JavaSE【 String 类】(1)(字符串比较,字符串查找、字符串转换、字符串拆分、字符串截取)
一、String 类
1、字符串构造
常用三种
String的构造方法:有带参数的,和不带参数的
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//字符串直接赋值
String str = "hello";
//string是一个引用类型,str这个变量存的是一个地址
//但我们输出str的时候,却输出了字符串str表示的内容"hello"
//因为String重写了toString方法
System.out.println(str);//hello,字符串常量,没有\0标记结尾
//String有自己的构造方法,有不带参数的,有带参数的
//实例化字符串对象
String str2 = new String();
System.out.println(str2);//输出的是一行空行
String str3 = new String("str3:hello");
System.out.println(str3);//str3:hello
//把字符数组,变成字符串
char[] array = {'a','b','c'};
String str4 = new String(array);
System.out.println(str4);
String str5 = new String(array,0,2);//从下标0位置,拿2个
System.out.println(str5);//ab
}
}
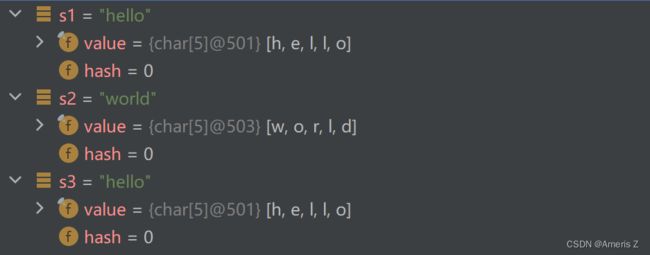
2.string对象里的value和hash
从Java源代码里可以看到String里有两个成员变量:value和hash
并且在调试代码的时候,能看到s1、s2、s3里都有这两个成员变量
3.String对象的长度(字符串长度)
public static void main2(String[] args) {
// s1和s2引用的是不同对象 s1和s3引用的是同一对象
String s1 = new String("hello");
String s2 = new String("world");
String s3 = s1;
System.out.println(s1);
System.out.println(s2);
System.out.println(s3);
System.out.println(s1.length());
System.out.println(s2.length());
System.out.println(s3.length());
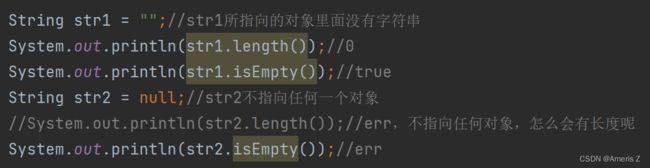
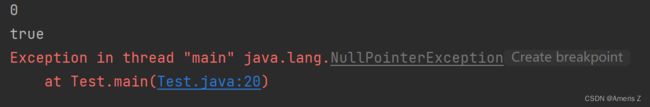
String str1 = "";//str1所指向的对象里面没有字符串
System.out.println(str1.length());//0
System.out.println(str1.isEmpty());//true
String str2 = null;//str2不指向任何一个对象
//System.out.println(str2.length());//err,不指向任何对象,怎么会有长度呢
//System.out.println(str2.isEmpty());//err
//字符串.length()
System.out.println("hello".length());
}System . out . println ( str1 . length ()); // 获取字符串长度 --- 输出 0System . out . println ( str1 . isEmpty ()); // 判断字符串是否为空, 如果字符串长度为 0 ,返回 true ,否则返回 false
二、字符串比较
public static void main3(String[] args) {
String s1 = new String("hello");
String s2 = new String("hello");
System.out.println(s1 == s2);//false,因为s1和s2存的是地址,两个地址是不一样的
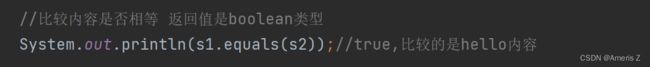
//比较内容 返回值是boolean类型
System.out.println(s1.equals(s2));//true,比较的是hello内容
//比较字符串大小 compareTo
/**
* 类似于C语言的strcmp()
* 逐个字符比较,如果 s1 > s2返回正数,如果 s1 < s2返回负数,s1 = s2返回 0
*/
String str1 = new String("abc");
String str2 = new String("acd");
System.out.println(str1.compareTo(str2));//-1
/**
* 忽略大小写比较 compareToIgnoreCase
*/
String str3 = new String("Abc");
String str4 = new String("abC");
System.out.println(str3.compareToIgnoreCase(str4));//0,忽略大小写都是abc,一样的
}1. ==比较是否引用同一个对象
注意:对于内置类型, == 比较的是变量中的值;对于引用类型 == 比较的是引用中的地址。2.字符串内容比较
1)比较内容是否相等(equals)
boolean equals(Object anObject) 方法:按照字典序比较字典序:字符大小的顺序2)比较字符串大小(compareTo)
3)比较字符串大小忽略大小写(compareTo)
一般验证码就是忽略大小写比较的
三、字符串查找
1.char charAt(index)查找下标index位置的字符
char charAt(int index)返回 index 位置上字符如果 index 为负数或者越界,抛出 IndexOutOfBoundsException异常
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "hello";
char ch = s1.charAt(1);//返回下标1的字符,e
System.out.println(ch);//如果,下标超过字符串长度,报错StringIndexOutOfBoundsException字符串下标越界异常
for (int i = 0; i < s1.length(); i++) {
System.out.println(s1.charAt(i));
}
}2. int indexOf 从前往后,找字符或者字符串第一次出现的位置
1) int indexOf(ch)
int indexOf(int ch)默认,从头往后查找。返回 ch 第一次出现的位置,没有返回 -1
