Linux 内核编译 LOCALVERSION 配置(分析内核版本号自动添加的"+"号)
1 问题发现
编译主线 kernel 版本的时候发现, 的内核版本编译成功后生成的版本号变成了 "x.y.z+", 为什么后面会多一个加号呢?
刚开始考虑是不是 CONFIG_LOCALVERSION 的问题, 配置了 CONFIG_LOCALVERSION, 还是会在内核版本的最后加上一个 "+" 后, 安装完成之后, 每次 uname -a 都会出现 + 后真的感觉很郁闷, 强迫症的我真的受不了.
2 原因分析
问题必然出现在 linux 构建过程中的版本控制这一块, 既然是在构建的过程中添加的, 那我们就可以从 Makefile 中发现一些端倪.
2.1 Makefile 中 LOCALVERSION 信息
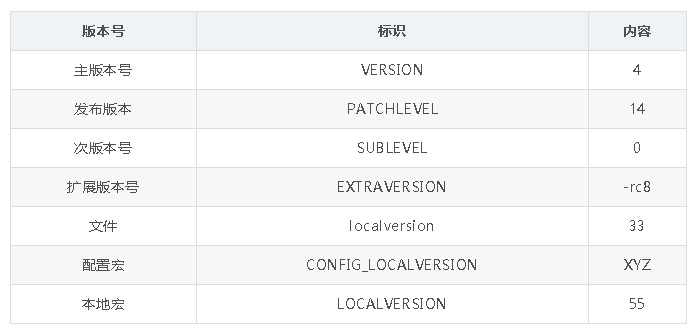
VERSION = 2
PATCHLEVEL = 6
SUBLEVEL = 35
EXTRAVERSION = .7
NAME = Yokohama
这些是我们内核版本的版本号, 生成出来的版本号理论上不应带 + 号, 但为什么带 + 号呢.
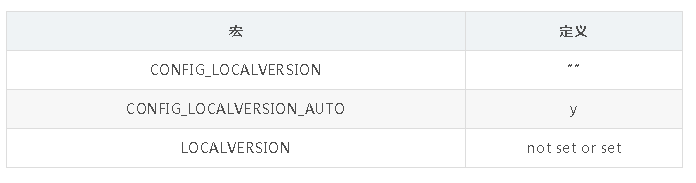
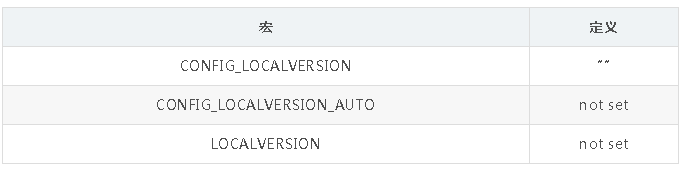
内核中有两个配置宏 CONFIG_LOCALVERSION 和 CONFIG_LOCALVERSION_AUTO 配置了系统内核版本号和后缀的信息.
2.2 Makefile 中读取和设置版本号
我们检索与这两个宏相关的信息, 检查 LOCALVERSION 宏排除 arch/*/configs 和 Documentation 等目录.
scripts/setlocalversion:# CONFIG_LOCALVERSION and LOCALVERSION (if set)
scripts/setlocalversion:res="${res}${CONFIG_LOCALVERSION}${LOCALVERSION}"
scripts/setlocalversion:if test "$CONFIG_LOCALVERSION_AUTO" = "y"; then
scripts/setlocalversion: # LOCALVERSION= is not specified
scripts/setlocalversion: if test "${LOCALVERSION+set}" != "set"; then
可以看到 scripts/setlocalversion 脚本中读取了相关的信息.
