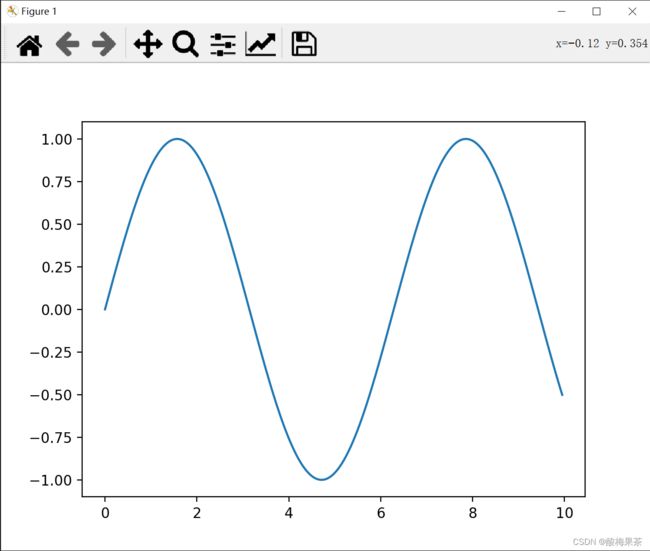
vs2019中采用C++编程使用python中的matplotlib画图库
在写代码的过程中,有时候需要对数据进行可视化,但是对于C++来说,并没有一个像python中matplotlib一样方便使用且功能强大的绘图包。这里可以采用C++调用python,将matplotlib进行了封装。
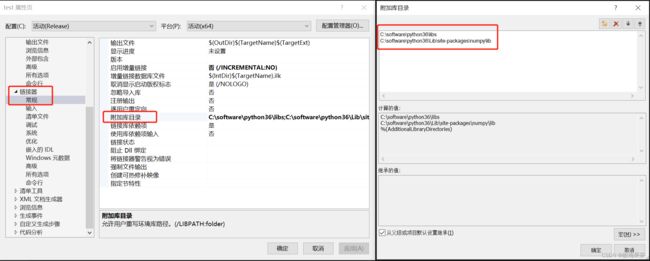
1 先装python,numpy
2 然后新建VS工程
3 添加matplotlib头文件 matplotlibcpp.h
matplotlib-cpp项目地址
#pragma once
// Python headers must be included before any system headers, since
// they define _POSIX_C_SOURCE
#include requires c++11 support
#include { const static NPY_TYPES type = NPY_INT64; };
static_assert(sizeof(unsigned long long) == 8, "long type must occupy 8 bytes");
//template <> struct select_npy_type { const static NPY_TYPES type = NPY_UINT64; };
template<typename Numeric>
PyObject* get_array(const std::vector<Numeric>& v)
{
npy_intp vsize = v.size();
NPY_TYPES type = select_npy_type<Numeric>::type;
if (type == NPY_NOTYPE) {
size_t memsize = v.size() * sizeof(double);
double* dp = static_cast<double*>(::malloc(memsize));
for (size_t i = 0; i < v.size(); ++i)
dp[i] = v[i];
PyObject* varray = PyArray_SimpleNewFromData(1, &vsize, NPY_DOUBLE, dp);
PyArray_UpdateFlags(reinterpret_cast<PyArrayObject*>(varray), NPY_ARRAY_OWNDATA);
return varray;
}
PyObject* varray = PyArray_SimpleNewFromData(1, &vsize, type, (void*)(v.data()));
return varray;
}
template<typename Numeric>
PyObject* get_2darray(const std::vector<::std::vector<Numeric>>& v)
{
if (v.size() < 1) throw std::runtime_error("get_2d_array v too small");
npy_intp vsize[2] = { static_cast<npy_intp>(v.size()),
static_cast<npy_intp>(v[0].size()) };
PyArrayObject* varray =
(PyArrayObject*)PyArray_SimpleNew(2, vsize, NPY_DOUBLE);
double* vd_begin = static_cast<double*>(PyArray_DATA(varray));
for (const ::std::vector<Numeric>& v_row : v) {
if (v_row.size() != static_cast<size_t>(vsize[1]))
throw std::runtime_error("Missmatched array size");
std::copy(v_row.begin(), v_row.end(), vd_begin);
vd_begin += vsize[1];
}
return reinterpret_cast<PyObject*>(varray);
}
#else // fallback if we don't have numpy: copy every element of the given vector
template<typename Numeric>
PyObject* get_array(const std::vector<Numeric>& v)
{
PyObject* list = PyList_New(v.size());
for (size_t i = 0; i < v.size(); ++i) {
PyList_SetItem(list, i, PyFloat_FromDouble(v.at(i)));
}
return list;
}
#endif // WITHOUT_NUMPY
// sometimes, for labels and such, we need string arrays
inline PyObject* get_array(const std::vector<std::string>& strings)
{
PyObject* list = PyList_New(strings.size());
for (std::size_t i = 0; i < strings.size(); ++i) {
PyList_SetItem(list, i, PyString_FromString(strings[i].c_str()));
}
return list;
}
// not all matplotlib need 2d arrays, some prefer lists of lists
template<typename Numeric>
PyObject* get_listlist(const std::vector<std::vector<Numeric>>& ll)
{
PyObject* listlist = PyList_New(ll.size());
for (std::size_t i = 0; i < ll.size(); ++i) {
PyList_SetItem(listlist, i, get_array(ll[i]));
}
return listlist;
}
} // namespace detail
/// Plot a line through the given x and y data points..
///
/// See: https://matplotlib.org/3.2.1/api/_as_gen/matplotlib.pyplot.plot.html
template<typename Numeric>
bool plot(const std::vector<Numeric>& x, const std::vector<Numeric>& y, const std::map<std::string, std::string>& keywords)
{
assert(x.size() == y.size());
detail::_interpreter::get();
// using numpy arrays
PyObject* xarray = detail::get_array(x);
PyObject* yarray = detail::get_array(y);
// construct positional args
PyObject* args = PyTuple_New(2);
PyTuple_SetItem(args, 0, xarray);
PyTuple_SetItem(args, 1, yarray);
// construct keyword args
PyObject* kwargs = PyDict_New();
for (std::map<std::string, std::string>::const_iterator it = keywords.begin(); it != keywords.end(); ++it)
{
PyDict_SetItemString(kwargs, it->first.c_str(), PyString_FromString(it->second.c_str()));
}
PyObject* res = PyObject_Call(detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_function_plot, args, kwargs);
Py_DECREF(args);
Py_DECREF(kwargs);
if (res) Py_DECREF(res);
return res;
}
// TODO - it should be possible to make this work by implementing
// a non-numpy alternative for `detail::get_2darray()`.
#ifndef WITHOUT_NUMPY
template <typename Numeric>
void plot_surface(const std::vector<::std::vector<Numeric>>& x,
const std::vector<::std::vector<Numeric>>& y,
const std::vector<::std::vector<Numeric>>& z,
const std::map<std::string, std::string>& keywords =
std::map<std::string, std::string>(),
const long fig_number = 0)
{
detail::_interpreter::get();
// We lazily load the modules here the first time this function is called
// because I'm not sure that we can assume "matplotlib installed" implies
// "mpl_toolkits installed" on all platforms, and we don't want to require
// it for people who don't need 3d plots.
static PyObject* mpl_toolkitsmod = nullptr, * axis3dmod = nullptr;
if (!mpl_toolkitsmod) {
detail::_interpreter::get();
PyObject* mpl_toolkits = PyString_FromString("mpl_toolkits");
PyObject* axis3d = PyString_FromString("mpl_toolkits.mplot3d");
if (!mpl_toolkits || !axis3d) { throw std::runtime_error("couldnt create string"); }
mpl_toolkitsmod = PyImport_Import(mpl_toolkits);
Py_DECREF(mpl_toolkits);
if (!mpl_toolkitsmod) { throw std::runtime_error("Error loading module mpl_toolkits!"); }
axis3dmod = PyImport_Import(axis3d);
Py_DECREF(axis3d);
if (!axis3dmod) { throw std::runtime_error("Error loading module mpl_toolkits.mplot3d!"); }
}
assert(x.size() == y.size());
assert(y.size() == z.size());
// using numpy arrays
PyObject* xarray = detail::get_2darray(x);
PyObject* yarray = detail::get_2darray(y);
PyObject* zarray = detail::get_2darray(z);
// construct positional args
PyObject* args = PyTuple_New(3);
PyTuple_SetItem(args, 0, xarray);
PyTuple_SetItem(args, 1, yarray);
PyTuple_SetItem(args, 2, zarray);
// Build up the kw args.
PyObject* kwargs = PyDict_New();
PyDict_SetItemString(kwargs, "rstride", PyInt_FromLong(1));
PyDict_SetItemString(kwargs, "cstride", PyInt_FromLong(1));
PyObject* python_colormap_coolwarm = PyObject_GetAttrString(
detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_colormap, "coolwarm");
PyDict_SetItemString(kwargs, "cmap", python_colormap_coolwarm);
for (std::map<std::string, std::string>::const_iterator it = keywords.begin();
it != keywords.end(); ++it) {
if (it->first == "linewidth" || it->first == "alpha") {
PyDict_SetItemString(kwargs, it->first.c_str(),
PyFloat_FromDouble(std::stod(it->second)));
}
else {
PyDict_SetItemString(kwargs, it->first.c_str(),
PyString_FromString(it->second.c_str()));
}
}
PyObject* fig_args = PyTuple_New(1);
PyObject* fig = nullptr;
PyTuple_SetItem(fig_args, 0, PyLong_FromLong(fig_number));
PyObject* fig_exists =
PyObject_CallObject(
detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_function_fignum_exists, fig_args);
if (!PyObject_IsTrue(fig_exists)) {
fig = PyObject_CallObject(detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_function_figure,
detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_empty_tuple);
}
else {
fig = PyObject_CallObject(detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_function_figure,
fig_args);
}
Py_DECREF(fig_exists);
if (!fig) throw std::runtime_error("Call to figure() failed.");
PyObject* gca_kwargs = PyDict_New();
PyDict_SetItemString(gca_kwargs, "projection", PyString_FromString("3d"));
PyObject* gca = PyObject_GetAttrString(fig, "gca");
if (!gca) throw std::runtime_error("No gca");
Py_INCREF(gca);
PyObject* axis = PyObject_Call(
gca, detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_empty_tuple, gca_kwargs);
if (!axis) throw std::runtime_error("No axis");
Py_INCREF(axis);
Py_DECREF(gca);
Py_DECREF(gca_kwargs);
PyObject* plot_surface = PyObject_GetAttrString(axis, "plot_surface");
if (!plot_surface) throw std::runtime_error("No surface");
Py_INCREF(plot_surface);
PyObject* res = PyObject_Call(plot_surface, args, kwargs);
if (!res) throw std::runtime_error("failed surface");
Py_DECREF(plot_surface);
Py_DECREF(axis);
Py_DECREF(args);
Py_DECREF(kwargs);
if (res) Py_DECREF(res);
}
template <typename Numeric>
void contour(const std::vector<::std::vector<Numeric>>& x,
const std::vector<::std::vector<Numeric>>& y,
const std::vector<::std::vector<Numeric>>& z,
const std::map<std::string, std::string>& keywords = {})
{
detail::_interpreter::get();
// using numpy arrays
PyObject* xarray = detail::get_2darray(x);
PyObject* yarray = detail::get_2darray(y);
PyObject* zarray = detail::get_2darray(z);
// construct positional args
PyObject* args = PyTuple_New(3);
PyTuple_SetItem(args, 0, xarray);
PyTuple_SetItem(args, 1, yarray);
PyTuple_SetItem(args, 2, zarray);
// Build up the kw args.
