自动化运维ansible入门篇
目录
- 一、ansible简介
- 二、ansible特点
- 三、ansible基本架构
- 四、ansible部署
-
-
- 4.1基本环境
- 4.2安装epel-release
- 4.2安装ansible
- 4.3修改ansible host配置文件
- 4.4设置ansible免密登录两台node节点
-
- 五、ansible命令基本用法
-
-
- 5.1、ansible命令格式
- 5.2、command模块
- 5.3、cron模块
- 5.4、user模块
- 5.5、group模块
- 5.6、copy模块
- 5.7、file模块
- 5.8、ping模块
- 5.9、yum模块
- 5.9、service模块
- 5.10、shell模块
- 5.11、script模块
- 5.12、setup模块
-
一、ansible简介
ansible是新出现的自动化运维工具,基于Python开发,集合了众多运维工具(puppet、chef、func、fabric)的优点,实现了批量系统配置、批量程序部署、批量运行命令等功能。
ansible是基于 paramiko 开发的,并且基于模块化工作,本身没有批量部署的能力。真正具有批量部署的是ansible所运行的模块,ansible只是提供一种框架。ansible不需要在远程主机上安装client/agents,因为它们是基于ssh来和远程主机通讯的。ansible目前已经已经被红帽官方收购,是自动化运维工具中大家认可度最高的,并且上手容易,学习简单。是每位运维工程师必须掌握的技能之一。
二、ansible特点
- 部署简单,只需在主控端部署Ansible环境,被控端无需做任何操作;
- 默认使用SSH协议对设备进行管理;
- 有大量常规运维操作模块,可实现日常绝大部分操作;
- 配置简单、功能强大、扩展性强;
- 支持API及自定义模块,可通过Python轻松扩展;
- 通过Playbooks来定制强大的配置、状态管理;
- 轻量级,无需在客户端安装agent,更新时,只需在操作机上进行一次更新即可;
- 提供一个功能强大、操作性强的Web管理界面和REST API接口——AWX平台。
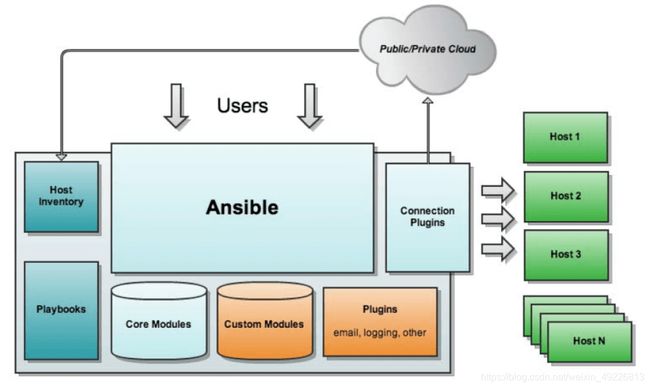
三、ansible基本架构
核心:ansible
核心模块(Core Modules):这些都是ansible自带的模块
扩展模块(Custom Modules):如果核心模块不足以完成某种功能,可以添加扩展模块
插件(Plugins):完成模块功能的补充
剧本(Playbooks):ansible的任务配置文件,将多个任务定义在剧本中,由ansible自动执行
连接插件(Connectior Plugins):ansible基于连接插件连接到各个主机上,虽然ansible是使用ssh连接到各个主机的,但是它还支持其他的连接方法,所以需要有连接插件
主机群(Host Inventory):定义ansible管理的主机
四、ansible部署
| 名称 | 主机名 | IP地址 |
|---|---|---|
| ansible服务器 | ansible | 20.0.0.10/24 |
| 节点1 | node-1 | 20.0.0.20/24 |
| 节点1 | node-1 | 20.0.0.30/24 |
4.1基本环境
关闭防火墙
[root@ansible ~]# systemctl stop firewalld
[root@ansible ~]# setenforce 0
使用centos 7自带的yum源
[root@ansible ~]# cd /etc/yum.repos.d/
[root@ansible yum.repos.d]# ls
CentOS-Base.repo
[root@ansible yum.repos.d]# vim CentOS-Base.repo
[base]
name=CentOS-$releasever - Base
mirrorlist=http://mirrorlist.centos.org/?release=$releasever&arch=$basearch&repo=os&infra=$infra
#baseurl=http://mirror.centos.org/centos/$releasever/os/$basearch/
gpgcheck=1
gpgkey=file:///etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-CentOS-7
#released updates
[updates]
name=CentOS-$releasever - Updates
mirrorlist=http://mirrorlist.centos.org/?release=$releasever&arch=$basearch&repo=updates&infra=$infra
#baseurl=http://mirror.centos.org/centos/$releasever/updates/$basearch/
