MySQL-DML语句
DML语句
- Create
-
- 单行插入数据
- 多行插入数据
- 插入否则更新
- replace into
- 查看受影响行数的函数
- Retrieve
-
- 全列查询
- 指定列查询
- select+函数/表达式
- 对查询出的列重命名-as
- distinct
- order by
- limit
- where 子句
- 比较运算符
- 逻辑运算符
- Update
- Delete
-
- delete
- truncate
- delete和truncate的区别
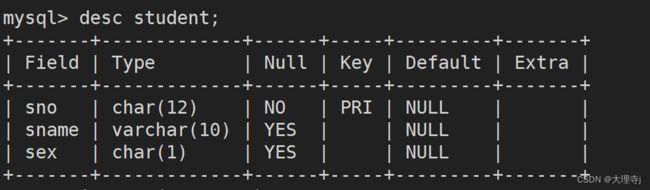
Create
单行插入数据
insert into tb_name [(要插入的属性列...)]---全列插入时可省略 values(属性值);
insert into student values('1003','李四','男');
多行插入数据
insert into ... values(),(),()...;//多条记录用分号隔开
向学生表中插入多条数据
insert into student values('1004','王五','女'),('1005','赵六','男'),('1006','田七','女');
插入否则更新
insert ... on duplicate key update 属性名 = 属性值,属性名 = 属性值...;
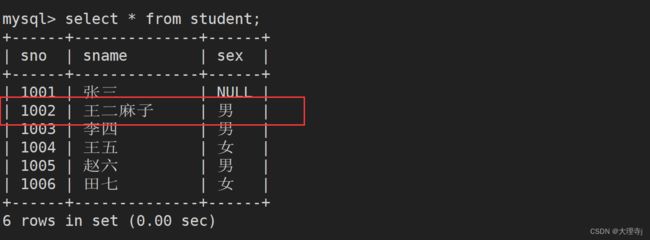
当我们插入某条记录时可能会和表中已经存在的数据发生键值冲突,此时使用上述语句当发生冲突时修改原表中冲突的语句。
![]()
insert into student values('1002','王二麻子','男') on duplicate key update sno='1002',sname='王二麻子',sex='男';
replace into
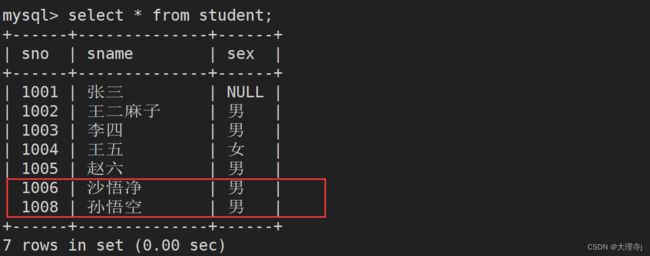
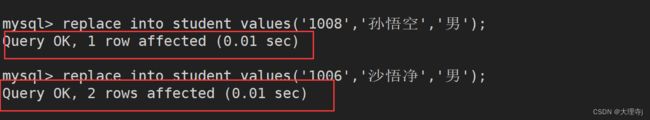
replace into的意思是,当插入记录时不发生键值冲突那就相当于普通的insert into,如果发生冲突那么就将新插入的数据替换老的数据。
replace into student values('1008','孙悟空','男');
replace into student values('1006','沙悟净','男');
插入学号为1008的数据时没有发生冲突,插入学号为1006的数据时发生了冲突并且将老数据进行了替换。
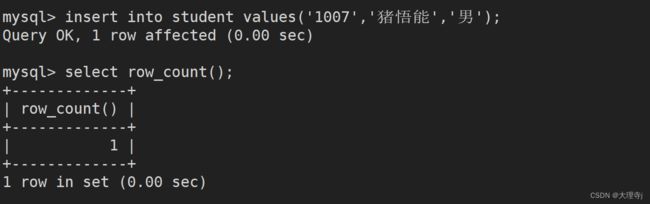
查看受影响行数的函数
在用户进行CRUD操作结束时,通常会显示此条请求影响了几行数据。
select row_count(); //也可以使用此函数查看
Retrieve
SELECT [DISTINCT] {* | {column [, column] ...}
[FROM table_name]
[WHERE ...]
[ORDER BY column [ASC | DESC], ...]
LIMIT ...
