【Ansible】
Ansible
- 一.市场运行的自动化工具
- 二.Ansible概述(是一个批量操作的工具,可以自动完成多个服务的部署)
- 三.Ansible工作机制(日常模块)
- 四.ansible特点
- 五.操作Ansible案例
-
- 1.command模块
- 2.shell 模块
- 3.cron 模块
- 4.user 模块
- 5.group 模块
- 7.copy模块
- 8.file模块
- 9.hostname模块
- 10.ping模块
- 11.yum模块
- 12.script模块
- 13.setup模块
一.市场运行的自动化工具
自动化运维三剑客:pupet(ruby) saltstack(python) Ansible
chef C/S
fabric ssh
二.Ansible概述(是一个批量操作的工具,可以自动完成多个服务的部署)
基于python开发的配置管理和应用部署工具,现在也能在自动化管理领域大方异彩。
它融合了众多老牌运维工具的优点,Pubbent和Saltstack能实现的功能,Ansible基本上都可以实现。
是基于模块工作的,它只是提供了一种运行框架,本身没有完成任务的能力
三.Ansible工作机制(日常模块)
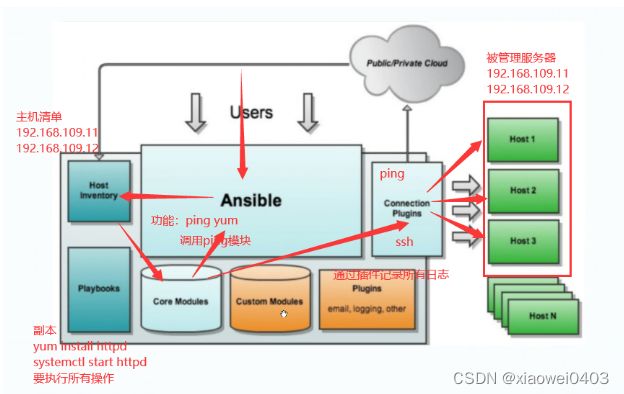
Ansible:核心程序
HostInventory:记录Ansible管理的主机信息,端口、密码、IP等
Playbooks:剧本 YMAL格式文件中,多任务定义在一个文件中,定义主机需要调用哪些模块来完成的功能
core modules:核心模块 主要操作通过调用核心模块来完成管理任务的
connection plugins:连接主机 插件,ansible 和 host (主机) 通信使用
custom Modules:自定义模块,完成核心模块无法完成的功能,支持多种语言
1.加载自己的配置文件,默认/etc/ansible/ansible.cfg
2.查找对应的主机的配置文件,找到要执行的主机或组/etc/ansible/hosts文件
3.加载自己对应的模块文件,如command、yum、ping
4.通过ansible将模块命令生成对应的临时py文件(类似python脚本),并将该文件传输至被管理端
5.传输到在被控制端的对应用户的家目录下./ansible/tmp/xxx/xxx.py
6.被控制端给传输过来的py文件加执行权限
