【LeetCode-面试经典150题-day23】
目录
108. 将有序数组转换为二叉搜索树
148.排序链表
427.建立四叉树
23.合并K个升序链表
108. 将有序数组转换为二叉搜索树
题意:
给你一个整数数组
nums,其中元素已经按 升序 排列,请你将其转换为一棵 高度平衡 二叉搜索树。高度平衡 二叉树是一棵满足「每个节点的左右两个子树的高度差的绝对值不超过 1 」的二叉树。
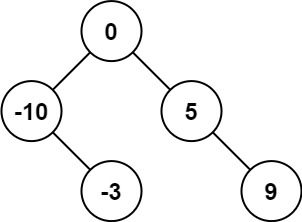
【输入样例】nums = [-10,-3,0,5,9]
【输出样例】[0,-3,9,-10,null,5] 或 [0,-10,5,null,-3,null,9]
解题思路:
二叉搜索树进行中序遍历的时候,得到的序列是升序序列,因此我们可以将给定的序列作为中序遍历的结果,来构建二叉搜索树;
左右两棵子树高度差绝对值不超过1,则考虑将中间位置的数字作为根节点(向下取整),mid=(left+right)/2.
class Solution {
public TreeNode sortedArrayToBST(int[] nums) {
return helper(nums, 0, nums.length - 1);
}
public TreeNode helper(int[] nums, int left, int right){
if(left > right){
return null;
}
//总是选择中间位置左边的数字作为根节点
int mid = (left + right) /2;
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(nums[mid]);
root.left = helper(nums, left, mid - 1);
root.right = helper(nums, mid+1, right);
return root;
}
}时间: 击败了100.00%
内存: 击败了49.75%
148.排序链表
题意:
给你链表的头结点
head,请将其按 升序 排列并返回 排序后的链表 。
【输入样例】head = [4,2,1,3]
【输出样例】[1,2,3,4]
解题思路:
使用排序算法即可,这边我们使用自顶向下归并排序。
1.每次找到链表中点,将链表拆分成两个子链表。链表无法像数组一样直接根据下标找到中点,我们可以使用快慢指针,快指针移动2步,慢指针移动1步。当快指针到链表末尾时,慢指针所指的就是中点。
2.分别对两个子链表进行排序
3. 将两个排序后的子链表合并,得到完成的排列后的链表。
class Solution {
public ListNode sortList(ListNode head) {
return mergeSort(head,null);
}
//tail是指最后一个节点的下一节点,在样例中是节点3的next,所以主函数调用时传过来的是null
public ListNode mergeSort(ListNode head, ListNode tail){
if(head == null){
//链表为空
return head;
}
if(head.next == tail){
//链表中只包含head一个节点
head.next = null;
return head;
}
//快慢指针寻找中点
ListNode slow = head,fast = head;
while(fast != tail){
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next;
//快指针一次走两步,当走完第一步后,又可能已经走到尾节点,此时就不需要再走第二步了
if(fast != tail){
fast = fast.next;
}
}
ListNode mid = slow;
ListNode list1 = mergeSort(head,mid);
ListNode list2 = mergeSort(mid,tail);
ListNode sorted = merge(list1,list2);
return sorted;
}
public ListNode merge(ListNode list1, ListNode list2){
ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(0);
ListNode temp = dummyHead,temp1 = list1,temp2 = list2;
while(temp1 != null && temp2 != null){
if(temp1.val <= temp2.val){
temp.next = temp1;
temp1 = temp1.next;
}else{
temp.next = temp2;
temp2 = temp2.next;
}
temp = temp.next;
}
if (temp1 != null) {
temp.next = temp1;
} else if (temp2 != null) {
temp.next = temp2;
}
return dummyHead.next;
}
}时间: 击败了56.72%
内存: 击败了21.21%
427.建立四叉树
题意:
给你一个
n * n矩阵grid,矩阵由若干0和1组成。请你用四叉树表示该矩阵grid。你需要返回能表示矩阵
grid的 四叉树 的根结点。四叉树数据结构中,每个内部节点只有四个子节点。此外,每个节点都有两个属性:
val:储存叶子结点所代表的区域的值。1 对应 True,0 对应 False。注意,当isLeaf为 False 时,你可以把 True 或者 False 赋值给节点,两种值都会被判题机制 接受 。isLeaf: 当这个节点是一个叶子结点时为 True,如果它有 4 个子节点则为 False 。class Node { public boolean val; public boolean isLeaf; public Node topLeft; public Node topRight; public Node bottomLeft; public Node bottomRight; }我们可以按以下步骤为二维区域构建四叉树:
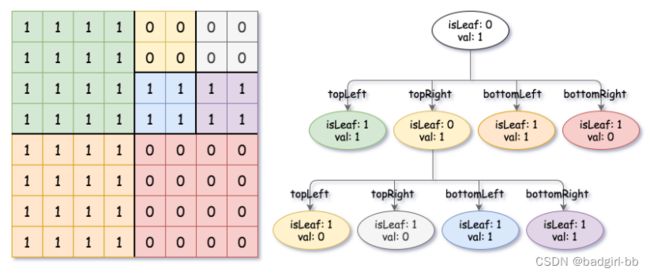
- 如果当前网格的值相同(即,全为
0或者全为1),将isLeaf设为 True ,将val设为网格相应的值,并将四个子节点都设为 Null 然后停止。- 如果当前网格的值不同,将
isLeaf设为 False, 将val设为任意值,然后如下图所示,将当前网格划分为四个子网格。- 使用适当的子网格递归每个子节点。
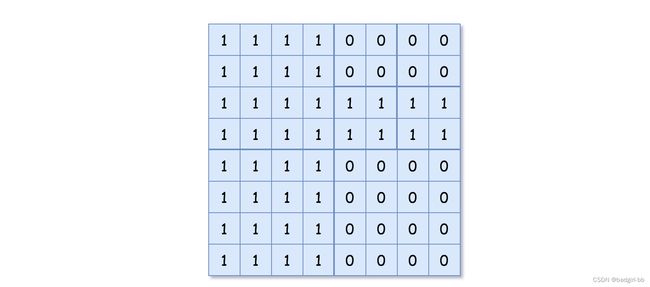