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "hello";
int index = s1.indexOf('l');//默认从头往后,返回s1里字符l第一次出现的位置
System.out.println(index);//2
}2)int indexOf(char ch, int fromIndex)
int indexOf(char ch, int fromIndex)从 fromIndex 位置开始找 ch 第一次出现的位置,没有返回 -1
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "hello";
//indexOf('l',1);从指定位置1下标开始往后找
int index = s1.indexOf('l',1);
System.out.println(index);//2
}3)int indexOf(String str)
int indexOf(String str)返回 str 第一次出现的位置,没有返回 -1
public static void main(String[] args) {
//可以找字符串
String s2 = "aababcabcd";
int index2 = s2.indexOf("abc");
System.out.println(index2);//3
}4)int indexOf(String str, int fromIndex)
int indexOf(String str, int fromIndex)从 fromIndex 位置开始找 str 第一次出现的位置,没有返回 -1
public static void main(String[] args) {
//可以找字符串,同理
//indexOf("abc");默认从头往后,找字符串abc第一次出现的位置
//indexOf("abc",1);从指定位置1下标开始往后找
String s2 = "aababcabcd";
int index2 = s2.indexOf("abc",1);
System.out.println(index2);//3
}3.int lastIndexOf 从后往前,找字符或者字符串第一次出现的位置
1)int lastIndexOf(int ch)
int lastIndexOf(int ch)从后往前 找,返回 ch 第一次出现的位置,没有返回 -1
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "aababcabcd";
int index = s1.lastIndexOf('c');
System.out.println(index);//8
}2)int lastIndexOf(int ch, int fromIndex)
int lastIndexOf(int ch, int fromIndex)从 fromIndex 位置开始找, 从后往前 找 ch 第一次出现的位置,没有返回-1
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "aababcabcd";
int index = s1.lastIndexOf('a',5);
System.out.println(index);//3
}3)int lastIndexOf(String str)
int lastIndexOf(String str)从后往前 找,返回 str 第一次出现的位置,没有返回 -1
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "aababcabcd";
int index = s1.lastIndexOf("abc");
System.out.println(index);//6
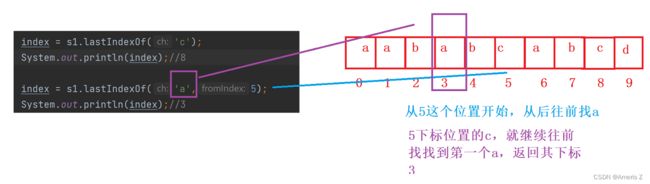
}4)int lastIndexOf(String str, int fromIndex)
int lastIndexOf(String str, int fromIndex)从 fromIndex 位置开始找, 从后往前 找 str 第一次出现的位置,没有返回-1
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "aababcabcd";
int index = s1.lastIndexOf("abc",3);
System.out.println(index);//3
}四、转化
1.数字、字符串之间转换
数字转化为字符串 String.valueOf
字符串转数字 Integer.parseInt
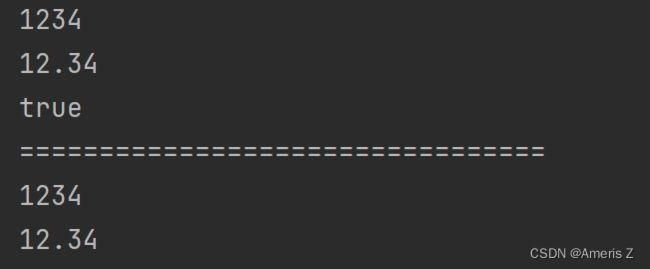
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 数字转字符串 可以支持整型 浮点型 boolean 以及自定义类型
String s1 = String.valueOf(1234);
String s2 = String.valueOf(12.34);
String s3 = String.valueOf(true);
//String s4 = String.valueOf(new Student("Hanmeimei", 18));
System.out.println(s1);
System.out.println(s2);
System.out.println(s3);
//System.out.println(s4);
System.out.println("=================================");
// 字符串转数字
// 注意:Integer、Double等是Java中的包装类型,这个后面会讲到
int data1 = Integer.parseInt("1234");
double data2 = Double.parseDouble("12.34");
System.out.println(data1);
System.out.println(data2);
}2.大小写转换
// 小写转大写s1 . toUpperCase ()// 大写转小写s2 . toLowerCase ()
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "hello";
//转变为大写后,是一个新的对象,用ret来接收
String ret = s1.toUpperCase();
System.out.println(s1);
System.out.println(ret); //HELLO
String s2 = "HELLO";
String ret2 = s2.toLowerCase();
System.out.println(s2);
System.out.println(ret2);//hello
