SpringMVC常用注解、参数传递、返回值
一、常用注解
1.1.@RequestMapping *
@RequestMapping注解是一个用来处理请求地址映射的注解,可用于映射一个请求或一个方法,可以用在类或方法上。
- 标注在方法上
用于方法上,表示在类的父路径下追加方法上注解中的地址将会访问到该方法
@Controller
public class HelloController {
@RequestMapping("/requestTest")
public String requestTest(){
return "index";
}
}
此时请求映射所映射的请求的请求路径为:
http://localhost:8080/springmvc/requestTest
springmvc表示项目名
- 标注在类和方法上
用于类上,表示类中的所有响应请求的方法都是以该地址作为父路径。
注意:当你在类上添加RequestMapping注解后,如果要请求映射,就意味着请求要先映射到标注类的位置,然后再映射到该类的方法上
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public class HelloController {
@RequestMapping("/requestTest")
public String requestTest(){
return "index";
}
}
此时请求映射所映射的请求的请求路径为:
http://localhost:8080/springmvc/hello/requestTest
springmvc表示项目名
- 参数列表
| 参数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| value | @RequestMapping 的 value 属性必须设值;@RequestMapping 的 value 属性是通过当前请求的请求地址来匹配请求;从源码中可以看到value属性是一个字符串类型的数组,因此说明可以将多个请求映射到一个方法上,只需要给 value 来指定一个包含多个路径的数组。 |
| method | @RequestMapping的method属性是通过当前请求的请求方式来匹配请求;浏览器向服务器发送请求,请求方式有很多GET、HEAD、POST、PUT、PATCH、DELETE、OPTIONS、TRACE。可以使用 method 属性来约束请求方式。 |
| headers | @RequestMapping的headers属性是通过当前请求的请求头信息来匹配请求;@RequestMapping的headers属性是一个字符串类型的数组,可以通过下面四种表达是来设置匹配关系例如: “header”:要求请求映射的请求必须为包含 header的请求头信息 “!header”:要求请求映射的请求必须为不包含 header的请求头信息 “header=value”:要求请求映射的请求必须为包含 header的请求头信息,并且header的值必须为value “header!=value”:要求请求映射的请求必须为包含 header的请求头信息,并且header的值必须不是value |
| params | @RequestMapping的params属性是通过当前请求的请求参数来匹配请求;@RequestMapping的params属性是一个字符串类型的数组,可以通过下面四种表达是来设置匹配关系例如: “param”:要求请求映射的请求必须为包含 param的请求参数 “!param”:要求请求映射的请求是不能包含param的请求参数 “param=value”:要求请求映射的请求必须包含 param 的请求参数,且 param 参数的值必须为 value “param!=value”: 要求请求映射的请求是必须包含 param 的请求参数,其值不能为 value。 |
示例一:@RequestMapping的params属性
@RequestMapping(value = "/test",params = "username")
public String test(){
return "index";
}
注意:我们设置了params属性,就意味着该请求映射的请求必须包含username才能够请求成功。
示例二:@RequestMapping的headers属性
@RequestMapping(value = "/test",headers = "Host = localhost:8081")
public String test(){
return "index";
}
注意:如果当前请求不满足headers属性,此时页面就会显示404错误,即资源未找到。
扩展:
@GetMapping:处理get方式请求的映射
@PostMapping:处理post方式请求的映射
@PutMapping:处理put方式请求的映射
@DeleteMapping:处理delete方式请求的映射
@GetMapping就相当@RequestMapping(method=RequestMethod.GET),它会将get映射到特定的方法上。
1.2.@RequestParam *
@RequestParam主要用于将请求参数区域的数据映射到控制层方法的参数上
| 参数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| value | 请求中传入参数的名称,如果不设置后台接口的value值,则会默认为该变量名。 |
| required | 该参数是否为必传项。默认是true,表示请求中一定要传入对应的参数,否则会报404错误,如果设置为false时,当请求中没有此参数,将会默认为null,而对于基本数据类型的变量,则必须有值,这时会抛出空指针异常。如果允许空值,则接口中变量需要使用包装类来声明。 |
| defaultValue | 参数的默认值,如果请求中没有同名的参数时,该变量默认为此值。注意默认值可以使用SpEL表达式,如"#{systemProperties[‘java.vm.version’]}" |
示例:
@RequestMapping("/list")
public List<Book> list(
@RequestParam(required = false,defaultValue = "0",value="page") int page,
@RequestParam(required = false,defaultValue = "10",value = "rows") int rows){
return bookService.list(page,rows);
}
1.3.@ModelAttribute
@ModelAttribute一个具有如下三个作用:
-
绑定请求参数到命令对象:放在功能处理方法的入参上时,用于将多个请求参数绑定到一个命令对象,从而简化绑定流程,而且自动暴露为模型数据用于视图页面展示时使用;
-
暴露表单引用对象为模型数据:放在处理器的一般方法(非功能处理方法)上时,是为表单准备要展示的表单引用对象,如注册时需要选择的所在城市等,而且在执行功能处理方法(
@RequestMapping注解的方法)之前,自动添加到模型对象中,用于视图页面展示时使用; -
暴露@RequestMapping方法返回值为模型数据:放在功能处理方法的返回值上时,是暴露功能处理方法的返回值为模型数据,用于视图页面展示时使用。
示例一:绑定请求参数到命令对象
如用户登录,我们需要捕获用户登录的请求参数(用户名、密码)并封装为用户对象,此时我们可以使用@ModelAttribute绑定多个请求参数到我们的命令对象。
public String test1(@ModelAttribute("student") StuModel stu)