不着急, 我们慢慢分析, 看看 Makefile 是怎么读取和设置这些信息. 继续从 Makefile 中分析 LOVALVERSION 的信息.
define filechk_kernel.release
echo "$(KERNELVERSION)$$($(CONFIG_SHELL) $(srctree)/scripts/setlocalversion $(srctree))"
endef
# Store (new) KERNELRELEASE string in include/config/kernel.release
include/config/kernel.release: include/config/auto.conf FORCE
$(call filechk,kernel.release)
Makefile 使用 scripts/setlocalversion 工具来生成 include/config/kernel.release. “+” 号就是在调用这个脚本时添加的.
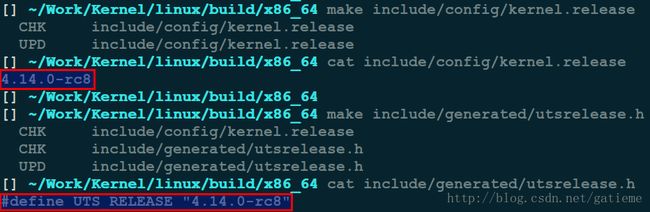
那么可以通过执行如下命令生成版本文件
make include/config/kernel.release
OR
make include/generated/utsrelease.h
查看这两个文件的信息就可以看到版本号信息
另外 Makefile 还有如下定义 :
kernelrelease:
@echo "$(KERNELVERSION)$$($(CONFIG_SHELL) $(srctree)/scripts/setlocalversion $(srctree))"
也可以直接使用如下命令来显示版本号信息
make kernelrelease
2.3 setlocalversion 函数设置版本号信息
阅读 scripts/setlocalversion 文件, 并查阅资料, 做如下笔记 :
# 如果当前内核使用SVN托管, 则只从.scmversion中读取版本号信息
if $scm_only; then
if test ! -e .scmversion; then
res=$(scm_version)
echo "$res" >.scmversion
fi
exit
fi
# 确认 auto.conf 文件是否存在
if test -e include/config/auto.conf; then
. include/config/auto.conf
else
echo "Error: kernelrelease not valid - run 'make prepare' to update it" >&2
exit 1
fi
# 调用 localversion 从源码根目录下的localversion文件中读取信息
# localversion* files in the build and source directory
res="$(collect_files localversion*)"
if test ! "$srctree" -ef .; then
res="$res$(collect_files "$srctree"/localversion*)"
fi
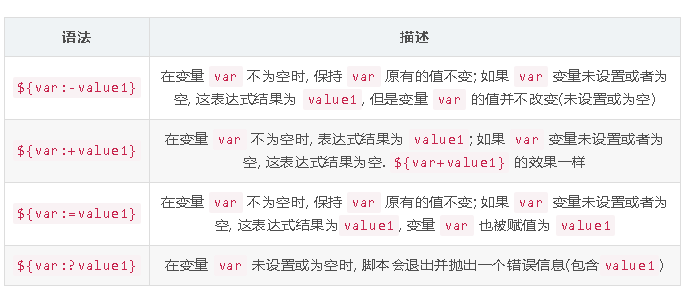
# 设置 LOCALVERSION 信息
# CONFIG_LOCALVERSION and LOCALVERSION (if set)
res="${res}${CONFIG_LOCALVERSION}${LOCALVERSION}"
# 调用 scm_version 函数读取后缀信息
# scm version string if not at a tagged commit
if test "$CONFIG_LOCALVERSION_AUTO" = "y"; then
# full scm version string
res="$res$(scm_version)"
else
# append a plus sign if the repository is not in a clean
# annotated or signed tagged state (as git describe only
# looks at signed or annotated tags - git tag -a/-s) and
# LOCALVERSION= is not specified
if test "${LOCALVERSION+set}" != "set"; then
scm=$(scm_version --short)
res="$res${scm:++}"
fi
fi
2.3.1 LOCALVERSION 的设置
在 scripts/setlocalversion 文件中还有有这么一段 :
# CONFIG_LOCALVERSION and LOCALVERSION (if set)
res="${res}${CONFIG_LOCALVERSION}${LOCALVERSION}"
可以发现如果配置了 CONFIG_LOCALVERSION 和 LOCALVERSION 则会在版本号后面意思添加此后缀.