PyObject* kwargs = PyDict_New();
PyObject* python_colormap_coolwarm = PyObject_GetAttrString(
detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_colormap, "coolwarm");
PyDict_SetItemString(kwargs, "cmap", python_colormap_coolwarm);
for (std::map<std::string, std::string>::const_iterator it = keywords.begin();
it != keywords.end(); ++it) {
PyDict_SetItemString(kwargs, it->first.c_str(),
PyString_FromString(it->second.c_str()));
}
PyObject* res = PyObject_Call(detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_function_contour, args, kwargs);
if (!res)
throw std::runtime_error("failed contour");
Py_DECREF(args);
Py_DECREF(kwargs);
if (res) Py_DECREF(res);
}
template <typename Numeric>
void spy(const std::vector<::std::vector<Numeric>>& x,
const double markersize = -1, // -1 for default matplotlib size
const std::map<std::string, std::string>& keywords = {})
{
detail::_interpreter::get();
PyObject* xarray = detail::get_2darray(x);
PyObject* kwargs = PyDict_New();
if (markersize != -1) {
PyDict_SetItemString(kwargs, "markersize", PyFloat_FromDouble(markersize));
}
for (std::map<std::string, std::string>::const_iterator it = keywords.begin();
it != keywords.end(); ++it) {
PyDict_SetItemString(kwargs, it->first.c_str(),
PyString_FromString(it->second.c_str()));
}
PyObject* plot_args = PyTuple_New(1);
PyTuple_SetItem(plot_args, 0, xarray);
PyObject* res = PyObject_Call(
detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_function_spy, plot_args, kwargs);
Py_DECREF(plot_args);
Py_DECREF(kwargs);
if (res) Py_DECREF(res);
}
#endif // WITHOUT_NUMPY
template <typename Numeric>
void plot3(const std::vector<Numeric>& x,
const std::vector<Numeric>& y,
const std::vector<Numeric>& z,
const std::map<std::string, std::string>& keywords =
std::map<std::string, std::string>(),
const long fig_number = 0)
{
detail::_interpreter::get();
// Same as with plot_surface: We lazily load the modules here the first time
// this function is called because I'm not sure that we can assume "matplotlib
// installed" implies "mpl_toolkits installed" on all platforms, and we don't
// want to require it for people who don't need 3d plots.
static PyObject* mpl_toolkitsmod = nullptr, * axis3dmod = nullptr;
if (!mpl_toolkitsmod) {
detail::_interpreter::get();
PyObject* mpl_toolkits = PyString_FromString("mpl_toolkits");
PyObject* axis3d = PyString_FromString("mpl_toolkits.mplot3d");
if (!mpl_toolkits || !axis3d) { throw std::runtime_error("couldnt create string"); }
mpl_toolkitsmod = PyImport_Import(mpl_toolkits);
Py_DECREF(mpl_toolkits);
if (!mpl_toolkitsmod) { throw std::runtime_error("Error loading module mpl_toolkits!"); }
axis3dmod = PyImport_Import(axis3d);
Py_DECREF(axis3d);
if (!axis3dmod) { throw std::runtime_error("Error loading module mpl_toolkits.mplot3d!"); }
}
assert(x.size() == y.size());
assert(y.size() == z.size());
PyObject* xarray = detail::get_array(x);
PyObject* yarray = detail::get_array(y);
PyObject* zarray = detail::get_array(z);
// construct positional args
PyObject* args = PyTuple_New(3);
PyTuple_SetItem(args, 0, xarray);
PyTuple_SetItem(args, 1, yarray);
PyTuple_SetItem(args, 2, zarray);
// Build up the kw args.
PyObject* kwargs = PyDict_New();
for (std::map<std::string, std::string>::const_iterator it = keywords.begin();
it != keywords.end(); ++it) {
PyDict_SetItemString(kwargs, it->first.c_str(),
PyString_FromString(it->second.c_str()));
}
PyObject* fig_args = PyTuple_New(1);
PyObject* fig = nullptr;
PyTuple_SetItem(fig_args, 0, PyLong_FromLong(fig_number));
PyObject* fig_exists =
PyObject_CallObject(detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_function_fignum_exists, fig_args);
if (!PyObject_IsTrue(fig_exists)) {
fig = PyObject_CallObject(detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_function_figure,
detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_empty_tuple);
}
else {
fig = PyObject_CallObject(detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_function_figure,
fig_args);
}
if (!fig) throw std::runtime_error("Call to figure() failed.");
PyObject* gca_kwargs = PyDict_New();
PyDict_SetItemString(gca_kwargs, "projection", PyString_FromString("3d"));
PyObject* gca = PyObject_GetAttrString(fig, "gca");
if (!gca) throw std::runtime_error("No gca");
Py_INCREF(gca);
PyObject* axis = PyObject_Call(
gca, detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_empty_tuple, gca_kwargs);
if (!axis) throw std::runtime_error("No axis");
Py_INCREF(axis);
Py_DECREF(gca);
Py_DECREF(gca_kwargs);
PyObject* plot3 = PyObject_GetAttrString(axis, "plot");
if (!plot3) throw std::runtime_error("No 3D line plot");
Py_INCREF(plot3);
PyObject* res = PyObject_Call(plot3, args, kwargs);
if (!res) throw std::runtime_error("Failed 3D line plot");
Py_DECREF(plot3);
Py_DECREF(axis);
Py_DECREF(args);
Py_DECREF(kwargs);
if (res) Py_DECREF(res);
}
template<typename Numeric>
bool stem(const std::vector<Numeric>& x, const std::vector<Numeric>& y, const std::map<std::string, std::string>& keywords)
{
assert(x.size() == y.size());
detail::_interpreter::get();
// using numpy arrays
PyObject* xarray = detail::get_array(x);
PyObject* yarray = detail::get_array(y);
// construct positional args
PyObject* args = PyTuple_New(2);
PyTuple_SetItem(args, 0, xarray);
PyTuple_SetItem(args, 1, yarray);
// construct keyword args
PyObject* kwargs = PyDict_New();
for (std::map<std::string, std::string>::const_iterator it =
keywords.begin(); it != keywords.end(); ++it) {
PyDict_SetItemString(kwargs, it->first.c_str(),
PyString_FromString(it->second.c_str()));
}
PyObject* res = PyObject_Call(
detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_function_stem, args, kwargs);
Py_DECREF(args);
Py_DECREF(kwargs);
if (res)
Py_DECREF(res);
return res;
}
template< typename Numeric >
bool fill(const std::vector<Numeric>& x, const std::vector<Numeric>& y, const std::map<std::string, std::string>& keywords)
{
assert(x.size() == y.size());
detail::_interpreter::get();
// using numpy arrays
PyObject* xarray = detail::get_array(x);
PyObject* yarray = detail::get_array(y);
// construct positional args
PyObject* args = PyTuple_New(2);
PyTuple_SetItem(args, 0, xarray);
PyTuple_SetItem(args, 1, yarray);
// construct keyword args
PyObject* kwargs = PyDict_New();
for (auto it = keywords.begin(); it != keywords.end(); ++it) {
PyDict_SetItemString(kwargs, it->first.c_str(), PyUnicode_FromString(it->second.c_str()));
}
PyObject* res = PyObject_Call(detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_function_fill, args, kwargs);
Py_DECREF(args);
Py_DECREF(kwargs);
if (res) Py_DECREF(res);
return res;
}
template< typename Numeric >
bool fill_between(const std::vector<Numeric>& x, const std::vector<Numeric>& y1, const std::vector<Numeric>& y2, const std::map<std::string, std::string>& keywords)
{
assert(x.size() == y1.size());
assert(x.size() == y2.size());
detail::_interpreter::get();
// using numpy arrays
PyObject* xarray = detail::get_array(x);
PyObject* y1array = detail::get_array(y1);
PyObject* y2array = detail::get_array(y2);
// construct positional args
PyObject* args = PyTuple_New(3);
PyTuple_SetItem(args, 0, xarray);
PyTuple_SetItem(args, 1, y1array);
PyTuple_SetItem(args, 2, y2array);
// construct keyword args
PyObject* kwargs = PyDict_New();
for (std::map<std::string, std::string>::const_iterator it = keywords.begin(); it != keywords.end(); ++it) {
PyDict_SetItemString(kwargs, it->first.c_str(), PyUnicode_FromString(it->second.c_str()));
}
PyObject* res = PyObject_Call(detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_function_fill_between, args, kwargs);
Py_DECREF(args);
Py_DECREF(kwargs);
if (res) Py_DECREF(res);
return res;
}
template <typename Numeric>
bool arrow(Numeric x, Numeric y, Numeric end_x, Numeric end_y, const std::string& fc = "r",
const std::string ec = "k", Numeric head_length = 0.25, Numeric head_width = 0.1625) {
PyObject* obj_x = PyFloat_FromDouble(x);
PyObject* obj_y = PyFloat_FromDouble(y);
PyObject* obj_end_x = PyFloat_FromDouble(end_x);
PyObject* obj_end_y = PyFloat_FromDouble(end_y);
PyObject* kwargs = PyDict_New();
PyDict_SetItemString(kwargs, "fc", PyString_FromString(fc.c_str()));
PyDict_SetItemString(kwargs, "ec", PyString_FromString(ec.c_str()));
PyDict_SetItemString(kwargs, "head_width", PyFloat_FromDouble(head_width));
PyDict_SetItemString(kwargs, "head_length", PyFloat_FromDouble(head_length));
PyObject* plot_args = PyTuple_New(4);
PyTuple_SetItem(plot_args, 0, obj_x);
PyTuple_SetItem(plot_args, 1, obj_y);
PyTuple_SetItem(plot_args, 2, obj_end_x);
PyTuple_SetItem(plot_args, 3, obj_end_y);
PyObject* res =
PyObject_Call(detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_function_arrow, plot_args, kwargs);
Py_DECREF(plot_args);
Py_DECREF(kwargs);
if (res)
Py_DECREF(res);
return res;
}
template< typename Numeric>
bool hist(const std::vector<Numeric>& y, long bins = 10, std::string color = "b",
double alpha = 1.0, bool cumulative = false)
{
detail::_interpreter::get();
PyObject* yarray = detail::get_array(y);
PyObject* kwargs = PyDict_New();
PyDict_SetItemString(kwargs, "bins", PyLong_FromLong(bins));
PyDict_SetItemString(kwargs, "color", PyString_FromString(color.c_str()));
PyDict_SetItemString(kwargs, "alpha", PyFloat_FromDouble(alpha));
PyDict_SetItemString(kwargs, "cumulative", cumulative ? Py_True : Py_False);
PyObject* plot_args = PyTuple_New(1);
PyTuple_SetItem(plot_args, 0, yarray);
PyObject* res = PyObject_Call(detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_function_hist, plot_args, kwargs);
Py_DECREF(plot_args);
Py_DECREF(kwargs);
if (res) Py_DECREF(res);
return res;
}
#ifndef WITHOUT_NUMPY
namespace detail {
inline void imshow(void* ptr, const NPY_TYPES type, const int rows, const int columns, const int colors, const std::map<std::string, std::string>& keywords, PyObject** out)
{
assert(type == NPY_UINT8 || type == NPY_FLOAT);
assert(colors == 1 || colors == 3 || colors == 4);
detail::_interpreter::get();
// construct args
npy_intp dims[3] = { rows, columns, colors };
PyObject* args = PyTuple_New(1);
PyTuple_SetItem(args, 0, PyArray_SimpleNewFromData(colors == 1 ? 2 : 3, dims, type, ptr));
// construct keyword args
PyObject* kwargs = PyDict_New();
for (std::map<std::string, std::string>::const_iterator it = keywords.begin(); it != keywords.end(); ++it)
{
PyDict_SetItemString(kwargs, it->first.c_str(), PyUnicode_FromString(it->second.c_str()));
}
PyObject* res = PyObject_Call(detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_function_imshow, args, kwargs);
Py_DECREF(args);
Py_DECREF(kwargs);
if (!res)
throw std::runtime_error("Call to imshow() failed");
if (out)
*out = res;
else
Py_DECREF(res);
}
} // namespace detail