它的作用是将该绑定的命令对象以“user”为名称添加到模型对象中供视图页面展示使用。我们此时可以在视图页面使用${user.username}来获取绑定的命令对象的属性。
示例二:暴露表单引用对象为模型数据
@ModelAttribute
public void init(Model model){
model.addAttribute("Student",new Student());
}
如上代码会在执行功能处理方法之前执行,并将其自动添加到模型对象中。
@RequestMapping("/toStudentList")
public String toStudentList(){
System.out.println("toStudentList");
return "Student/StudentList";
}
示例三:暴露@RequestMapping方法返回值为模型数据
@ModelAttribute注解的返回值会覆盖@RequestMapping注解方法中的@ModelAttribute注解的同名命令对象。
public @ModelAttribute("stu2") StudentModel test3(@ModelAttribute("stu2") StudentModel stu)
1.4.@SessionAttributes
在默认情况下,当ModelMap中的属性作用域是request级别时,也就是说,当本次请求结束后,ModelMap中的属性将销毁。如果希望在多个请求中共享ModelMap中的属性,必须将其属性转存到session中,这样ModelMap的属性才会被跨请求访问;
spring允许我们有选择地指定ModelMap中的哪些属性需要转存到session中,以便下一个请求属对应的ModelMap的属性列表中还能访问到这些属性。
SpringMVC为我们提供这样一个注解来实现上面的场景:@SessionAttributes:将ModelMap的属性值共享到session中。
注意:
@SessionAttributes注解只能使用在类上,用于在多个请求之间传递参数,类似于Session的Attribute,但不完全一样,一般来说@SessionAttributes设置的参数只用于暂时的传递(存入sessionAttributeStore),而不是长期的保存,长期保存的数据还是要放到Session中。
有两种方式将ModelMap中的属性值共享到session中:
- 使用注解的value属性:可以通过属性名指定需要放到会话中的属性;
@Controller
@SessionAttributes("stu") //将ModelMap中key为user的属性共享到session中
public class DemoController {
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public String hello(ModelMap model) {
//向ModelMap中添加key为user和user1的属性
model.addAttribute("Student", new Student(520, "U love me"));
model.addAttribute("Student1", new Student("I love U"));
return "index";
}
}
- 使用注解的types属性:还可以通过模型属性的对象类型指定哪些模型属性需要放到会话中。
@SessionAttributes(types = {Student.class})
@Controller
public class DemoController{
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public String hello(Map<String, Object> map){
map.put("user1", new User(520, "U love me"));
return "hello";
}
}
1.5.@RequestBody *
@RequestBody主要用来接收前端传递给后端的json字符串中的数据的(即请求体中的数据的);
GET方式无请求体,所以使用@RequestBody接收数据时,前端不能使用GET方式提交数据,而是用POST方式进行提交。在后端的同一个接收方法里,@RequestBody与@RequestParam()可以同时使用,@RequestBody最多只能有一个,而@RequestParam()可以有多个。
简言之:
- 一个请求:只有一个
@RequestBody; - 一个请求:可以有多个
@RequestParam。
Content-type:
- application/x-www-form-urlencoded:
@RequestBody不是必须加的- mutipart/form-data:
@RequestBody不能处理这种格式- 其他格式,比如application/json,application/xml等,必须使用@RequestBody来处理
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public String toHello1(@RequestBody Student stu){
log.info("@RequestBody传递JSON格式的参数:{}", JSON.toJSONString(book));
return "index";
}
@RequestBody注解对应的类在将HTTP的输入流(含请求体)装配到目标类(即:@RequestBody后面的类)时,会根据json字符串中的key来匹配对应实体类的属性,如果匹配一致且json中的该key对应的值符合(或可转换为)实体类的对应属性的类型要求时,会调用实体类的setter方法将值赋给该属性。
1.6.@RequestHeader *
使用 @RequestHeader 注解可以获取指定的请求头信息。如果想要获取所有的请求头信息,可以使用 Map
参数列表
| 参数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| name | name 和 value 互为别名,当只有一个参数时,可以省略 value,直接(“xxx”) 就可以了 |
| value | name 和 value 互为别名,当只有一个参数时,可以省略 value,直接(“xxx”) 就可以了 |
| required | 默认情况下,如果请求头中缺少了指定的 name,那么将会报错。 如果没有添加required = false,当请求头中没有这个tgq请求头时就会报错。 |
| defaultValue | 如果请求头中缺少了指定的 name ,那么会报错,可以使用 defaultValue 这个属性指定默认值,就可以避免报错 ;如果请求头缺少指定 name ,该属性设置的值将会作为默认值,如果该属性不设置值,它有自己的默认值 DEFAULT_NONE |
示例:
@GetMapping("/headParams")
public Map userInfo(
@RequestHeader(value = "zking",defaultValue = "hello tgq") String username,
// 将请求头中 name=Accept-Encoding 赋值给形参 encoding
@RequestHeader("Accept-Encoding") String encoding,
// 将请求头中 name=Host 赋值给形参 host
@RequestHeader("Host") String host,