gpgcheck=1
gpgkey=file:///etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-CentOS-7
#additional packages that may be useful
[extras]
name=CentOS-$releasever - Extras
mirrorlist=http://mirrorlist.centos.org/?release=$releasever&arch=$basearch&repo=extras&infra=$infra
#baseurl=http://mirror.centos.org/centos/$releasever/extras/$basearch/
gpgcheck=1
gpgkey=file:///etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-CentOS-7
#additional packages that extend functionality of existing packages
[centosplus]
name=CentOS-$releasever - Plus
mirrorlist=http://mirrorlist.centos.org/?release=$releasever&arch=$basearch&repo=centosplus&infra=$infra
#baseurl=http://mirror.centos.org/centos/$releasever/centosplus/$basearch/
gpgcheck=1
enabled=0
gpgkey=file:///etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-CentOS-7
[root@ansible yum.repos.d]# ls
CentOS-Base.repo
可以连接网络
[root@ansible yum.repos.d]# ping www.baidu.com
PING www.a.shifen.com (180.101.49.11) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from 180.101.49.11 (180.101.49.11): icmp_seq=1 ttl=128 time=3.64 ms
64 bytes from 180.101.49.11 (180.101.49.11): icmp_seq=2 ttl=128 time=3.38 ms
4.2安装epel-release
[root@server1 ~]# yum install -y epel-release
已安装:
epel-release.noarch 0:7-11
4.2安装ansible
[root@server1 ~]# yum install ansible -y
已安装:
ansible.noarch 0:2.9.16-1.el7
作为依赖被安装:
PyYAML.x86_64 0:3.10-11.el7 libyaml.x86_64 0:0.1.4-11.el7_0
python-babel.noarch 0:0.9.6-8.el7 python-jinja2.noarch 0:2.7.2-4.el7
python-markupsafe.x86_64 0:0.11-10.el7 python-paramiko.noarch 0:2.1.1-9.el7
python2-httplib2.noarch 0:0.18.1-3.el7 python2-jmespath.noarch 0:0.9.4-2.el7
sshpass.x86_64 0:1.06-2.el7
完毕!
4.3修改ansible host配置文件
[root@ansible ~]# vim /etc/ansible/hosts
[node]
20.0.0.20
20.0.0.30
设置一个组名,成员为:20.0.0.20、20.0.0.30
4.4设置ansible免密登录两台node节点
[root@ansible ~]# ssh-keygen -t rsa
Generating public/private rsa key pair.
Enter file in which to save the key (/root/.ssh/id_rsa): #秘钥存放的位置
Created directory '/root/.ssh'.
Enter passphrase (empty for no passphrase): #设置密码:123456
Enter same passphrase again: #设置密码:123456
Your identification has been saved in /root/.ssh/id_rsa.
Your public key has been saved in /root/.ssh/id_rsa.pub.
