linux早期内存管理:memblock完全介绍
内核版本
4.19.114
背景
linux启动阶段,在伙伴系统初始化之前,也是需要动态内存分配的,比如dts、sparse_vmemmap、页表等,称早期内存管理,early mem manger。此阶段采用简单的内存管理器,有bootmem和memblock,bootmem是早期内核采用。4.x以后内核内核采用memblock,配置了NO_BOOTMEM宏。
实现
memblock内存分配采用first match算法。刚开始,内存是一整个大块,随着内存分配被切成,多个小块。内存分配查找的方向可以是从高到低,也可以是从低到高。内存管理的区域是从linux代码段数据段等的结束到低端内存最高地址。
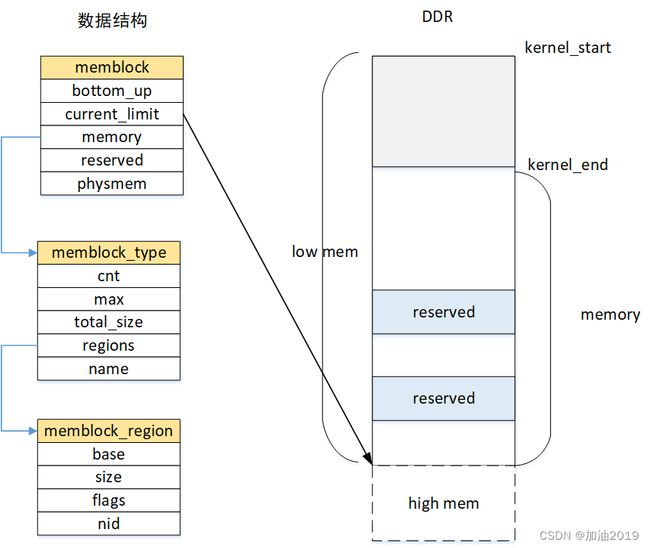
数据结构
管理结构
全局context
struct memblock {
bool bottom_up; /* is bottom up direction? */
phys_addr_t current_limit;
struct memblock_type memory;
struct memblock_type reserved;
#ifdef CONFIG_HAVE_MEMBLOCK_PHYS_MAP
struct memblock_type physmem;
#endif
};
bottom_up: 内存分配的方向:从高到低,还是从低到高。
current_limit:最大内存地址。
memblock_type: 内存区域的类型。有memory和reserve、physmem。
-
memory 可管理的总内存区域
-
reserve: 已分配的内存区域
-
physmem: 物理映射内存区域,固定映射的内存。
struct memblock_type {
unsigned long cnt;
unsigned long max;
phys_addr_t total_size;
struct memblock_region *regions;
char *name;
};
memblock_type 形容内存区域
-
regions 内存块的描述,数组串起来。
-
cnt:当前内存块的个数
-
max: 最大内存块限制。
-
total_size: 内存区域的总大小。
memblock_region: 形容内存块
- base: 起始地址
- size:大小
- flags:分配的flag
- nid: NUMA架构的nid信息。
struct memblock_region {
phys_addr_t base;
phys_addr_t size;
enum memblock_flags flags;
#ifdef CONFIG_HAVE_MEMBLOCK_NODE_MAP
int nid;
#endif
};
memblock_flags的取值。
enum memblock_flags {
MEMBLOCK_NONE = 0x0, /* No special request */
MEMBLOCK_HOTPLUG = 0x1, /* hotpluggable region */
MEMBLOCK_MIRROR = 0x2, /* mirrored region */
MEMBLOCK_NOMAP = 0x4, /* don't add to kernel direct mapping */
};
管理结构都是全局静态数据,分配在BSS段中。
struct memblock memblock __initdata_memblock = {
.memory.regions = memblock_memory_init_regions,
.memory.cnt = 1, /* empty dummy entry */
.memory.max = INIT_MEMBLOCK_REGIONS,
.memory.name = "memory",
.reserved.regions = memblock_reserved_init_regions,
.reserved.cnt = 1, /* empty dummy entry */
.reserved.max = INIT_MEMBLOCK_REGIONS,
.reserved.name = "reserved",
#ifdef CONFIG_HAVE_MEMBLOCK_PHYS_MAP
.physmem.regions = memblock_physmem_init_regions,
.physmem.cnt = 1, /* empty dummy entry */
.physmem.max = INIT_PHYSMEM_REGIONS,
.physmem.name = "physmem",
#endif
.bottom_up = false,
.current_limit = MEMBLOCK_ALLOC_ANYWHERE,
};
regions的管理结构,也是提前预分配的静态数组。INIT_MEMBLOCK_REGIONS值为128,每个区域最大支持128个内存块(region)。
static struct memblock_region memblock_memory_init_regions[INIT_MEMBLOCK_REGIONS] __initdata_memblock;
static struct memblock_region memblock_reserved_init_regions[INIT_MEMBLOCK_REGIONS] __initdata_memblock;
#ifdef CONFIG_HAVE_MEMBLOCK_PHYS_MAP
static struct memblock_region memblock_physmem_init_regions[INIT_PHYSMEM_REGIONS] __initdata_memblock;
#endif
数据结构图
API
- memblock_add:将内存区域加入memblock可管理的内存区域,即memory的region队列。
