京东爬虫,包括数据绘图(python基于Anaconda3的Spyder开发)
京东网页爬商品数据与绘制数据变化图像
- python简介
-
- 开发环境
- 效果(这里爬5页举例)
- 爬虫代码与其解释
- 对上述产生的数据进行绘图分析(可以先对获取的数据进行处理,我这里举例就直接用的 >=< )
- 绘图代码及相关分析
- 最后小结
python简介
Python由荷兰数学和计算机科学研究学会的Guido van Rossum 于1990 年代初设计,作为一门叫做ABC语言的替代品。Python提供了高效的高级数据结构,还能简单有效地面向对象编程。Python语法和动态类型,以及解释型语言的本质,使它成为多数平台上写脚本和快速开发应用的编程语言,随着版本的不断更新和语言新功能的添加,逐渐被用于独立的、大型项目的开发。
Python解释器易于扩展,可以使用C或C++(或者其他可以通过C调用的语言)扩展新的功能和数据类型。Python 也可用于可定制化软件中的扩展程序语言。Python丰富的标准库,提供了适用于各个主要系统平台的源码或机器码。
Python的设计哲学是“优雅”、“明确”、“简单”。因此,Perl语言中“总是有多种方法来做同一件事”的理念在Python开发者中通常是难以忍受的。Python开发者的哲学是“用一种方法,最好是只有一种方法来做一件事”。在设计Python语言时,如果面临多种选择,Python开发者一般会拒绝花俏的语法,而选择明确的没有或者很少有歧义的语法。由于这种设计观念的差异,Python源代码通常被认为比Perl具备更好的可读性,并且能够支撑大规模的软件开发。这些准则被称为Python格言。在Python解释器内运行import this可以获得完整的列表。
开发环境
Anaconda3
Spyder python(3.8)
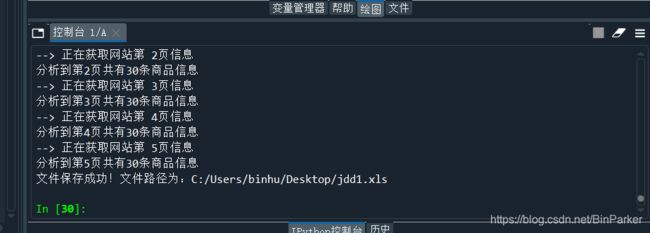
效果(这里爬5页举例)
爬虫代码与其解释
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Wed Jun 9 22:33:39 2021
@author: binhu
"""
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import xlwt
# 表格标题
TITLE_LABEL = ['商品编号', '商品名称', '价格', '商家', '商品详情地址']
GOOD_LABEL = ['no', 'name', 'price', 'shop', 'detail_addr']
class Excel:
# 表格列数
TABLE_COL = len(TITLE_LABEL)
# 当前行数
_current_row = 1
# 初始化,创建文件及写入title
def __init__(self, sheet_name='sheet1'):
self.write_work = xlwt.Workbook(encoding='ascii')
self.write_sheet = self.write_work.add_sheet(sheet_name)
for item in range(len(TITLE_LABEL)):
self.write_sheet.write(0, item, label=TITLE_LABEL[item])
# 写入内容
def write_content(self, content):
for item in range(self.TABLE_COL):
self.write_sheet.write(self._current_row, item, label=content[GOOD_LABEL[item]])
# 插入完一条记录后,换行
self._current_row += 1
# 保存文件
def save_file(self, file_url='./dj_data.xls'):
try:
self.write_work.save(file_url)
print("文件保存成功!文件路径为:" + file_url)
except IOError:
print("文件保存失败!")