inline void imshow(const unsigned char* ptr, const int rows, const int columns, const int colors, const std::map<std::string, std::string>& keywords = {}, PyObject** out = nullptr)
{
detail::imshow((void*)ptr, NPY_UINT8, rows, columns, colors, keywords, out);
}
inline void imshow(const float* ptr, const int rows, const int columns, const int colors, const std::map<std::string, std::string>& keywords = {}, PyObject** out = nullptr)
{
detail::imshow((void*)ptr, NPY_FLOAT, rows, columns, colors, keywords, out);
}
#ifdef WITH_OPENCV
void imshow(const cv::Mat& image, const std::map<std::string, std::string>& keywords = {})
{
// Convert underlying type of matrix, if needed
cv::Mat image2;
NPY_TYPES npy_type = NPY_UINT8;
switch (image.type() & CV_MAT_DEPTH_MASK) {
case CV_8U:
image2 = image;
break;
case CV_32F:
image2 = image;
npy_type = NPY_FLOAT;
break;
default:
image.convertTo(image2, CV_MAKETYPE(CV_8U, image.channels()));
}
// If color image, convert from BGR to RGB
switch (image2.channels()) {
case 3:
cv::cvtColor(image2, image2, CV_BGR2RGB);
break;
case 4:
cv::cvtColor(image2, image2, CV_BGRA2RGBA);
}
detail::imshow(image2.data, npy_type, image2.rows, image2.cols, image2.channels(), keywords);
}
#endif // WITH_OPENCV
#endif // WITHOUT_NUMPY
template<typename NumericX, typename NumericY>
bool scatter(const std::vector<NumericX>& x,
const std::vector<NumericY>& y,
const double s = 1.0, // The marker size in points**2
const std::map<std::string, std::string>& keywords = {})
{
detail::_interpreter::get();
assert(x.size() == y.size());
PyObject* xarray = detail::get_array(x);
PyObject* yarray = detail::get_array(y);
PyObject* kwargs = PyDict_New();
PyDict_SetItemString(kwargs, "s", PyLong_FromLong(s));
for (const auto& it : keywords)
{
PyDict_SetItemString(kwargs, it.first.c_str(), PyString_FromString(it.second.c_str()));
}
PyObject* plot_args = PyTuple_New(2);
PyTuple_SetItem(plot_args, 0, xarray);
PyTuple_SetItem(plot_args, 1, yarray);
PyObject* res = PyObject_Call(detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_function_scatter, plot_args, kwargs);
Py_DECREF(plot_args);
Py_DECREF(kwargs);
if (res) Py_DECREF(res);
return res;
}
template<typename NumericX, typename NumericY, typename NumericColors>
bool scatter_colored(const std::vector<NumericX>& x,
const std::vector<NumericY>& y,
const std::vector<NumericColors>& colors,
const double s = 1.0, // The marker size in points**2
const std::map<std::string, std::string>& keywords = {})
{
detail::_interpreter::get();
assert(x.size() == y.size());
PyObject* xarray = detail::get_array(x);
PyObject* yarray = detail::get_array(y);
PyObject* colors_array = detail::get_array(colors);
PyObject* kwargs = PyDict_New();
PyDict_SetItemString(kwargs, "s", PyLong_FromLong(s));
PyDict_SetItemString(kwargs, "c", colors_array);
for (const auto& it : keywords)
{
PyDict_SetItemString(kwargs, it.first.c_str(), PyString_FromString(it.second.c_str()));
}
PyObject* plot_args = PyTuple_New(2);
PyTuple_SetItem(plot_args, 0, xarray);
PyTuple_SetItem(plot_args, 1, yarray);
PyObject* res = PyObject_Call(detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_function_scatter, plot_args, kwargs);
Py_DECREF(plot_args);
Py_DECREF(kwargs);
if (res) Py_DECREF(res);
return res;
}
template<typename NumericX, typename NumericY, typename NumericZ>
bool scatter(const std::vector<NumericX>& x,
const std::vector<NumericY>& y,
const std::vector<NumericZ>& z,
const double s = 1.0, // The marker size in points**2
const std::map<std::string, std::string>& keywords = {},
const long fig_number = 0) {
detail::_interpreter::get();
// Same as with plot_surface: We lazily load the modules here the first time
// this function is called because I'm not sure that we can assume "matplotlib
// installed" implies "mpl_toolkits installed" on all platforms, and we don't
// want to require it for people who don't need 3d plots.
static PyObject* mpl_toolkitsmod = nullptr, * axis3dmod = nullptr;
if (!mpl_toolkitsmod) {
detail::_interpreter::get();
PyObject* mpl_toolkits = PyString_FromString("mpl_toolkits");
PyObject* axis3d = PyString_FromString("mpl_toolkits.mplot3d");
if (!mpl_toolkits || !axis3d) { throw std::runtime_error("couldnt create string"); }
mpl_toolkitsmod = PyImport_Import(mpl_toolkits);
Py_DECREF(mpl_toolkits);
if (!mpl_toolkitsmod) { throw std::runtime_error("Error loading module mpl_toolkits!"); }
axis3dmod = PyImport_Import(axis3d);
Py_DECREF(axis3d);
if (!axis3dmod) { throw std::runtime_error("Error loading module mpl_toolkits.mplot3d!"); }
}
assert(x.size() == y.size());
assert(y.size() == z.size());
PyObject* xarray = detail::get_array(x);
PyObject* yarray = detail::get_array(y);
PyObject* zarray = detail::get_array(z);
// construct positional args
PyObject* args = PyTuple_New(3);
PyTuple_SetItem(args, 0, xarray);
PyTuple_SetItem(args, 1, yarray);
PyTuple_SetItem(args, 2, zarray);
// Build up the kw args.
PyObject* kwargs = PyDict_New();
for (std::map<std::string, std::string>::const_iterator it = keywords.begin();
it != keywords.end(); ++it) {
PyDict_SetItemString(kwargs, it->first.c_str(),
PyString_FromString(it->second.c_str()));
}
PyObject* fig_args = PyTuple_New(1);
PyObject* fig = nullptr;
PyTuple_SetItem(fig_args, 0, PyLong_FromLong(fig_number));
PyObject* fig_exists =
PyObject_CallObject(detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_function_fignum_exists, fig_args);
if (!PyObject_IsTrue(fig_exists)) {
fig = PyObject_CallObject(detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_function_figure,
detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_empty_tuple);
}
else {
fig = PyObject_CallObject(detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_function_figure,
fig_args);
}
Py_DECREF(fig_exists);
if (!fig) throw std::runtime_error("Call to figure() failed.");
PyObject* gca_kwargs = PyDict_New();
PyDict_SetItemString(gca_kwargs, "projection", PyString_FromString("3d"));
PyObject* gca = PyObject_GetAttrString(fig, "gca");
if (!gca) throw std::runtime_error("No gca");
Py_INCREF(gca);
PyObject* axis = PyObject_Call(
gca, detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_empty_tuple, gca_kwargs);
if (!axis) throw std::runtime_error("No axis");
Py_INCREF(axis);
Py_DECREF(gca);
Py_DECREF(gca_kwargs);
PyObject* plot3 = PyObject_GetAttrString(axis, "scatter");
if (!plot3) throw std::runtime_error("No 3D line plot");
Py_INCREF(plot3);
PyObject* res = PyObject_Call(plot3, args, kwargs);
if (!res) throw std::runtime_error("Failed 3D line plot");
Py_DECREF(plot3);
Py_DECREF(axis);
Py_DECREF(args);
Py_DECREF(kwargs);
Py_DECREF(fig);
if (res) Py_DECREF(res);
return res;
}
template<typename Numeric>
bool boxplot(const std::vector<std::vector<Numeric>>& data,
const std::vector<std::string>& labels = {},
const std::map<std::string, std::string>& keywords = {})
{
detail::_interpreter::get();
PyObject* listlist = detail::get_listlist(data);
PyObject* args = PyTuple_New(1);
PyTuple_SetItem(args, 0, listlist);
PyObject* kwargs = PyDict_New();
// kwargs needs the labels, if there are (the correct number of) labels
if (!labels.empty() && labels.size() == data.size()) {
PyDict_SetItemString(kwargs, "labels", detail::get_array(labels));
}
// take care of the remaining keywords
for (const auto& it : keywords)
{
PyDict_SetItemString(kwargs, it.first.c_str(), PyString_FromString(it.second.c_str()));
}
PyObject* res = PyObject_Call(detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_function_boxplot, args, kwargs);
Py_DECREF(args);
Py_DECREF(kwargs);
if (res) Py_DECREF(res);
return res;
}
template<typename Numeric>
bool boxplot(const std::vector<Numeric>& data,
const std::map<std::string, std::string>& keywords = {})
{
detail::_interpreter::get();
PyObject* vector = detail::get_array(data);
PyObject* args = PyTuple_New(1);
PyTuple_SetItem(args, 0, vector);
PyObject* kwargs = PyDict_New();
for (const auto& it : keywords)
{
PyDict_SetItemString(kwargs, it.first.c_str(), PyString_FromString(it.second.c_str()));
}
PyObject* res = PyObject_Call(detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_function_boxplot, args, kwargs);
Py_DECREF(args);
Py_DECREF(kwargs);
if (res) Py_DECREF(res);
return res;
}
template <typename Numeric>
bool bar(const std::vector<Numeric>& x,
const std::vector<Numeric>& y,
std::string ec = "black",
std::string ls = "-",
double lw = 1.0,
const std::map<std::string, std::string>& keywords = {})
{
detail::_interpreter::get();
PyObject* xarray = detail::get_array(x);
PyObject* yarray = detail::get_array(y);
PyObject* kwargs = PyDict_New();
PyDict_SetItemString(kwargs, "ec", PyString_FromString(ec.c_str()));
PyDict_SetItemString(kwargs, "ls", PyString_FromString(ls.c_str()));
PyDict_SetItemString(kwargs, "lw", PyFloat_FromDouble(lw));
for (std::map<std::string, std::string>::const_iterator it =
keywords.begin();
it != keywords.end();
++it) {
PyDict_SetItemString(
kwargs, it->first.c_str(), PyUnicode_FromString(it->second.c_str()));
}
PyObject* plot_args = PyTuple_New(2);
PyTuple_SetItem(plot_args, 0, xarray);
PyTuple_SetItem(plot_args, 1, yarray);
PyObject* res = PyObject_Call(
detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_function_bar, plot_args, kwargs);
Py_DECREF(plot_args);
Py_DECREF(kwargs);
if (res) Py_DECREF(res);
return res;
}
template <typename Numeric>
bool bar(const std::vector<Numeric>& y,
std::string ec = "black",
std::string ls = "-",
double lw = 1.0,
const std::map<std::string, std::string>& keywords = {})
{
using T = typename std::remove_reference<decltype(y)>::type::value_type;
detail::_interpreter::get();
std::vector<T> x;
for (std::size_t i = 0; i < y.size(); i++) { x.push_back(i); }
return bar(x, y, ec, ls, lw, keywords);
}
template<typename Numeric>
bool barh(const std::vector<Numeric>& x, const std::vector<Numeric>& y, std::string ec = "black", std::string ls = "-", double lw = 1.0, const std::map<std::string, std::string>& keywords = { }) {
PyObject* xarray = detail::get_array(x);
PyObject* yarray = detail::get_array(y);
PyObject* kwargs = PyDict_New();
PyDict_SetItemString(kwargs, "ec", PyString_FromString(ec.c_str()));
PyDict_SetItemString(kwargs, "ls", PyString_FromString(ls.c_str()));
PyDict_SetItemString(kwargs, "lw", PyFloat_FromDouble(lw));
for (std::map<std::string, std::string>::const_iterator it = keywords.begin(); it != keywords.end(); ++it) {
PyDict_SetItemString(kwargs, it->first.c_str(), PyUnicode_FromString(it->second.c_str()));
}
PyObject* plot_args = PyTuple_New(2);
PyTuple_SetItem(plot_args, 0, xarray);
PyTuple_SetItem(plot_args, 1, yarray);
PyObject* res = PyObject_Call(detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_function_barh, plot_args, kwargs);