int memblock_add(phys_addr_t base, phys_addr_t size);
- memblock_remove:从可管理的内存区域中去掉一些内存。
int memblock_remove(phys_addr_t base, phys_addr_t size);
- memblock_alloc:分配内存
phys_addr_t memblock_alloc(phys_addr_t size, phys_addr_t align);
- memblock_free:释放内存,释放时进行响铃内存块合并。
int memblock_free(phys_addr_t base, phys_addr_t size);
- memblock_reserve:将内存区域加入reserved链表
int memblock_reserve(phys_addr_t base, phys_addr_t size);
初始化
memblock如何初始化可管理的内存区域,可以通过2种方式
- bootargs
- dts
bootargs方式
通过linux的启动参数bootargs,传递内存大小,初始化memblock。
early_mem-> arm_add_memory->memblock_add
bootargs的格式
mem=size@start
bootargs的解析
static int __init early_mem(char *p)
{
static int usermem __initdata = 0;
u64 size;
u64 start;
char *endp;
/*
* If the user specifies memory size, we
* blow away any automatically generated
* size.
*/
if (usermem == 0) {
usermem = 1;
memblock_remove(memblock_start_of_DRAM(),
memblock_end_of_DRAM() - memblock_start_of_DRAM());
}
start = PHYS_OFFSET;
size = memparse(p, &endp);
if (*endp == '@')
start = memparse(endp + 1, NULL);
arm_add_memory(start, size);
return 0;
}
early_param("mem", early_mem);
fdt方式
需要打开宏CONFIG_OF_EARLY_FLATTREE。
调用链:
early_init_dt_scan_memory->early_init_dt_add_memory_arch-> memblock_add
dts的解析的代码在
解析dts的memory节点。
另外说明下,dts中的“reserved-memory"节点的解析过程:
early_init_fdt_scan_reserved_mem->\__fdt_scan_reserved_mem ->__reserved_mem_reserve_reg-> early_init_dt_reserve_memory_arch
此reserved-memory不会加入到memblock的reserved节点,而是直接就从memblock的可管理区域去掉了。
内核等代码段的reserved
setup_arch-> arm_memblock_init
void __init arm_memblock_init(const struct machine_desc *mdesc)
{
/* Register the kernel text, kernel data and initrd with memblock. */
memblock_reserve(__pa(KERNEL_START), KERNEL_END - KERNEL_START);
arm_initrd_init();
arm_mm_memblock_reserve();
/* reserve any platform specific memblock areas */
if (mdesc->reserve)
mdesc->reserve();
early_init_fdt_reserve_self();
early_init_fdt_scan_reserved_mem();
/* reserve memory for DMA contiguous allocations */
dma_contiguous_reserve(arm_dma_limit);
arm_memblock_steal_permitted = false;
memblock_dump_all();
}
reserved的内存:
- 内核代码段等各段段区域
- fdt使用区域。
alloc
早期内存分配的API为early_alloc
early_alloc->early_alloc_aligned->memblock_alloc
内存分配过程,调用链:
memblock_alloc->memblock_alloc_base->__memblock_alloc_base->memblock_alloc_base_nid->memblock_alloc_range_nid
/*找到在memory中,但是不在reserved中的内存*/
->memblock_find_in_range_node
/*将内存区域加入到reserve链表*/
->memblock_reserve
1)遍历memblock的可用区域(即memory的region链表),具体区域是从kernel_end到current_limit (低端内存最高地址)。具体方向从高往低还是从低往高,由bottom_up决定。默认是从上往下分配的,bottom_up=false。
memblock_find_in_range_node函数用于查找可用内存:
phys_addr_t __init_memblock memblock_find_in_range_node(phys_addr_t size,
