chain); rth;
rth = rcu_dereference(rth->dst.rt_next)) {
if ((((__force u32)rth->rt_key_dst ^ (__force u32)daddr) |
((__force u32)rth->rt_key_src ^ (__force u32)saddr) |
(rth->rt_route_iif ^ iif) |
(rth->rt_key_tos ^ tos)) == 0 &&
rth->rt_mark == skb->mark &&
net_eq(dev_net(rth->dst.dev), net) &&
!rt_is_expired(rth)) {
ipv4_validate_peer(rth);
if (noref) {
dst_use_noref(&rth->dst, jiffies);
skb_dst_set_noref(skb, &rth->dst);
} else {
dst_use(&rth->dst, jiffies);
skb_dst_set(skb, &rth->dst);
}
RT_CACHE_STAT_INC(in_hit);
rcu_read_unlock();
return 0;
}
RT_CACHE_STAT_INC(in_hlist_search);
}
...
If kernel can not find the entry in cache, it will find the rounting table. It will insert the new entry into the cache at the head of the bucket’s list.
The cache will be update with manually, ICMP_REDIRECT message and ARP table(???).
If the lookup secceeds, the existing cache route is simply moved to the head of the bucket’s list.
可以看出,首先对目标和本身的地址以及 interface index(iif) 还有 net 结构计算出 hash-key。然后在 hash list 中尝试找到现有的 routing cache 。 代码中的 skb_dst_set() 和 skb_dst_set() 是协议无关函数,其位于 linux-3.4.11/include/net/dst.h 和 /linux-3.4.11/net/core/dst.c 中。 他们的目的是设置 skb->_skb_refdst 以便在接下来的 dst_input() 继续传递数据包,以及增加该路由条目的使用计数。
Multicast
这个代码的上面内核是有对此的注释的。
Multicast recognition logic is moved from route cache to here.
The problem was that too many Ethernet cards have broken/missing
hardware multicast filters As result the host on multicasting
network acquires a lot of useless route cache entries, sort of
SDR messages from all the world. Now we try to get rid of them.
Really, provided software IP multicast filter is organized
reasonably (at least, hashed), it does not result in a slowdown
comparing with route cache reject entries.
Note, that multicast routers are not affected, because
route cache entry is created eventually.
对于RCU(Read-Copy Update)是数据同步的一种方式,细节暂时搁置。在 ip_route_input_mc() 的一些列检查之后,从后面的代码还是可以看出会将收包方向为自身。
if (ipv4_is_multicast(daddr)) {
struct in_device *in_dev = __in_dev_get_rcu(dev);
if (in_dev) {
...
int res = ip_route_input_mc(skb, daddr, saddr,
tos, dev, our);
...
}
}
res = ip_route_input_slow(skb, daddr, saddr, tos, dev);
return res;
}
static int ip_route_input_mc(struct sk_buff *skb, __be32 daddr, __be32 saddr,
u8 tos, struct net_device *dev, int our)
{
....
rth = rt_dst_alloc(dev_net(dev)->loopback_dev,
IN_DEV_CONF_GET(in_dev, NOPOLICY), false);
if (!rth)
goto e_nobufs;
#ifdef CONFIG_IP_ROUTE_CLASSID
rth->dst.tclassid = itag;
#endif
rth->dst.output = ip_rt_bug;
rth->rt_key_dst = daddr;
rth->rt_key_src = saddr;
rth->rt_genid = rt_genid(dev_net(dev));
rth->rt_flags = RTCF_MULTICAST;
rth->rt_type = RTN_MULTICAST;
rth->rt_key_tos = tos;
rth->rt_dst = daddr;
rth->rt_src = saddr;
rth->rt_route_iif = dev->ifindex;
rth->rt_iif = dev->ifindex;
rth->rt_oif = 0;
rth->rt_mark = skb->mark;
rth->rt_gateway = daddr;
rth->rt_spec_dst= spec_dst;
rth->rt_peer_genid = 0;
rth->peer = NULL;
rth->fi = NULL;
if (our) {
rth->dst.input= ip_local_deliver;
rth->rt_flags |= RTCF_LOCAL;
}
#ifdef CONFIG_IP_MROUTE
if (!ipv4_is_local_multicast(daddr) && IN_DEV_MFORWARD(in_dev))
rth->dst.input = ip_mr_input;
#endif
RT_CACHE_STAT_INC(in_slow_mc);
hash = rt_hash(daddr, saddr, dev->ifindex, rt_genid(dev_net(dev)));
rth = rt_intern_hash(hash, rth, skb, dev->ifindex);
return IS_ERR(rth) ? PTR_ERR(rth) : 0;
}
The kernel allocates a new cache entry with dst_alloc,initializes some of its fields based on the results from the routing table, and finally calls rt_intern_hashto insert the new entry into the cache at the head of the bucket’s list.