7.执行并返回结果,执行完成后删除py文件并sleep 0退出
四.ansible特点
部署简单,只需要在主端部署ansible环境
默认使用ssh协议设备进行管理
主从集中化管理
配置简单、功能强大、扩张性强
支持API及自定义模块,可以通过python轻松扩展
通过playbooks来定制强大的配置、状态管理
对云计算平台、大数据都有很好的支持
五.操作Ansible案例
---------- ansible 环境安装部署 ----------
管理端: 192.168.10.23 ansible
被管理端: 192.168.10.14
被管理端: 192.168.10.15
管理安装ansible
yum install -y epel-release //先安装 epel 源
yum install -y ansible
//ansible 目录结构
/etc/ansible/
├── ansible.cfg #ansible的配置文件,一般无需修改
├── hosts #ansible的主机清单,用于存储需要管理的远程主机的相关信息
└── roles/ #公共角色目录
//配置主机清单
cd /etc/ansible
vim hosts
[webservers] #配置组名
192.168.10.17 #组里包含的被管理的主机IP地址或主机名(主机名需要先修改/etc/hosts文件)
[dbservers]
192.168.10.18
//配置密钥对验证
ssh-keygen -t rsa #一路回车,使用免密登录
sshpass -p 'abc1234' ssh-copy-id [email protected]
sshpass -p 'abc1234' ssh-copy-id [email protected]

ansible命令行模块
命令格式:ansible <组名> -m <模块> -a <参数列表>
ansible-doc -l #列出所有已经安装的模块,按q退出
1.command模块
//在远程主机执行命令,不支持管道,重定向等shell的特性。
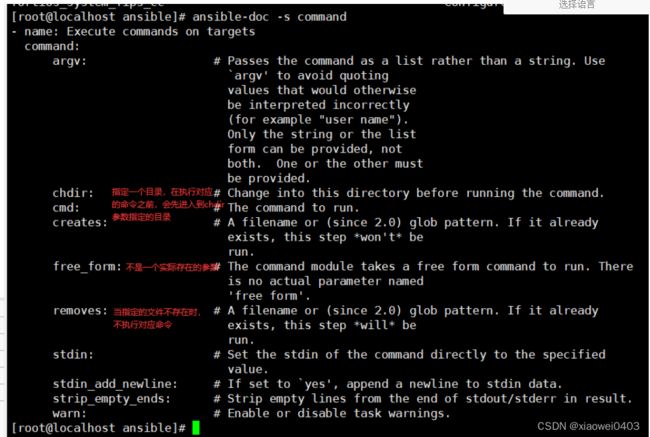
ansible-doc -s command #-s列出指定模块的描述信息和操作动作
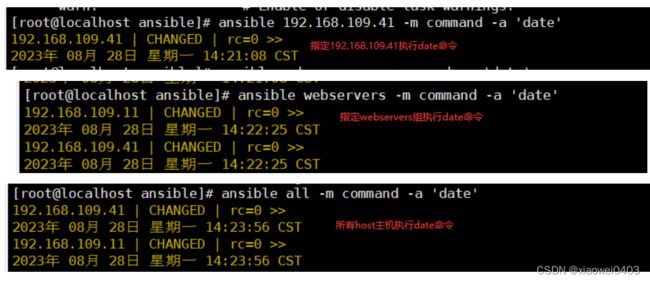
ansible 192.168.109.41 -m command -a 'date' #指定ip执行date
