项目实战— pytorch搭建CNN处理MNIST数据集
项目文件夹介绍
CNN_MNIST_practice文件夹是整个项目的文件夹,里面存放了六个子文件夹以及四个 .py 程序,接下来我们分别来介绍这些文件的内容。
其中 minist_all_CPU.py 是CPU版本的模型训练+测试程序,而 minist_all_GPU.py 则是GPU版本的模型训练+测试程序。
minist_convert_png.py 是将MNIST数据集中的训练集和测试集转换为图像的程序。test_minist_nine.py 是用于测试一个手写数字 2 的程序。
pixel_show文件夹中包含了一个程序和一个 .txt 文件,该程序用于将某一个图片进行像素化展示,该文件夹中的程序名为: pixel_show.py;.txt 文件中包括了对这个要进行像素化展示的图片每个像素点的值。
model与model_GPU 两个文件夹中包括了训练好的模型,共训练了五轮。其中model文件夹中存放的是CPU版本的模型,而model_GPU文件夹存放的是GPU版本的模型。
MNIST文件夹包括了MNIST数据集所有信息,这其中也包括了转换好的图片部分。
batch_size_graph_show文件夹中包括了一个名为 batch_show.py 的程序,该程序用于绘制某一个batch_size的图像。
数据集介绍
MNIST数据集
MNIST数据集(Mixed National Institute of Standards and Technology database)是一个用来训练各种图像处理系统的二进制图像数据集,广泛应用于机器学习中的训练和测试。
MNIST数据集来自美国国家标准与技术研究所, National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST)。训练集(training set)由来自250个不同人手写的数字构成,其中50%是高中学生,50%来自人口普查局(the Census Bureau)的工作人员。测试集(test set)也是同样比例的手写数字数据,但保证了测试集和训练集的作者集不相交。
MNIST数据集一共有7万张图片,其中6万张是训练集,1万张是测试集。每张图片是28 × 28 28的 0 − 9 的手写数字图片组成。每个图片是黑底白字的形式,黑底用0表示,白字用0-1之间的浮点数表示,越接近1,颜色越白。
MNIST数据集下载地址是http://yann.lecun.com/exdb/mnist/,它包含了 4 个部分:
训练数据集:train-images-idx3-ubyte.gz (9.45 MB,包含60,000个样本)。
训练数据集标签:train-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz(28.2 KB,包含60,000个标签)。
测试数据集:t10k-images-idx3-ubyte.gz(1.57 MB ,包含10,000个样本)。
测试数据集标签:t10k-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz(4.43 KB,包含10,000个样本的标签)。
我们使用程序,将上述数据集可视化,该程序名为:mnist_convert_png.py。
# mnist_convert_png.py
import os
from skimage import io
import torchvision.datasets.mnist as mnist
root = "./MNIST/MNIST/raw"
train_set = (
mnist.read_image_file(os.path.join(root, 'train-images-idx3-ubyte')),
mnist.read_label_file(os.path.join(root, 'train-labels-idx1-ubyte'))
)
test_set = (
mnist.read_image_file(os.path.join(root, 't10k-images-idx3-ubyte')),
mnist.read_label_file(os.path.join(root, 't10k-labels-idx1-ubyte'))
)
print("training set :", train_set[0].size())
print("test set :", test_set[0].size())
def convert_to_img(train=True):
if(train):
f = open(root+'train.txt', 'w')
data_path = root+'/train/'
if(not os.path.exists(data_path)):
os.makedirs(data_path)
for i, (img, label) in enumerate(zip(train_set[0], train_set[1])):
img_path = data_path+str(i)+'.jpg'
io.imsave(img_path, img.numpy())
f.write(img_path+' '+str(label)+'\n')
f.close()
else:
f = open(root + 'test.txt', 'w')
data_path = root + '/test/'
if (not os.path.exists(data_path)):
os.makedirs(data_path)
for i, (img, label) in enumerate(zip(test_set[0], test_set[1])):
img_path = data_path + str(i) + '.jpg'
io.imsave(img_path, img.numpy())
f.write(img_path + ' ' + str(label) + '\n')
f.close()
convert_to_img(True)#转换训练集
convert_to_img(False)#转换测试集
可视化结果如下所示。可视化的所有图像存放于MNIST文件夹中的MNIST文件夹的raw文件夹中。
我们相对训练数据集中的一个batch(batch_size = 64) 进行预览,我们可以执行以下示例代码,如下示例1所示:(该程序名为:batch_show.py)
# 选取其中一个批次batch的数据进行预览
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from torchvision.datasets import MNIST
import torchvision
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
from torchvision import transforms
# 训练数据集
train_data = MNIST(root='../MNIST', train=True, download=True, transform=transforms.ToTensor())
train_loader = DataLoader(train_data, batch_size=64)
images, labels = next(iter(train_loader)) # images:Tensor(64,1,28,28)、labels:Tensor(64,)
img = torchvision.utils.make_grid(images) # 把64张图片拼接为1张图片
# pytorch网络输入图像的格式为(C, H, W),而numpy中的图像的shape为(H,W,C)。故需要变换通道才能有效输出
img = img.numpy().transpose(1, 2, 0)
# MNIST数据集的均值和方差(三分量顺序是RGB)
std = [0.5, 0.5, 0.5]
mean = [0.5, 0.5, 0.5]
img = img * std + mean
print("batch批数据:\n", labels) # 打印batch小批次数据集中的每个数字的标签
plt.imshow(img)
plt.show()
运行上述代码,得到结果为:
打印batch小批次数据集中的每个数字的真实标签。
batch批数据:
tensor([5, 0, 4, 1, 9, 2, 1, 3, 1, 4, 3, 5, 3, 6, 1, 7, 2, 8, 6, 9, 4, 0, 9, 1,
1, 2, 4, 3, 2, 7, 3, 8, 6, 9, 0, 5, 6, 0, 7, 6, 1, 8, 7, 9, 3, 9, 8, 5,
9, 3, 3, 0, 7, 4, 9, 8, 0, 9, 4, 1, 4, 4, 6, 0])我们可以对其中某一张图片进行像素化展示,如下示例2所示:(piex_show.py)
# 对其中某一个图片进行像素化展示
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from torchvision.datasets import MNIST
from torchvision import transforms
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
# 训练数据集
train_data = MNIST(root='../MNIST', train=True, download=True, transform=transforms.ToTensor())
train_loader = DataLoader(train_data, batch_size=64)
# images:Tensor(64,1,28,28)、labels:Tensor(64,)
images, labels = next(iter(train_loader)) #(1,28,28)表示该图像的 height、width、color(颜色通道,即单通道)
images = images.reshape(64, 28, 28)
img = images[0, :, :] # 取batch_size中的第一张图像
np.savetxt('img.txt', img.cpu().numpy(), fmt="%f", encoding='UTF-8') # 将像素值写入txt文件,以便查看
img = img.cpu().numpy() #转为numpy类型,方便有效输出
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(12, 12))