class Goods:
# 初始化方法
def __init__(self, li_info):
self.li_info = li_info
self.good_info_dic = {}
def find_attr(self, attr):
try:
if attr == GOOD_LABEL[0]:
# 商品编号
result = self.li_info['data-sku']
elif attr == GOOD_LABEL[1]:
# 商品名称
result = self.li_info.find(class_='p-name p-name-type-2').find('em').get_text()
elif attr == GOOD_LABEL[2]:
# 价格
result = self.li_info.find(class_='p-price').find('i').get_text()
elif attr == GOOD_LABEL[3]:
# 商家
result = self.li_info.find(class_='p-shop').find('a').get_text()
elif attr == GOOD_LABEL[4]:
# 商品详情地址
result = self.li_info.find(class_='p-name p-name-type-2').find('a')['href']
except AttributeError:
result = '无'
self.good_info_dic.setdefault(attr, result)
# 添加商品信息
def add_good_info(self):
for item in GOOD_LABEL:
self.find_attr(item)
# 获取产品列表
def get_good(self):
return self.good_info_dic
def get_html(url, currentPage, pageSize):
# 模拟浏览器访问
headers = {
'User-Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) '
'AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) '
'Chrome/81.0.4044.138 Safari/537.36',
'accept-language': 'zh-CN,zh;q=0.9'
}
print("--> 正在获取网站第 " + str(currentPage) + "页信息")
if currentPage != 1:
url = url + '&page=' + str(currentPage) + '&s=' + str(pageSize) + '&click=0'
response = requests.get(url, headers=headers) # 请求访问网站
if response.status_code == 200:
html = response.text # 获取网页源码
return html # 返回网页源码
else:
print("获取网站信息失败!")
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 创建文件
excel = Excel()
# 搜索关键字
keyword = '叶菜类'
# 搜索地址
search_url = 'https://search.jd.com/Search?keyword=' + keyword + '&enc=utf-8'
total = input('请输入需要爬取页数: ')
page = {
'total': 0, # 总页数
'currentPage': 1, # 当前页数
'pageSize': 0 # 每页显示多少条
}
if not total.isdigit():
print("非法字符,程序退出!")
exit(0)
page['total'] = eval(total)
for i in range(page['total']):
# 初始化BeautifulSoup库,并设置解析器
soup = BeautifulSoup(get_html(search_url, page['currentPage'], page['currentPage'] * page['pageSize']), 'lxml')
# 商品列表
goods_list = soup.find_all('li', class_='gl-item')
print("分析到第" + str(page['currentPage']) + '页共有' + str(len(goods_list)) + '条商品信息')
for li in goods_list: # 遍历父节点
goods = Goods(li)
# 添加信息
goods.add_good_info()
# 获取信息
good_info = goods.get_good()
# 写入excel
excel.write_content(good_info)
page['currentPage'] = page['currentPage'] + 1
page['pageSize'] = len(goods_list) * page['currentPage']
excel.save_file('C:/Users/binhu/Desktop/jdd1.xls')