ansible webservers -m command -a 'date' #指定组执行 date
ansible dbservers -m command -a 'date'
ansible all -m command -a 'date' #all 代表所有 hosts 主机
ansible all -a 'ls /' #如省略 -m 模块,则默认运行 command 模块
chdir:在远程主机上运行命令前提前进入目录
creates:判断指定文件是否存在,如果存在,不执行后面的操作
removes:判断指定文件是否存在,如果存在,执行后面的操作
ansible all -m command -a "chdir=/home ls ./"
2.shell 模块
//在远程主机执行命令,相当于调用远程主机的shell进程,然后在该shell下打开一个子shell运行命令(支持管道符号等功能)
ansible-doc -s shell
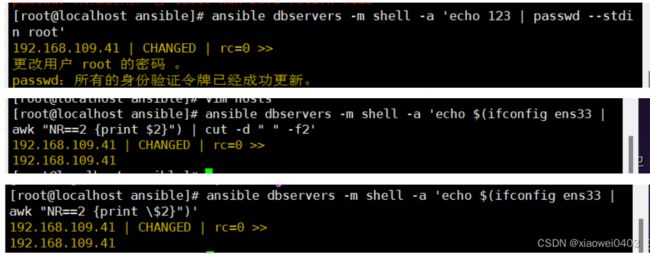
ansible dbservers -m shell -a 'echo 123456 | passwd --stdin test'
ansible dbservers -m shell -a 'echo $(ifconfig ens33 | awk "NR==2 {print $2}") | cut -d " " -f2'
ansible dbservers -m shell -a 'echo $(ifconfig ens33 | awk "NR==2 {print \$2}")'
3.cron 模块
//在远程主机定义任务计划。其中有两种状态(state):present表示添加(可以省略),absent表示移除。
ansible-doc -s cron #按 q 退出
//常用的参数:
minute/hour/day/month/weekday:分/时/日/月/周
job:任务计划要执行的命令
name:任务计划的名称
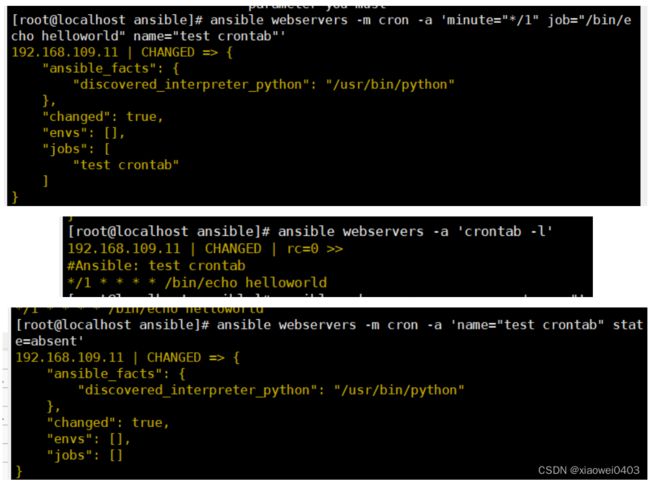
ansible webservers -m cron -a 'minute="*/1" job="/bin/echo helloworld" name="test crontab"'
ansible webservers -a 'crontab -l'
