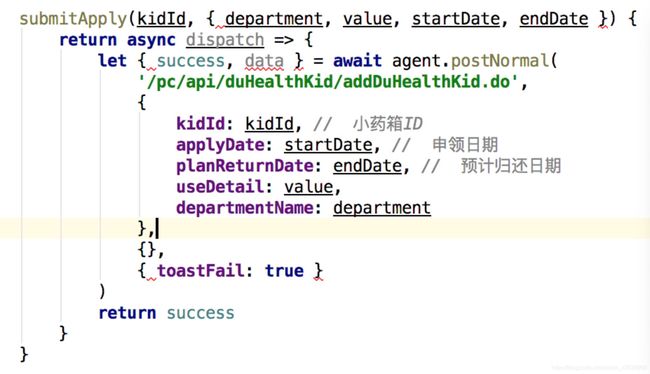
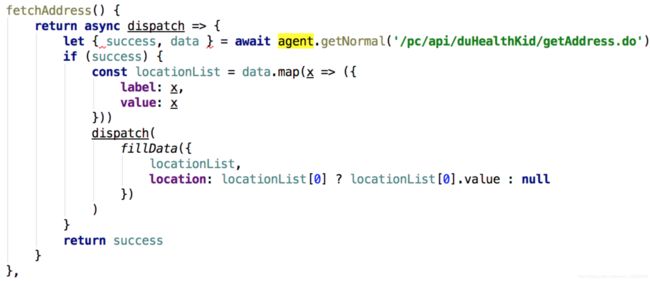
async和await的作用
词法定义
-
async
async 是“异步”的简写, async 用于申明一个异步的 function
-
await
await 可以认为是 async wait 的简写,await 用于等待一个异步方法执行完成。
特点:
- asayc的用法,它作为一个关键字放到函数前面,这样普通函数就变为了异步函数
- 异步async函数调用,跟普通函数的使用方式一样
- 异步async函数返回一个promise对象
- async函数配合await关键字使用(阻塞代码往下执行)
是异步方法,但是阻塞式的
案例
模拟出一个摇色子的异步操作,先通过一个方法三秒之后拿到一个筛子数,第二步进行输出
//基本用法的async函数
let asyncFun = async function(){
return 1
}
console.log(asyncFun())
//会返回一个promise对象
//使用场景
//摇色子方法
function dice(){
return new Promise((resolve,reject)=>{
let sino = parseInt(Math.random()*6+1) //生成一个1~6之间的随机小数
setTimeout(()=>{
resolve(sino)
},2000)
})
}
//异步方法
async function text(){
let n= await dice()
//await 关键字后面调用摇色子方法执行完毕之后,才进行变量赋值
console.log("摇出来"+n) //最后打印出摇出来的数
}
text()
async/await的优点
方便级联调用:即调用依次发生的场景;同步代码编写方式: Promise使用then函数进行链式调用,一直点点点,是一种从左向右的横向写法;async/await从上到下,顺序执行,就像写同步代码一样,更符合代码编写习惯;多个参数传递:Promise的then函数只能传递一个参数,虽然可以通过包装成对象来传递多个参数,但是会导致传递冗余信息,频繁的解析又重新组合参数,比较麻烦;async/await没有这个限制,可以当做普通的局部变量来处理,用let或者const定义的块级变量想怎么用就怎么用,想定义几个就定义几个,完全没有限制,也没有冗余工作;同步代码和异步代码可以一起编写: 使用Promise的时候最好将同步代码和异步代码放在不同的then节点中,这样结构更加清晰;async/await整个书写习惯都是同步的,不需要纠结同步和异步的区别,当然,异步过程需要包装成一个Promise对象放在await关键字后面;sync/await是对Promise的优化:async/await是基于Promise的,是进一步的一种优化,不过在写代码时,Promise本身的API出现得很少,很接近同步代码的写法;
使用场景
async主要来处理异步的操作,
需求:执行第一步,将执行第一步的结果返回给第二步使用。在ajax中先拿到一个接口的返回数据,后使用第一部返回的数据执行第二步操作的接口调用,达到异步操作。
Vue项目案例
普通案例promise:
methods: {
getLocation(phoneNum) {
return axios.post('/one接口', {
phoneNum
})
},
getFaceList(province, city) {
return axios.post('/two接口', {
province,
city
})
},
getFaceResult () {
this.getLocation(this.phoneNum).then(res => {
if (res.status === 200 && res.data.success) {
let province = res.data.obj.province;
let city = res.data.obj.city;
this.getFaceList(province, city).then(res => {
if(res.status === 200 && res.data.success) {
this.faceList = res.data.obj
}
})
}
}).catch(err => {
console.log(err)
})
}
}
这时你看到了then 的链式写法,有一点回调地域的感觉。现在我们在有async/ await 来改造一下。
async/ await案例:
首先把 getFaceResult 转化成一个async 函数,就是在其前面加async, 因为它的调用方法和普通函数的调用方法是一致,所以没有什么问题。然后就把 getLocation 和getFaceList 放到await 后面,等待执行, getFaceResult 函数修改如下:
async getFaceResult () {
let location = await this.getLocation(this.phoneNum);
if (location.data.success) {
let province = location.data.obj.province;
let city = location.data.obj.city;