phys_addr_t align, phys_addr_t start,
phys_addr_t end, int nid,
enum memblock_flags flags)
{
phys_addr_t kernel_end, ret;
/* pump up @end */
if (end == MEMBLOCK_ALLOC_ACCESSIBLE)
end = memblock.current_limit;
/* avoid allocating the first page */
start = max_t(phys_addr_t, start, PAGE_SIZE);
end = max(start, end);
/*内核各段的结束地址*/
kernel_end = __pa_symbol(_end);
/*
* try bottom-up allocation only when bottom-up mode
* is set and @end is above the kernel image.
*/
if (memblock_bottom_up() && end > kernel_end) {
phys_addr_t bottom_up_start;
/* make sure we will allocate above the kernel */
bottom_up_start = max(start, kernel_end);
/* ok, try bottom-up allocation first */
ret = __memblock_find_range_bottom_up(bottom_up_start, end,
size, align, nid, flags);
if (ret)
return ret;
/*
* we always limit bottom-up allocation above the kernel,
* but top-down allocation doesn't have the limit, so
* retrying top-down allocation may succeed when bottom-up
* allocation failed.
*
* bottom-up allocation is expected to be fail very rarely,
* so we use WARN_ONCE() here to see the stack trace if
* fail happens.
*/
WARN_ONCE(IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_MEMORY_HOTREMOVE),
"memblock: bottom-up allocation failed, memory hotremove may be affected\n");
}
return __memblock_find_range_top_down(start, end, size, align, nid,
flags);
}
current_limit默认为MEMBLOCK_ALLOC_ANYWHERE,即0xFFFFFFFF,在adjust_lowmem_bounds中设置最大限制,即低端内存。
void __init adjust_lowmem_bounds(void)
{
phys_addr_t memblock_limit = 0;
u64 vmalloc_limit;
struct memblock_region *reg;
phys_addr_t lowmem_limit = 0;
/*
* Let's use our own (unoptimized) equivalent of __pa() that is
* not affected by wrap-arounds when sizeof(phys_addr_t) == 4.
* The result is used as the upper bound on physical memory address
* and may itself be outside the valid range for which phys_addr_t
* and therefore __pa() is defined.
*/
vmalloc_limit = (u64)(uintptr_t)vmalloc_min - PAGE_OFFSET + PHYS_OFFSET;
/*
* The first usable region must be PMD aligned. Mark its start
* as MEMBLOCK_NOMAP if it isn't
*/
for_each_memblock(memory, reg) {
if (!memblock_is_nomap(reg)) {
if (!IS_ALIGNED(reg->base, PMD_SIZE)) {
phys_addr_t len;
len = round_up(reg->base, PMD_SIZE) - reg->base;
memblock_mark_nomap(reg->base, len);
}
break;
}
}
for_each_memblock(memory, reg) {
phys_addr_t block_start = reg->base;
phys_addr_t block_end = reg->base + reg->size;
if (memblock_is_nomap(reg))
continue;
if (reg->base < vmalloc_limit) {
if (block_end > lowmem_limit)
/*
* Compare as u64 to ensure vmalloc_limit does
* not get truncated. block_end should always
* fit in phys_addr_t so there should be no
* issue with assignment.
