队列(Queue)的顶级理解
目录
1.队列(Queue) 的概念
2.单链表模拟实现队列
2.1创建队列
2.2入队列
2.3判断是否为空
2.4出队列
2.5获取队头元素
2.6完整代码:
2.7双向链表模拟实现队列代码
3.数组模拟实现队列代码
3.1创建队列
3.2判断是否为满
3.3检查是否为空
3.4插入元素
3.5删除元素
3.6从队首获取元素
3.7 从队尾获取元素
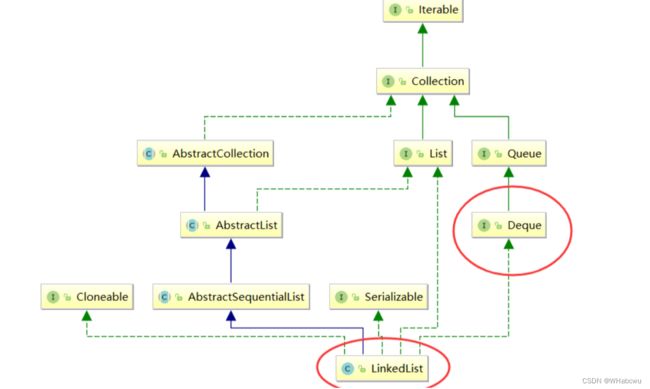
4.双端队列 (Deque)
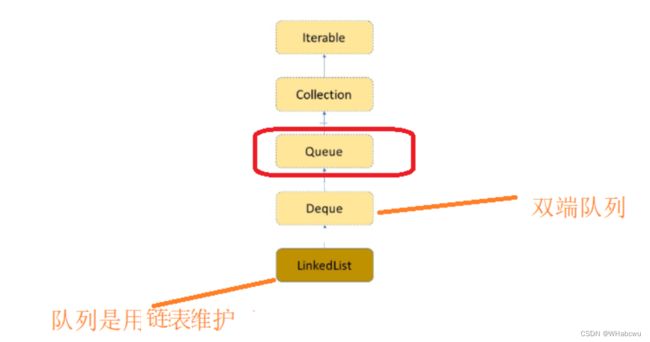
1.队列(Queue) 的概念
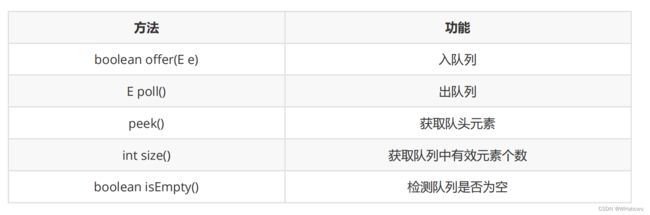
队列在使用时有以下方法:
 注意:Queue是个接口,在实例化时必须实例化LinkedList的对象,因为LinkedList实现了Queue接口。
注意:Queue是个接口,在实例化时必须实例化LinkedList的对象,因为LinkedList实现了Queue接口。
Queue<Integer> q = new LinkedList<>();
2.单链表模拟实现队列
2.1创建队列
代码:
public class Myqueue {
class Node{
public int val;
public Node next;
public Node(int val){
this.val=val;
}
}
public Node head;
public Node last;
public int size;
}2.2入队列
(1)创建一个节点node。
(2)判断该head是否为null,若为null,则该node就是head和last。
(3)若不为null,则 last.next=node, last=node;
(4)size++。
代码:
public void offer(int val){
Node node = new Node(val);
if(head==null){
head=node;
last=node;
}else{
last.next=node;
last=node;
}
size++;
}2.3判断是否为空
public boolean empty(){
return size==0;
}2.4出队列
(1)队列为空,则直接返回队列为空的异常。
自定义异常如下:
public class EmptyException extends RuntimeException{
public EmptyException(String message) {
super(message);
}
}
(2)队列为空不为,先ret=head.val,后删除头结点。
(3)size--;
代码:
public int poll(){
if(empty()){
throw new EmptyException("队列为空");
}
int ret=head.val;
head=head.next;
size--;
return ret;
}2.5获取队头元素
代码:
public int peek(){
if(empty()){
throw new EmptyException("队列为空");
}
int ret=head.val;
return ret;
}2.6完整代码:
public class Myqueue {
class Node{
public int val;
public Node next;
public Node(int val){
this.val=val;
}
}
public Node head;
public Node last;
public int size;
public void offer(int val){
Node node = new Node(val);
if(head==null){
head=node;
last=node;
}else{
last.next=node;
last=node;
}
size++;
}
public int poll(){
if(empty()){
throw new EmptyException("队列为空");
}
int ret=head.val;
head=head.next;
size--;
return ret;
}
public boolean empty(){
return size==0;
}
public int peek(){
if(empty()){
throw new EmptyException("队列为空");
}
int ret=head.val;
return ret;
}
}2.7双向链表模拟实现队列代码
public class MyQueue {
// 双向链表节点
public static class ListNode {
ListNode next;
ListNode prev;
int value;
ListNode(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
}
ListNode first; // 队头
ListNode last; // 队尾
int size = 0;
// 入队列---向双向链表位置插入新节点
public void offer(int e) {
ListNode newNode = new ListNode(e);
if (first == null) {
first = newNode;
// last = newNode;
} else {
last.next = newNode;
newNode.prev = last;
// last = newNode;
}
last = newNode;
size++;
}
// 出队列---将双向链表第一个节点删除掉
public int poll() {
// 1. 队列为空
// 2. 队列中只有一个元素----链表中只有一个节点---直接删除
// 3. 队列中有多个元素---链表中有多个节点----将第一个节点删除
int value = 0;
if (first == null) {
throw new EmptyException("队列为空");
} else if (first == last) {
last = null;
first = null;
} else {
value = first.value;