// 将所有请求头的 name 和 value 封装到 Map 集合 headsMap 中
@RequestHeader Map<String,String> headsMap) {
Map map = new HashMap<String, Object>();
map.put("username",username);
map.put("Accept-Encoding",encoding);
map.put("Host",host);
map.put("headsMap",headsMap);
return map;
}
由于请求头中不存在 name=tgq这个信息,所以如果只用 value=tgq会抛出异常。
解决方案:
1、required 的默认值为 true ,也就是请求头中没有 name=tgq会报错,将其值改为 false,即没有该头信息也不报错
@RequestHeader(value = "tgq",required = "false") String username
2、不修改 required=true 这个默认值,当头信息中不包含 name=tgq,给它一个默认值 hello tgq
@RequestHeader(value = "tgq",defaultValue = "hello tgq") String username
1.7.@PathVariable *
该注解请求URI中的模板变量部分到处理器功能处理方法的方法参数上的绑定。
即当使用@RequestMapping URI template 样式映射时, 即 someUrl/{paramId}, 这时的paramId可通过 @Pathvariable注解绑定它传过来的值到方法的参数上。
//@PathVariable可以用来映射URL中的占位符到目标方法的参数中
@RequestMapping("/testPathVariable/{id}")
public String testPathVariable(@PathVariable("id") Integer id)
{
System.out.println("testPathVariable:"+id);
return SUCCESS;
}
Rest
即 Representational State Transfer。(资源)表现层状态转化。是目前最流行的一种互联网软件架构。它结构清晰、符合标准、易于理解、扩展方便,所以正得到越来越多网站的采用。
- 资源(Resources):网络上的一个实体,或者说是网络上的一个具体信息。它可以是一段文本、一张图片、一首歌曲、一种服务,总之就是一个具体的存在。可以用一个URI(统一资源定位符)指向它,每种资源对应一个特定的 URI 。要获取这个资源,访问它的URI就可以,因此 URI 即为每一个资源的独一无二的识别符。
- 表现层(Representation):把资源具体呈现出来的形式,叫做它的表现层(Representation)。比如,文本可以用 txt 格式表现,也可以用 HTML 格式、XML 格式、JSON 格式表现,甚至可以采用二进制格式。
- 状态转化(State Transfer):每发出一个请求,就代表了客户端和服务器的一次交互过程。HTTP协议,是一个无状态协议,即所有的状态都保存在服务器端。因此,如果客户端想要操作服务器,必须通过某种手段,让服务器端发生**“状态转化”**(State Transfer)。而这种转化是建立在表现层之上的,所以就是 “表现层状态转化”。具体说,就是 HTTP 协议里面,四个表示操作方式的动词:GET、POST、PUT、DELETE。它们分别对应四种基本操作:GET 用来获取资源,POST 用来新建资源,PUT 用来更新资源,DELETE 用来删除资源。
示例:
- /order/1 HTTP GET :得到 id = 1 的 order
- /order/1 HTTP DELETE :删除 id = 1 的 order
- /order/1 HTTP PUT :更新 id = 1 的 order
- /order HTTP POST :新增 order
1.8.@CookieValue
@CookieValue注解主要是将请求的Cookie数据,映射到功能处理方法的参数上。
参数列表
| 参数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| value | 绑定的参数名称,String类型。 |
| required | 是否必须包含value,boolean类型,默认为 true,表示请求参数中必须包含对应的参数;若不存在,将抛出异常。 |
| defaultValue | 默认值,String类型。当没有传参时将使用此值赋值。 |
示例:
@RequestMapping("/testCookieValue")
public Map<String, Object> testCookieValue(
@CookieValue("JSESSIONID") String cookie) {
response.put("cookie", cookie);
return response;
}
二、参数传递
配置pom.xml
<log4j2.version>2.9.1log4j2.version>
<log4j2.disruptor.version>3.2.0log4j2.disruptor.version>
<slf4j.version>1.7.13slf4j.version>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4jgroupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-apiartifactId>
<version>${slf4j.version}version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4jgroupId>
<artifactId>jcl-over-slf4jartifactId>
<version>${slf4j.version}version>
<scope>runtimescope>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.logging.log4jgroupId>
<artifactId>log4j-apiartifactId>
<version>${log4j2.version}version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.logging.log4jgroupId>
<artifactId>log4j-coreartifactId>
<version>${log4j2.version}version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.logging.log4jgroupId>
<artifactId>log4j-slf4j-implartifactId>
<version>${log4j2.version}version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.logging.log4jgroupId>
<artifactId>log4j-webartifactId>
<version>${log4j2.version}version>
<scope>runtimescope>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.lmaxgroupId>
<artifactId>disruptorartifactId>