*/
lowmem_limit = min_t(u64,
vmalloc_limit,
block_end);
/*
* Find the first non-pmd-aligned page, and point
* memblock_limit at it. This relies on rounding the
* limit down to be pmd-aligned, which happens at the
* end of this function.
*
* With this algorithm, the start or end of almost any
* bank can be non-pmd-aligned. The only exception is
* that the start of the bank 0 must be section-
* aligned, since otherwise memory would need to be
* allocated when mapping the start of bank 0, which
* occurs before any free memory is mapped.
*/
if (!memblock_limit) {
if (!IS_ALIGNED(block_start, PMD_SIZE))
memblock_limit = block_start;
else if (!IS_ALIGNED(block_end, PMD_SIZE))
memblock_limit = lowmem_limit;
}
}
}
arm_lowmem_limit = lowmem_limit;
high_memory = __va(arm_lowmem_limit - 1) + 1;
if (!memblock_limit)
memblock_limit = arm_lowmem_limit;
/*
* Round the memblock limit down to a pmd size. This
* helps to ensure that we will allocate memory from the
* last full pmd, which should be mapped.
*/
memblock_limit = round_down(memblock_limit, PMD_SIZE);
if (!IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_HIGHMEM) || cache_is_vipt_aliasing()) {
if (memblock_end_of_DRAM() > arm_lowmem_limit) {
phys_addr_t end = memblock_end_of_DRAM();
pr_notice("Ignoring RAM at %pa-%pa\n",
&memblock_limit, &end);
pr_notice("Consider using a HIGHMEM enabled kernel.\n");
memblock_remove(memblock_limit, end - memblock_limit);
}
}
memblock_set_current_limit(memblock_limit);
}
以从小到大方向为例,看一下可用内存查找过程:
static phys_addr_t __init_memblock
__memblock_find_range_bottom_up(phys_addr_t start, phys_addr_t end,
phys_addr_t size, phys_addr_t align, int nid,
enum memblock_flags flags)
{
phys_addr_t this_start, this_end, cand;
u64 i;
for_each_free_mem_range(i, nid, flags, &this_start, &this_end, NULL) {
this_start = clamp(this_start, start, end);
this_end = clamp(this_end, start, end);
cand = round_up(this_start, align);
if (cand < this_end && this_end - cand >= size)
return cand;
}
return 0;
}
for_each_free_mem_range 是查找在memory中,但是没有在reserved中的内存,然后判断内存大小是否够用。
#define for_each_free_mem_range(i, nid, flags, p_start, p_end, p_nid) \
for_each_mem_range(i, &memblock.memory, &memblock.reserved, \
nid, flags, p_start, p_end, p_nid)
for_each_mem_range是遍历在type_a中,但是不在type_b中的内存。
/**
* for_each_mem_range - iterate through memblock areas from type_a and not
* included in type_b. Or just type_a if type_b is NULL.