ansible webservers -m cron -a 'name="test crontab" state=absent' #移除计划任务,假如该计划任务没有取名字,name=None即可
4.user 模块
//用户管理的模块
ansible-doc -s user
//常用的参数:
name:用户名,必选参数
state=present|absent:创建账号或者删除账号,present表示创建,absent表示删除
system=yes|no:是否为系统账号
uid:用户uid
group:用户基本组
shell:默认使用的shell
move_home=yse|no:如果设置的家目录已经存在,是否将已经存在的家目录进行移动
password:用户的密码,建议使用加密后的字符串
comment:用户的注释信息
remove=yes|no:当state=absent时,是否删除用户的家目录
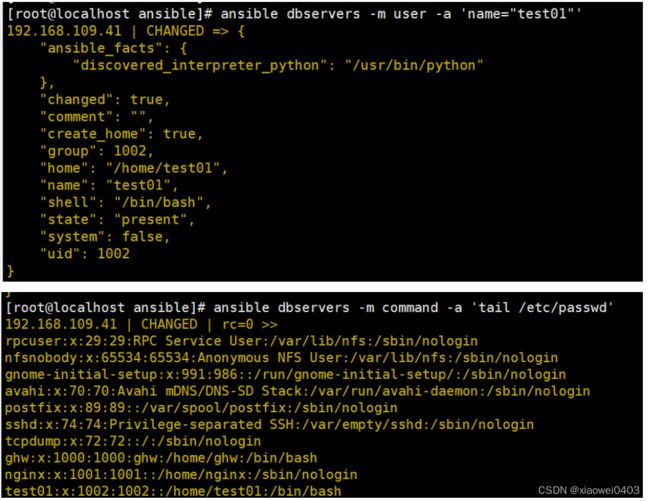
ansible dbservers -m user -a 'name="test01"' #创建用户test01
ansible dbservers -m command -a 'tail /etc/passwd'
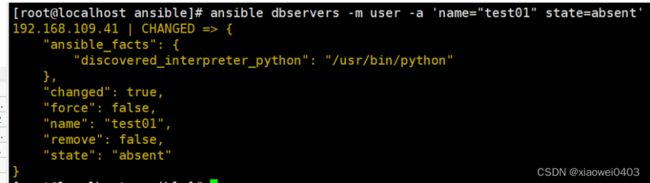
ansible dbservers -m user -a 'name="test01" state=absent' #删除用户test01
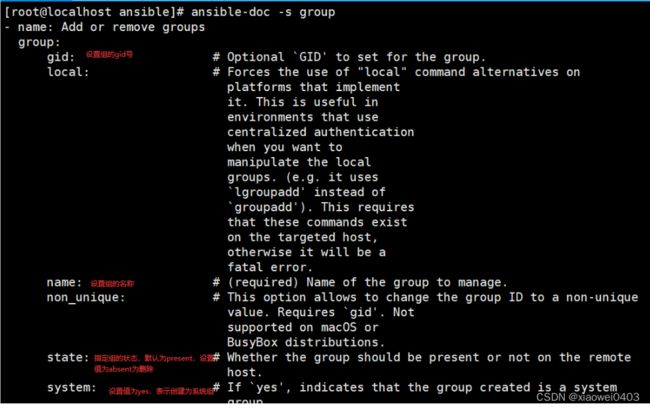
5.group 模块
//用户组管理的模块
ansible-doc -s group
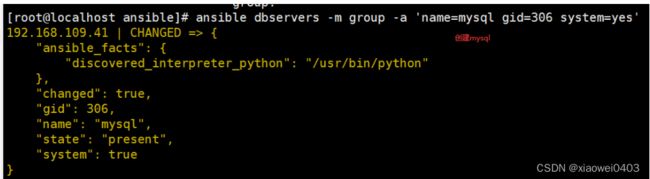
ansible dbservers -m group -a 'name=mysql gid=306 system=yes' #创建mysql组
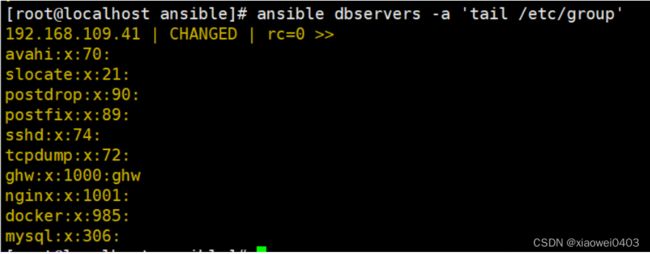
ansible dbservers -a 'tail /etc/group'
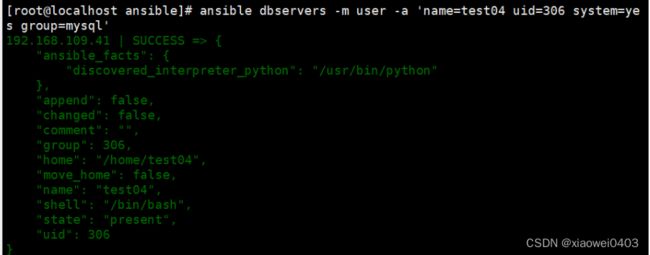
ansible dbservers -m user -a 'name=test01 uid=306 system=yes group=mysql' #将test01用户添加到mysql组中