The key fingerprint is:
SHA256:G+kExqK+oT2xof8zMUIj5rPNyGlJDV1SR+l4cxQsFpA root@ansible
The key's randomart image is:
+---[RSA 2048]----+
| .o+++.. |
| . E.+ o |
| . + B o |
|.ooo + = o |
|oo+. . S |
| =+.o o o |
|o.@= o o |
|.Xo=o |
|o.+o.o |
+----[SHA256]-----+
[root@ansible ~]# ssh-copy-id root@20.0.0.20
/usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: Source of key(s) to be installed: "/root/.ssh/id_rsa.pub"
The authenticity of host '20.0.0.20 (20.0.0.20)' can't be established.
ECDSA key fingerprint is SHA256:yELtpt+yAiWNtPQb5bPu3PyWman5X5xL5zwU607sqHE.
ECDSA key fingerprint is MD5:b1:3f:1c:fa:eb:42:fc:bf:02:40:80:ea:8e:01:0a:7a.
Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)? yes
/usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: attempting to log in with the new key(s), to filter out any that are already installed
/usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: 1 key(s) remain to be installed -- if you are prompted now it is to install the new keys
root@20.0.0.20's password: #输入20.0.0.20服务器登录密码
Number of key(s) added: 1
Now try logging into the machine, with: "ssh '[email protected]'"
and check to make sure that only the key(s) you wanted were added.
[root@ansible ~]# ssh-copy-id root@20.0.0.30
/usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: Source of key(s) to be installed: "/root/.ssh/id_rsa.pub"
The authenticity of host '20.0.0.30 (20.0.0.30)' can't be established.
ECDSA key fingerprint is SHA256:S2ANKK3sAHs5II74zKqBXVTVfAQUFrImRm7pq/hOrpg.
ECDSA key fingerprint is MD5:bc:99:68:b2:2a:25:31:37:bc:2b:01:49:35:98:de:f0.
Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)? yes
/usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: attempting to log in with the new key(s), to filter out any that are already installed
/usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: 1 key(s) remain to be installed -- if you are prompted now it is to install the new keys
root@20.0.0.30's password: #输入20.0.0.30服务器登录密码
Number of key(s) added: 1
Now try logging into the machine, with: "ssh '[email protected]'"
and check to make sure that only the key(s) you wanted were added.
[root@ansible ~]# ssh-agent bash
[root@ansible ~]# ssh-add
Enter passphrase for /root/.ssh/id_rsa: #输入创建密钥时设置的密码
Identity added: /root/.ssh/id_rsa (/root/.ssh/id_rsa)
五、ansible命令基本用法
5.1、ansible命令格式
ansible 主机表示/IP地址 -m 模块 -a '参数'
5.2、command模块
1、查看已安装的模块
[root@ansible ~]# ansible-doc -l
2、查看节点1的时间
[root@ansible ~]# ansible 20.0.0.20 -m command -a 'date'
20.0.0.20 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
2021年 01月 11日 星期一 15:15:38 CST
3、查看指定标签下的所有节点时间时间
[root@ansible ~]# ansible node -m command -a 'date'
20.0.0.20 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
2021年 01月 11日 星期一 15:16:35 CST
20.0.0.30 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
2021年 01月 11日 星期一 15:16:35 CST
4、如果不知道模块默认使用的是command
[root@ansible ~]# ansible 20.0.0.20 -a 'date'
20.0.0.20 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
2021年 01月 11日 星期一 15:18:08 CST
5、对所有标签都执行
[root@ansible ~]# ansible all -m command -a 'date'
20.0.0.20 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
2021年 01月 11日 星期一 15:54:12 CST