* @i: u64 used as loop variable
* @type_a: ptr to memblock_type to iterate
* @type_b: ptr to memblock_type which excludes from the iteration
* @nid: node selector, %NUMA_NO_NODE for all nodes
* @flags: pick from blocks based on memory attributes
* @p_start: ptr to phys_addr_t for start address of the range, can be %NULL
* @p_end: ptr to phys_addr_t for end address of the range, can be %NULL
* @p_nid: ptr to int for nid of the range, can be %NULL
*/
#define for_each_mem_range(i, type_a, type_b, nid, flags, \
p_start, p_end, p_nid) \
for (i = 0, __next_mem_range(&i, nid, flags, type_a, type_b, \
p_start, p_end, p_nid); \
i != (u64)ULLONG_MAX; \
__next_mem_range(&i, nid, flags, type_a, type_b, \
p_start, p_end, p_nid))
2)找到可用内存后,加入reserved队列。
memblock_reserve函数:
int __init_memblock memblock_reserve(phys_addr_t base, phys_addr_t size)
{
phys_addr_t end = base + size - 1;
memblock_dbg("memblock_reserve: [%pa-%pa] %pF\n",
&base, &end, (void *)_RET_IP_);
return memblock_add_range(&memblock.reserved, base, size, MAX_NUMNODES, 0);
}
free
从reserved链表中移除
int __init_memblock memblock_free(phys_addr_t base, phys_addr_t size)
{
phys_addr_t end = base + size - 1;
memblock_dbg(" memblock_free: [%pa-%pa] %pF\n",
&base, &end, (void *)_RET_IP_);
kmemleak_free_part_phys(base, size);
return memblock_remove_range(&memblock.reserved, base, size);
}
memblock_remove_range:
1)memblock_isolate_range:将要释放的区域隔离出来,即若释放区域不是刚好的region对齐,而是一头一尾处在某个region中间,则新建两个region节点,把这两个头尾两个节点切割成两半,使得要释放的区域刚好占n个region。
2)memblock_remove_region:从region数组中删除对应的节点,后续的region节点前移。
static int __init_memblock memblock_remove_range(struct memblock_type *type,
phys_addr_t base, phys_addr_t size)
{
int start_rgn, end_rgn;
int i, ret;
ret = memblock_isolate_range(type, base, size, &start_rgn, &end_rgn);
if (ret)
return ret;
for (i = end_rgn - 1; i >= start_rgn; i--)
memblock_remove_region(type, i);
return 0;
}
exit
在初始化好伙伴系统后,memblock内存管理器要退出,将空闲内存加速伙伴系统管理(页框分配器
mem_init中:
-
free_unused_memmap
释放memblock的memory中的空洞内存。
-
free_all_bootmem
释放memblock未使用的内存。memory中出去resev
void __init mem_init(void)
{
#ifdef CONFIG_HAVE_TCM
/* These pointers are filled in on TCM detection */
extern u32 dtcm_end;
extern u32 itcm_end;
#endif
set_max_mapnr(pfn_to_page(max_pfn) - mem_map);
/* this will put all unused low memory onto the freelists */
free_unused_memmap();
free_all_bootmem();
#ifdef CONFIG_SA1111
/* now that our DMA memory is actually so designated, we can free it */
free_reserved_area(__va(PHYS_OFFSET), swapper_pg_dir, -1, NULL);
#endif
free_highpages();
mem_init_print_info(NULL);
#define MLK(b, t) b, t, ((t) - (b)) >> 10
#define MLM(b, t) b, t, ((t) - (b)) >> 20
#define MLK_ROUNDUP(b, t) b, t, DIV_ROUND_UP(((t) - (b)), SZ_1K)
pr_notice("Virtual kernel memory layout:\n"
" vector : 0x%08lx - 0x%08lx (%4ld kB)\n"
#ifdef CONFIG_HAVE_TCM
" DTCM : 0x%08lx - 0x%08lx (%4ld kB)\n"
" ITCM : 0x%08lx - 0x%08lx (%4ld kB)\n"
#endif
" fixmap : 0x%08lx - 0x%08lx (%4ld kB)\n"
" vmalloc : 0x%08lx - 0x%08lx (%4ld MB)\n"