ax = fig.add_subplot(111)
ax.imshow(img, cmap='gray')
width, height = img.shape
thresh = img.max()/2.5
for x in range(width):
for y in range(height):
val = round(img[x][y], 2) if img[x][y] !=0 else 0
ax.annotate(str(val), xy=(y, x),
horizontalalignment='center',
verticalalignment='center',
color='white' if img[x][y] < thresh else 'black')
plt.show()
运行上述代码,得到如下图像。
代码
模型训练与测试
GPU版本
# minist_all_GPU.py
import numpy as np
import torch
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from torchvision.datasets import MNIST
from torchvision import transforms
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
from torch import nn
import torch.nn.functional as f
# 训练数据集
train_data = MNIST(root='./MNIST', train=True, download=True, transform=transforms.ToTensor())
train_loader = DataLoader(train_data, batch_size=64)
# 测试数据集
test_data = MNIST(root='./MNIST', train=False, download=True, transform=transforms.ToTensor())
test_loader = DataLoader(test_data, batch_size=64)
# 观察训练数据集、测试数据集中的图像有多少张
train_data_size = len(train_data)
test_data_size = len(test_data)
print("训练数据集的长度为:{}".format(train_data_size)) # 训练数据集的长度为:60000
print("测试数据集的长度为:{}".format(test_data_size)) # 测试数据集的长度为:10000
"""
"""
# 模型
class Model(nn.Module):
"""
编写一个卷积神经网络类
"""
def __init__(self):
""" 初始化网络,将网络需要的模块拼凑出来。 """
super(Model, self).__init__()
# 卷积层:
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 6, 5, padding=2)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(6, 16, 5, padding=2)
# 最大池化处理:
self.pooling = nn.MaxPool2d(2, 2)
# 全连接层:
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(16 * 7 * 7, 512)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(512, 10)
def forward(self, x):
"""前馈函数"""
x = f.relu(self.conv1(x)) # = [b, 6, 28, 28]
x = self.pooling(x) # = [b, 6, 14, 14]
x = f.relu(self.conv2(x)) # = [b, 16, 14, 14]
x = self.pooling(x) # = [b, 16, 7, 7]
x = x.view(x.shape[0], -1) # = [b, 16 * 7 * 7]
x = f.relu(self.fc1(x))
x = self.fc2(x)
output = f.log_softmax(x, dim=1)
return output
# CrossEntropyLoss
learn_rate = 0.01 # 学习率
model = Model() # 模型实例化
model = model.cuda() # 使用GPU
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss() # 交叉熵损失,相当于Softmax+Log+NllLoss
criterion = criterion.cuda() # 使用GPU
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(params=model.parameters(), lr=learn_rate) # 第一个参数是初始化参数值,第二个参数是学习率