上面引用的《Linux Understanding networking》中内容,申请空间、计算 hash-key、插入到 routing cache 中。
Other
除了可以在 cache 中找到、多播地址。还有一种情况就是这两种之外的情况。这时就要搜索 routing table,这种情况肯定要影响速度,所以这个函数的名字就叫做 ip_route_input_slow 。
static int ip_route_input_slow(struct sk_buff *skb, __be32 daddr, __be32 saddr,
u8 tos, struct net_device *dev)
{
...
fl4.flowi4_oif = 0;
fl4.flowi4_iif = dev->ifindex;
fl4.flowi4_mark = skb->mark;
fl4.flowi4_tos = tos;
fl4.flowi4_scope = RT_SCOPE_UNIVERSE;
fl4.daddr = daddr;
fl4.saddr = saddr;
err = fib_lookup(net, &fl4, &res);
if (err != 0) {
if (!IN_DEV_FORWARD(in_dev))
goto e_hostunreach;
goto no_route;
}
RT_CACHE_STAT_INC(in_slow_tot);
if (res.type == RTN_BROADCAST)
goto brd_input;
if (res.type == RTN_LOCAL) {
err = fib_validate_source(skb, saddr, daddr, tos,
net->loopback_dev->ifindex,
dev, &spec_dst, &itag);
if (err < 0)
goto martian_source_keep_err;
if (err)
flags |= RTCF_DIRECTSRC;
spec_dst = daddr;
goto local_input;
}
if (!IN_DEV_FORWARD(in_dev))
goto e_hostunreach;
if (res.type != RTN_UNICAST)
goto martian_destination;
err = ip_mkroute_input(skb, &res, &fl4, in_dev, daddr, saddr, tos);
out: return err;
brd_input:
if (skb->protocol != htons(ETH_P_IP))
goto e_inval;
if (ipv4_is_zeronet(saddr))
spec_dst = inet_select_addr(dev, 0, RT_SCOPE_LINK);
else {
err = fib_validate_source(skb, saddr, 0, tos, 0, dev, &spec_dst,
&itag);
if (err < 0)
goto martian_source_keep_err;
if (err)
flags |= RTCF_DIRECTSRC;
}
flags |= RTCF_BROADCAST;
res.type = RTN_BROADCAST;
RT_CACHE_STAT_INC(in_brd);
local_input:
rth = rt_dst_alloc(net->loopback_dev,
IN_DEV_CONF_GET(in_dev, NOPOLICY), false);
if (!rth)
goto e_nobufs;
rth->dst.input= ip_local_deliver;
rth->dst.output= ip_rt_bug;
...
hash = rt_hash(daddr, saddr, fl4.flowi4_iif, rt_genid(net));
rth = rt_intern_hash(hash, rth, skb, fl4.flowi4_iif);
err = 0;
if (IS_ERR(rth))
err = PTR_ERR(rth);
goto out;
no_route:
RT_CACHE_STAT_INC(in_no_route);
spec_dst = inet_select_addr(dev, 0, RT_SCOPE_UNIVERSE);
res.type = RTN_UNREACHABLE;
if (err == -ESRCH)
err = -ENETUNREACH;
goto local_input;
}
会根据不同的情况选择不同的路由(比如发向本地、转发、丢弃),这里如果不考虑实现细节,单独看流程还是比较容易理解的。这里的路由已经不能从 cache 中获得了,所以只能去路由表查询。
fib_lookup() 从代码中也可以看出,要是还找不到的话,会直接回一个 消息不可达(unreach)的 ICMP 报文。
事情的关键目前就是 fib_lookup() 这个函数了 这个 lookup 查找的不再是 cache 而是 routing table。并且Forwarding Information Base (FIB) 也是 routing table 的另外一个名字而已。
Routing Table
通过这样的一个调用关系到了实际要去找 routing table entry 的地方了。
fib_lookup()
->fib_rules_lookup()
->fib_rules_lookup()
这里遍历 rules_list 匹配到符合的 rule 使用 action 函数。下面重点看好以下action函数。
int fib_rules_lookup(struct fib_rules_ops *ops, struct flowi *fl,
int flags, struct fib_lookup_arg *arg)
{
struct fib_rule *rule;
...