" lowmem : 0x%08lx - 0x%08lx (%4ld MB)\n"
#ifdef CONFIG_HIGHMEM
" pkmap : 0x%08lx - 0x%08lx (%4ld MB)\n"
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_MODULES
" modules : 0x%08lx - 0x%08lx (%4ld MB)\n"
#endif
" .text : 0x%p" " - 0x%p" " (%4td kB)\n"
" .init : 0x%p" " - 0x%p" " (%4td kB)\n"
" .data : 0x%p" " - 0x%p" " (%4td kB)\n"
" .bss : 0x%p" " - 0x%p" " (%4td kB)\n",
MLK(VECTORS_BASE, VECTORS_BASE + PAGE_SIZE),
#ifdef CONFIG_HAVE_TCM
MLK(DTCM_OFFSET, (unsigned long) dtcm_end),
MLK(ITCM_OFFSET, (unsigned long) itcm_end),
#endif
MLK(FIXADDR_START, FIXADDR_END),
MLM(VMALLOC_START, VMALLOC_END),
MLM(PAGE_OFFSET, (unsigned long)high_memory),
#ifdef CONFIG_HIGHMEM
MLM(PKMAP_BASE, (PKMAP_BASE) + (LAST_PKMAP) *
(PAGE_SIZE)),
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_MODULES
MLM(MODULES_VADDR, MODULES_END),
#endif
MLK_ROUNDUP(_text, _etext),
MLK_ROUNDUP(__init_begin, __init_end),
MLK_ROUNDUP(_sdata, _edata),
MLK_ROUNDUP(__bss_start, __bss_stop));
#undef MLK
#undef MLM
#undef MLK_ROUNDUP
/*
* Check boundaries twice: Some fundamental inconsistencies can
* be detected at build time already.
*/
#ifdef CONFIG_MMU
BUILD_BUG_ON(TASK_SIZE > MODULES_VADDR);
BUG_ON(TASK_SIZE > MODULES_VADDR);
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_HIGHMEM
BUILD_BUG_ON(PKMAP_BASE + LAST_PKMAP * PAGE_SIZE > PAGE_OFFSET);
BUG_ON(PKMAP_BASE + LAST_PKMAP * PAGE_SIZE > PAGE_OFFSET);
#endif
}
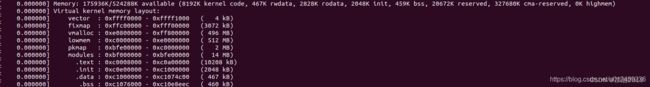
另外,mem_init中会打印启动内存信息,如:
- free_unused_memmap
遍历memblock的memory节点,释放pre_end和start之间的内存,即空洞内存。
static void __init free_unused_memmap(void)
{
unsigned long start, prev_end = 0;
struct memblock_region *reg;
/*
* This relies on each bank being in address order.
* The banks are sorted previously in bootmem_init().
*/
for_each_memblock(memory, reg) {
start = memblock_region_memory_base_pfn(reg);
#ifdef CONFIG_SPARSEMEM
/*
* Take care not to free memmap entries that don't exist
* due to SPARSEMEM sections which aren't present.
*/
start = min(start,
ALIGN(prev_end, PAGES_PER_SECTION));
#else
/*
* Align down here since the VM subsystem insists that the
* memmap entries are valid from the bank start aligned to
* MAX_ORDER_NR_PAGES.
*/
start = round_down(start, MAX_ORDER_NR_PAGES);
#endif
/*
* If we had a previous bank, and there is a space
* between the current bank and the previous, free it.
*/
if (prev_end && prev_end < start)
free_memmap(prev_end, start);
/*
* Align up here since the VM subsystem insists that the
* memmap entries are valid from the bank end aligned to
* MAX_ORDER_NR_PAGES.
*/
prev_end = ALIGN(memblock_region_memory_end_pfn(reg),
MAX_ORDER_NR_PAGES);
}
#ifdef CONFIG_SPARSEMEM
if (!IS_ALIGNED(prev_end, PAGES_PER_SECTION))
free_memmap(prev_end,
ALIGN(prev_end, PAGES_PER_SECTION));
#endif
}
- free_all_bootmem
free_all_bootmem 时遍历memory中没有reserved的,将其加入totlram_pages,归伙伴系统管理。
/**
* free_all_bootmem - release free pages to the buddy allocator
*
* Return: the number of pages actually released.