20.0.0.30 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
2021年 01月 11日 星期一 15:54:12 CST
对都所有标签下的主机都执行date,我这里只设置一个标签
5.3、cron模块
1、查看cron可以使用的参数
[root@ansible ~]# ansible-doc -s cron
2、在节点1上面创建一个任务计划
[root@ansible ~]# ansible 20.0.0.20 -m cron -a 'minute="*/1" job="/usr/bin/echo hello,ansible >>/opt/ansible.txt" name="abc"'
20.0.0.20 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": true, #true表示执行成功
"envs": [],
"jobs": [
"abc"
]
}
[root@ansible ~]# ansible 20.0.0.20 -a 'crontab -l'
20.0.0.20 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
#Ansible: abc
*/1 * * * * /usr/bin/echo hello,ansible >>/opt/ansible.txt
#在节点1上查看什么生效
[root@node-1 ~]# cd /opt/
[root@node-1 opt]# ls
ansible.txt rh
[root@node-1 opt]# cat ansible.txt
hello,ansible
hello,ansible
在节点1上面创建一个周期型任务计划,每一分钟向/opt/ansible.txt目录里输入hello,ansible
3、删除任务计划
[root@ansible ~]# ansible 20.0.0.20 -m cron -a 'name="abc" state=absent'
20.0.0.20 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": true,
"envs": [],
"jobs": []
}
[root@ansible ~]# ansible 20.0.0.20 -a 'crontab -l'
20.0.0.20 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
#删除成功
4、如果创建任务计划没有设置名称删除
[root@ansible ~]# ansible 20.0.0.20 -m cron -a 'minute="*/1" job="/usr/bin/echo hello >>/opt/ansible.txt"'
[DEPRECATION WARNING]: The 'name' parameter will be required in future releases.. This feature will be removed in
version 2.12. Deprecation warnings can be disabled by setting deprecation_warnings=False in ansible.cfg.
20.0.0.20 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": true,
"envs": [],
"jobs": [
"None"
]
}
[root@ansible ~]# ansible 20.0.0.20 -a 'crontab -l'
20.0.0.20 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
#Ansible: None
*/1 * * * * /usr/bin/echo hello >>/opt/ansible.txt
[root@ansible ~]# ansible 20.0.0.20 -m cron -a 'name="None" state=absent'
20.0.0.20 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": true,
"envs": [],
"jobs": []
}
[root@ansible ~]# ansible 20.0.0.20 -a 'crontab -l'
20.0.0.20 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
5.4、user模块
1、查看user可以使用的参数
[root@ansible ~]# ansible-doc -s user
2、给node标签下的所有主机都创建一个lisi用户
[root@ansible ~]# ansible node -m user -a 'name="lisi"'
20.0.0.30 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": true,
"comment": "",
"create_home": true,
"group": 1001,
"home": "/home/lisi",
"name": "lisi",
"shell": "/bin/bash",
"state": "present",
"system": false,
"uid": 1001
}
20.0.0.20 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": true,
"comment": "",
"create_home": true,
"group": 1001,
"home": "/home/lisi",
"name": "lisi",
"shell": "/bin/bash",
"state": "present",
"system": false,
"uid": 1001
}
#在节点一二验证lisi账号是否创建成功
node-1:
[root@node-1 opt]# id lisi
uid=1001(lisi) gid=1001(lisi) 组=1001(lisi)
node-2:
[root@node-2 ~]# id lisi
uid=1001(lisi) gid=1001(lisi) 组=1001(lisi)
3、删除node标签下的所有主机lisi用户
[root@ansible ~]# ansible node -m user -a 'name="lisi" state=absent'
20.0.0.30 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": true,
"force": false,
"name": "lisi",
"remove": false,
"state": "absent"
}
20.0.0.20 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": true,
"force": false,
"name": "lisi",
"remove": false,
"state": "absent"