而 res 就是获取到的本地版本号信息, 比如 4.14-rc8
2.3.2 SCM_VERSION 后缀信息的添加
最后根据是否配置了 CONFIG_LOCALVERSION_AUTO 和 CONFIG_LOCALVERSION 宏, 添加版本后缀信息
如果定义了
CONFIG_LOCALVERSION_AUTO=y
此时会执行执行
res="$res$(scm_version)"
其中 res 就是我们的版本号信息, 而 scm_version 函数获取了版本号后缀.
否则如果没有设置 CONFIG_LOCALVERSION_AUTO, 则执行如下片段.
# 调用 scm_version 函数读取后缀信息
# scm version string if not at a tagged commit
if test "$CONFIG_LOCALVERSION_AUTO" = "y"; then
# full scm version string
res="$res$(scm_version)"
else
# append a plus sign if the repository is not in a clean
# annotated or signed tagged state (as git describe only
# looks at signed or annotated tags - git tag -a/-s) and
# LOCALVERSION= is not specified
if test "${LOCALVERSION+set}" != "set"; then
scm=$(scm_version --short)
res="$res${scm:++}"
fi
fi
对于 setlocalversion 中的一个语法解释一下 :
那么上面的 shell 语句
如果
CONFIG_LOCALVERSION_AUTO = y这段程序会通过scm_version函数(不加参数)配置本地版本号.如果
CONFIG_LOCALVERSION_AUTO未被设置, 而LOVALVERSION为空, 则"${LOCALVERSION+set}" != "set", 那么调用scm_version --short会在最后添加一个+号.
原来如此, 加号是这样加上去的. 那么加号具体怎么添加上去的, 然后, scm_version 具体做了什么工作, 这些配置宏是如何影响版本号和后缀信息的, 那只有研究 scm_version 函数了.
2.3.3 版本后缀信息获取
scm_version()
{
local short
short=false
cd "$srctree"
# 如果存在 .scmversion 文件则直接获取该文件的后缀信息
if test -e .scmversion; then
cat .scmversion
return
fi
# --short 参数的设置
if test "$1" = "--short"; then
short=true
fi
# Check for git and a git repo.
# 读取 git 仓库的版本信息
# 如果 --short 被设置则直接打印 + 号
# 否则git读取版本号信息,
# 如果git tag号存在git describe | awk -F- '{printf("-%05d-%s", $(NF-1),$(NF))}'
# 否则直接打印commit号信息
if test -z "$(git rev-parse --show-cdup 2>/dev/null)" &&
head=`git rev-parse --verify --short HEAD 2>/dev/null`; then
# If we are at a tagged commit (like "v2.6.30-rc6"), we ignore
# it, because this version is defined in the top level Makefile.
if [ -z "`git describe --exact-match 2>/dev/null`" ]; then
# If only the short version is requested, don't bother
# running further git commands
if $short; then
echo "+"
return
fi
# If we are past a tagged commit (like
# "v2.6.30-rc5-302-g72357d5"), we pretty print it.
if atag="`git describe 2>/dev/null`"; then
echo "$atag" | awk -F- '{printf("-%05d-%s", $(NF-1),$(NF))}'
# If we don't have a tag at all we print -g{commitish}.
else
printf '%s%s' -g $head
fi
fi
# Is this git on svn?
if git config --get svn-remote.svn.url >/dev/null; then
printf -- '-svn%s' "`git svn find-rev $head`"
fi
# Check for uncommitted changes
# 如果有未提交的文件则会添加-dirty后缀
if git diff-index --name-only HEAD | grep -qv "^scripts/package"; then
printf '%s' -dirty
fi
# All done with git
return
fi
# Check for mercurial and a mercurial repo.
if test -d .hg && hgid=`hg id 2>/dev/null`; then
# Do we have an tagged version? If so, latesttagdistance == 1
if [ "`hg log -r . --template '{latesttagdistance}'`" == "1" ]; then
id=`hg log -r . --template '{latesttag}'`
printf '%s%s' -hg "$id"
else
tag=`printf '%s' "$hgid" | cut -d' ' -f2`
if [ -z "$tag" -o "$tag" = tip ]; then
id=`printf '%s' "$hgid" | sed 's/[+ ].*//'`
printf '%s%s' -hg "$id"