# 模型训练
def train():
# 记录训练的次数 训练次数——每次训练一个batch_size(64)的图片,每轮要训练60000/64次
total_train_step = 0
batch_losses = [] # 存放每batch训练后的损失
step = [] # 损失曲线x轴的间隔
for index, data in enumerate(train_loader): # index表示data的索引 或者 for data in train_loader:
input, target = data # input为输入数据,target为标签
# 使用GPU
input = input.cuda()
target = target.cuda()
y_predict = model(input) # 模型预测
loss = criterion(y_predict, target) # 计算损失
# 优化器优化模型
optimizer.zero_grad() # 梯度清零
loss.backward() # 反向传播
optimizer.step() # 更新参数
total_train_step = total_train_step + 1
if total_train_step % 64 == 0: # 每一个batch_size打印损失
print("训练次数:{},模型训练时的损失值为:{}".format(total_train_step, loss.item()))
batch_losses.append(loss)
step.append(total_train_step)
return batch_losses, step
# 模型测试
def test():
correct = 0 # 正确预测的个数
total = 0 # 总数
with torch.no_grad(): # 测试不用计算梯度
for data in test_loader:
input, target = data
# 使用GPU
input = input.cuda()
target = target.cuda()
output = model(input) # output输出10个预测取值,其中最大的即为预测的数
probability, predict = torch.max(output.data, dim=1) # 返回一个元组,第一个为最大概率值,第二个为最大值的下标
total += target.size(0) # target是形状为(batch_size,1)的矩阵,使用size(0)取出该批的大小
correct += (predict == target).sum().item() # predict和target均为(batch_size,1)的矩阵,sum()求出相等的个数
print("模型测试时准确率为: %.2f" % (correct / total))
epoch = 5 # 训练轮数 训练轮数——每轮训练整体60000张图片,轮数越多,模型准确率越高
for i in range(epoch): # 训练和测试进行5轮
print("———————第{}轮训练开始——————".format(i + 1))
batch_losses, step = train()
# 绘制每轮训练的损失曲线
plt.plot(step, batch_losses, '.-')
plt.title('BATCH_SIZE = 64; LEARNING_RATE:0.01;epoch:{}'.format(i+1))
plt.xlabel('per 64 times')
x = np.linspace(0, 896, 15) # 0,64,128,...,896共15个
plt.xticks(x)
plt.ylabel('LOSS')
y = np.linspace(0, 3, 4) # 0,1,2,3
plt.yticks(y)
plt.show()
# 保存网络模型及优化模型
torch.save(model, "./model_GPU/model{}_GPU.pth".format(i + 1)) # 保存模型
torch.save(optimizer, "./model_GPU/optimizer{}_GPU.pth".format(i + 1))
# 模型测试
test()
CPU版本
import torch
from PIL import Image
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from torchvision.datasets import MNIST
from torchvision import transforms
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
from torch import nn
import os
import torch.nn.functional as f
# 训练数据集
train_data = MNIST(root='./MNIST', train=True, download=True, transform=transforms.ToTensor())