<version>${log4j2.disruptor.version}version>
dependency>
完整pom.xml
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/maven-v4_0_0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0modelVersion>
<groupId>org.examplegroupId>
<artifactId>SpringMyBatisartifactId>
<packaging>warpackaging>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOTversion>
<name>SpringMyBatis Maven Webappname>
<url>http://maven.apache.orgurl>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8project.build.sourceEncoding>
<maven.compiler.source>1.8maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>1.8maven.compiler.target>
<maven.compiler.plugin.version>3.7.0maven.compiler.plugin.version>
<spring.version>5.0.2.RELEASEspring.version>
<mybatis.version>3.4.5mybatis.version>
<mysql.version>5.1.44mysql.version>
<pagehelper.version>5.1.2pagehelper.version>
<mybatis.spring.version>1.3.1mybatis.spring.version>
<commons.dbcp2.version>2.1.1commons.dbcp2.version>
<commons.pool2.version>2.4.3commons.pool2.version>
<log4j2.version>2.9.1log4j2.version>
<log4j2.disruptor.version>3.2.0log4j2.disruptor.version>
<slf4j.version>1.7.13slf4j.version>
<junit.version>4.12junit.version>
<servlet.version>4.0.0servlet.version>
<lombok.version>1.18.2lombok.version>
<jstl.version>1.2jstl.version>
<standard.version>1.1.2standard.version>
<spring.version>5.0.2.RELEASEspring.version>
properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframeworkgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-contextartifactId>
<version>${spring.version}version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframeworkgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-ormartifactId>
<version>${spring.version}version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframeworkgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-txartifactId>
<version>${spring.version}version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframeworkgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-aspectsartifactId>
<version>${spring.version}version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframeworkgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-webartifactId>
<version>${spring.version}version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframeworkgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-testartifactId>
<version>${spring.version}version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatisgroupId>
<artifactId>mybatisartifactId>
<version>${mybatis.version}version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysqlgroupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-javaartifactId>
<version>${mysql.version}version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.github.pagehelpergroupId>
<artifactId>pagehelperartifactId>
<version>${pagehelper.version}version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatisgroupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-springartifactId>
<version>${mybatis.spring.version}version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.commonsgroupId>
<artifactId>commons-dbcp2artifactId>
<version>${commons.dbcp2.version}version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.commonsgroupId>
<artifactId>commons-pool2artifactId>
<version>${commons.pool2.version}version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4jgroupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-apiartifactId>