后序的查/改/删都建立在下面表结构的基础上。
create table exam(
id int primary key,
name varchar(10) not null,
chinese int,
math int,
english int);
在表中插入一些数据。
insert into exam values
(1,'张三',67,98,56),
(2,'李四',87,78,77),
(3,'王五',88,98,90),
(4,'赵六',82,84,67),
(5,'田七',55,85,45),
(6,'小明',70,73,78),
(7,'小红',75,65,30);
全列查询
select *from tb_name;
指定列查询
select col1,col2... from tb_name;
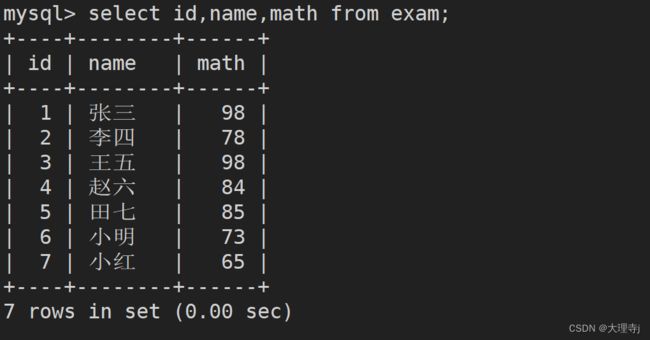
查询成绩表中的人员信息与数学成绩
select id,name,math from exam;
select+函数/表达式
select后可以跟函数调用,例如查看当前时间等。
select current_time();
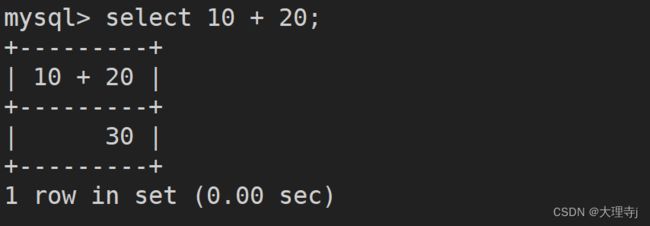
select 10 + 20;
对查询出的列重命名-as
select col1 as 名字,... ...;
查询出每个人的信息与总成绩
select id,name,chinese + math + english as total from exam;
distinct
select distinct ...; //可以对查询的结果做去重
order by
select ... order by col1 [asc | desc],col2[asc|desc],...;
//默认为asc升序排序
//desc降序排序
//可以根据多列进行排序,规则是当col1数据相同时,再根据col2数据排序...
根据学生的总成绩进行排序
select id,name,chinese + math + english as total from exam order by total desc;
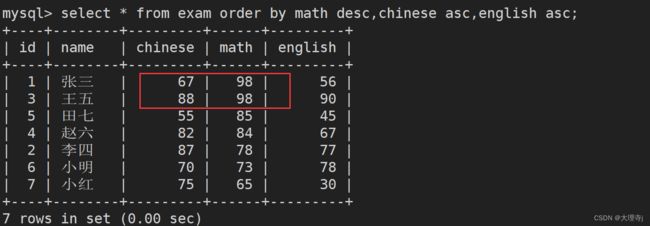
select * from exam order by math desc,chinese asc,english asc;
limit
1.limit n//显示前n行数据
2.limit s,n//从s行开始显示n行数据,行数是从第0行开始的
3.limit n offset s//显示n行数据从第s行开始显示
找出总分前三名的学生信息
select id,name,chinese + math + english as total from exam order by total desc limit 3;
//或者
select id,name,chinese + math + english as total from exam order by total desc limit 0,3;
//或者
select id,name,chinese + math + english as total from exam order by total desc limit 3 offset 0;
找出数学成绩后三名的学生信息(成绩只需显示数学成绩)
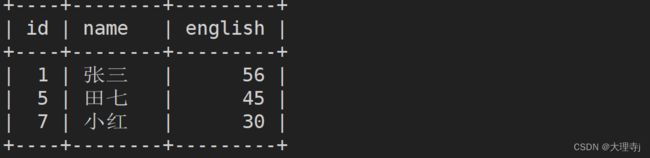
select id,name,math from exam order by math asc limit 3 offset 0;
select id,name,chinese + math + english as total from exam order by total desc limit 4 offset 1;
where 子句
where子句用于作筛选条件,筛选出符合要求的记录。
select ... where col...;
找出总分高于240分的学生信息
select id,name,chinese + math + english as total from exam where total > 240;
//错误的
注意:上面这中写法是错误的,where子句是优先于select执行的,where作为筛选条件,而select是将通过筛选条件的相关列显示出来。并且还要注意一点的是在where子句处不能对相关列作重命名。
select id,name,chinese + math + english as total from exam where chinese+math+english > 240;
比较运算符