Py_DECREF(plot_args);
Py_DECREF(kwargs);
if (res) Py_DECREF(res);
return res;
}
inline bool subplots_adjust(const std::map<std::string, double>& keywords = {})
{
detail::_interpreter::get();
PyObject* kwargs = PyDict_New();
for (std::map<std::string, double>::const_iterator it =
keywords.begin(); it != keywords.end(); ++it) {
PyDict_SetItemString(kwargs, it->first.c_str(),
PyFloat_FromDouble(it->second));
}
PyObject* plot_args = PyTuple_New(0);
PyObject* res = PyObject_Call(detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_function_subplots_adjust, plot_args, kwargs);
Py_DECREF(plot_args);
Py_DECREF(kwargs);
if (res) Py_DECREF(res);
return res;
}
template< typename Numeric>
bool named_hist(std::string label, const std::vector<Numeric>& y, long bins = 10, std::string color = "b", double alpha = 1.0)
{
detail::_interpreter::get();
PyObject* yarray = detail::get_array(y);
PyObject* kwargs = PyDict_New();
PyDict_SetItemString(kwargs, "label", PyString_FromString(label.c_str()));
PyDict_SetItemString(kwargs, "bins", PyLong_FromLong(bins));
PyDict_SetItemString(kwargs, "color", PyString_FromString(color.c_str()));
PyDict_SetItemString(kwargs, "alpha", PyFloat_FromDouble(alpha));
PyObject* plot_args = PyTuple_New(1);
PyTuple_SetItem(plot_args, 0, yarray);
PyObject* res = PyObject_Call(detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_function_hist, plot_args, kwargs);
Py_DECREF(plot_args);
Py_DECREF(kwargs);
if (res) Py_DECREF(res);
return res;
}
template<typename NumericX, typename NumericY>
bool plot(const std::vector<NumericX>& x, const std::vector<NumericY>& y, const std::string& s = "")
{
assert(x.size() == y.size());
detail::_interpreter::get();
PyObject* xarray = detail::get_array(x);
PyObject* yarray = detail::get_array(y);
PyObject* pystring = PyString_FromString(s.c_str());
PyObject* plot_args = PyTuple_New(3);
PyTuple_SetItem(plot_args, 0, xarray);
PyTuple_SetItem(plot_args, 1, yarray);
PyTuple_SetItem(plot_args, 2, pystring);
PyObject* res = PyObject_CallObject(detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_function_plot, plot_args);
Py_DECREF(plot_args);
if (res) Py_DECREF(res);
return res;
}
template <typename NumericX, typename NumericY, typename NumericZ>
bool contour(const std::vector<NumericX>& x, const std::vector<NumericY>& y,
const std::vector<NumericZ>& z,
const std::map<std::string, std::string>& keywords = {}) {
assert(x.size() == y.size() && x.size() == z.size());
PyObject* xarray = detail::get_array(x);
PyObject* yarray = detail::get_array(y);
PyObject* zarray = detail::get_array(z);
PyObject* plot_args = PyTuple_New(3);
PyTuple_SetItem(plot_args, 0, xarray);
PyTuple_SetItem(plot_args, 1, yarray);
PyTuple_SetItem(plot_args, 2, zarray);
// construct keyword args
PyObject* kwargs = PyDict_New();
for (std::map<std::string, std::string>::const_iterator it = keywords.begin();
it != keywords.end(); ++it) {
PyDict_SetItemString(kwargs, it->first.c_str(), PyUnicode_FromString(it->second.c_str()));
}
PyObject* res =
PyObject_Call(detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_function_contour, plot_args, kwargs);
Py_DECREF(kwargs);
Py_DECREF(plot_args);
if (res)
Py_DECREF(res);
return res;
}
template<typename NumericX, typename NumericY, typename NumericU, typename NumericW>
bool quiver(const std::vector<NumericX>& x, const std::vector<NumericY>& y, const std::vector<NumericU>& u, const std::vector<NumericW>& w, const std::map<std::string, std::string>& keywords = {})
{
assert(x.size() == y.size() && x.size() == u.size() && u.size() == w.size());
detail::_interpreter::get();
PyObject* xarray = detail::get_array(x);
PyObject* yarray = detail::get_array(y);
PyObject* uarray = detail::get_array(u);
PyObject* warray = detail::get_array(w);
PyObject* plot_args = PyTuple_New(4);
PyTuple_SetItem(plot_args, 0, xarray);
PyTuple_SetItem(plot_args, 1, yarray);
PyTuple_SetItem(plot_args, 2, uarray);
PyTuple_SetItem(plot_args, 3, warray);
// construct keyword args
PyObject* kwargs = PyDict_New();
for (std::map<std::string, std::string>::const_iterator it = keywords.begin(); it != keywords.end(); ++it)
{
PyDict_SetItemString(kwargs, it->first.c_str(), PyUnicode_FromString(it->second.c_str()));
}
PyObject* res = PyObject_Call(
detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_function_quiver, plot_args, kwargs);
Py_DECREF(kwargs);
Py_DECREF(plot_args);
if (res)
Py_DECREF(res);
return res;
}
template<typename NumericX, typename NumericY, typename NumericZ, typename NumericU, typename NumericW, typename NumericV>
bool quiver(const std::vector<NumericX>& x, const std::vector<NumericY>& y, const std::vector<NumericZ>& z, const std::vector<NumericU>& u, const std::vector<NumericW>& w, const std::vector<NumericV>& v, const std::map<std::string, std::string>& keywords = {})
{
//set up 3d axes stuff
static PyObject* mpl_toolkitsmod = nullptr, * axis3dmod = nullptr;
if (!mpl_toolkitsmod) {
detail::_interpreter::get();
PyObject* mpl_toolkits = PyString_FromString("mpl_toolkits");
PyObject* axis3d = PyString_FromString("mpl_toolkits.mplot3d");
if (!mpl_toolkits || !axis3d) { throw std::runtime_error("couldnt create string"); }
mpl_toolkitsmod = PyImport_Import(mpl_toolkits);
Py_DECREF(mpl_toolkits);
if (!mpl_toolkitsmod) { throw std::runtime_error("Error loading module mpl_toolkits!"); }
axis3dmod = PyImport_Import(axis3d);
Py_DECREF(axis3d);
if (!axis3dmod) { throw std::runtime_error("Error loading module mpl_toolkits.mplot3d!"); }
}
//assert sizes match up
assert(x.size() == y.size() && x.size() == u.size() && u.size() == w.size() && x.size() == z.size() && x.size() == v.size() && u.size() == v.size());
//set up parameters
detail::_interpreter::get();
PyObject* xarray = detail::get_array(x);
PyObject* yarray = detail::get_array(y);
PyObject* zarray = detail::get_array(z);
PyObject* uarray = detail::get_array(u);
PyObject* warray = detail::get_array(w);
PyObject* varray = detail::get_array(v);
PyObject* plot_args = PyTuple_New(6);
PyTuple_SetItem(plot_args, 0, xarray);
PyTuple_SetItem(plot_args, 1, yarray);
PyTuple_SetItem(plot_args, 2, zarray);
PyTuple_SetItem(plot_args, 3, uarray);
PyTuple_SetItem(plot_args, 4, warray);
PyTuple_SetItem(plot_args, 5, varray);
// construct keyword args
PyObject* kwargs = PyDict_New();
for (std::map<std::string, std::string>::const_iterator it = keywords.begin(); it != keywords.end(); ++it)
{
PyDict_SetItemString(kwargs, it->first.c_str(), PyUnicode_FromString(it->second.c_str()));
}
//get figure gca to enable 3d projection
PyObject* fig =
PyObject_CallObject(detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_function_figure,
detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_empty_tuple);
if (!fig) throw std::runtime_error("Call to figure() failed.");
PyObject* gca_kwargs = PyDict_New();
PyDict_SetItemString(gca_kwargs, "projection", PyString_FromString("3d"));
PyObject* gca = PyObject_GetAttrString(fig, "gca");
if (!gca) throw std::runtime_error("No gca");
Py_INCREF(gca);
PyObject* axis = PyObject_Call(
gca, detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_empty_tuple, gca_kwargs);
if (!axis) throw std::runtime_error("No axis");
Py_INCREF(axis);
Py_DECREF(gca);
Py_DECREF(gca_kwargs);
//plot our boys bravely, plot them strongly, plot them with a wink and clap
PyObject* plot3 = PyObject_GetAttrString(axis, "quiver");
if (!plot3) throw std::runtime_error("No 3D line plot");
Py_INCREF(plot3);
PyObject* res = PyObject_Call(
plot3, plot_args, kwargs);
if (!res) throw std::runtime_error("Failed 3D plot");
Py_DECREF(plot3);
Py_DECREF(axis);
Py_DECREF(kwargs);
Py_DECREF(plot_args);
if (res)
Py_DECREF(res);
return res;
}
template<typename NumericX, typename NumericY>
bool stem(const std::vector<NumericX>& x, const std::vector<NumericY>& y, const std::string& s = "")
{
assert(x.size() == y.size());
detail::_interpreter::get();
PyObject* xarray = detail::get_array(x);
PyObject* yarray = detail::get_array(y);
PyObject* pystring = PyString_FromString(s.c_str());
PyObject* plot_args = PyTuple_New(3);
PyTuple_SetItem(plot_args, 0, xarray);
PyTuple_SetItem(plot_args, 1, yarray);
PyTuple_SetItem(plot_args, 2, pystring);
PyObject* res = PyObject_CallObject(
detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_function_stem, plot_args);
Py_DECREF(plot_args);
if (res)
Py_DECREF(res);
return res;
}
template<typename NumericX, typename NumericY>
bool semilogx(const std::vector<NumericX>& x, const std::vector<NumericY>& y, const std::string& s = "")
{
assert(x.size() == y.size());
detail::_interpreter::get();
PyObject* xarray = detail::get_array(x);
PyObject* yarray = detail::get_array(y);
PyObject* pystring = PyString_FromString(s.c_str());
PyObject* plot_args = PyTuple_New(3);
PyTuple_SetItem(plot_args, 0, xarray);
PyTuple_SetItem(plot_args, 1, yarray);
PyTuple_SetItem(plot_args, 2, pystring);
PyObject* res = PyObject_CallObject(detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_function_semilogx, plot_args);
Py_DECREF(plot_args);
if (res) Py_DECREF(res);
return res;
}
template<typename NumericX, typename NumericY>
bool semilogy(const std::vector<NumericX>& x, const std::vector<NumericY>& y, const std::string& s = "")
{
assert(x.size() == y.size());
detail::_interpreter::get();
PyObject* xarray = detail::get_array(x);
PyObject* yarray = detail::get_array(y);
PyObject* pystring = PyString_FromString(s.c_str());
PyObject* plot_args = PyTuple_New(3);
PyTuple_SetItem(plot_args, 0, xarray);
PyTuple_SetItem(plot_args, 1, yarray);
PyTuple_SetItem(plot_args, 2, pystring);
PyObject* res = PyObject_CallObject(detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_function_semilogy, plot_args);
Py_DECREF(plot_args);
if (res) Py_DECREF(res);
return res;
}
template<typename NumericX, typename NumericY>
bool loglog(const std::vector<NumericX>& x, const std::vector<NumericY>& y, const std::string& s = "")
{
assert(x.size() == y.size());
detail::_interpreter::get();
PyObject* xarray = detail::get_array(x);
PyObject* yarray = detail::get_array(y);
PyObject* pystring = PyString_FromString(s.c_str());
PyObject* plot_args = PyTuple_New(3);
PyTuple_SetItem(plot_args, 0, xarray);
PyTuple_SetItem(plot_args, 1, yarray);
PyTuple_SetItem(plot_args, 2, pystring);
PyObject* res = PyObject_CallObject(detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_function_loglog, plot_args);
Py_DECREF(plot_args);
if (res) Py_DECREF(res);
return res;
}
template<typename NumericX, typename NumericY>
bool errorbar(const std::vector<NumericX>& x, const std::vector<NumericY>& y, const std::vector<NumericX>& yerr, const std::map<std::string, std::string>& keywords = {})
{
assert(x.size() == y.size());
detail::_interpreter::get();