<version>${slf4j.version}version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4jgroupId>
<artifactId>jcl-over-slf4jartifactId>
<version>${slf4j.version}version>
<scope>runtimescope>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.logging.log4jgroupId>
<artifactId>log4j-apiartifactId>
<version>${log4j2.version}version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.logging.log4jgroupId>
<artifactId>log4j-coreartifactId>
<version>${log4j2.version}version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.logging.log4jgroupId>
<artifactId>log4j-slf4j-implartifactId>
<version>${log4j2.version}version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.logging.log4jgroupId>
<artifactId>log4j-webartifactId>
<version>${log4j2.version}version>
<scope>runtimescope>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.lmaxgroupId>
<artifactId>disruptorartifactId>
<version>${log4j2.disruptor.version}version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junitgroupId>
<artifactId>junitartifactId>
<version>${junit.version}version>
<scope>testscope>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servletgroupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet-apiartifactId>
<version>${servlet.version}version>
<scope>providedscope>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombokgroupId>
<artifactId>lombokartifactId>
<version>${lombok.version}version>
<scope>providedscope>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframeworkgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvcartifactId>
<version>${spring.version}version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>jstlgroupId>
<artifactId>jstlartifactId>
<version>${jstl.version}version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>taglibsgroupId>
<artifactId>standardartifactId>
<version>${standard.version}version>
dependency>
dependencies>
<build>
<finalName>SpringMyBatisfinalName>
<resources>
<resource>
<directory>src/main/javadirectory>
<includes>
<include>**/*.xmlinclude>
includes>
resource>
<resource>
<directory>src/main/resourcesdirectory>
<includes>
<include>jdbc.propertiesinclude>
<include>*.xmlinclude>
includes>
resource>
resources>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.pluginsgroupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-pluginartifactId>
<version>${maven.compiler.plugin.version}version>
<configuration>
<source>${maven.compiler.source}source>
<target>${maven.compiler.target}target>
<encoding>${project.build.sourceEncoding}encoding>
configuration>
plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.mybatis.generatorgroupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-generator-maven-pluginartifactId>
<version>1.3.2version>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysqlgroupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-javaartifactId>
<version>${mysql.version}version>
dependency>
dependencies>
<configuration>
<overwrite>trueoverwrite>
configuration>
plugin>
plugins>
build>
project>
2.1.基础类型+String
package com.tgq.web;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
/**
* @软件包名 com.tgq.web
* @用户 tgq
* @注释说明:
*/
@Slf4j
@Controller
@RequestMapping(value = "/param")
public class indexController {
@RequestMapping(value = "/hello1")
public String hello1(Integer bid, String bname) {
log.info("基础类型+String传参:bid:{},bname:{}", bid, bname);