*/
unsigned long __init free_all_bootmem(void)
{
unsigned long pages;
reset_all_zones_managed_pages();
pages = free_low_memory_core_early();
totalram_pages += pages;
return pages;
}
调用链:
free_all_bootmem->free_low_memory_core_early->__free_memory_core->__free_pages_memory->__free_pages_bootmem->__free_pages_boot_core->__free_pages
page_zone(page)->managed_pages += nr_pages;
free_low_memory_core_early:
static unsigned long __init free_low_memory_core_early(void)
{
unsigned long count = 0;
phys_addr_t start, end;
u64 i;
memblock_clear_hotplug(0, -1);
for_each_reserved_mem_region(i, &start, &end)
reserve_bootmem_region(start, end);
/*
* We need to use NUMA_NO_NODE instead of NODE_DATA(0)->node_id
* because in some case like Node0 doesn't have RAM installed
* low ram will be on Node1
*/
for_each_free_mem_range(i, NUMA_NO_NODE, MEMBLOCK_NONE, &start, &end,
NULL)
count += __free_memory_core(start, end);
return count;
}
启动阶段打印的reverved内存。
mem_init_print_info:
reserved内存:(physpages - totalram_pages - totalcma_pages) << (PAGE_SHIFT - 10)。
void __init mem_init_print_info(const char *str)
{
unsigned long physpages, codesize, datasize, rosize, bss_size;
unsigned long init_code_size, init_data_size;
physpages = get_num_physpages();
codesize = _etext - _stext;
datasize = _edata - _sdata;
rosize = __end_rodata - __start_rodata;
bss_size = __bss_stop - __bss_start;
init_data_size = __init_end - __init_begin;
init_code_size = _einittext - _sinittext;
/*
* Detect special cases and adjust section sizes accordingly:
* 1) .init.* may be embedded into .data sections
* 2) .init.text.* may be out of [__init_begin, __init_end],
* please refer to arch/tile/kernel/vmlinux.lds.S.
* 3) .rodata.* may be embedded into .text or .data sections.
*/
#define adj_init_size(start, end, size, pos, adj) \
do { \
if (start <= pos && pos < end && size > adj) \
size -= adj; \
} while (0)
adj_init_size(__init_begin, __init_end, init_data_size,
_sinittext, init_code_size);
adj_init_size(_stext, _etext, codesize, _sinittext, init_code_size);
adj_init_size(_sdata, _edata, datasize, __init_begin, init_data_size);
adj_init_size(_stext, _etext, codesize, __start_rodata, rosize);
adj_init_size(_sdata, _edata, datasize, __start_rodata, rosize);
#undef adj_init_size
pr_info("Memory: %luK/%luK available (%luK kernel code, %luK rwdata, %luK rodata, %luK init, %luK bss, %luK reserved, %luK cma-reserved"
#ifdef CONFIG_HIGHMEM
", %luK highmem"
#endif
"%s%s)\n",
nr_free_pages() << (PAGE_SHIFT - 10),
physpages << (PAGE_SHIFT - 10),
codesize >> 10, datasize >> 10, rosize >> 10,
(init_data_size + init_code_size) >> 10, bss_size >> 10,
(physpages - totalram_pages - totalcma_pages) << (PAGE_SHIFT - 10),
totalcma_pages << (PAGE_SHIFT - 10),
#ifdef CONFIG_HIGHMEM
totalhigh_pages << (PAGE_SHIFT - 10),
#endif
str ? ", " : "", str ? str : "");
}
debug
-
启动阶段:打开log bootargs
memblock=debug -
debugfs
debugfs可以查看memblock的memory和reserved信息。
使用
-
zero_page
零页的分配,在paging_init调用。
-
create_mapping
-
early_pte_alloc
-
kmemleak_init
参考
https://www.iteye.com/blog/wx1568397608-2454954
https://blog.csdn.net/u012489236/article/details/106796880
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/44565320
https://www.cnblogs.com/qinglan1210/p/14779073.html