train_loader = DataLoader(train_data, batch_size=64)
# 测试数据集
test_data = MNIST(root='./MNIST', train=False, download=True, transform=transforms.ToTensor())
test_loader = DataLoader(test_data, batch_size=64)
# 观察训练数据集、测试数据集中的图像有多少张
train_data_size = len(train_data)
test_data_size = len(test_data)
print("训练数据集的长度为:{}".format(train_data_size)) # 训练数据集的长度为:60000
print("测试数据集的长度为:{}".format(test_data_size)) # 测试数据集的长度为:10000
# 模型
class Model(nn.Module):
"""
编写一个卷积神经网络类
"""
def __init__(self):
""" 初始化网络,将网络需要的模块拼凑出来。 """
super(Model, self).__init__()
# 卷积层:
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 6, 5, padding=2)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(6, 16, 5, padding=2)
# 最大池化处理:
self.pooling = nn.MaxPool2d(2, 2)
# 全连接层:
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(16 * 7 * 7, 512)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(512, 10)
def forward(self, x):
"""前馈函数"""
x = f.relu(self.conv1(x)) # = [b, 6, 28, 28]
x = self.pooling(x) # = [b, 6, 14, 14]
x = f.relu(self.conv2(x)) # = [b, 16, 14, 14]
x = self.pooling(x) # = [b, 16, 7, 7]
x = x.view(x.shape[0], -1) # = [b, 16 * 7 * 7]
x = f.relu(self.fc1(x))
x = self.fc2(x)
output = f.softmax(x, dim=1)
return output
# CrossEntropyLoss
learn_rate = 0.01 # 学习率
model = Model() # 模型实例化
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss() # 交叉熵损失,相当于Softmax+Log+NllLoss
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(params=model.parameters(), lr=learn_rate) # 第一个参数是初始化参数值,第二个参数是学习率
# 模型训练
def train(total_train_step):
"""
:param total_train_step: 训练的次数
"""
for index, data in enumerate(train_loader): # index表示data的索引 或者 for data in train_loader:
input, target = data # input为输入数据,target为标签
y_predict = model(input) # 模型预测
loss = criterion(y_predict, target) # 计算损失
# 优化器优化模型
optimizer.zero_grad() # 梯度清零
loss.backward() # 反向传播
optimizer.step() # 更新参数
total_train_step = total_train_step + 1
if total_train_step % 100 == 0: # 每一百次打印损失
print("训练次数:{},模型训练时的损失值为:{}" .format(total_train_step, loss.item()))
# # 加载模型
# if os.path.exists('./model/model.pkl'): # ./表示当前所在的目录 ; ../表示当前目录的上一层目录
# model.load_state_dict(torch.load("./model/model.pkl")) # 加载保存模型的参数
# 模型测试
def test():
correct = 0 # 正确预测的个数
total = 0 # 总数
with torch.no_grad(): # 测试不用计算梯度
for data in test_loader:
input, target = data
output = model(input) # output输出10个预测取值,其中最大的即为预测的数