PyObject* xarray = detail::get_array(x);
PyObject* yarray = detail::get_array(y);
PyObject* yerrarray = detail::get_array(yerr);
// construct keyword args
PyObject* kwargs = PyDict_New();
for (std::map<std::string, std::string>::const_iterator it = keywords.begin(); it != keywords.end(); ++it)
{
PyDict_SetItemString(kwargs, it->first.c_str(), PyString_FromString(it->second.c_str()));
}
PyDict_SetItemString(kwargs, "yerr", yerrarray);
PyObject* plot_args = PyTuple_New(2);
PyTuple_SetItem(plot_args, 0, xarray);
PyTuple_SetItem(plot_args, 1, yarray);
PyObject* res = PyObject_Call(detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_function_errorbar, plot_args, kwargs);
Py_DECREF(kwargs);
Py_DECREF(plot_args);
if (res)
Py_DECREF(res);
else
throw std::runtime_error("Call to errorbar() failed.");
return res;
}
template<typename Numeric>
bool named_plot(const std::string& name, const std::vector<Numeric>& y, const std::string& format = "")
{
detail::_interpreter::get();
PyObject* kwargs = PyDict_New();
PyDict_SetItemString(kwargs, "label", PyString_FromString(name.c_str()));
PyObject* yarray = detail::get_array(y);
PyObject* pystring = PyString_FromString(format.c_str());
PyObject* plot_args = PyTuple_New(2);
PyTuple_SetItem(plot_args, 0, yarray);
PyTuple_SetItem(plot_args, 1, pystring);
PyObject* res = PyObject_Call(detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_function_plot, plot_args, kwargs);
Py_DECREF(kwargs);
Py_DECREF(plot_args);
if (res) Py_DECREF(res);
return res;
}
template<typename NumericX, typename NumericY>
bool named_plot(const std::string& name, const std::vector<NumericX>& x, const std::vector<NumericY>& y, const std::string& format = "")
{
detail::_interpreter::get();
PyObject* kwargs = PyDict_New();
PyDict_SetItemString(kwargs, "label", PyString_FromString(name.c_str()));
PyObject* xarray = detail::get_array(x);
PyObject* yarray = detail::get_array(y);
PyObject* pystring = PyString_FromString(format.c_str());
PyObject* plot_args = PyTuple_New(3);
PyTuple_SetItem(plot_args, 0, xarray);
PyTuple_SetItem(plot_args, 1, yarray);
PyTuple_SetItem(plot_args, 2, pystring);
PyObject* res = PyObject_Call(detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_function_plot, plot_args, kwargs);
Py_DECREF(kwargs);
Py_DECREF(plot_args);
if (res) Py_DECREF(res);
return res;
}
template<typename NumericX, typename NumericY>
bool named_semilogx(const std::string& name, const std::vector<NumericX>& x, const std::vector<NumericY>& y, const std::string& format = "")
{
detail::_interpreter::get();
PyObject* kwargs = PyDict_New();
PyDict_SetItemString(kwargs, "label", PyString_FromString(name.c_str()));
PyObject* xarray = detail::get_array(x);
PyObject* yarray = detail::get_array(y);
PyObject* pystring = PyString_FromString(format.c_str());
PyObject* plot_args = PyTuple_New(3);
PyTuple_SetItem(plot_args, 0, xarray);
PyTuple_SetItem(plot_args, 1, yarray);
PyTuple_SetItem(plot_args, 2, pystring);
PyObject* res = PyObject_Call(detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_function_semilogx, plot_args, kwargs);
Py_DECREF(kwargs);
Py_DECREF(plot_args);
if (res) Py_DECREF(res);
return res;
}
template<typename NumericX, typename NumericY>
bool named_semilogy(const std::string& name, const std::vector<NumericX>& x, const std::vector<NumericY>& y, const std::string& format = "")
{
detail::_interpreter::get();
PyObject* kwargs = PyDict_New();
PyDict_SetItemString(kwargs, "label", PyString_FromString(name.c_str()));
PyObject* xarray = detail::get_array(x);
PyObject* yarray = detail::get_array(y);
PyObject* pystring = PyString_FromString(format.c_str());
PyObject* plot_args = PyTuple_New(3);
PyTuple_SetItem(plot_args, 0, xarray);
PyTuple_SetItem(plot_args, 1, yarray);
PyTuple_SetItem(plot_args, 2, pystring);
PyObject* res = PyObject_Call(detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_function_semilogy, plot_args, kwargs);
Py_DECREF(kwargs);
Py_DECREF(plot_args);
if (res) Py_DECREF(res);
return res;
}
template<typename NumericX, typename NumericY>
bool named_loglog(const std::string& name, const std::vector<NumericX>& x, const std::vector<NumericY>& y, const std::string& format = "")
{
detail::_interpreter::get();
PyObject* kwargs = PyDict_New();
PyDict_SetItemString(kwargs, "label", PyString_FromString(name.c_str()));
PyObject* xarray = detail::get_array(x);
PyObject* yarray = detail::get_array(y);
PyObject* pystring = PyString_FromString(format.c_str());
PyObject* plot_args = PyTuple_New(3);
PyTuple_SetItem(plot_args, 0, xarray);
PyTuple_SetItem(plot_args, 1, yarray);
PyTuple_SetItem(plot_args, 2, pystring);
PyObject* res = PyObject_Call(detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_function_loglog, plot_args, kwargs);
Py_DECREF(kwargs);
Py_DECREF(plot_args);
if (res) Py_DECREF(res);
return res;
}
template<typename Numeric>
bool plot(const std::vector<Numeric>& y, const std::string& format = "")
{
std::vector<Numeric> x(y.size());
for (size_t i = 0; i < x.size(); ++i) x.at(i) = i;
return plot(x, y, format);
}
template<typename Numeric>
bool plot(const std::vector<Numeric>& y, const std::map<std::string, std::string>& keywords)
{
std::vector<Numeric> x(y.size());
for (size_t i = 0; i < x.size(); ++i) x.at(i) = i;
return plot(x, y, keywords);
}
template<typename Numeric>
bool stem(const std::vector<Numeric>& y, const std::string& format = "")
{
std::vector<Numeric> x(y.size());
for (size_t i = 0; i < x.size(); ++i) x.at(i) = i;
return stem(x, y, format);
}
template<typename Numeric>
void text(Numeric x, Numeric y, const std::string& s = "")
{
detail::_interpreter::get();
PyObject* args = PyTuple_New(3);
PyTuple_SetItem(args, 0, PyFloat_FromDouble(x));
PyTuple_SetItem(args, 1, PyFloat_FromDouble(y));
PyTuple_SetItem(args, 2, PyString_FromString(s.c_str()));
PyObject* res = PyObject_CallObject(detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_function_text, args);
if (!res) throw std::runtime_error("Call to text() failed.");
Py_DECREF(args);
Py_DECREF(res);
}
inline void colorbar(PyObject* mappable = NULL, const std::map<std::string, float>& keywords = {})
{
if (mappable == NULL)
throw std::runtime_error("Must call colorbar with PyObject* returned from an image, contour, surface, etc.");
detail::_interpreter::get();
PyObject* args = PyTuple_New(1);
PyTuple_SetItem(args, 0, mappable);
PyObject* kwargs = PyDict_New();
for (std::map<std::string, float>::const_iterator it = keywords.begin(); it != keywords.end(); ++it)
{
PyDict_SetItemString(kwargs, it->first.c_str(), PyFloat_FromDouble(it->second));
}
PyObject* res = PyObject_Call(detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_function_colorbar, args, kwargs);
if (!res) throw std::runtime_error("Call to colorbar() failed.");
Py_DECREF(args);
Py_DECREF(kwargs);
Py_DECREF(res);
}
inline long figure(long number = -1)
{
detail::_interpreter::get();
PyObject* res;
if (number == -1)
res = PyObject_CallObject(detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_function_figure, detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_empty_tuple);
else {
assert(number > 0);
// Make sure interpreter is initialised
detail::_interpreter::get();
PyObject* args = PyTuple_New(1);
PyTuple_SetItem(args, 0, PyLong_FromLong(number));
res = PyObject_CallObject(detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_function_figure, args);
Py_DECREF(args);
}
if (!res) throw std::runtime_error("Call to figure() failed.");
PyObject* num = PyObject_GetAttrString(res, "number");
if (!num) throw std::runtime_error("Could not get number attribute of figure object");
const long figureNumber = PyLong_AsLong(num);
Py_DECREF(num);
Py_DECREF(res);
return figureNumber;
}
inline bool fignum_exists(long number)
{
detail::_interpreter::get();
PyObject* args = PyTuple_New(1);
PyTuple_SetItem(args, 0, PyLong_FromLong(number));
PyObject* res = PyObject_CallObject(detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_function_fignum_exists, args);
if (!res) throw std::runtime_error("Call to fignum_exists() failed.");
bool ret = PyObject_IsTrue(res);
Py_DECREF(res);
Py_DECREF(args);
return ret;
}
inline void figure_size(size_t w, size_t h)
{
detail::_interpreter::get();
const size_t dpi = 100;
PyObject* size = PyTuple_New(2);
PyTuple_SetItem(size, 0, PyFloat_FromDouble((double)w / dpi));
PyTuple_SetItem(size, 1, PyFloat_FromDouble((double)h / dpi));
PyObject* kwargs = PyDict_New();
PyDict_SetItemString(kwargs, "figsize", size);
PyDict_SetItemString(kwargs, "dpi", PyLong_FromSize_t(dpi));
PyObject* res = PyObject_Call(detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_function_figure,
detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_empty_tuple, kwargs);
Py_DECREF(kwargs);
if (!res) throw std::runtime_error("Call to figure_size() failed.");
Py_DECREF(res);
}
inline void legend()
{
detail::_interpreter::get();
PyObject* res = PyObject_CallObject(detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_function_legend, detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_empty_tuple);
if (!res) throw std::runtime_error("Call to legend() failed.");
Py_DECREF(res);
}
inline void legend(const std::map<std::string, std::string>& keywords)
{
detail::_interpreter::get();
// construct keyword args
PyObject* kwargs = PyDict_New();
for (std::map<std::string, std::string>::const_iterator it = keywords.begin(); it != keywords.end(); ++it)
{
PyDict_SetItemString(kwargs, it->first.c_str(), PyString_FromString(it->second.c_str()));
}
PyObject* res = PyObject_Call(detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_function_legend, detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_empty_tuple, kwargs);
if (!res) throw std::runtime_error("Call to legend() failed.");
Py_DECREF(kwargs);
Py_DECREF(res);
}
template<typename Numeric>
inline void set_aspect(Numeric ratio)
{
detail::_interpreter::get();
PyObject* args = PyTuple_New(1);
PyTuple_SetItem(args, 0, PyFloat_FromDouble(ratio));
PyObject* kwargs = PyDict_New();
PyObject* ax =
PyObject_CallObject(detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_function_gca,
detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_empty_tuple);
if (!ax) throw std::runtime_error("Call to gca() failed.");
Py_INCREF(ax);
PyObject* set_aspect = PyObject_GetAttrString(ax, "set_aspect");
if (!set_aspect) throw std::runtime_error("Attribute set_aspect not found.");
Py_INCREF(set_aspect);
PyObject* res = PyObject_Call(set_aspect, args, kwargs);
if (!res) throw std::runtime_error("Call to set_aspect() failed.");
Py_DECREF(set_aspect);
Py_DECREF(ax);
Py_DECREF(args);
Py_DECREF(kwargs);
}
inline void set_aspect_equal()
{
// expect ratio == "equal". Leaving error handling to matplotlib.