}
#在节点一二验证lisi账号是否删除成功
node-1:
[root@node-1 opt]# id lisi
id: lisi: no such user
node-2:
[root@node-2 ~]# id lisi
id: lisi: no such user
5.5、group模块
1、查看group可以使用的参数
[root@ansible ~]# ansible-doc -s group
2、创建一个组
[root@ansible ~]# ansible 20.0.0.20 -m group -a 'name="abc" gid=1004 system=yes'
20.0.0.20 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": true,
"gid": 1004,
"name": "abc",
"state": "present",
"system": true
}
#ansible上查看是否创建成功
[root@ansible ~]# ansible 20.0.0.20 -a 'tail /etc/group'
20.0.0.20 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
nfsnobody:x:65534:
gnome-initial-setup:x:986:
avahi:x:70:
slocate:x:21:
postdrop:x:90:
postfix:x:89:
sshd:x:74:
tcpdump:x:72:
abc:x:1004:
#节点1验证
[root@node-1 opt]# tail /etc/group
nfsnobody:x:65534:
gnome-initial-setup:x:986:
avahi:x:70:
slocate:x:21:
postdrop:x:90:
postfix:x:89:
sshd:x:74:
tcpdump:x:72:
abc:x:1004:
3、创建一个用户加入组里
[root@ansible ~]# ansible 20.0.0.20 -m user -a 'name="wangwu"'
20.0.0.20 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": true,
"comment": "",
"create_home": true,
"group": 1002,
"home": "/home/wangwu",
"name": "wangwu",
"shell": "/bin/bash",
"state": "present",
"system": false,
"uid": 1002
}
[root@ansible ~]# ansible 20.0.0.20 -m user -a 'name=zhaoyun uid=10006 system=yes group=abc'
20.0.0.20 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": true,
"comment": "",
"create_home": true,
"group": 1004,
"home": "/home/zhaoyun",
"name": "zhaoyun",
"shell": "/bin/bash",
"state": "present",
"system": true,
"uid": 10006
}
#节点一验证
[root@node-1 opt]# id zhaoyun
uid=10006(zhaoyun) gid=1004(abc) 组=1004(abc)
创建一个abc组,创建用户zhaoyun并加入abc组
5.6、copy模块
1、查看copy可以使用的参数
[root@ansible ~]# ansible-doc -s copy
2、拷贝一个文件到节点1里
[root@ansible ~]# ansible 20.0.0.20 -m copy -a 'src=/root/abc dest=/opt owner=lisi mode=755'
20.0.0.20 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": true,
"checksum": "512ba0e938d862261a9914c7f5370dab3d7c1695",
"dest": "/opt/abc",
"gid": 0,
"group": "root",
"md5sum": "1bfd09afae8b4b7fde31ac5e6005342e",
"mode": "0755",
"owner": "lisi",
"size": 5,
"src": "/root/.ansible/tmp/ansible-tmp-1610353993.21-15430-36258874554335/source",
"state": "file",
"uid": 1001
}
#在节点1里验证
[root@node-1 opt]# ls -l
总用量 8
-rwxr-xr-x 1 lisi root 5 1月 11 16:33 abc
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 180 1月 11 15:51 ansible.txt
drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 6 3月 26 2015 rh
[root@node-1 opt]# cat abc
hell
3、将指定内容写节点1制定文件里
[root@ansible ~]# ansible 20.0.0.20 -m copy -a 'content="abc123" dest=/opt/abc'
20.0.0.20 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": true,
"checksum": "6367c48dd193d56ea7b0baad25b19455e529f5ee",
"dest": "/opt/abc",
"gid": 0,
"group": "root",
"md5sum": "e99a18c428cb38d5f260853678922e03",
"mode": "0755",
"owner": "lisi",
"size": 6,
"src": "/root/.ansible/tmp/ansible-tmp-1610354219.77-15497-100936071941447/source",
"state": "file",
"uid": 1001
}
#节点1验证
[root@node-1 opt]# cat abc
abc123
如果写入的内容直接覆盖文件里面的所有内容
5.7、file模块
1、查看file可以使用的参数
[root@ansible ~]# ansible-doc -s file
2、修改节点1上文件abc的属主和属组
[root@ansible ~]# ansible 20.0.0.20 -m user -a 'name=nginx system=yes'