probability, predict = torch.max(output.data, dim=1) # 返回一个元组,第一个为最大概率值,第二个为最大值的下标
total += target.size(0) # target是形状为(batch_size,1)的矩阵,使用size(0)取出该批的大小
correct += (predict == target).sum().item() # predict和target均为(batch_size,1)的矩阵,sum()求出相等的个数
print("模型测试时准确率为:%.2f" % (correct / total))
epoch = 5 # 训练轮数 训练轮数——每轮训练整体60000张图片,轮数越多,模型准确率越高
# 记录训练的次数 训练次数——每次训练一个batch_size(64)的图片,每轮要训练60000/64次
total_train_step = 0
# 记录测试的次数
total_test_step = 0
for i in range(epoch): # 训练和测试进行5轮
print("———————第{}轮训练开始——————".format(i+1))
train(total_train_step)
torch.save(model.state_dict(), "./model/model{}.pkl".format(i + 1)) # 保存模型
torch.save(optimizer.state_dict(), "./model/optimizer{}.pkl".format(i + 1))
test()
"""
每轮:
每次训练
获取一个batch_size(64)的图片及对应targets
将一个batch_size的图片送入模型
计算损失值
优化器清零梯度
利用误差反向传播
优化器优化参数
每100次
打印一次训练次数,绘制此时损失值图
达到60000/64次,一轮训练部分完成,开始测试部分
设置初始损失值=0,准确率 =0
每次测试
获取一个batch_size(64)的图片及对应targets
将图片送入网络
计算每次损失值
累计每轮损失值
计算每次准确率
累计每轮准确率
达到10000/64次,一轮测试部分完成
绘制一轮的测试损失值图,打印准确率
"""
# 自定义手写数字识别测试
def test_mydata():
image = Image.open('./test_image/test_nine.jpg') # 读取自定义手写图片
image = image.resize((28, 28)) # 裁剪尺寸为28*28
image = image.convert('L') # 转换为灰度图像
transform = transforms.ToTensor()
image = transform(image) # 对灰度图像进行transform变换,将其转换为张量形式
image = image.resize(1, 1, 28, 28) # 尺寸变换
output = model(image) # 将image送入模型进行检测
probability, predict = torch.max(output.data, dim=1)
print("此手写图片值为:%d,其最大概率为:%.2f" % (predict[0], probability[0]))
plt.title('此手写图片值为:{},预测为{}的概率为:{}%'.format((int(predict)), predict[0], 100*probability[0]), fontname="SimHei")
plt.imshow(image.squeeze())
plt.show()
print(image.shape)
test_mydata()
下述结果均基于GPU版本的代码
运行GPU版本的代码,得到下面结果:
我们发现,用第五轮训练好的模型在测试集上的准确率高达97%,说明模型还是很不错的。
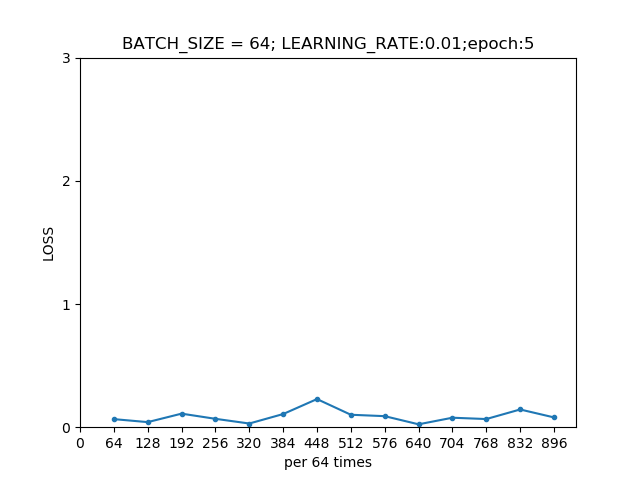
我们绘制出每一轮模型在训练集上的损失曲线。
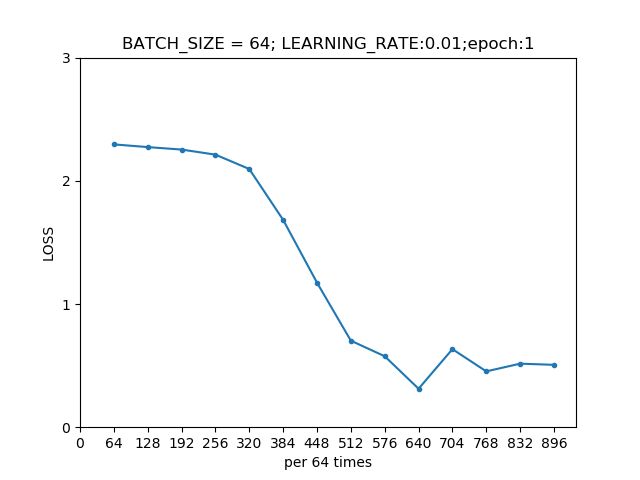 第一轮模型在训练集上的损失曲线
第一轮模型在训练集上的损失曲线 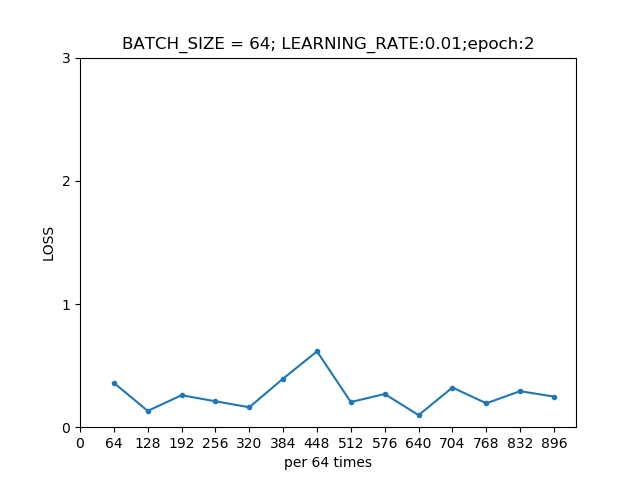 第二轮模型在训练集上的损失曲线
第二轮模型在训练集上的损失曲线 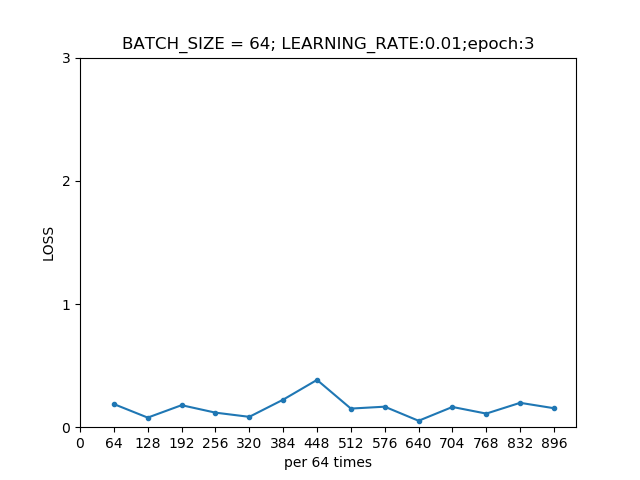 第三轮模型在训练集上的损失曲线
第三轮模型在训练集上的损失曲线 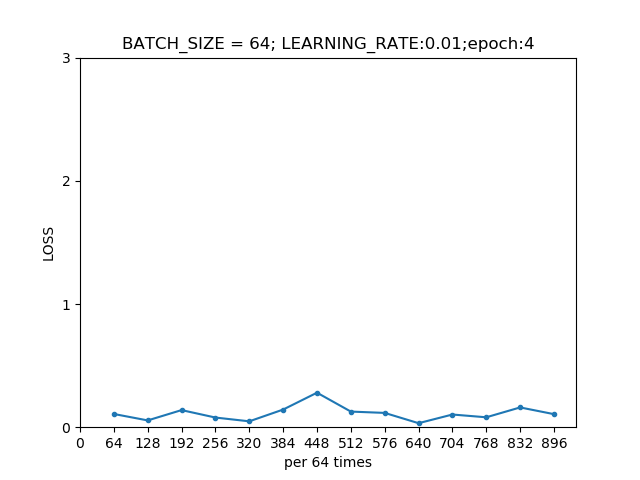 第四轮模型在训练集上的损失曲线
第四轮模型在训练集上的损失曲线
实际测试
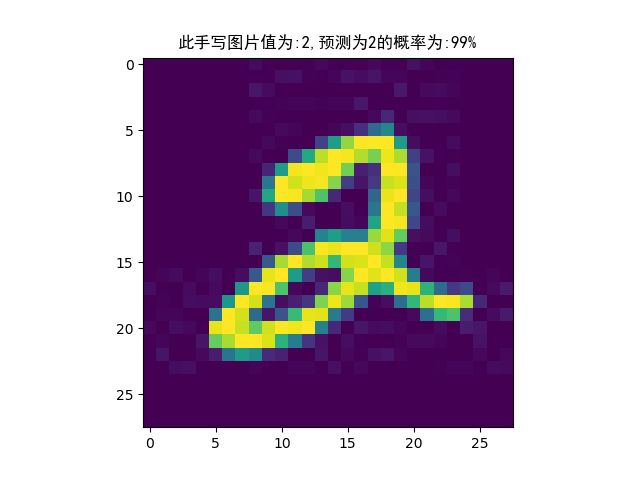
我们向训练好的第五轮模型送入我们手写的图像数据2,如下图所示。该图像保存在test_image文件夹中,命名为test_two.jpg。该图像的尺寸为28✖28像素。
我们用下述程序来检测我们向模型输入的图像数据2,如下所示 。
# test_minist_nine.py文件
from PIL import Image