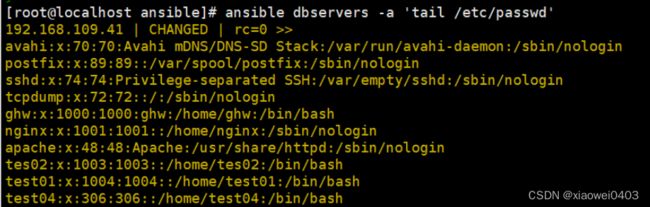
ansible dbservers -a 'tail /etc/passwd'
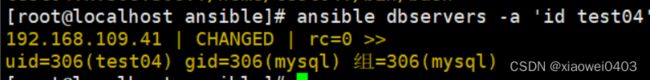
ansible dbservers -a 'id test01'
用户组管理模块
ansible-doc -s group
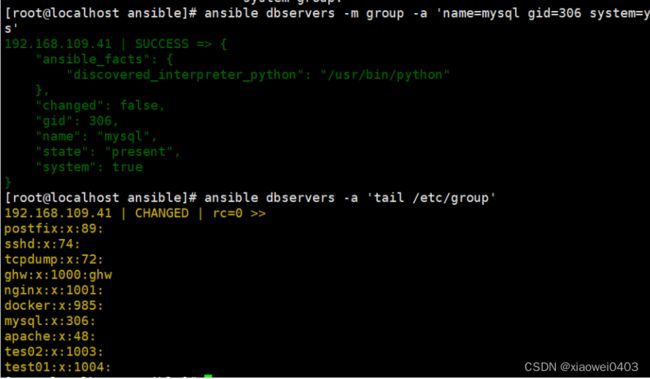
ansible dbservers -m group -a 'name=mysql gid=306 system=yes' #创建mysql组
ansible dbservers -a 'tail /etc/group'
ansible dbservers -m user -a 'name=test04 uid=306 system=yes group=mysql'将test04用户添加到mysql组中
ansible dbservers -a 'tail /etc/passwd'
ansible dbservers -a 'id test04'
7.copy模块
//用于复制指定主机文件到远程主机的
ansible-doc -s copy
常用的参数
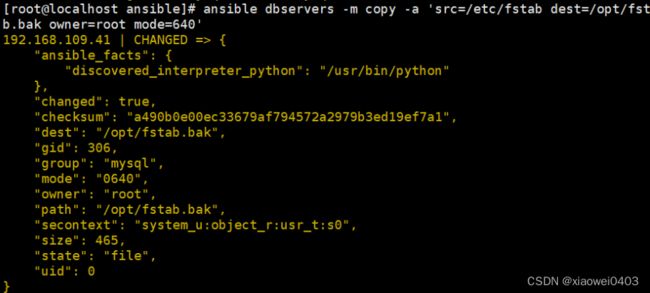
dest:指出复制文件的目标及位置,使用绝对路径,如果是源目录,指目标也要是目录,如果目标文件已经存在覆盖原有的内容
src:指出源文件的路径,可以使用相对路径或绝对路径,支持直接指定目录,如果源是目录则目标也要是目录
mode:指出复制时,目标文件的权限
owner:指出复制时,目标文件的属主
group:指出复制时,目标文件的属组
content:指出复制到目标主机上的内容,不能与src一起使用
ansible dbservers -m copy -a 'src=/etc/fstab dest=/opt/fstab.bak owner=root mode=640'
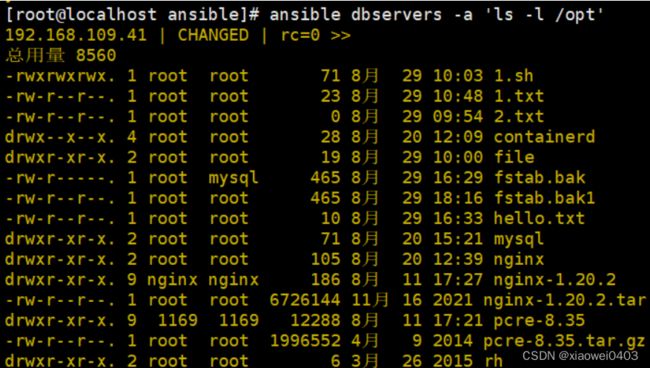
ansible dbservers -a 'ls -l /opt'
ansible dbservers -a 'cat /opt/fstab.bak'
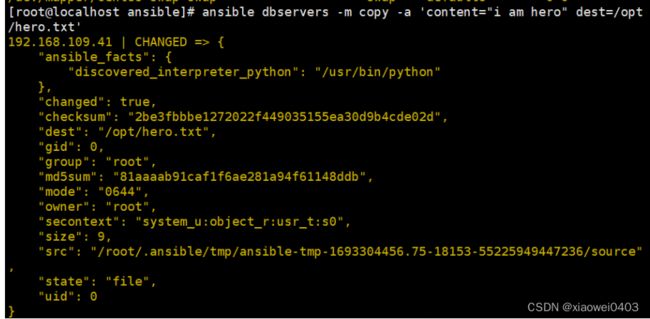