detail::_interpreter::get();
PyObject* args = PyTuple_New(1);
PyTuple_SetItem(args, 0, PyString_FromString("equal"));
PyObject* kwargs = PyDict_New();
PyObject* ax =
PyObject_CallObject(detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_function_gca,
detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_empty_tuple);
if (!ax) throw std::runtime_error("Call to gca() failed.");
Py_INCREF(ax);
PyObject* set_aspect = PyObject_GetAttrString(ax, "set_aspect");
if (!set_aspect) throw std::runtime_error("Attribute set_aspect not found.");
Py_INCREF(set_aspect);
PyObject* res = PyObject_Call(set_aspect, args, kwargs);
if (!res) throw std::runtime_error("Call to set_aspect() failed.");
Py_DECREF(set_aspect);
Py_DECREF(ax);
Py_DECREF(args);
Py_DECREF(kwargs);
}
template<typename Numeric>
void ylim(Numeric left, Numeric right)
{
detail::_interpreter::get();
PyObject* list = PyList_New(2);
PyList_SetItem(list, 0, PyFloat_FromDouble(left));
PyList_SetItem(list, 1, PyFloat_FromDouble(right));
PyObject* args = PyTuple_New(1);
PyTuple_SetItem(args, 0, list);
PyObject* res = PyObject_CallObject(detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_function_ylim, args);
if (!res) throw std::runtime_error("Call to ylim() failed.");
Py_DECREF(args);
Py_DECREF(res);
}
template<typename Numeric>
void xlim(Numeric left, Numeric right)
{
detail::_interpreter::get();
PyObject* list = PyList_New(2);
PyList_SetItem(list, 0, PyFloat_FromDouble(left));
PyList_SetItem(list, 1, PyFloat_FromDouble(right));
PyObject* args = PyTuple_New(1);
PyTuple_SetItem(args, 0, list);
PyObject* res = PyObject_CallObject(detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_function_xlim, args);
if (!res) throw std::runtime_error("Call to xlim() failed.");
Py_DECREF(args);
Py_DECREF(res);
}
inline std::array<double, 2> xlim()
{
PyObject* args = PyTuple_New(0);
PyObject* res = PyObject_CallObject(detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_function_xlim, args);
if (!res) throw std::runtime_error("Call to xlim() failed.");
Py_DECREF(res);
PyObject* left = PyTuple_GetItem(res, 0);
PyObject* right = PyTuple_GetItem(res, 1);
return { PyFloat_AsDouble(left), PyFloat_AsDouble(right) };
}
inline std::array<double, 2> ylim()
{
PyObject* args = PyTuple_New(0);
PyObject* res = PyObject_CallObject(detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_function_ylim, args);
if (!res) throw std::runtime_error("Call to ylim() failed.");
Py_DECREF(res);
PyObject* left = PyTuple_GetItem(res, 0);
PyObject* right = PyTuple_GetItem(res, 1);
return { PyFloat_AsDouble(left), PyFloat_AsDouble(right) };
}
template<typename Numeric>
inline void xticks(const std::vector<Numeric>& ticks, const std::vector<std::string>& labels = {}, const std::map<std::string, std::string>& keywords = {})
{
assert(labels.size() == 0 || ticks.size() == labels.size());
detail::_interpreter::get();
// using numpy array
PyObject* ticksarray = detail::get_array(ticks);
PyObject* args;
if (labels.size() == 0) {
// construct positional args
args = PyTuple_New(1);
PyTuple_SetItem(args, 0, ticksarray);
}
else {
// make tuple of tick labels
PyObject* labelstuple = PyTuple_New(labels.size());
for (size_t i = 0; i < labels.size(); i++)
PyTuple_SetItem(labelstuple, i, PyUnicode_FromString(labels[i].c_str()));
// construct positional args
args = PyTuple_New(2);
PyTuple_SetItem(args, 0, ticksarray);
PyTuple_SetItem(args, 1, labelstuple);
}
// construct keyword args
PyObject* kwargs = PyDict_New();
for (std::map<std::string, std::string>::const_iterator it = keywords.begin(); it != keywords.end(); ++it)
{
PyDict_SetItemString(kwargs, it->first.c_str(), PyString_FromString(it->second.c_str()));
}
PyObject* res = PyObject_Call(detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_function_xticks, args, kwargs);
Py_DECREF(args);
Py_DECREF(kwargs);
if (!res) throw std::runtime_error("Call to xticks() failed");
Py_DECREF(res);
}
template<typename Numeric>
inline void xticks(const std::vector<Numeric>& ticks, const std::map<std::string, std::string>& keywords)
{
xticks(ticks, {}, keywords);
}
template<typename Numeric>
inline void yticks(const std::vector<Numeric>& ticks, const std::vector<std::string>& labels = {}, const std::map<std::string, std::string>& keywords = {})
{
assert(labels.size() == 0 || ticks.size() == labels.size());
detail::_interpreter::get();
// using numpy array
PyObject* ticksarray = detail::get_array(ticks);
PyObject* args;
if (labels.size() == 0) {
// construct positional args
args = PyTuple_New(1);
PyTuple_SetItem(args, 0, ticksarray);
}
else {
// make tuple of tick labels
PyObject* labelstuple = PyTuple_New(labels.size());
for (size_t i = 0; i < labels.size(); i++)
PyTuple_SetItem(labelstuple, i, PyUnicode_FromString(labels[i].c_str()));
// construct positional args
args = PyTuple_New(2);
PyTuple_SetItem(args, 0, ticksarray);
PyTuple_SetItem(args, 1, labelstuple);
}
// construct keyword args
PyObject* kwargs = PyDict_New();
for (std::map<std::string, std::string>::const_iterator it = keywords.begin(); it != keywords.end(); ++it)
{
PyDict_SetItemString(kwargs, it->first.c_str(), PyString_FromString(it->second.c_str()));
}
PyObject* res = PyObject_Call(detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_function_yticks, args, kwargs);
Py_DECREF(args);
Py_DECREF(kwargs);
if (!res) throw std::runtime_error("Call to yticks() failed");
Py_DECREF(res);
}
template<typename Numeric>
inline void yticks(const std::vector<Numeric>& ticks, const std::map<std::string, std::string>& keywords)
{
yticks(ticks, {}, keywords);
}
template <typename Numeric> inline void margins(Numeric margin)
{
// construct positional args
PyObject* args = PyTuple_New(1);
PyTuple_SetItem(args, 0, PyFloat_FromDouble(margin));
PyObject* res =
PyObject_CallObject(detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_function_margins, args);
if (!res)
throw std::runtime_error("Call to margins() failed.");
Py_DECREF(args);
Py_DECREF(res);
}
template <typename Numeric> inline void margins(Numeric margin_x, Numeric margin_y)
{
// construct positional args
PyObject* args = PyTuple_New(2);
PyTuple_SetItem(args, 0, PyFloat_FromDouble(margin_x));
PyTuple_SetItem(args, 1, PyFloat_FromDouble(margin_y));
PyObject* res =
PyObject_CallObject(detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_function_margins, args);
if (!res)
throw std::runtime_error("Call to margins() failed.");
Py_DECREF(args);
Py_DECREF(res);
}
inline void tick_params(const std::map<std::string, std::string>& keywords, const std::string axis = "both")
{
detail::_interpreter::get();
// construct positional args
PyObject* args;
args = PyTuple_New(1);
PyTuple_SetItem(args, 0, PyString_FromString(axis.c_str()));
// construct keyword args
PyObject* kwargs = PyDict_New();
for (std::map<std::string, std::string>::const_iterator it = keywords.begin(); it != keywords.end(); ++it)
{
PyDict_SetItemString(kwargs, it->first.c_str(), PyString_FromString(it->second.c_str()));
}
PyObject* res = PyObject_Call(detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_function_tick_params, args, kwargs);
Py_DECREF(args);
Py_DECREF(kwargs);
if (!res) throw std::runtime_error("Call to tick_params() failed");
Py_DECREF(res);
}
inline void subplot(long nrows, long ncols, long plot_number)
{
detail::_interpreter::get();
// construct positional args
PyObject* args = PyTuple_New(3);
PyTuple_SetItem(args, 0, PyFloat_FromDouble(nrows));
PyTuple_SetItem(args, 1, PyFloat_FromDouble(ncols));