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from torch import nn
import torch.nn.functional as f
from torchvision import transforms
import torch
# 模型
class Model(nn.Module):
"""
编写一个卷积神经网络类
"""
def __init__(self):
""" 初始化网络,将网络需要的模块拼凑出来。 """
super(Model, self).__init__()
# 卷积层:
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 6, 5, padding=2)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(6, 16, 5, padding=2)
# 最大池化处理:
self.pooling = nn.MaxPool2d(2, 2)
# 全连接层:
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(16 * 7 * 7, 512)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(512, 10)
def forward(self, x):
"""前馈函数"""
x = f.relu(self.conv1(x)) # = [b, 6, 28, 28]
x = self.pooling(x) # = [b, 6, 14, 14]
x = f.relu(self.conv2(x)) # = [b, 16, 14, 14]
x = self.pooling(x) # = [b, 16, 7, 7]
x = x.view(x.shape[0], -1) # = [b, 16 * 7 * 7]
x = f.relu(self.fc1(x))
x = self.fc2(x)
output = f.softmax(x, dim=1)
return output
# 加载网络模型参数
# 方式1 不需要导入模型结构
model = torch.load("./model_GPU/model5_GPU.pth", map_location=torch.device("cpu"))
# map_location=torch.device("cpu") 将GPU版本的模型对应到CPU上
# 方式2 需要导入模型结构
# model = Model()
# # model = model.load_state_dict(torch.load("./model/model5.pkl")) # 会报错
# model.load_state_dict(torch.load("./model/model5.pkl")) # 正确的加载方式
# print(model)
"""
Model(
(conv1): Conv2d(1, 6, kernel_size=(5, 5), stride=(1, 1), padding=(2, 2))
(conv2): Conv2d(6, 16, kernel_size=(5, 5), stride=(1, 1), padding=(2, 2))
(pooling): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
(fc1): Linear(in_features=784, out_features=512, bias=True)
(fc2): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=10, bias=True)
)
"""
# 自定义手写数字识别测试
def test_mydata():
image = Image.open('./test_image/test_two.jpg') # 读取自定义手写图片
image = image.resize((28, 28)) # 裁剪尺寸为28*28
image = image.convert('L') # 转换为灰度图像
transform = transforms.ToTensor()
image = transform(image) # 对灰度图像进行transform变换,将其转换为张量形式
image = image.resize(1, 1, 28, 28) # 尺寸变换
output = model(image) # 将image送入模型进行检测
proability, predict = torch.max(output.data, dim=1)
print("此手写图片值为:{},预测为{}的概率为:{}%".format(predict[0], predict[0], int(100*proability)))
plt.title('此手写图片值为:{},预测为{}的概率为:{}%'.format(int(predict), predict[0], int(100*proability)), fontname="SimHei")
plt.imshow(image.squeeze())
plt.show()
test_mydata()
打印结果为:
此手写图片值为:2,预测为2的概率为:99%预测为2的概率为99%,预测效果还是很不错的。