| 运算符 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| >,>=,<.<= | 大于,大于等于,小于,小于等于 |
| = | 等于,对NULL值的比较是不安全的,例如NULL=NULL结果还是NULL |
| <=> | 等于,对NULL值的比较是安全的 |
| != | 不等于,对NULL值的比较是不安全的 |
| <> | 不等于,对NULL值的比较是安全的 |
| between a0 and a1 | 范围匹配 [a0,a1] |
| in (option…) | 如果是option中的任意一个就返回true |
| is NULL | 是NULL |
| is not NULL | 不是NULL |
| like | 模糊匹配,%表示人0个或多个字符,_表示任意一个字符 |
找出英语不及格的学生信息(成绩只包含英语成绩)
select id,name,english from exam where english < 60;
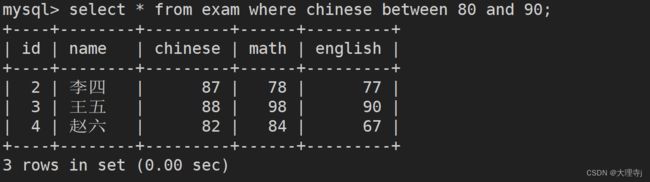
select * from exam where chinese between 80 and 90;
select * from exam where math in(98,99);
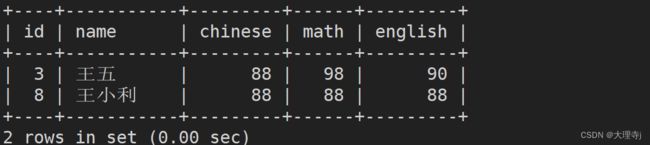
insert into exam values (8,'王小利',88,88,88); //先插入一条记录
select * from exam where name like'王_' or name like '王%';
逻辑运算符
| Column 1 | Column 2 |
|---|---|
| and | 多个条件都为true时,结果才为true |
| or | 多个条件只要满足一个结果就为true |
| not | 如果条件为true,那么结果就为false |
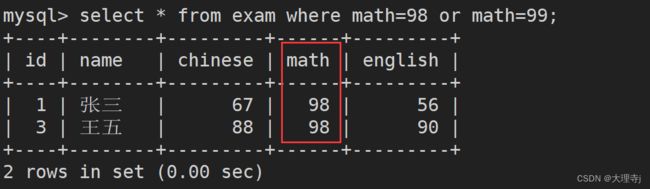
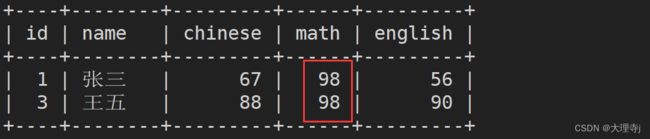
找出数学成绩为98或99的同学
select * from exam where math=98 or math=99;
Update
update tb_name set column=expr [,column=expr,column=expr,column=expr...]
[where...][order by][limit ]
将王小利同学的英语成绩改为80分
update exam set english=80 where id=8;
update exam set math=math+30 order by math+english+chinese asc limit 3 ;
Delete
为了测试新建一张新的表
create table test_delete (id int auto_increment primary key,name varchar(10));
在表中插入数据
insert into test_delete (name) values
('张三'),
('李四'),
('王五');
delete
delete from tb_name [where][order by][limit];
删除id为2的记录
delete from test_delete where id=2;
delete from test_delete;
//查看auto_increment的值
show create table test_delete\G;
truncate
truncate [table] tb_name;
重新插入数据:
insert into test_delete (name) values
('张三'),
('李四'),
('王五');
truncate table test_delete;
//查看auto_increment的值
show create table test_delete\G;
insert into test_delete (name) values('测试');
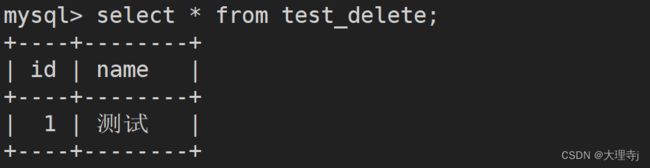
事实证明truncate清空表的数据时,auto_increment也会被清空。
delete和truncate的区别
1.delete 走事务,truncate不走事务,也就是说不会将truncate记录在日志中。
2.truncate只能整体删除表的所有数据,不能选择的删除
3.delete清除表的数据后auto_increment值不会被重置,truncate清空表的数据 auto_increment也会被重置