Spring 家族框架常用注解
反射相关
@Target
Spring核心注解,指定自定义注解MyAnno可以应用到的java类型,从而提供编译时的类型检查和错误检测
指定类型时用枚举类ElementType下的具体枚举值,包括:
ElementType.TYPE:表示MyAnno适用于类、接口、枚举。
ElementType.FIELD:表示MyAnno适用于字段(成员变量)。
ElementType.METHOD:表示MyAnno适用于方法。
ElementType.PARAMETER:表示MyAnno适用于方法参数。
ElementType.CONSTRUCTOR:表示MyAnno适用适用于构造函数。
ElementType.LOCAL_VARIABLE:表示MyAnno适用于局部变量。
ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE:表示MyAnno适用于注解类型。
ElementType.PACKAGE:表示MyAnno适用于包。
@Retention
指定自定义注解MyAnno的在何时保留,有三种保留策略:
- RetentionPolicy.SOURCE:源代码级别保留。这种保留策略表示注解仅在源代码中可见,编译器在编译时会丢弃这些注解,不会包含在编译后的字节码中。这种注解主要用于提供编译时检查和警告,不会对运行时产生任何影响。
- RetentionPolicy.CLASS:类级别保留。这种保留策略表示注解会被保留到编译后的字节码中,但在运行时不可访问。这是默认的保留策略,如果在注解上未显式指定保留策略,则默认为 CLASS。这种注解可以用于编译时处理,例如使用反射来处理注解。
- RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME:运行时级别保留。这种保留策略表示注解会被保留到编译后的字节码中,并在运行时可以通过反射机制访问和使用。这种注解可以在运行时用于执行某些操作,例如配置、依赖注入、动态代理等。
示例
定义自定义注解MyAnno
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface MyAnnotation {
// 注解的成员声明
// ...
}
使用自定义注解MyAnno
@MyAnnotation(value=")
public class Person extends xxx implements xxx{}
启动类相关
通用
@ComponentScan
注解 @ComponentScan 是 Spring 框架中的一个核心注解,用于告诉 Spring 在哪些包下扫描组件,并将其注册到应用程序的上下文中。它可以应用于配置类(带有 @Configuration 注解的类)或启动类(带有 @SpringBootApplication 注解的类)。
@ComponentScan 提供了以下几种用法:
- 扫描指定包:
可以使用@ComponentScan注解的value或basePackages属性来指定要扫描的包。可以将一个或多个包名作为参数传递给这些属性,如下所示:
@ComponentScan(value = "com.example.package")
// 或
@ComponentScan(basePackages = {"com.example.package1", "com.example.package2"})
这将使 Spring 扫描指定的包及其子包,并注册所有的组件(带有 @Component 注解及其派生注解,如 @Controller、@Service、@Repository 等)。
- 扫描指定类所在的包:
除了直接指定包名,还可以使用@ComponentScan注解的basePackageClasses属性来指定一个或多个类,Spring 将扫描这些类所在的包。例如:
@ComponentScan(basePackageClasses = {MyController.class, MyService.class})
这将扫描 MyController 和 MyService 类所在的包及其子包。
- 自动检测并注册组件:
@ComponentScan注解默认会自动检测并注册带有@Component及其派生注解的组件。如果需要自动检测并注册其他类型的组件,可以使用includeFilters属性。例如,要自动注册带有@Controller和@Repository注解的组件,可以这样配置:
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "com.example.package", includeFilters = {
@ComponentScan.Filter(type = FilterType.ANNOTATION, classes = {Controller.class, Repository.class})
})
通过 type 属性设置过滤器类型为 FilterType.ANNOTATION,并指定要包含的注解类型。
- 排除特定组件:
如果想要排除特定类型的组件,可以使用excludeFilters属性。例如,要排除带有@Configuration注解的组件,可以这样配置:
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "com.example.package", excludeFilters = {
@ComponentScan.Filter(type = FilterType.ANNOTATION, classes = Configuration.class)
})
通过 type 属性设置过滤器类型为 FilterType.ANNOTATION,并指定要排除的注解类型。
以上是 @ComponentScan 注解的常见用法。它可以帮助 Spring 自动扫描和注册组件,使得我们可以方便地使用依赖注入和其他 Spring 特性来开发应用程序。
Spring Cloud 相关
@EnableDiscoveryClient
是 Spring Cloud 中的一个注解,用于启用服务发现客户端功能。它通常与服务注册中心(如 Eureka、Consul、Zookeeper 等)一起使用,以便将应用程序注册到服务注册中心并发现其他服务。