}3.字符串、数组之间的转换
// 字符串转数组char [] ch = s . toCharArray ();// 数组转字符串String s2 = new String ( ch );
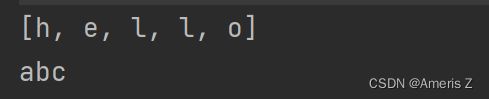
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "hello";
//字符串 转化为 数组
char[] array = s1.toCharArray();
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array));
char[] array2 = {'a','b','c'};
//数组 转化为 字符串
String s2 = new String(array2);
System.out.println(s2);
}4.格式化
String s = String . format ( "%d-%d-%d" , 2019 , 9 , 14 );
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = String.format("%d-%d-%d",2023,8,6);
System.out.println(s);
}五、字符串替换 replace
String replace(CharSequence target, CharSequence replacement) 替换字符序列 String replace(char oldChar, char newChar) 替换字符 String replaceAll(String regex, String replacement) 替换所有的指定内容 String replaceFirst(String regex, String replacement) 替换首个内容(字符串)
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "abcabcabcabc";
//把ab替换为666
String ret = str.replace("ab","666");
System.out.println(ret);
//把a替换为9
ret = str.replace('a','9');
System.out.println(ret);
//只替换第一个ab为666
ret = str.replaceFirst("ab","666");
System.out.println(ret);
//把所有的ab替换成666 replace包含replaceAll
ret = str.replaceAll("ab","666");
System.out.println(ret);
}六、字符串拆分 split
String[] split(String regex) 将字符串全部拆分String[] split(String regex, int limit) 将字符串以指定的格式,拆分为limit 组注意事项 :1. 字符 "|","*","+" 都得加上转义字符,前面加上 "\\" .2. 而如果是 "\\" ,那么就得写成 "\\\\" .3. 如果一个字符串中有多个分隔符,可以用 "|" 作为连字符
1.普通字符串拆分
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "hello abc world";
//通过空格将字符串分割
String[] ret = str.split(" ");
for (int i = 0; i < ret.length; i++) {
System.out.println(ret[i]);
}
System.out.println("===========");
//通过空格将字符串分割成 2 部分
ret = str.split(" ",2);
for (int i = 0; i < ret.length; i++) {
System.out.println(ret[i]);
}
}2.特殊符号拆分
1)拆分ip地址 的.
public static void main(String[] args) { //拆分ip地址 String str = "192.168.1.1"; String[] ret = str.split("\\."); for (int i = 0; i < ret.length; i++) { System.out.println(ret[i]); } }
2)拆分\\
public static void main(String[] args) { //拆分\\ String str = "192\\168\\1\\1"; String[] ret = str.split("\\\\"); for (int i = 0; i < ret.length; i++) { System.out.println(ret[i]); } }
3)多个分隔符 拆分
public static void main(String[] args) { //多个分隔符 用|连接 String str = "name=zhangsan&age=10"; String[] ret = str.split("=|&"); for (int i = 0; i < ret.length; i++) { System.out.println(ret[i]); } }多次拆分:在第一次分割的基础上,进行第二次分割
public static void main(String[] args) { //也可以在第一次分割的基础上,进行第二次分割 String str = "name=zhangsan&age=10"; String[] ret = str.split("&"); for (int i = 0; i < ret.length; i++) { //System.out.println(ret[i]); String str2 = ret[i]; String[] ret2 = str2.split("="); for (int j = 0; j < ret2.length; j++) { System.out.println(ret2[j]); } } }
七、字符串截取
String substring(int beginIndex)从指定索引截取到结尾String substring(int beginIndex, int endIndex)截取部分内容
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "abcdefghi";
//字符串截取
//区间截取[ )左闭右开
String ret = str.substring(0,3);
System.out.println(ret);//abc
//截取指定起始位置后的字符串
ret = str.substring(2);
System.out.println(ret);//cdefghi
}