first = first.next;
first.prev.next = null;
first.prev = null;
}
--size;
return value;
}
// 获取队头元素---获取链表中第一个节点的值域
public int peek() {
if (first == null) {
throw new EmptyException("队列为空");
}
return first.value;
}
public int size() {
return size;
}
public boolean isEmpty(){
return first == null;
}
}
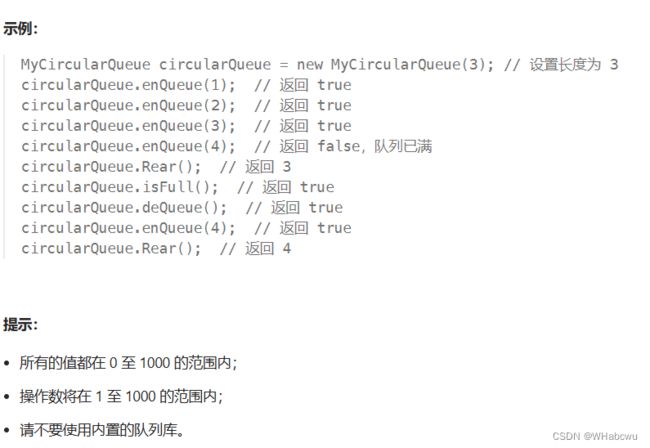
3.数组模拟实现队列代码
实际中我们有时还会使用一种队列叫循环队列,环形队列通常使用数组实现。
循环队列![]() https://leetcode.cn/problems/design-circular-queue/description/描述:
https://leetcode.cn/problems/design-circular-queue/description/描述:
要解决循环队列的有如下几个难题:
(1)数组的下标如何实现循环
rear=(rear+1)%elem.length
front=(front+1)%elem.length
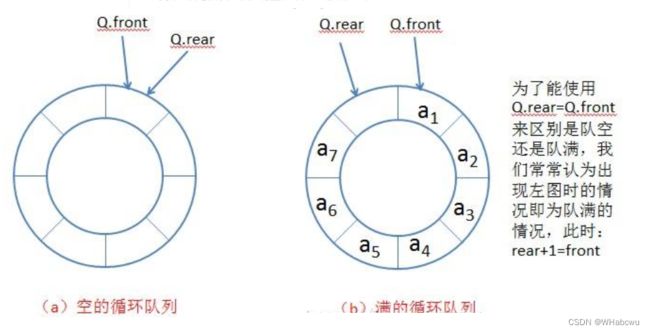
(2)区分空与满
有三个方法:
通过添加 size 属性记录
保留一个位置
使用标记
本博主采用第二个方法,如下图所示:
3.1创建队列
由于我们需要浪费一个空间来判断是否为满,在构造方法时多构造一个空间。
class MyCircularQueue {
private int[] elem;
private int front;//表示队列的头
private int rear;//表示队列的尾
public MyCircularQueue(int k) {
this.elem=new int[k+1];
}
}3.2判断是否为满
public boolean isFull() {
return (rear+1)%elem.length==front;
}3.3检查是否为空
public boolean isEmpty() {
return rear == front;
}3.4插入元素
(1)判断是否为满,若为满。返回false
(2)若不为满,则在elem下标为rear处插入该元素
(3)队尾向后走一步rear=(rear+1)%elem.length,返回true;
public boolean enQueue(int value) {
if(isFull()){
return false;
}
elem[rear]=value;
rear=(rear+1)%elem.length;
return true;
}3.5删除元素
判断是否为null
(1)若为null。返回false
(2)若不为null,队首向后走一步 front = (front+1)%elem.length;,返回true;
public boolean deQueue() {
if (isEmpty()){
return false;
}
front = (front+1)%elem.length;
return true;
}
3.6从队首获取元素
public int Front(){
if(isEmpty()){
return -1;
}
return elem[front];
}3.7 从队尾获取元素
(1)如果队列为空,返回-1
(2)不为空,如果为队尾下标为0,返回下elem[elem.length-1]的值
(3)下标不为0,返回数组下标为rear-1的值
public int Rear() {
if(isEmpty() ) {
return -1;
}
if(rear == 0) {
return elem[elem.length-1];
}
return elem[rear-1];
}3.8完整代码
class MyCircularQueue {
private int[] elem;
private int front;//表示队列的头
private int rear;//表示队列的尾
public MyCircularQueue(int k) {
this.elem = new int[k + 1];
}
public boolean enQueue(int value) {
if (isFull()) {
return false;
}
elem[rear] = value;
rear = (rear + 1) % elem.length;
return true;
}
public boolean deQueue() {
if (isEmpty()){
return false;
}
front = (front+1)%elem.length;
return true;
}
//从队首获取元素。如果队列为空,返回 -1 。
public int Front() {
if(isEmpty() ) {
return -1;
}
return elem[front];
}
//从队尾获取元素。如果队列为空,返回 -1 。
public int Rear() {
if(isEmpty() ) {
return -1;
}
if(rear == 0) {
return elem[elem.length-1];
}
return elem[rear-1];
}
//检查循环队列是否为空。
public boolean isEmpty() {
return rear == front;
}
public boolean isFull() {
return (rear + 1) % elem.length == front;
}
}4.双端队列 (Deque)
Deque是一个接口,使用时必须创建LinkedList的对象。
在实际工程中,使用Deque接口是比较多的,栈和队列均可以使用该接口
Deque stack = new ArrayDeque<>();//双端队列的线性实现
Deque queue = new LinkedList<>();//双端队列的链式实现
以上为我个人的小分享,如有问题,欢迎讨论!!!
都看到这了,不如关注一下,给个免费的赞 ![]()
![]()