return "demo";
}
}
手动输入:http://localhost:8080/param/hello1?bid=1&bname=我的名字
![]()
2.2.复杂类型
@RequestMapping("/hello2")
public String hello2(Book book,
HttpServletRequest req) {
log.info("复杂类型参数: book{}", book.toString());
log.info("复杂类型 req参数:bid:{},bname:{}", req.getParameter("bname"), req.getParameter("bid"));
return "index";
}
手动输入:http://localhost:8080/param/hello1?bid=1&bname=我的名字

2.3.@RequestParam
@RequestMapping("/hello3")
public String hello3(@RequestParam Integer bid,
@RequestParam(required = false) String bname) {
log.info(" 使用@RequestParam传递参数:{},{}", bid, bname);
return "index";
}
输入:http://localhost:8080/param/hello3会有一个报错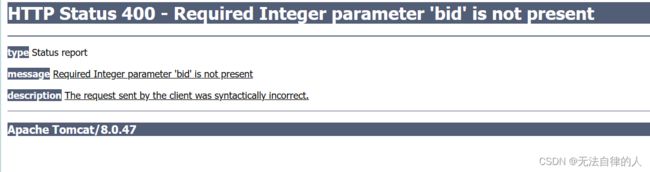
这里说明我的bid是必须要的;输入:http://localhost:8080/param/hello3?bid=1之后就有结果![]()
2.4.@PathVariable
@RequestMapping("/hello4/{bid}")
public String hello4(@PathVariable("bid") Integer bid) {
log.info("使用@PathVariable注解传递参数:bid:{}", bid);
return "index";
}
输入:http://localhost:8080/param/hello4/2
![]()
2.5.@RequestBody
在用**@RequestBody**之前我们需要导入依赖
<properties>
<jackson.version>2.9.3jackson.version>
properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.coregroupId>
<artifactId>jackson-databindartifactId>
<version>${jackson.version}version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.coregroupId>
<artifactId>jackson-coreartifactId>
<version>${jackson.version}version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.coregroupId>
<artifactId>jackson-annotationsartifactId>
<version>${jackson.version}version>
dependency>
dependencies>
// 能接受json数据,前提导入了Jackson依赖,没有导入Jackson依赖的话那进不了这个方法
@RequestMapping("/hello5")
public String hello5(@RequestBody Map map) {
System.out.println(map);
log.info("使用@RequestBody注解传递参数:map:{}", map);
return "index";
}
// 不能接受json数据
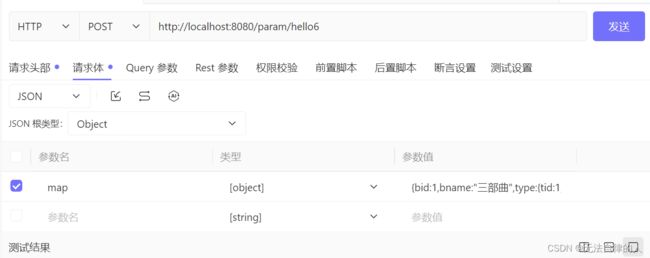
@RequestMapping("/hello6")
public String hello6(Map map) {
log.info("使用@RequestBody注解传递参数:map:{}", map);
return "index";
}
这里就需要使用测试工具发送请求数据。
测试hello5方法
参数名为map,参数值为json格式
测试结果为
如果测试hello6
它是没有数据的
2.5.1 requestMapping
requestMapping=GetMapping+PostMapping+PutMapping+DeleteMapping
2.6.@RequestHeader
@RequestMapping("/hello7")
public String toHello7(Book book, @RequestBody Map map, @RequestHeader("jwt") String jwt){
System.out.println(map);
System.out.println(book);
System.out.println(jwt);
return "index";
}
![]()
综合代码
package com.tgq.web;
import com.tgq.model.Book;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* @软件包名 com.tgq.web
* @用户 tgq
* @create 2023-09-05 下午3:51
* @注释说明:
*/
@Slf4j
@Controller
@RequestMapping(value = "/param")
public class indexController {
@RequestMapping(value = "/hello1")
public String hello1(Integer bid, String bname) {
log.info("基础类型+String传参:bid:{},bname:{}", bid, bname);
return "index";
}
@RequestMapping("/hello2")
public String hello2(Book book,
HttpServletRequest req) {
log.info("复杂类型参数: book{}", book.toString());
log.info("复杂类型 req参数:bid:{},bname:{}", req.getParameter("bname"), req.getParameter("bid"));
return "index";
}
@RequestMapping("/hello3")
public String hello3(@RequestParam Integer bid,
@RequestParam(required = false) String bname) {
log.info(" 使用@RequestParam传递参数:{},{}", bid, bname);
return "index";
}
@RequestMapping("/hello4/{bid}")
public String hello4(@PathVariable("bid") Integer bid) {
log.info("使用@PathVariable注解传递参数:bid:{}", bid);
return "index";
}
// 能接受json数据,前提导入了Jackson依赖,没有导入Jackson依赖的话那进不了这个方法