let result = await this.getFaceList(province, city);
if (result.data.success) {
this.faceList = result.data.obj;
}
}
}
现在代码的书写方式,就像写同步代码一样,没有回调的感觉,非常舒服。
现在就还差一点需要说明,那就是怎么处理异常,如果请求发生异常,怎么处理? 它用的是try/catch 来捕获异常,把await 放到 try 中进行执行,如有异常,就使用catch 进行处理。
async getFaceResult () {
try {
let location = await this.getLocation(this.phoneNum);
if (location.data.success) {
let province = location.data.obj.province;
let city = location.data.obj.city;
let result = await this.getFaceList(province, city);
if (result.data.success) {
this.faceList = result.data.obj;
}
}
} catch(err) {
console.log(err);
}
}
Vue项目案例(封装)
http.js
'use strict'
import axios from 'axios'
import qs from 'qs'
axios.interceptors.request.use(config => {
// loading
return config
}, error => {
return Promise.reject(error)
})
axios.interceptors.response.use(response => {
return response
}, error => {
return Promise.resolve(error.response)
})
function checkStatus (response) {
// loading
// 如果http状态码正常,则直接返回数据
if (response && (response.status === 200 || response.status === 304 || response.status === 400)) {
return response
// 如果不需要除了data之外的数据,可以直接 return response.data
}
// 异常状态下,把错误信息返回去
return {
status: -404,
msg: '网络异常'
}
}
function checkCode (res) {
// 如果code异常(这里已经包括网络错误,服务器错误,后端抛出的错误),可以弹出一个错误提示,告诉用户
if (res.status === -404) {
alert(res.msg)
}
if (res.data && (!res.data.success)) {
alert(res.data.error_msg)
}
return res
}
export default {
post (data,url) {
return axios({
method: 'post',
url: url,
data: qs.stringify(data),
timeout: 10000,
headers: {
'X-Requested-With': 'XMLHttpRequest',
'Content-Type': 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded; charset=UTF-8'
}
}).then(
(response) => {
return checkStatus(response)
}
)
},
get (url, params) {
return axios({
method: 'get',
baseURL: 'https://cnodejs.org/api/v1',
url,
params, // get 请求时带的参数
timeout: 10000,
headers: {
'X-Requested-With': 'XMLHttpRequest'
}
}).then(
(response) => {
return checkStatus(response)
}
).then(
(res) => {
return checkCode(res)
}
)
}
}
api.js
export default {
getCode: 'http://127.0.0.1:8888/.....'
}
auth.vue
import http from '../../utils/http'
import api from '../../utils/api'
methods: {
fetchData: async function () {
var that = this
var code = Store.fetchYqm();
let params = {
inviteCode: code
}
const response = await http.post(params,api.getCode)
var resJson = response.data;
}
}