JAVAEE初阶相关内容第八弹--多线程(初阶)
本文目录
阻塞队列
阻塞队列是什么?
标准库中的阻塞队列
生产者消费者模型
阻塞队列的实现
普通队列实现:
入队列:
出队列:
完整代码:
加阻塞
加锁
加阻塞
阻塞队列
队列:先进先出,实际上还有一些特殊的队列,不一定非得遵守先进先出。
例如:优先级队列。PriorityQueue
阻塞队列也是特殊的队列,虽然也是先进先出的,但是带有特殊的功能。
消息队列也是特殊的队列,相当于是在阻塞队列的基础上,加上个“消息的类型”按照制定的类别进行先进先出。
阻塞队列是什么?
阻塞队列是一种特殊的队列,也遵守“先进先出”的原则。
阻塞队列可以是一种线程安全的数据结构,并且具有以下的特征:
(1)当队列满时,继续入队列就会阻塞,直到有其他线程从队列中取走元素。
(2)当队列空的时候,继续出队列也会阻塞,直到有其他线程往队列里插入元素。
标准库中的阻塞队列
阻塞队列的一个典型的应用场景就是“生产者消费者模型”。
生产者消费者模式就是通过一个容器来解决生产者和消费者的强耦合问题。
生产者消费者彼此之间不直接通讯,而是通过阻塞队列来进行通讯,所以生产者生产完数据不需要等待消费者处理,直接扔给阻塞队列,消费者不找生产者要数据,而是直接从阻塞队列中取。
生产者消费者模型给我们带来了两个很重要的好处:
1.实现了发送方和接收方的解耦。(降低耦合的过程就叫解耦)
2.可以做到“削峰填谷”,保证了系统的稳定性。
代码实现要求:首先会使用标准库提供的阻塞队列。其次需要自己实现一个简单的阻塞队列。
Queue提供的方法有三个:
1.入队列 offer
2.出队列 poll
3.取队首元素 peek
阻塞队列主要是两个:[带有阻塞功能的]
1.入队列 put
2.出队列 take
阻塞队列代码:
public class ThreadD21 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
BlockingQueue blockingQueue = new LinkedBlockingQueue<>();
blockingQueue.put("hi");
String s = blockingQueue.take();
System.out.println(s);
}
} 生产者消费者模型
public class ThreadD22 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BlockingQueue blockingQueue = new LinkedBlockingQueue<>();
//创建两个线程
//消费者线程
Thread customer = new Thread(() ->{
while (true){
try {
Integer result = blockingQueue.take();
System.out.println("消费元素" +result);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
});
customer.start();
Thread producer = new Thread(() ->{
int count = 0;
while(true){
try {
blockingQueue.put(count);
System.out.println("生产元素 " + count);
count++;
Thread.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
});
producer.start();
}
}
运行代码结果:
阻塞队列的实现
普通队列实现:
实现阻塞队列,首先要实现普通队列,构建一个类,名为MyBlockingQueue1,在这个类中写出入队列和出队列的两个操作。
首先定义四个变量。定义一个数组,数组的长度,队首标记和队尾标记。
private int[] items= new int[1000];
private int tail = 0;
private int head = 0;
private int size = 0;入队列:
传值进入,进行条件判断
如果元素个数与数组的长度相同,这时队满,没空插入新元素,进行返回。
将想入队列的元素赋值给尾标记的位置,将尾标记向后加加指向后一个元素。
如果尾标记指向的位置大于或者等于数组的长度,则将尾标记置为0。
最后数组进行size++操作。
迷糊点:items.length与size的区别!一个是系统就给这个数组分配了这么多的存储空间,而size是实际上数组这里存储的长度。
还要注意tali++的位置!
//入队列操作
public void put(int value){
if(size == items.length){
return;
}
items[tail] = value;
tail ++;
if(tail >= items.length ){
tail = 0;
}
size++;
}出队列:
首先进行判断,假如队列为空,size等于0,则不能出队列,返回。
如果头标记的位置大于等于整个数组的长度,则需要将头标记位记为0.
进行修改,设置一个变量result,将头标记指向的元素存到result中,返回。
head标记为进行向后挪动,数组里真正的元素少1所以进行size--操作。
注意代码执行的位置!!