fi
fi
# Are there uncommitted changes?
# These are represented by + after the changeset id.
case "$hgid" in
*+|*+\ *) printf '%s' -dirty ;;
esac
# All done with mercurial
return
fi
# Check for svn and a svn repo.
# 获取 svn 仓库的版本号后缀信息
if rev=`LANG= LC_ALL= LC_MESSAGES=C svn info 2>/dev/null | grep '^Last Changed Rev'`; then
rev=`echo $rev | awk '{print $NF}'`
printf -- '-svn%s' "$rev"
# All done with svn
return
fi
}
用 bash 判断语句来判断
git rev-parse --verify --short
来判断当前是否是 git 版本库管理, 接着输出一个短的版本库HEAD revision 的短编码.
git rev-parse --verify --short HEAD 2>/dev/null
关键在下面这条语句的执行结果
git describe --exact-match
这一句是描述出当前的 tag 标识. 如果没有 tag 就为空, 那么整个 if 语句就为真, 就会执行下去, 下面的 echo "+", 这就会在版本号中输出一个 + 号.
如果我们在版本库中
git tag -a -m "v0.1" v0.1
然后, 我们在执行 git describe --exact-match 这一句, 发现输出的是我们的 tag 标识. 那 if 语句就不成里了, 就不会 echo "+" 了.
继续看上面的代码, 如果有未提交的代码, printf -dirty 的地方进行了 git diff 的检查, 也就是说我有修改过的, 没有上传的文件. 到此基本上原因全部查明, 我把文件进行上传后, 重新 make prepare 后, 生成的 kernel.release 果然正确.
结论, linux 对版本的管理相当严格,这也就让我们在进行代码管理中必须严格要求自己,比如发版本前,先检查是否还有修改为上传的文件,然后要在git版本库中打一个tag。
如果代码属于 git 管理
打了
tag, 则会添加tag相关字符-
如果
tag只是简单的标记, 比如4.14-rc8则跳过, 因为这些信息已经从前面makefile中获取到了如果
tag还有其他后缀标记, 比如v2.6.30-rc5-302-g72357d5, 则将这些打印出来
没有打
tag, 则会添加log字符
例如最新的commit是commit cdebe039ded3e7fcd00c6e5603a878b14d7e564e
则编译之后文件 include/config/kernel.release 的内容为 4.14.0-rc8-gcdebe03按照从之前传递的参数过来
如果没有定义了
CONFIG_LOCALVERSION_AUTO和LOCALVERSION, scm_version 函数会传递过去--short参数版本号后面会添加"+"号.if $short; then echo "+" return fi
2.4 总结
2.4.1 版本号的设置
脚本 script/setlocalversion 中读取了版本号的信息
# localversion* files in the build and source directory
res="$(collect_files localversion*)"
if test ! "$srctree" -ef .; then
res="$res$(collect_files "$srctree"/localversion*)"
fi
# CONFIG_LOCALVERSION and LOCALVERSION (if set)
res="${res}${CONFIG_LOCALVERSION}${LOCALVERSION}"
由此可看出, 如果想往版本号里添加字符, 有几种方式 :
使用
LOCALVERSION变量(或者在命令行, 或者添加为环境变量)在内核源代码根目录下添加文件
localversion文件内容会自动添加到版本号里去. 在本地创建 文件中添加定义
CONFIG_LOCALVERSION变量往版本号里添加字符的方式
LOCALVERSION 变量可在命令行定义 :
make LOCALVERSION=.44 include/config/kernel.release
或者添加为环境变量
export LOCALVERSION=.44
make include/config/kernel.release
当前内核版本为 4.14.0-rc8, 如果源码根目录下有文件 localversion(其内容为 .33), 也使用了 LOCALVERSION变量(make 时指定), 也定义了CONFIG_LOCALVERSION=".XYZ".
make LOCALVERSION=.44 include/config/kernel.release
此时对 4.14-rc8 的内核, include/config/kernel.release 的内容为 4.14-rc8.33.XYZ.55.
