SpringMVC应用
文章目录
- 一、常用注解
- 二、参数传递
-
- 2.1 基础类型+String
- 2.2 复杂类型
- 2.3 @RequestParam
- 2.4.路径传参 @PathVariable
- 2.4 Json数据传参 @RequestBody
- 2.5 @RequestHeader
- 三、方法返回值
-
- 3.1 void
- 3.2 String+model
- 3.3 ModelAndView
一、常用注解
SpringMVC是一个基于Java的Web框架,它提供了一系列的注解来简化开发过程。以下是一些常用的SpringMVC注解:
- @Controller: 用于标识一个类为控制器,处理用户请求并返回相应的结果
- @RequestMapping:、 用于映射请求URL和处理方法,可以用在类级别和方法级别。在类级别上,可以指定公共的URL前缀,而在方法级别上,可以指定具体的URL路径。
- @RequestParam: 用于将请求参数绑定到方法的参数上。可以指定参数的名称、是否必需以及默认值。
- @PathVariable: 用于将URL路径中的变量绑定到方法的参数上。可以指定变量的名称和是否必需。
- @ResponseBody: 用于将方法的返回值直接写入HTTP响应体中,而不是通过视图解析器进行渲染。
- @ModelAttribute:用于将请求参数绑定到方法的参数上,并将其添加到模型中。可以指定参数的名称和是否必需。
- @SessionAttributes:用于指定模型中的属性应该存储在会话中,以便在多个请求之间共享。
- @Valid:用于启用参数的校验功能,可以与JSR-303/JSR-349标准的注解一起使用。
这些注解只是SpringMVC中的一部分,还有其他很多注解可以用于处理拦截器、异常处理、文件上传等功能。具体使用哪些注解取决于你的需求和项目的架构。
二、参数传递
SLF4J(Simple Logging Facade for Java)是一个为Java应用程序提供日志记录的简单门面(facade)框架。它允许开发人员在应用程序中使用统一的API来记录日志,而无需关心底层日志实现的细节。SLF4J提供了一种灵活的方式来切换不同的日志实现,如Logback、Log4j和java.util.logging等。通过使用SLF4J,开发人员可以在不修改应用程序代码的情况下更改日志记录实现,从而提供了更好的可维护性和灵活性。
pom.xml
<log4j2.version>2.9.1log4j2.version>
<log4j2.disruptor.version>3.2.0log4j2.disruptor.version>
<slf4j.version>1.7.13slf4j.version>
//-------------------------------------------------
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4jgroupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-apiartifactId>
<version>${slf4j.version}version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4jgroupId>
<artifactId>jcl-over-slf4jartifactId>
<version>${slf4j.version}version>
<scope>runtimescope>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.logging.log4jgroupId>
<artifactId>log4j-apiartifactId>
<version>${log4j2.version}version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.logging.log4jgroupId>
<artifactId>log4j-coreartifactId>
<version>${log4j2.version}version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.logging.log4jgroupId>
<artifactId>log4j-slf4j-implartifactId>
<version>${log4j2.version}version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.logging.log4jgroupId>
<artifactId>log4j-webartifactId>
<version>${log4j2.version}version>
<scope>runtimescope>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.lmaxgroupId>
<artifactId>disruptorartifactId>
<version>${log4j2.disruptor.version}version>
dependency>
2.1 基础类型+String
package com.xqx.web;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
@Slf4j
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/param")
public class ParamController {
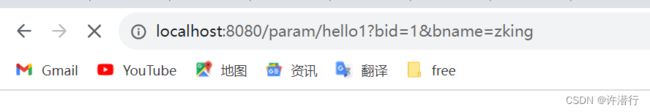
@RequestMapping("/hello1")
public String toHello1(Integer bid,String bname){
log.info("基础类型+String传参:bid:{},bname:{}",bid,bname);
return "index";
}
2.2 复杂类型
@Slf4j
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/param")
public String hello1(Book book, HttpServletRequest request){
//servlet参数获取方式
log.info("复杂类型参数:bname:{},bid:{}",
request.getParameter("bid"),
request.getParameter("bname")
);
//复杂传参
log.info("复杂类型参数:book:{}", book.toString());
return "index";
}
2.3 @RequestParam
@Slf4j
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/hello3")
public String requestParam(
@RequestParam String bname,
@RequestParam(required = false) Integer bid) {
log.info("requestParam类型参数 bname:{},bid:{}", bname, bid);
return "index";
}
这种参数传递类型,如果不传参会报错
被@RequestParam注解的参数required默认为true表示请求中一定要传入对应的参数,否则会报404错误如果设置为false时,当请求中没有此参数,将会默认为null,而对于基本数据类型的变量,则必须有值,这时会抛出空指针异常。如果允许空值,则接口中变量需要使用包装类来声明。
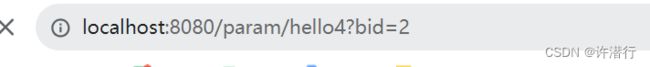
2.4.路径传参 @PathVariable