list_for_each_entry_rcu(rule, &ops->rules_list, list) {
if (!fib_rule_match(rule, ops, fl, flags))
continue;
if (rule->action == FR_ACT_GOTO) {
struct fib_rule *target;
target = rcu_dereference(rule->ctarget);
if (target == NULL) {
continue;
} else {
rule = target;
goto jumped;
}
} else if (rule->action == FR_ACT_NOP)
continue;
else
err = ops->action(rule, fl, flags, arg);
...
}
在 linux-3.4.11/net/ipv4/fib_rules.c 文件中被定义 fib_get_table() fib_table_lookup()这两个函数就是具体如何从routing table 中找到对应的 entry 的处理函数,里面涉及的细节暂时搁置~
static const struct fib_rules_ops __net_initdata fib4_rules_ops_template = {
.family = AF_INET,
.rule_size = sizeof(struct fib4_rule),
.addr_size = sizeof(u32),
.action = fib4_rule_action,
.match = fib4_rule_match,
.configure = fib4_rule_configure,
.compare = fib4_rule_compare,
.fill = fib4_rule_fill,
.default_pref = fib_default_rule_pref,
.nlmsg_payload = fib4_rule_nlmsg_payload,
.flush_cache = fib4_rule_flush_cache,
.nlgroup = RTNLGRP_IPV4_RULE,
.policy = fib4_rule_policy,
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
};
static int fib4_rule_action(struct fib_rule *rule, struct flowi *flp,
int flags, struct fib_lookup_arg *arg)
{
...
tbl = fib_get_table(rule->fr_net, rule->table);
if (!tbl)
goto errout;
err = fib_table_lookup(tbl, &flp->u.ip4, (struct fib_result *) arg->result, arg->flags);
if (err > 0)
err = -EAGAIN;
...
}
How To Add A New Rult
在/home/hert/studycode/linux-3.4.11/net/core/fib_rules.c 文件中涉及到路由表的 初始化 添加 删除 等操作。
并通过代码可以得知 routing table 是通过 netlink 的方式来进行添加的。 添加的细节以后具体涉及的时候再行研究………………
static int __init fib_rules_init(void)
{
int err;
rtnl_register(PF_UNSPEC, RTM_NEWRULE, fib_nl_newrule, NULL, NULL);
rtnl_register(PF_UNSPEC, RTM_DELRULE, fib_nl_delrule, NULL, NULL);
rtnl_register(PF_UNSPEC, RTM_GETRULE, NULL, fib_nl_dumprule, NULL);
err = register_pernet_subsys(&fib_rules_net_ops);
if (err < 0)
goto fail;
err = register_netdevice_notifier(&fib_rules_notifier);
if (err < 0)
goto fail_unregister;
return 0;
fail_unregister:
unregister_pernet_subsys(&fib_rules_net_ops);
fail:
rtnl_unregister(PF_UNSPEC, RTM_NEWRULE);
rtnl_unregister(PF_UNSPEC, RTM_DELRULE);
rtnl_unregister(PF_UNSPEC, RTM_GETRULE);
return err;
}
int fib_default_rule_add(struct fib_rules_ops *ops,
u32 pref, u32 table, u32 flags)
{
struct fib_rule *r;
r = kzalloc(ops->rule_size, GFP_KERNEL);
if (r == NULL)
return -ENOMEM;
atomic_set(&r->refcnt, 1);
r->action = FR_ACT_TO_TBL;
r->pref = pref;
r->table = table;
r->flags = flags;
r->fr_net = hold_net(ops->fro_net);
/* The lock is not required here, the list in unreacheable
* at the moment this function is called */
list_add_tail(&r->list, &ops->rules_list);
return 0;
}
static int fib_nl_newrule(struct sk_buff *skb, struct nlmsghdr* nlh, void *arg)
{
struct net *net = sock_net(skb->sk);
struct fib_rule_hdr *frh = nlmsg_data(nlh);
struct fib_rules_ops *ops = NULL;
struct fib_rule *rule, *r, *last = NULL;
struct nlattr *tb[FRA_MAX+1];