PyTuple_SetItem(args, 2, PyFloat_FromDouble(plot_number));
PyObject* res = PyObject_CallObject(detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_function_subplot, args);
if (!res) throw std::runtime_error("Call to subplot() failed.");
Py_DECREF(args);
Py_DECREF(res);
}
inline void subplot2grid(long nrows, long ncols, long rowid = 0, long colid = 0, long rowspan = 1, long colspan = 1)
{
detail::_interpreter::get();
PyObject* shape = PyTuple_New(2);
PyTuple_SetItem(shape, 0, PyLong_FromLong(nrows));
PyTuple_SetItem(shape, 1, PyLong_FromLong(ncols));
PyObject* loc = PyTuple_New(2);
PyTuple_SetItem(loc, 0, PyLong_FromLong(rowid));
PyTuple_SetItem(loc, 1, PyLong_FromLong(colid));
PyObject* args = PyTuple_New(4);
PyTuple_SetItem(args, 0, shape);
PyTuple_SetItem(args, 1, loc);
PyTuple_SetItem(args, 2, PyLong_FromLong(rowspan));
PyTuple_SetItem(args, 3, PyLong_FromLong(colspan));
PyObject* res = PyObject_CallObject(detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_function_subplot2grid, args);
if (!res) throw std::runtime_error("Call to subplot2grid() failed.");
Py_DECREF(shape);
Py_DECREF(loc);
Py_DECREF(args);
Py_DECREF(res);
}
inline void title(const std::string& titlestr, const std::map<std::string, std::string>& keywords = {})
{
detail::_interpreter::get();
PyObject* pytitlestr = PyString_FromString(titlestr.c_str());
PyObject* args = PyTuple_New(1);
PyTuple_SetItem(args, 0, pytitlestr);
PyObject* kwargs = PyDict_New();
for (auto it = keywords.begin(); it != keywords.end(); ++it) {
PyDict_SetItemString(kwargs, it->first.c_str(), PyUnicode_FromString(it->second.c_str()));
}
PyObject* res = PyObject_Call(detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_function_title, args, kwargs);
if (!res) throw std::runtime_error("Call to title() failed.");
Py_DECREF(args);
Py_DECREF(kwargs);
Py_DECREF(res);
}
inline void suptitle(const std::string& suptitlestr, const std::map<std::string, std::string>& keywords = {})
{
detail::_interpreter::get();
PyObject* pysuptitlestr = PyString_FromString(suptitlestr.c_str());
PyObject* args = PyTuple_New(1);
PyTuple_SetItem(args, 0, pysuptitlestr);
PyObject* kwargs = PyDict_New();
for (auto it = keywords.begin(); it != keywords.end(); ++it) {
PyDict_SetItemString(kwargs, it->first.c_str(), PyUnicode_FromString(it->second.c_str()));
}
PyObject* res = PyObject_Call(detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_function_suptitle, args, kwargs);
if (!res) throw std::runtime_error("Call to suptitle() failed.");
Py_DECREF(args);
Py_DECREF(kwargs);
Py_DECREF(res);
}
inline void axis(const std::string& axisstr)
{
detail::_interpreter::get();
PyObject* str = PyString_FromString(axisstr.c_str());
PyObject* args = PyTuple_New(1);
PyTuple_SetItem(args, 0, str);
PyObject* res = PyObject_CallObject(detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_function_axis, args);
if (!res) throw std::runtime_error("Call to title() failed.");
Py_DECREF(args);
Py_DECREF(res);
}
inline void axhline(double y, double xmin = 0., double xmax = 1., const std::map<std::string, std::string>& keywords = std::map<std::string, std::string>())
{
detail::_interpreter::get();
// construct positional args
PyObject* args = PyTuple_New(3);
PyTuple_SetItem(args, 0, PyFloat_FromDouble(y));
PyTuple_SetItem(args, 1, PyFloat_FromDouble(xmin));
PyTuple_SetItem(args, 2, PyFloat_FromDouble(xmax));
// construct keyword args
PyObject* kwargs = PyDict_New();
for (std::map<std::string, std::string>::const_iterator it = keywords.begin(); it != keywords.end(); ++it)
{
PyDict_SetItemString(kwargs, it->first.c_str(), PyString_FromString(it->second.c_str()));
}
PyObject* res = PyObject_Call(detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_function_axhline, args, kwargs);
Py_DECREF(args);
Py_DECREF(kwargs);
if (res) Py_DECREF(res);
}
inline void axvline(double x, double ymin = 0., double ymax = 1., const std::map<std::string, std::string>& keywords = std::map<std::string, std::string>())
{
detail::_interpreter::get();
// construct positional args
PyObject* args = PyTuple_New(3);
PyTuple_SetItem(args, 0, PyFloat_FromDouble(x));
PyTuple_SetItem(args, 1, PyFloat_FromDouble(ymin));
PyTuple_SetItem(args, 2, PyFloat_FromDouble(ymax));
// construct keyword args
PyObject* kwargs = PyDict_New();
for (std::map<std::string, std::string>::const_iterator it = keywords.begin(); it != keywords.end(); ++it)
{
PyDict_SetItemString(kwargs, it->first.c_str(), PyString_FromString(it->second.c_str()));
}
PyObject* res = PyObject_Call(detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_function_axvline, args, kwargs);
Py_DECREF(args);
Py_DECREF(kwargs);
if (res) Py_DECREF(res);
}
inline void axvspan(double xmin, double xmax, double ymin = 0., double ymax = 1., const std::map<std::string, std::string>& keywords = std::map<std::string, std::string>())
{
// construct positional args
PyObject* args = PyTuple_New(4);
PyTuple_SetItem(args, 0, PyFloat_FromDouble(xmin));
PyTuple_SetItem(args, 1, PyFloat_FromDouble(xmax));
PyTuple_SetItem(args, 2, PyFloat_FromDouble(ymin));
PyTuple_SetItem(args, 3, PyFloat_FromDouble(ymax));
// construct keyword args
PyObject* kwargs = PyDict_New();
for (auto it = keywords.begin(); it != keywords.end(); ++it) {
if (it->first == "linewidth" || it->first == "alpha") {
PyDict_SetItemString(kwargs, it->first.c_str(),
PyFloat_FromDouble(std::stod(it->second)));
}
else {
PyDict_SetItemString(kwargs, it->first.c_str(),
PyString_FromString(it->second.c_str()));
}
}
PyObject* res = PyObject_Call(detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_function_axvspan, args, kwargs);
Py_DECREF(args);
Py_DECREF(kwargs);
if (res) Py_DECREF(res);
}
inline void xlabel(const std::string& str, const std::map<std::string, std::string>& keywords = {})
{
detail::_interpreter::get();
PyObject* pystr = PyString_FromString(str.c_str());
PyObject* args = PyTuple_New(1);
PyTuple_SetItem(args, 0, pystr);
PyObject* kwargs = PyDict_New();
for (auto it = keywords.begin(); it != keywords.end(); ++it) {
PyDict_SetItemString(kwargs, it->first.c_str(), PyUnicode_FromString(it->second.c_str()));
}
PyObject* res = PyObject_Call(detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_function_xlabel, args, kwargs);
if (!res) throw std::runtime_error("Call to xlabel() failed.");
Py_DECREF(args);
Py_DECREF(kwargs);
Py_DECREF(res);
}
inline void ylabel(const std::string& str, const std::map<std::string, std::string>& keywords = {})
{
detail::_interpreter::get();
PyObject* pystr = PyString_FromString(str.c_str());
PyObject* args = PyTuple_New(1);
PyTuple_SetItem(args, 0, pystr);
PyObject* kwargs = PyDict_New();
for (auto it = keywords.begin(); it != keywords.end(); ++it) {
PyDict_SetItemString(kwargs, it->first.c_str(), PyUnicode_FromString(it->second.c_str()));
}
PyObject* res = PyObject_Call(detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_function_ylabel, args, kwargs);
if (!res) throw std::runtime_error("Call to ylabel() failed.");
Py_DECREF(args);
Py_DECREF(kwargs);
Py_DECREF(res);
}
inline void set_zlabel(const std::string& str, const std::map<std::string, std::string>& keywords = {})
{
detail::_interpreter::get();
// Same as with plot_surface: We lazily load the modules here the first time
// this function is called because I'm not sure that we can assume "matplotlib
// installed" implies "mpl_toolkits installed" on all platforms, and we don't
// want to require it for people who don't need 3d plots.