使用 @EnableDiscoveryClient 注解时,需要确保项目中已添加适当的服务发现客户端依赖,例如 spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client(对于 Eureka)或 spring-cloud-starter-consul-discovery(对于 Consul)。
使用 @EnableDiscoveryClient 的基本用法如下:
import org.springframework.cloud.client.discovery.EnableDiscoveryClient;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableDiscoveryClient
public class YourApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(YourApplication.class, args);
}
}
通过在 Spring Boot 应用程序的启动类上添加 @EnableDiscoveryClient 注解,应用程序将被标记为一个服务发现客户端。它会自动与配置的服务注册中心进行交互,并将应用程序的实例注册到注册中心。同时,它还会从注册中心获取其他服务的信息,以便在需要时进行服务调用。
请注意,@EnableDiscoveryClient 注解是 Spring Cloud 通用的服务发现注解,提供了与多个服务注册中心的集成能力。如果只需要与特定的服务注册中心集成,还可以使用更具体的注解,例如 @EnableEurekaClient(Eureka 注册中心)或 @EnableConsulClient(Consul 注册中心)。
使用 @EnableDiscoveryClient 注解后,你就可以在应用程序中使用服务发现的功能,例如通过服务名称进行服务调用、动态获取服务实例列表等。具体的使用方法会根据具体的服务注册中心和 Spring Cloud 组件而有所不同,你可以根据所选的注册中心和相关文档进行配置和使用。
@EnableFeignClients
@EnableFeignClients 是 Spring Cloud 中的一个注解,用于启用 Feign 客户端功能,而无需手动编写 HTTP 请求和处理响应。Feign 是一个声明式的 HTTP 客户端,可以简化服务间的 RESTful API 调用。
使用 @EnableFeignClients 注解时,需要确保项目中已添加适当的 Feign 依赖,例如 spring-cloud-starter-openfeign。
基本用法
import org.springframework.cloud.openfeign.EnableFeignClients;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableFeignClients
public class YourApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(YourApplication.class, args);
}
}
通过在 Spring Boot 应用程序的启动类上添加 @EnableFeignClients 注解,应用程序将被标记为使用 Feign 客户端。它会自动扫描指定的包,查找带有 @FeignClient 注解的接口,并生成对应的代理类。
接下来,你需要创建一个使用 @FeignClient 注解标记的接口,该注解指定了要调用的目标服务的名称或 URL。例如:
import org.springframework.cloud.openfeign.FeignClient;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
@FeignClient(name = "your-service")
public interface YourServiceClient {
@GetMapping("/api/resource")
String getResource();
}
在上述示例中,@FeignClient 注解的 name 属性指定了要调用的服务的名称。YourServiceClient 接口中的方法定义了要调用的具体 API。
现在,你可以将 YourServiceClient 接口注入到其他组件中,并使用它来调用目标服务的 API。Feign 会自动处理请求和响应的序列化、反序列化,并使用负载均衡等功能。
请注意,@EnableFeignClients 注解需要与其他 Spring Cloud 组件(如服务注册中心)一起使用,以便在 Feign 客户端中实现服务发现和负载均衡等功能。你需要根据具体的需求和配置,进行适当的配置和集成。
请求相关
@PathVariable
在 Spring MVC 中,@PathVariable 注解可以用于处理 RESTful 风格的 URL,其中 URL 的一部分包含可变的路径参数。通过使用 @PathVariable 注解,你可以将这些路径参数提取出来,并将它们传递给控制器方法进行处理。
@GetMapping("/users/{id}")
public ResponseEntity<User> getUserById(@PathVariable Long id) {
// 根据 id 查询用户
User user = userService.getUserById(id);
if (user != null) {
return ResponseEntity.ok(user);
} else {
return ResponseEntity.notFound().build();
}
}
@Data
用于自动实现类对象变量的set和get方法,类对象变量适用于包装类, 非基础数据类和非泛型类,如Integer, String, 自定义的ClassA
使用
- IDEA安装【lombok】plugin
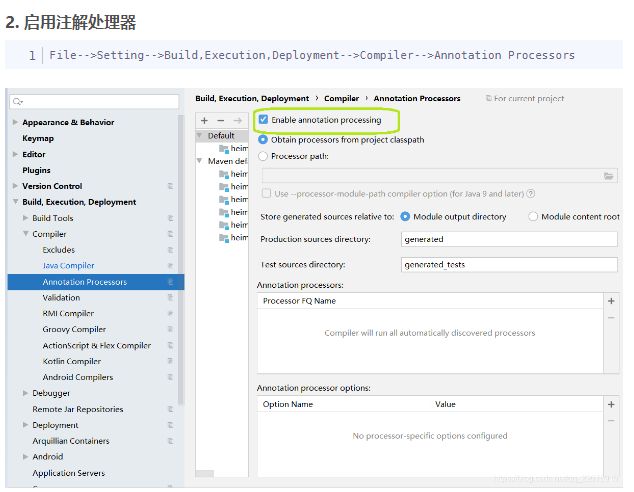
- IDEA Settings中打开注解处理器
- 在pom.xml中引入lombok依赖
org.projectlombok
lombok
true
- 在需要自动i实现类对象变量的set和get方法的类声明体上添加@Data
@Data
@ApiModel(value = "全局统一返回结果")
public class Result {
@ApiModelProperty(value = "返回码")
private int resultCode;
...
}