20.0.0.20 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": true,
"comment": "",
"create_home": true,
"group": 984,
"home": "/home/nginx",
"name": "nginx",
"shell": "/bin/bash",
"state": "present",
"system": true,
"uid": 989
}
[root@ansible ~]# ansible 20.0.0.20 -m group -a 'name=node system=yes'
20.0.0.20 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": true,
"gid": 983,
"name": "node",
"state": "present",
"system": true
}
[root@ansible ~]# ansible 20.0.0.20 -m file -a 'owner=nginx group=node mode=755 path=/opt/abc'
20.0.0.20 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": true,
"gid": 983,
"group": "node",
"mode": "0755",
"owner": "nginx",
"path": "/opt/abc",
"size": 6,
"state": "file",
"uid": 989
}
#在节点1上验证
[root@node-1 opt]# ls -l
总用量 8
-rwxr-xr-x 1 nginx node 6 1月 11 16:37 abc
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 180 1月 11 15:51 ansible.txt
drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 6 3月 26 2015 rh
3、将节点上面的文件做链接
[root@node-1 ~]# touch a2
[root@ansible ~]# ansible 20.0.0.20 -m file -a 'src=/root/a2 path=/opt/aa1 state=link'
20.0.0.20 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": true,
"dest": "/opt/aa1",
"gid": 0,
"group": "root",
"mode": "0777",
"owner": "root",
"size": 8,
"src": "/root/a2",
"state": "link",
"uid": 0
}
#节点1上面验证
[root@node-1 opt]# ls -l
总用量 8
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 8 1月 11 17:10 aa1 -> /root/a2
-rwxr-xr-x 1 nginx node 6 1月 11 16:37 abc
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 180 1月 11 15:51 ansible.txt
drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 6 3月 26 2015 rh
4、在节点1上面创建一个文件
[root@ansible ~]# ansible 20.0.0.20 -m file -a 'path=/opt/ax state=touch'
20.0.0.20 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": true,
"dest": "/opt/ax",
"gid": 0,
"group": "root",
"mode": "0644",
"owner": "root",
"size": 0,
"state": "file",
"uid": 0
}
#节点1上面验证
[root@node-1 opt]# ls -l
总用量 8
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 8 1月 11 17:10 aa1 -> /root/a2
-rwxr-xr-x 1 nginx node 6 1月 11 16:37 abc
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 180 1月 11 15:51 ansible.txt
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 1月 11 17:17 ax
drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 6 3月 26 2015 rh
5、在节点1上面删除一个文件
[root@ansible ~]# ansible 20.0.0.20 -m file -a 'path=/opt/ax state=absent'
20.0.0.20 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": true,
"path": "/opt/ax",
"state": "absent"
}
#节点1上面验证
[root@node-1 opt]# ls -l
总用量 8
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 8 1月 11 17:10 aa1 -> /root/a2
-rwxr-xr-x 1 nginx node 6 1月 11 16:37 abc
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 180 1月 11 15:51 ansible.txt
drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 6 3月 26 2015 rh
6、在节点1上面创建一个目录
[root@ansible ~]# ansible 20.0.0.20 -m file -a 'path=/opt/ansible-1 state=directory mode=755'
20.0.0.20 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": true,
"gid": 0,
"group": "root",
"mode": "0755",
"owner": "root",
"path": "/opt/ansible-1",
"size": 6,
"state": "directory",
"uid": 0
}
#节点1上面验证
[root@node-1 opt]# ls -l
总用量 8
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 8 1月 11 17:10 aa1 -> /root/a2