static PyObject* mpl_toolkitsmod = nullptr, * axis3dmod = nullptr;
if (!mpl_toolkitsmod) {
PyObject* mpl_toolkits = PyString_FromString("mpl_toolkits");
PyObject* axis3d = PyString_FromString("mpl_toolkits.mplot3d");
if (!mpl_toolkits || !axis3d) { throw std::runtime_error("couldnt create string"); }
mpl_toolkitsmod = PyImport_Import(mpl_toolkits);
Py_DECREF(mpl_toolkits);
if (!mpl_toolkitsmod) { throw std::runtime_error("Error loading module mpl_toolkits!"); }
axis3dmod = PyImport_Import(axis3d);
Py_DECREF(axis3d);
if (!axis3dmod) { throw std::runtime_error("Error loading module mpl_toolkits.mplot3d!"); }
}
PyObject* pystr = PyString_FromString(str.c_str());
PyObject* args = PyTuple_New(1);
PyTuple_SetItem(args, 0, pystr);
PyObject* kwargs = PyDict_New();
for (auto it = keywords.begin(); it != keywords.end(); ++it) {
PyDict_SetItemString(kwargs, it->first.c_str(), PyUnicode_FromString(it->second.c_str()));
}
PyObject* ax =
PyObject_CallObject(detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_function_gca,
detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_empty_tuple);
if (!ax) throw std::runtime_error("Call to gca() failed.");
Py_INCREF(ax);
PyObject* zlabel = PyObject_GetAttrString(ax, "set_zlabel");
if (!zlabel) throw std::runtime_error("Attribute set_zlabel not found.");
Py_INCREF(zlabel);
PyObject* res = PyObject_Call(zlabel, args, kwargs);
if (!res) throw std::runtime_error("Call to set_zlabel() failed.");
Py_DECREF(zlabel);
Py_DECREF(ax);
Py_DECREF(args);
Py_DECREF(kwargs);
if (res) Py_DECREF(res);
}
inline void grid(bool flag)
{
detail::_interpreter::get();
PyObject* pyflag = flag ? Py_True : Py_False;
Py_INCREF(pyflag);
PyObject* args = PyTuple_New(1);
PyTuple_SetItem(args, 0, pyflag);
PyObject* res = PyObject_CallObject(detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_function_grid, args);
if (!res) throw std::runtime_error("Call to grid() failed.");
Py_DECREF(args);
Py_DECREF(res);
}
inline void show(const bool block = true)
{
detail::_interpreter::get();
PyObject* res;
if (block)
{
res = PyObject_CallObject(
detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_function_show,
detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_empty_tuple);
}
else
{
PyObject* kwargs = PyDict_New();
PyDict_SetItemString(kwargs, "block", Py_False);
res = PyObject_Call(detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_function_show, detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_empty_tuple, kwargs);
Py_DECREF(kwargs);
}
if (!res) throw std::runtime_error("Call to show() failed.");
Py_DECREF(res);
}
inline void close()
{
detail::_interpreter::get();
PyObject* res = PyObject_CallObject(
detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_function_close,
detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_empty_tuple);
if (!res) throw std::runtime_error("Call to close() failed.");
Py_DECREF(res);
}
inline void xkcd() {
detail::_interpreter::get();
PyObject* res;
PyObject* kwargs = PyDict_New();
res = PyObject_Call(detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_function_xkcd,
detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_empty_tuple, kwargs);
Py_DECREF(kwargs);
if (!res)
throw std::runtime_error("Call to show() failed.");
Py_DECREF(res);
}
inline void draw()
{
detail::_interpreter::get();
PyObject* res = PyObject_CallObject(
detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_function_draw,
detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_empty_tuple);
if (!res) throw std::runtime_error("Call to draw() failed.");
Py_DECREF(res);
}
template<typename Numeric>
inline void pause(Numeric interval)
{
detail::_interpreter::get();
PyObject* args = PyTuple_New(1);
PyTuple_SetItem(args, 0, PyFloat_FromDouble(interval));
PyObject* res = PyObject_CallObject(detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_function_pause, args);
if (!res) throw std::runtime_error("Call to pause() failed.");
Py_DECREF(args);
Py_DECREF(res);
}
inline void save(const std::string& filename, const int dpi = 0)
{
detail::_interpreter::get();
PyObject* pyfilename = PyString_FromString(filename.c_str());
PyObject* args = PyTuple_New(1);
PyTuple_SetItem(args, 0, pyfilename);
PyObject* kwargs = PyDict_New();
if (dpi > 0)
{
PyDict_SetItemString(kwargs, "dpi", PyLong_FromLong(dpi));
}
PyObject* res = PyObject_Call(detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_function_save, args, kwargs);
if (!res) throw std::runtime_error("Call to save() failed.");
Py_DECREF(args);
Py_DECREF(kwargs);
Py_DECREF(res);
}
inline void rcparams(const std::map<std::string, std::string>& keywords = {}) {
detail::_interpreter::get();
PyObject* args = PyTuple_New(0);
PyObject* kwargs = PyDict_New();
for (auto it = keywords.begin(); it != keywords.end(); ++it) {
if ("text.usetex" == it->first)
PyDict_SetItemString(kwargs, it->first.c_str(), PyLong_FromLong(std::stoi(it->second.c_str())));
else PyDict_SetItemString(kwargs, it->first.c_str(), PyString_FromString(it->second.c_str()));
}
PyObject* update = PyObject_GetAttrString(detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_function_rcparams, "update");
PyObject* res = PyObject_Call(update, args, kwargs);
if (!res) throw std::runtime_error("Call to rcParams.update() failed.");
Py_DECREF(args);
Py_DECREF(kwargs);
Py_DECREF(update);
Py_DECREF(res);
}
inline void clf() {
detail::_interpreter::get();
PyObject* res = PyObject_CallObject(
detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_function_clf,
detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_empty_tuple);
if (!res) throw std::runtime_error("Call to clf() failed.");
Py_DECREF(res);
}
inline void cla() {
detail::_interpreter::get();
PyObject* res = PyObject_CallObject(detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_function_cla,
detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_empty_tuple);
if (!res)
throw std::runtime_error("Call to cla() failed.");
Py_DECREF(res);
}
inline void ion() {
detail::_interpreter::get();
PyObject* res = PyObject_CallObject(
detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_function_ion,
detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_empty_tuple);
if (!res) throw std::runtime_error("Call to ion() failed.");
Py_DECREF(res);
}
inline std::vector<std::array<double, 2>> ginput(const int numClicks = 1, const std::map<std::string, std::string>& keywords = {})
{
detail::_interpreter::get();
PyObject* args = PyTuple_New(1);
PyTuple_SetItem(args, 0, PyLong_FromLong(numClicks));
// construct keyword args
PyObject* kwargs = PyDict_New();
for (std::map<std::string, std::string>::const_iterator it = keywords.begin(); it != keywords.end(); ++it)
{
PyDict_SetItemString(kwargs, it->first.c_str(), PyUnicode_FromString(it->second.c_str()));
}
PyObject* res = PyObject_Call(
detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_function_ginput, args, kwargs);
Py_DECREF(kwargs);
Py_DECREF(args);
if (!res) throw std::runtime_error("Call to ginput() failed.");
const size_t len = PyList_Size(res);
std::vector<std::array<double, 2>> out;
out.reserve(len);
for (size_t i = 0; i < len; i++) {
PyObject* current = PyList_GetItem(res, i);
std::array<double, 2> position;
position[0] = PyFloat_AsDouble(PyTuple_GetItem(current, 0));
position[1] = PyFloat_AsDouble(PyTuple_GetItem(current, 1));
out.push_back(position);
}
Py_DECREF(res);
return out;
}
// Actually, is there any reason not to call this automatically for every plot?
inline void tight_layout() {
detail::_interpreter::get();
PyObject* res = PyObject_CallObject(
detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_function_tight_layout,
detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_empty_tuple);
if (!res) throw std::runtime_error("Call to tight_layout() failed.");
Py_DECREF(res);
}
// Support for variadic plot() and initializer lists:
namespace detail {
template<typename T>
using is_function = typename std::is_function<std::remove_pointer<std::remove_reference<T>>>::type;
template<bool obj, typename T>
struct is_callable_impl;
template<typename T>
struct is_callable_impl<false, T>
{
typedef is_function<T> type;
}; // a non-object is callable iff it is a function
template<typename T>
struct is_callable_impl<true, T>
{
struct Fallback { void operator()(); };
struct Derived : T, Fallback { };
template<typename U, U> struct Check;
template<typename U>
static std::true_type test(...); // use a variadic function to make sure (1) it accepts everything and (2) its always the worst match
template<typename U>
static std::false_type test(Check<void(Fallback::*)(), &U::operator()>*);
public:
typedef decltype(test<Derived>(nullptr)) type;
typedef decltype(&Fallback::operator()) dtype;
static constexpr bool value = type::value;
}; // an object is callable iff it defines operator()
template<typename T>
struct is_callable
{
// dispatch to is_callable_impl or is_callable_impl depending on whether T is of class type or not
typedef typename is_callable_impl<std::is_class<T>::value, T>::type type;
};
template<typename IsYDataCallable>
struct plot_impl { };
template<>
struct plot_impl<std::false_type>
{
template<typename IterableX, typename IterableY>
bool operator()(const IterableX& x, const IterableY& y, const std::string& format)
{
detail::_interpreter::get();
// 2-phase lookup for distance, begin, end
using std::distance;
using std::begin;
using std::end;
auto xs = distance(begin(x), end(x));
auto ys = distance(begin(y), end(y));
assert(xs == ys && "x and y data must have the same number of elements!");
PyObject* xlist = PyList_New(xs);
PyObject* ylist = PyList_New(ys);
PyObject* pystring = PyString_FromString(format.c_str());
auto itx = begin(x), ity = begin(y);
for (size_t i = 0; i < xs; ++i) {
PyList_SetItem(xlist, i, PyFloat_FromDouble(*itx++));
PyList_SetItem(ylist, i, PyFloat_FromDouble(*ity++));
}
PyObject* plot_args = PyTuple_New(3);
PyTuple_SetItem(plot_args, 0, xlist);
PyTuple_SetItem(plot_args, 1, ylist);
PyTuple_SetItem(plot_args, 2, pystring);
PyObject* res = PyObject_CallObject(detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_function_plot, plot_args);
Py_DECREF(plot_args);
if (res) Py_DECREF(res);
return res;
}
};
template<>
struct plot_impl<std::true_type>
{
template<typename Iterable, typename Callable>
bool operator()(const Iterable& ticks, const Callable& f, const std::string& format)
{
if (begin(ticks) == end(ticks)) return true;
// We could use additional meta-programming to deduce the correct element type of y,
// but all values have to be convertible to double anyways
std::vector<double> y;
for (auto x : ticks) y.push_back(f(x));
return plot_impl<std::false_type>()(ticks, y, format);
}
};
} // end namespace detail
// recursion stop for the above
template<typename... Args>
bool plot() { return true; }
template<typename A, typename B, typename... Args>
bool plot(const A& a, const B& b, const std::string& format, Args... args)
{
return detail::plot_impl<typename detail::is_callable<B>::type>()(a, b, format) && plot(args...);
}
/*
* This group of plot() functions is needed to support initializer lists, i.e. calling
* plot( {1,2,3,4} )
*/
inline bool plot(const std::vector<double>& x, const std::vector<double>& y, const std::string& format = "") {
return plot<double, double>(x, y, format);
}
inline bool plot(const std::vector<double>& y, const std::string& format = "") {
return plot<double>(y, format);
}
inline bool plot(const std::vector<double>& x, const std::vector<double>& y, const std::map<std::string, std::string>& keywords) {
return plot<double>(x, y, keywords);
}
/*
* This class allows dynamic plots, ie changing the plotted data without clearing and re-plotting
*/
class Plot
{
public:
// default initialization with plot label, some data and format
template<typename Numeric>
Plot(const std::string& name, const std::vector<Numeric>& x, const std::vector<Numeric>& y, const std::string& format = "") {
detail::_interpreter::get();
assert(x.size() == y.size());
PyObject* kwargs = PyDict_New();
if (name != "")
PyDict_SetItemString(kwargs, "label", PyString_FromString(name.c_str()));
PyObject* xarray = detail::get_array(x);
PyObject* yarray = detail::get_array(y);
PyObject* pystring = PyString_FromString(format.c_str());
PyObject* plot_args = PyTuple_New(3);
PyTuple_SetItem(plot_args, 0, xarray);
PyTuple_SetItem(plot_args, 1, yarray);
PyTuple_SetItem(plot_args, 2, pystring);
PyObject* res = PyObject_Call(detail::_interpreter::get().s_python_function_plot, plot_args, kwargs);
Py_DECREF(kwargs);
Py_DECREF(plot_args);
if (res)
{
line = PyList_GetItem(res, 0);
if (line)
set_data_fct = PyObject_GetAttrString(line, "set_data");
else
Py_DECREF(line);
Py_DECREF(res);
}
}
// shorter initialization with name or format only
// basically calls line, = plot([], [])
Plot(const std::string& name = "", const std::string& format = "")
: Plot(name, std::vector<double>(), std::vector<double>(), format) {}
template<typename Numeric>
bool update(const std::vector<Numeric>& x, const std::vector<Numeric>& y) {
assert(x.size() == y.size());
if (set_data_fct)
{
PyObject* xarray = detail::get_array(x);
PyObject* yarray = detail::get_array(y);
PyObject* plot_args = PyTuple_New(2);
PyTuple_SetItem(plot_args, 0, xarray);
PyTuple_SetItem(plot_args, 1, yarray);
PyObject* res = PyObject_CallObject(set_data_fct, plot_args);
if (res) Py_DECREF(res);
return res;
}
return false;
}
// clears the plot but keep it available
bool clear() {
return update(std::vector<double>(), std::vector<double>());
}
// definitely remove this line
void remove() {
if (line)
{
auto remove_fct = PyObject_GetAttrString(line, "remove");
PyObject* args = PyTuple_New(0);
PyObject* res = PyObject_CallObject(remove_fct, args);
if (res) Py_DECREF(res);
}
decref();
}
~Plot() {
decref();
}
private:
void decref() {
if (line)
Py_DECREF(line);
if (set_data_fct)
Py_DECREF(set_data_fct);
}
PyObject* line = nullptr;
PyObject* set_data_fct = nullptr;
};
} // end namespace matplotlibcpp
4 编写源文件 test.cpp
#include