【输入样例】grid = [[1,1,1,1,0,0,0,0],[1,1,1,1,0,0,0,0],[1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1],[1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1],[1,1,1,1,0,0,0,0],[1,1,1,1,0,0,0,0],[1,1,1,1,0,0,0,0],[1,1,1,1,0,0,0,0]]
【输出样例】[[0,1],[1,1],[0,1],[1,1],[1,0],null,null,null,null,[1,0],[1,0],[1,1],[1,1]]
解题思路:
1. 使用递归函数判断区域(r0,r1,c0,c1)内的值是否为全0或全1,如果是,这一部分为叶子节点,构造出节点后return,因为叶节点不需要再遍历;如果不是,构造一个非叶节点,之后将其划分为四个子区域,行的分界线是(r0+r1)/2,列的分界线是(c0+c1)/2,继续调用递归函数判断。
class Solution {
public Node construct(int[][] grid) {
return findLeaf(grid, 0, grid.length, 0, grid.length);
}
public Node findLeaf(int[][] grid, int r0, int r1, int c0, int c1){
boolean same = true;
for(int i=r0; i < r1; i++){
for(int j=c0; j< c1; j++){
if(grid[i][j] != grid[r0][c0]){
//不是叶子节点,直接跳出就可以了,只能跳出j循环
same = false;
break;
}
}
//跳出i循环
if(!same){
break;
}
}
if(same){
//叶子节点,构造,return
return new Node(grid[r0][c0] == 1,true);
}
Node ret = new Node(
true,//值默认给true
false,//不是叶子节点
findLeaf(grid, r0, (r0+r1)/2, c0, (c0+c1)/2),
findLeaf(grid, r0, (r0+r1)/2, (c0+c1)/2, c1),
findLeaf(grid, (r0+r1)/2, r1, c0, (c0+c1)/2),
findLeaf(grid, (r0+r1)/2, r1, (c0+c1)/2, c1)
);
return ret;
}
}
/*
// Definition for a QuadTree node.
class Node {
public boolean val;
public boolean isLeaf;
public Node topLeft;
public Node topRight;
public Node bottomLeft;
public Node bottomRight;
public Node() {
this.val = false;
this.isLeaf = false;
this.topLeft = null;
this.topRight = null;
this.bottomLeft = null;
this.bottomRight = null;
}
public Node(boolean val, boolean isLeaf) {
this.val = val;
this.isLeaf = isLeaf;
this.topLeft = null;
this.topRight = null;
this.bottomLeft = null;
this.bottomRight = null;
}
public Node(boolean val, boolean isLeaf, Node topLeft, Node topRight, Node bottomLeft, Node bottomRight) {
this.val = val;
this.isLeaf = isLeaf;
this.topLeft = topLeft;
this.topRight = topRight;
this.bottomLeft = bottomLeft;
this.bottomRight = bottomRight;
}
};
*/时间: 击败了100.00%
内存: 击败了26.98%
23.合并K个升序链表
题意:
给你一个链表数组,每个链表都已经按升序排列。
请你将所有链表合并到一个升序链表中,返回合并后的链表。
【输入样例】lists = [[1,4,5],[1,3,4],[2,6]]
【输出样例】[1,1,2,3,4,4,5,6]
解题思路:
使用排序算法即可,这边我们使用自顶向下归并排序。
1.每次找到链表数组中点,将链表数组拆分成两个子链表数组。
2.分别对两个子链表数组进行排序
3. 将两个排序后的子链表数组合并,得到完成的排列后的链表。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists) {
return mergeLists(lists, 0, lists.length-1);
}
public ListNode mergeLists(ListNode[] lists, int start, int end){
if(start == end){
return lists[start];
}
if(start > end){
return null;
}
int mid = (start + end) / 2;
return merge(mergeLists(lists, start, mid), mergeLists(lists, mid+1, end));
}
public ListNode merge(ListNode a, ListNode b){
if( a== null || b == null){
return a != null ? a : b;
}
ListNode head = new ListNode(0);
ListNode tail = head, temp1 = a, temp2 = b;
while(temp1 != null && temp2 != null){
if(temp1.val <= temp2.val){
tail.next = temp1;
temp1 = temp1.next;
}else{
tail.next = temp2;
temp2 = temp2.next;
}
tail = tail.next;
}
tail.next = (temp1 != null ? temp1 : temp2);
return head.next;
}
}时间: 击败了100.00%
内存: 击败了57.58%