对上述产生的数据进行绘图分析(可以先对获取的数据进行处理,我这里举例就直接用的 >=< )
绘图代码及相关分析
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Thu Jun 10 08:03:16 2021
@author: binhu
"""
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from pylab import *
import matplotlib as mpl
import xlrd
from xlrd import open_workbook
#导入需要用到的模块
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib import rcParams
# windows下设置汉字库
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif']='SimHei'
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus']=False
#读取目标表格文件
data = pd.read_excel('C:/Users/binhu/Desktop/jdd1.xls')
#在控制台中输出表格数据
print(data)
# 对数量统计
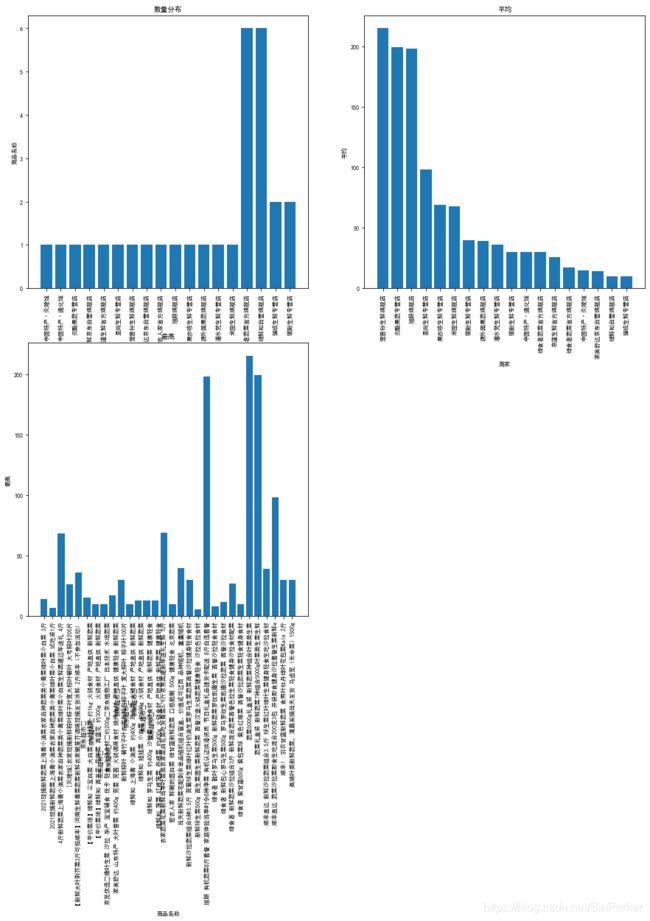
data1 = data.groupby(['商家'])['商品名称'].count().reset_index()
# 平均
data2 = data.groupby(['商家','商品名称'])['价格'].mean().reset_index().sort_values(by='价格',ascending=False)#降序显示
# 最高
data3 = data.groupby(['商品名称'])['价格'].min().reset_index()
# 画图
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(15,15)) #创建画布
ax_1 = fig.add_subplot(2,2,1) #添加子图
ax_2 = fig.add_subplot(2,2,2)
ax_3 = fig.add_subplot(2,2,3)
ax_1.set_title("数量分布")
ax_1.set_xlabel('商家')
ax_1.set_ylabel('商品名称')
ax_1.set_xticklabels(data1['商家'],rotation=90) #rotation=90文字显示旋转90度
ax_1.bar(data1['商家'],data1['商品名称'])
ax_2.set_title("平均")
ax_2.set_xlabel('商家')
ax_2.set_ylabel('平均')
ax_2.set_xticklabels(data2['商家'],rotation=90)
ax_2.bar(data2['商家'],data2['价格'])
ax_3.set_title("最高")
ax_3.set_xlabel('商品名称')
ax_3.set_ylabel('最高')
ax_3.set_xticklabels(data3['商品名称'],rotation=90)
ax_3.bar(data3['商品名称'],data3['价格'])
# #x轴是商家,y轴是价格
# data.plot.bar(x='商家',y='价格')
plt.show()
#多个数据对照
x_data=[]
y_data=[]
x_data1=[]
y_data1=[]
x_data2=[]
y_data2=[]
x_data3=[]
y_data3=[]
x_volte=[]
temp=[]
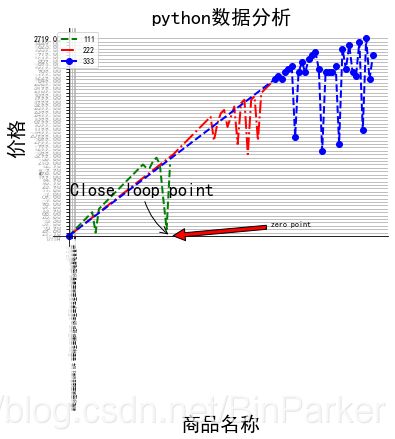
# plt.annotate(标注文字, 标注的数据点, 标注文字坐标, 箭头形状)
plt.annotate('zero point', xy=(30,0), xytext=(60,3), arrowprops=dict(facecolor='red', shrink=0.03),)
plt.annotate('Close loop point',size=18, xy=(30, 0.1), xycoords='data',
xytext=(-100, 40), textcoords='offset points',
arrowprops=dict(arrowstyle="->",connectionstyle="arc3,rad=.2")
)
# plt.annotate(' ', xy=(0.02, -0.2), xycoords='data',
# xytext=(200, -90), textcoords='offset points',
# arrowprops=dict(arrowstyle="->",connectionstyle="arc3,rad=-.2")
# )
# plt.annotate('Zero point in non-monotonic region', size=16,xy=(1.97, -0.3), xycoords='data',
# xytext=(-290, -110), textcoords='offset points',
# arrowprops=dict(arrowstyle="->",connectionstyle="arc3,rad=.2")
# )
wb = open_workbook('C:/Users/binhu/Desktop/jdd1.xls')