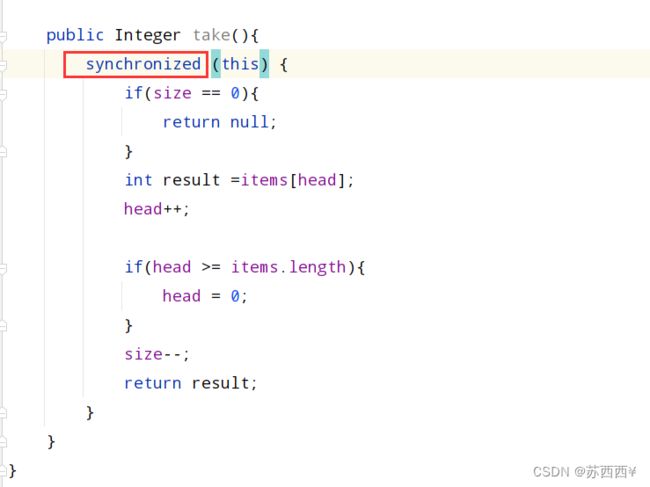
//出队列操作
public Integer take(){
if(size == 0){
return null;
}
int result =items[head];
head++;
if(head >= items.length){
head = 0;
}
size--;
return result;
}完整代码:
在主函数中需要注意的点:
拿出元素queue.take()
放入元素queue.put(value)
class MyBlockingQueue1{
private int[] items= new int[1000];
private int tail = 0;
private int head = 0;
private int size = 0;
//入队列
public void put(int value){
if(size == items.length){
return;
}
items[tail] = value;
tail ++;
if(tail >= items.length ){
tail = 0;
}
size++;
}
//出队列
public Integer take(){
if(size == 0){
return null;
}
int result =items[head];
head++;
if(head >= items.length){
head = 0;
}
size--;
return result;
}
}
public class ThreadD23 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
MyBlockingQueue queue = new MyBlockingQueue();
queue.put(1);
queue.put(2);
queue.put(3);
queue.put(4);
int result = queue.take();
System.out.println("result = "+result);
result = queue.take();
System.out.println("result = "+result);
result = queue.take();
System.out.println("result = "+result);
result = queue.take();
System.out.println("result = "+result);
}
}加阻塞
需要注意的是,这里加阻塞功能就以为着程序是要在多线程条件下。要想实现阻塞功能,首先要保证需要实现线程安全。
加锁
首先为了保证线程安全,就需要将代码上锁,如图:
加阻塞
自己版本的阻塞队列最终版代码实现:
class MyBlockingQueue1{
private int[] items= new int[1000];
private int tail = 0;
private int head = 0;
private int size = 0;
//入队列
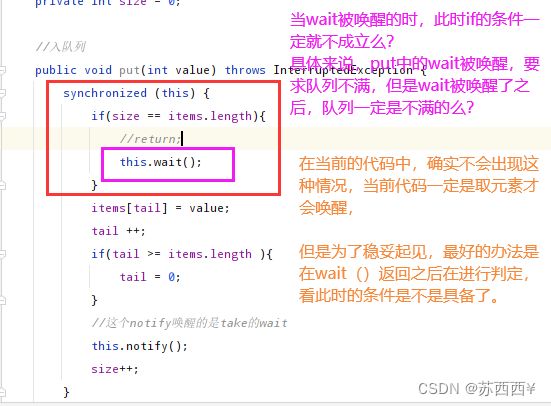
public void put(int value) throws InterruptedException {
synchronized (this) {
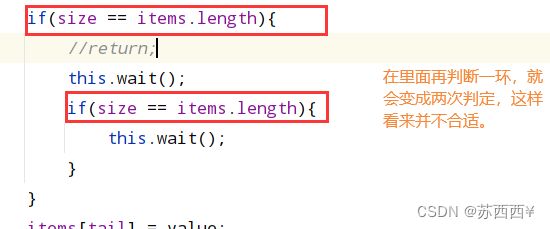
while(size == items.length){
//return;
this.wait();
}
items[tail] = value;
tail ++;
if(tail >= items.length ){
tail = 0;
}
//这个notify唤醒的是take的wait
this.notify();
size++;
}
}
//出队列
public Integer take() throws InterruptedException {
int result = 0;
synchronized (this) {
while(size == 0){
// return null;
this.wait();
}
result =items[head];
head++;
if(head >= items.length){
head = 0;
}
size--;
//唤醒put中的wait;
this.notify();
}
return result;
}
}
public class ThreadD23 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
MyBlockingQueue queue = new MyBlockingQueue();
queue.put(1);
queue.put(2);
queue.put(3);
queue.put(4);
int result = queue.take();
System.out.println("result = "+result);
result = queue.take();
System.out.println("result = "+result);
result = queue.take();
System.out.println("result = "+result);
result = queue.take();
System.out.println("result = "+result);
}
}