可看到添加的三种字符的顺序
文件 localversion 内容在前, 然后是 CONFIG_LOCALVERSION 的值, 最后是 LOCALVERSION 的值
即
2.4.2 后缀信息的获取
如果
CONFIG_LOCALVERSION_AUTO = y这段程序会通过scm_version函数(不加参数)配置本地版本号后缀信息. 后缀信息一般都是托管仓库的版本号, 比如git tag/commit等如果
CONFIG_LOCALVERSION_AUTO未被设置, 而LOVALVERSION为空, 则"${LOCALVERSION+set}" != "set", 那么调用scm_version --short会在最后添加一个+号.
另外, 关于
scripts/setlocalversion文件.在 `scripts/setlocalversion文件中,可用echo “aaa” >&2来输出显示相关信息,例如:
echo “LOCALVERSION=${LOCALVERSION}” >&2需要仔细注意
使用
modinfo可查看编译出来的ko文件对应的内核版本号
使用uname或者cat /proc/version可在目标系统上查看内核版本号.可查看
kernel编译过程生成的文件include/config/kernel.release或者include/generated/utsrelease.h, 确定编译出来的内核的版本号.
2.4.3 验证
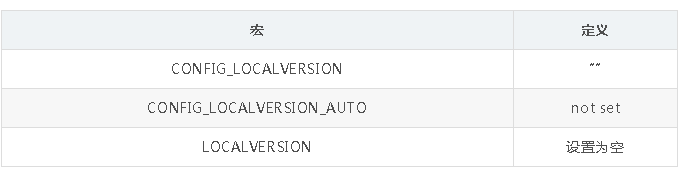
LOCALVERSION可以在版本号之后追加后缀信息, 如果再定义CONFIG_LOCALVERSION_AUTO, 将在最后进一步追加git版本号为后缀信息不定义
CONFIG_LOCALVERSION_AUTO将不显示git仓库信息, 如果此时LOCALVERSION变量定义也未定义, 将追加 “+”.
此时 scm_version –short 添加了一个 “+” 号
cat .config | grep -E "CONFIG_LOCALVERSION"
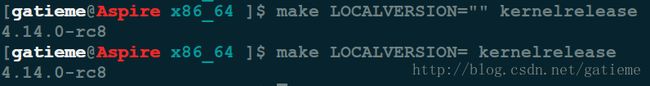
make kernelrelease
make LOCALVERSION= kernelrelease
make LOCALVERSION="" kernelrelease
此时将不会添加 “+” 号
3 解决
LOCALVERSION可以在版本号之后追加后缀信息, 如果再定义CONFIG_LOCALVERSION_AUTO, 将在最后进一步追加git版本号为后缀信息.不定义
CONFIG_LOCALVERSION_AUTO将不显示git仓库信息, 如果此时LOCALVERSION变量定义也未定义, 将追加 “+”.如果既不想添加后缀, 又不想有
"+"号 : 不定义CONFIG_LOCALVERSION_AUTO, 将LOCALVERSION变量定义为空 :LOCALVERSION=.只要定义了
LOCALVERSION, 则就不会追加 “+” 号了
4 参考资料
向 linux 内核版本号添加字符/为何有时会自动添加 + 号
向linux内核版本号添加字符/为何有时会自动添加”+”号或者”xxx-dirty”
向linux内核版本号添加字符/为何有时会自动添加“+”号
去掉linux内核版本号自动添加的“+”号
LINUX KERNEL编译生成的版本多一个加号”+”
本博文由 成坚(gatieme) 创作, 原文链接:
http://blog.csdn.net/gatieme