-rwxr-xr-x 1 nginx node 6 1月 11 16:37 abc
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 6 1月 11 17:23 ansible-1
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 180 1月 11 15:51 ansible.txt
drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 6 3月 26 2015 rh
7、删除节点1上面的目录
[root@ansible ~]# ansible 20.0.0.20 -m file -a 'path=/opt/ansible-1 state=absent'
20.0.0.20 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": true,
"path": "/opt/ansible-1",
"state": "absent"
}
#节点1上面验证
[root@node-1 opt]# ls -l
总用量 8
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 8 1月 11 17:10 aa1 -> /root/a2
-rwxr-xr-x 1 nginx node 6 1月 11 16:37 abc
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 180 1月 11 15:51 ansible.txt
drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 6 3月 26 2015 rh
5.8、ping模块
1、查看ping可以使用的参数
[root@ansible ~]# ansible-doc -s ping
2、测试所有节点主机和ansible服务器网络是否互通
[root@ansible ~]# ansible all -m ping
3、测试某一个标签下的主机和ansible服务器网络是否互通
[root@ansible ~]# ansible node -m ping
4、测试某一个主机和ansible服务器网络是否互通
[root@ansible ~]# ansible 20.0.0.20 -m ping
5.9、yum模块
1、查看yum可以使用的参数
[root@ansible ~]# ansible-doc -s yum
2、给node标签下面的主机安装httpd服务
[root@ansible ~]# ansible node -m yum -a 'name=httpd'
节点验证1验证:
[root@node-1 ~]# rpm -q httpd
httpd-2.4.6-67.el7.centos.x86_64
节点验证2验证:
[root@node-2 ~]# rpm -q httpd
httpd-2.4.6-67.el7.centos.x86_64
3、卸载node标签下面的主机安装httpd服务
[root@ansible ~]# ansible node -m yum -a 'name=httpd state=absent'
节点验证1验证:
[root@node-1 ~]# rpm -q httpd
未安装软件包 httpd
节点验证2验证:
[root@node-2 ~]# rpm -q httpd
未安装软件包 httpd
5.9、service模块
1、查看service可以使用的参数
[root@ansible ~]# ansible-doc -s service
2、开启node标签下的所有主机httpd服务状态
[root@ansible ~]# ansible node -m yum -a 'name=httpd'
[root@ansible ~]# ansible node -m service -a 'enabled=true name=httpd state=started'
节点1验证:
[root@node-1 ~]# netstat -anpt|grep 80
tcp6 0 0 :::80 :::* LISTEN 3005/httpd
节点2验证:
[root@node-2 ~]# netstat -anpt|grep 80
tcp6 0 0 :::80 :::* LISTEN 3005/httpd
3、关闭node标签下的所有节点的防火墙
[root@ansible ~]# ansible node -m service -a 'name=firewalld state=stopped'
5.10、shell模块
1、查看service可以使用的参数
[root@ansible ~]# ansible-doc -s shell
2、将指定内容输入到node标签下的所有节点
[root@ansible ~]# ansible node -m shell -a 'chdir=/opt/ echo ansible123 > aba.txt' #command模块是不识别从定向符号
20.0.0.30 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
20.0.0.20 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
节点1验证
[root@node-1 ~]# cd /opt/
[root@node-1 opt]# ls
aa1 aba.txt abc ansible.txt rh
[root@node-1 opt]# cat aba.txt
ansible123
节点2验证
[root@node-2 ~]# cd /opt/
[root@node-2 opt]# ls
aba.txt rh
[root@node-2 opt]# cat aba.txt
ansible123
5.11、script模块
1、查看script可以使用的参数
[root@ansible ~]# ansible-doc -s script
2、创建一个脚本让node标签下的主机都执行该脚本
[root@ansible ~]# vim an.sh
[root@ansible ~]# chmod +x an.sh
[root@ansible ~]# ansible node -m script -a 'an.sh'
节点1验证:
[root@node-1 opt]# ls
aa1 aba.txt abc abcd.txt ansible.txt rh
[root@node-1 opt]# cat abcd.txt
123456abc
节点2验证:
[root@node-2 opt]# ls
aa1 aba.txt abc abcd.txt ansible.txt rh
[root@node-2 opt]# cat abcd.txt
123456abc
5.12、setup模块
1、查看setup可以使用的参数
[root@ansible ~]# ansible-doc -s setup
2、查看node标签下的服务器facts信息
[root@ansible ~]# ansible node -m setup