如果我要通过id进行删除某一项可以用PathVariable注释
@RequestMapping("/hello4/{bid}")
public String rjcc(@PathVariable("bid")Integer bid) {
log.info("PathVariable bid:{}",bid);
return "index";
}
2.4 Json数据传参 @RequestBody
在实际开发中运用最多的就是通过Json数据进行传输,SpringMVC默认使用的是jackson来处理json的转换,所以需要在pom.xml添加jackson依赖。另外推荐使用postman或者apipost/eolink等工具发送请求数据。
<jackson.version>2.9.3jackson.version>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.coregroupId>
<artifactId>jackson-databindartifactId>
<version>${jackson.version}version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.coregroupId>
<artifactId>jackson-coreartifactId>
<version>${jackson.version}version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.coregroupId>
<artifactId>jackson-annotationsartifactId>
<version>${jackson.version}version>
dependency>
// 能接受json数据,前提导入了Jackson依赖,没有导入Jackson依赖的话那进不了这个方法
@RequestMapping("/hello6")
public String RequestBody2(@RequestBody Map map) {
log.info("RequestBody map:{}",map);
return "index";
}
// 不能接受json数据
@RequestMapping("/hello5")
public String RequestBody1(Map map) {
log.info("RequestBody map:{}",map);
return "index";
}
![]()
2.5 @RequestHeader
@RequestHeader 注解可以用在方法的参数上,用于将指定的请求头的值注入到方法参数中。
@RequestMapping("/hello7")
public String RequestHeader(@RequestHeader("jwt") String jwt) {
log.info("RequestHeader jwt:{}",jwt);
return "index";
}
三、方法返回值
为了方便模拟效果,借助ResponseUtil工具类,ResponseUtil类提供了一种方便的方式来将对象以文本或JSON格式写入HTTP响应流中,以便在Web应用程序中向客户端返回数据。
ResponseUtil:
package com.xqx.util;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
public class ResponseUtil {
public static void write(HttpServletResponse response,Object o)throws Exception{
response.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8");
PrintWriter out=response.getWriter();
out.println(o.toString());
out.flush();
out.close();
}
public static void writeJson(HttpServletResponse response,Object o)throws Exception{
ObjectMapper om = new ObjectMapper();
// om.writeValueAsString(o)代表了json串
write(response, om.writeValueAsString(o));
}
}
3.1 void
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/rs")
public class ReturnController {
@RequestMapping("/hello1")
public void hello1(HttpServletResponse response){
Map<String,Object> map=new HashMap<>();
map.put("code",200);
map.put("msg","成功添加...");
try {
ResponseUtil.writeJson(response,map);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
3.2 String+model
jsp
<%--
Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
User: 86156
Date: 2023/9/5
Time: 15:49
To change this template use File | Settings | File Templates.
--%>
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Titletitle>
head>
<body>
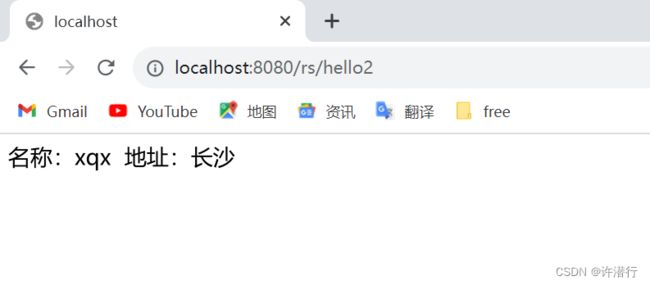
名称:${name}
地址:${address}
body>
html>
测试
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/rs")
public class ReturnController {
@RequestMapping("/hello2")
public String hello2(Model model,
HttpServletRequest request){
model.addAttribute("name","xqx");
request.setAttribute("address","长沙");
return "index";
}
}
3.3 ModelAndView
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/rs")
public class ReturnController {
@RequestMapping("/hello3")
public ModelAndView hello3(){
ModelAndView mv=new ModelAndView();
mv.addObject("xqx","666");
mv.setViewName("index");
return mv;
}
}
jsp
<%--
Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
User: 86156
Date: 2023/9/5
Time: 17:00
To change this template use File | Settings | File Templates.
--%>
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Titletitle>
head>
<body>
名称:${name}
地址:${address}
评价:${xqx}
body>
html>