for s in wb.sheets():
print ('Sheet:'),s.name
for row in range(s.nrows):
print ('the row is:'),row
values = []
for col in range(s.ncols):
values.append(s.cell(row,col).value)
print (values)
x_data1.append(values[1])
y_data1.append(values[2])
plt.plot(x_data1, y_data1, 'g--',label=u"111",linewidth=2)
wb = open_workbook('C:/Users/binhu/Desktop/jdd.xls')
for s in wb.sheets():
print ('Sheet:'),s.name
for row in range(s.nrows):
print ('the row is:'),row
values = []
for col in range(s.ncols):
values.append(s.cell(row,col).value)
print (values)
x_data2.append(values[1])
y_data2.append(values[2])
plt.plot(x_data2, y_data2, 'r-.',label=u"222",linewidth=2)
wb = open_workbook('C:/Users/binhu/Desktop/jdd3.xls')
for s in wb.sheets():
print ('Sheet:'),s.name
for row in range(s.nrows):
print ('the row is:'),row
values = []
for col in range(s.ncols):
values.append(s.cell(row,col).value)
print (values)
#x_data.append(values[0])
x_data.append(values[1])
y_data.append(values[2])
plt.plot(x_data, y_data, 'bo--',label=u"333",linewidth=2)
# plt.title(u"测试")
plt.title(u"python数据分析",size=20)
plt.legend(loc=0)#显示label
# 移动坐标轴,首先要把旧的坐标拆了
ax = gca()
ax.spines['right'].set_color('none')
ax.spines['top'].set_color('none')
ax.xaxis.set_ticks_position('bottom')
ax.spines['bottom'].set_position(('data',0))
ax.yaxis.set_ticks_position('left')
ax.spines['left'].set_position(('data',0))
plt.xlabel(u"商品名称",size=20)#角度单位为pi
plt.ylabel(u"价格",size=20)
plt.xticks([0, 0.5, 1, 1.5, 2],size=4,rotation=90)#这里举5个头
for label in ax.get_xticklabels() + ax.get_yticklabels():
#label.set_fontsize(16)
label.set_bbox(dict(facecolor='white', edgecolor='None', alpha=0.65 ))
plt.grid(True)
plt.show()
最后小结
-
Python的优势有必要作为第一步去了解,Python作为面向对象的脚本语言,优势就是数据处理和挖掘,这也注定了它和AI、互联网技术的紧密联系。
-
网站开发。Python数据处理很在线,用它编写网站可以为大众提供优秀的服务,主要使用django和flask框架,著名的网站像知乎、YouTube就是Python写的。
-
自动化运维。Python运行在Linux系统上可以作为服务器脚本不停工作,实现对主机的自动化操作,自动登录等就是应用之一。
-
网络爬虫。顾名思义,从互联网上爬取信息的脚本,主要由urllib、requests等库编写,实用性很强,小编就曾写过爬取5w数据量的爬虫。在大数据风靡的时代,爬虫绝对是新秀。
-
人工智能。AI使Python一战成名,AI的实现可以通过tensorflow库。小编认为,神经网络的核心在于激活函数、损失函数和数据,数据可以通过爬虫获得。训练时大量的数据运算又是Python的show
time。 -
游戏并不适合用Python开发,Python虽有pygame库,但是功能不强,游戏运行效率低下,写游戏还是要靠游戏引擎。
END(=.=)
注意事项:
欢迎各位萌新入坑Python
一朝入坑,数载付出,做好准备,努力前行吧!