int err = -EINVAL, unresolved = 0;
if (nlh->nlmsg_len < nlmsg_msg_size(sizeof(*frh)))
goto errout;
ops = lookup_rules_ops(net, frh->family);
if (ops == NULL) {
err = -EAFNOSUPPORT;
goto errout;
}
err = nlmsg_parse(nlh, sizeof(*frh), tb, FRA_MAX, ops->policy);
if (err < 0)
goto errout;
err = validate_rulemsg(frh, tb, ops);
if (err < 0)
goto errout;
rule = kzalloc(ops->rule_size, GFP_KERNEL);
if (rule == NULL) {
err = -ENOMEM;
goto errout;
}
rule->fr_net = hold_net(net);
if (tb[FRA_PRIORITY])
rule->pref = nla_get_u32(tb[FRA_PRIORITY]);
if (tb[FRA_IIFNAME]) {
struct net_device *dev;
rule->iifindex = -1;
nla_strlcpy(rule->iifname, tb[FRA_IIFNAME], IFNAMSIZ);
dev = __dev_get_by_name(net, rule->iifname);
if (dev)
rule->iifindex = dev->ifindex;
}
if (tb[FRA_OIFNAME]) {
struct net_device *dev;
rule->oifindex = -1;
nla_strlcpy(rule->oifname, tb[FRA_OIFNAME], IFNAMSIZ);
dev = __dev_get_by_name(net, rule->oifname);
if (dev)
rule->oifindex = dev->ifindex;
}
if (tb[FRA_FWMARK]) {
rule->mark = nla_get_u32(tb[FRA_FWMARK]);
if (rule->mark)
/* compatibility: if the mark value is non-zero all bits
* are compared unless a mask is explicitly specified.
*/
rule->mark_mask = 0xFFFFFFFF;
}
if (tb[FRA_FWMASK])
rule->mark_mask = nla_get_u32(tb[FRA_FWMASK]);
rule->action = frh->action;
rule->flags = frh->flags;
rule->table = frh_get_table(frh, tb);
if (!tb[FRA_PRIORITY] && ops->default_pref)
rule->pref = ops->default_pref(ops);
err = -EINVAL;
if (tb[FRA_GOTO]) {
if (rule->action != FR_ACT_GOTO)
goto errout_free;
rule->target = nla_get_u32(tb[FRA_GOTO]);
/* Backward jumps are prohibited to avoid endless loops */
if (rule->target <= rule->pref)
goto errout_free;
list_for_each_entry(r, &ops->rules_list, list) {
if (r->pref == rule->target) {
RCU_INIT_POINTER(rule->ctarget, r);
break;
}
}
if (rcu_dereference_protected(rule->ctarget, 1) == NULL)
unresolved = 1;
} else if (rule->action == FR_ACT_GOTO)
goto errout_free;
err = ops->configure(rule, skb, frh, tb);
if (err < 0)
goto errout_free;
list_for_each_entry(r, &ops->rules_list, list) {
if (r->pref > rule->pref)
break;
last = r;
}
fib_rule_get(rule);
if (last)
list_add_rcu(&rule->list, &last->list);
else
list_add_rcu(&rule->list, &ops->rules_list);
if (ops->unresolved_rules) {
/*
* There are unresolved goto rules in the list, check if
* any of them are pointing to this new rule.
*/
list_for_each_entry(r, &ops->rules_list, list) {
if (r->action == FR_ACT_GOTO &&
r->target == rule->pref &&
rtnl_dereference(r->ctarget) == NULL) {
rcu_assign_pointer(r->ctarget, rule);
if (--ops->unresolved_rules == 0)
break;
}
}
}
if (rule->action == FR_ACT_GOTO)
ops->nr_goto_rules++;
if (unresolved)
ops->unresolved_rules++;
notify_rule_change(RTM_NEWRULE, rule, ops, nlh, NETLINK_CB(skb).pid);
flush_route_cache(ops);
rules_ops_put(ops);
return 0;
errout_free:
release_net(rule->fr_net);
kfree(rule);
errout:
rules_ops_put(ops);
return err;
}