@RequestMapping("/hello5")
public String hello5(@RequestBody Map map) {
System.out.println(map);
log.info("使用@RequestBody注解传递参数:map:{}", map);
return "index";
}
// 不能接受json数据
@RequestMapping("/hello6")
public String hello6(Map map) {
log.info("使用@RequestBody注解传递参数:map:{}", map);
return "index";
}
@RequestMapping("/hello7")
public String hello7(Book book, @RequestBody Map map, @RequestHeader("jwt") String jwt) {
log.info("使用@RequestBody注解传递参数:book:{},map:{},jwt:{}", book, map, jwt);
return "index";
}
}
三、返回值
3.0.前言
我们在开始之前编写一个
ResponseUtil帮助类,更好让我测试
package com.tgq.utils;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
public class ResponseUtil {
public static void write(HttpServletResponse response,Object o)throws Exception{
response.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8");
PrintWriter out=response.getWriter();
out.println(o.toString());
out.flush();
out.close();
}
public static void writeJson(HttpServletResponse response,Object o)throws Exception{
ObjectMapper om = new ObjectMapper();
// om.writeValueAsString(o)代表了json串
write(response, om.writeValueAsString(o));
}
}
3.1.void
处理器对请求处理后,无需跳转到其它任何资源,此时可以让处理器方法返回 void。
处理器方法返回 void 的应用场景,AJAX 响应。
package com.tgq.web;
import com.tgq.utils.ResponseUtil;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* @软件包名 com.tgq.web
* @用户 tgq
* @create 2023-09-05 下午6:37
* @注释说明:
*/
@Controller
@RequestMapping(value = "/rs")
public class ReturnController {
@RequestMapping("/demo1")
public void demo1(HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException {
Map map = new HashMap();
map.put("code", 200);
map.put("msg", "成功添加......");
try {
ResponseUtil.writeJson(response, map);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
3.2.String
通过http://localhost:8080/rs/toHello访问请求方法,并经过视图解析器跳转指定页面。
@RequestMapping("/toHello")
public String toHello(){
//逻辑视图名
return "hello";
}
返回类型为String,默认被作为视图名,指定逻辑视图名,经过视图解析器解析为jsp物理路径:/WEB-INF/page/success.jsp
3.3.String+Model
通过http://localhost:8080/rs/toHello1访问请求方法,并经过视图解析器跳转指定页面,最后完成视图模型数据渲染操作。
@RequestMapping("/toHello1")
public String toHello1(Model model,HttpServletRequest request){
//填充模型数据
model.addAttribute("name","张三");
request.setAttribute("role","管理员");
//逻辑视图名
return "hello";
}
3.4.ModelAndView
通过http://localhost:8080/springmvc01/toHello访问请求方法。
@RequestMapping("/toHello2")
public ModelAndView toHello2(){
ModelAndView mv = new ModelAndView();
//填充模型数据
mv.addObject("name","张三");
mv.addObject("role","管理员");
mv.setViewName("hello");
//逻辑视图名
return mv;
}
四、页面跳转
转发forward:path和重定向redirect:path这两种跳转方式将会绕开视图解析器的前缀和后缀;还有就是如果是在同一controller中则不用使用"/"从根目录开始,而如果是在不同的controller则一定要从根目录开始。
path为请求处理方法名,而非逻辑视图名。
转发(地址栏不变)
@RequestMapping("/index1")
public String index1(){
System.out.println("helloPage1");
return "forward:toHello2";
}
它相当于
“request.getRequestDispatcher("url").forward(request,response)”。使用转发,既可以转发到jsp, 也可以转发到其他的控制器方法。
重定向(地址栏改变)
@RequestMapping("/helloPage2")
public String toHelloPage2(){
System.out.println("helloPage2");
return "redirect:toHello2";
}
它相当于
“response.sendRedirect(url)”。需要注意的是,如果重定向到jsp页面,则jsp页面不能写在WEB-INF目录中,否则无法找到。
跳其它的controller
@RequestMapping("/helloPage3")
public String toHelloPage3(){
System.out.println("helloPage3");
return "forward:/demo/hello";
}
@RequestMapping("/helloPage4")
public String toHelloPage4(){
System.out.println("helloPage4");
return "redirect:/demo/hello";
}