java 容器 set_从零开始的Java容器学习(九):Set系列
前言
前面学了List,Map,现在来学Set。在存储元素时,List允许重复,如果不允许重复时就要使用Set了,在jdk中提供的Set实现是利用Map中Key不可重复,将Set的value作为Map的Key来存储实现的。那么既然底层是Map,key有了那value存什么呢?且看下文分析
Set系列容器的简要介绍
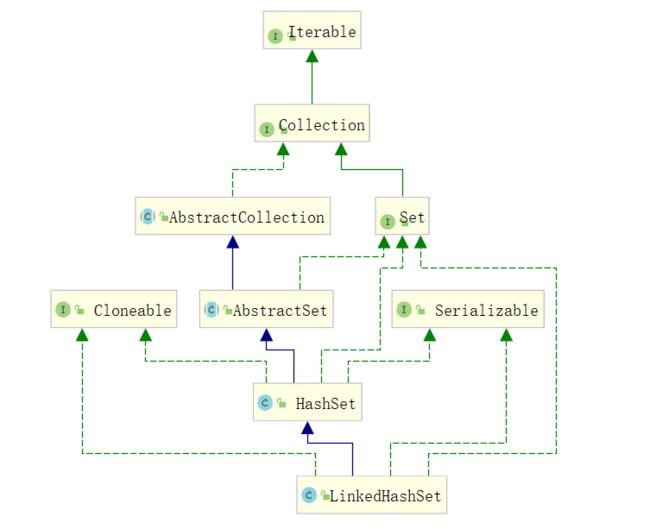
HashSet继承自AbstractSet,实现了Cloneable、Set、Serializable接口,LinkedHashSet继承自HashSet,同样实现了父类实现的接口。
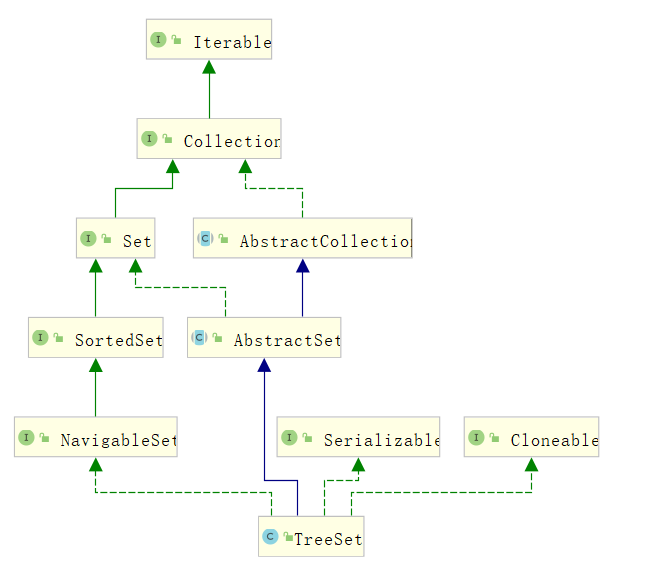
TreeSet继承自AbstractSet,实现了NavigableSet、Serializable、Cloneable接口。
从源码分析
成员变量
//HashSet
private transient HashMap map;
private static final Object PRESENT = new Object();
//TreeSet
private transient NavigableMap m;
private static final Object PRESENT = new Object();
//PRESENT:Dummy value to associate with an Object in the backing Map
//即一个用来和底层Map关联的Object哑值
复制代码
构造方法
//HashSet
public HashSet(){
map = new HashMap<>();
}
public HashSet(Collection extends E> c){
map = new HashMap<>(Math.max((int) (c.size()/.75f) + 1, 16));
addAll(c);
}
//LinkedHashSet
public LinkedHashSet(){
super(16, .75f, true);
}
HashSet(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor, boolean dummy) {
map = new LinkedHashMap<>(initialCapacity, loadFactor);
}
//TreeSet
public TreeSet(){
this(new TreeMap());
}
public TreeSet(Comparator super E> comparator){//比较器
this(new TreeMap<>(comparator));
}
public TreeSet(Collection extends E> c){
this();
addAll(c);
}
public TreeSet(SortedSet s){
this(s.comparator());
addAll(s);
}
复制代码
添加
public boolean add(E e){
return map.put(e, PRESENT)==null;
}
//Set的add都是调用底层Map的put,key用来存e,value是个哑值
复制代码
删除
public boolean remove(Object o){
return map.remove(o)==PRESENT;
}
//remove也是直接调用map的remove
复制代码
查询
//TreeSet
public E first(){ return m.firstKey(); }//获取第一个元素
public E last(){ return m.lastKey(); }//获取最后一个元素
//还有lower、floor、ceiling、higher等方法来获取TreeSet内的元素
复制代码
遍历
//HaseSet
public Iterator iterator(){
return map.keySet().iterator();
}
//TreeSet
public Iterator iterator(){
return m.navigableKeySet().iterator();
}
//获取子集,默认是含头不含尾,如果是没有两个boolean的重载方法
public NavigableSet subSet(E fromElement, boolean fromInclusive,
E toElement, boolean toInclusive){
return new TreeSet<>(m.subMap(fromElement, fromInclusive,
toElement, toInclusive));
}
复制代码
总结
这次学了HashSet、LinkedHashSet、TreeSet,经过源码的阅读可以解决一开始提出的问题,value实际是个哑值,一个用来和底层Map关联的Object哑值。下面简单区分下它们:
HashSet:无序,允许null,底层是HashMap(数组+链表、红黑树),非线程安全。
LinkedHashSet:迭代有序,允许null,底层是HashMap+双向链表,非线程安全。
TreeSet:有序,不允许null,底层是TreeMap(红黑树),非线程安全。