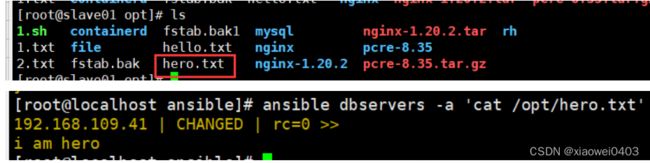
ansible dbservers -m copy -a 'content="helloworld" dest=/opt/hello.txt' #将helloworld写入/opt/hello.txt文件中
ansible dbservers -a 'cat /opt/hello.txt'
8.file模块
//设置文件属性
ansible-doc -s file
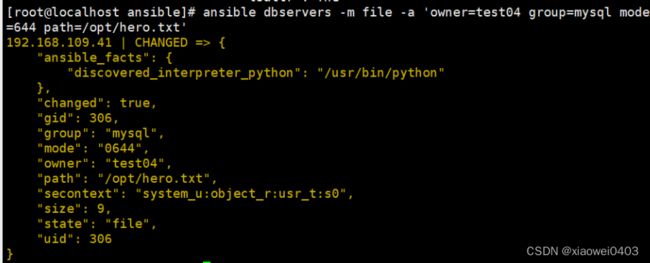
ansible dbservers -m file -a 'owner=test01 group=mysql mode=644
path=/opt/fstab.bak' #修改文件的数组权限等
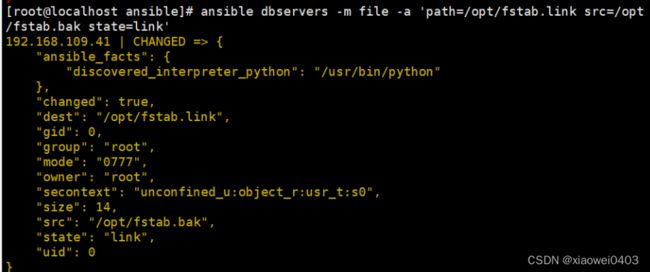
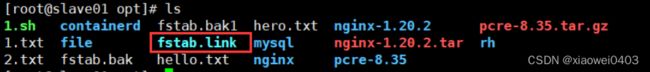
ansible dbservers -m file -a 'path=/opt/fstab.link src=/opt/fstab.bak state=link'
#设置/opt/fstab.link为/opt/fstab.bak的链接文件
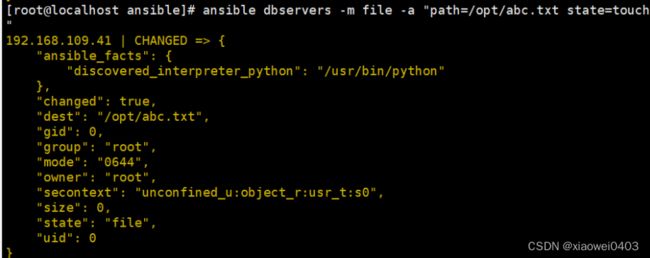
ansible dbservers -m file -a "path=/opt/abc.txt state=touch" #创建一个文件
ansible dbservers -m file -a "path=/opt/abc.txt state=absent" #删除一个文件
9.hostname模块
//用于管理远程主机上的主机名
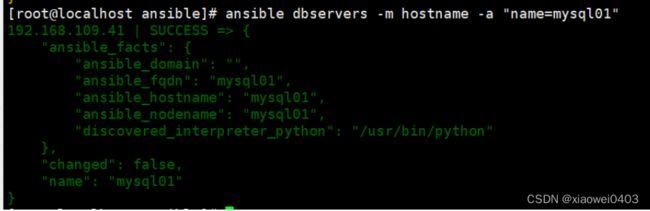
ansible dbservers -m hostname -a "name=mysql01"
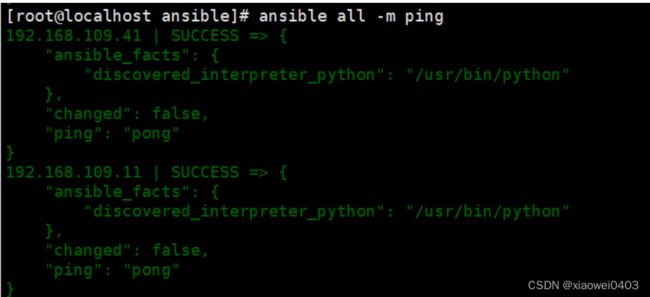
10.ping模块
//检测远程主机的联通性
ansible all -m ping
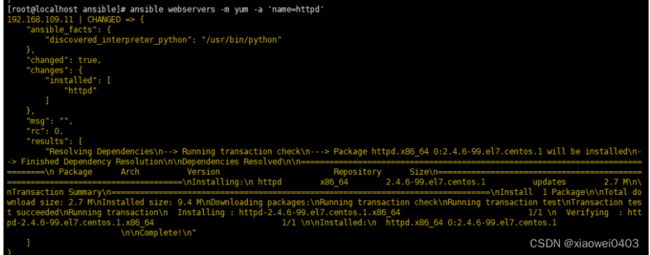
11.yum模块
//在远程主机上安装与卸载软件包
ansible-doc -s yum
ansible webservers -m yum -a 'name=httpd' #安装服务
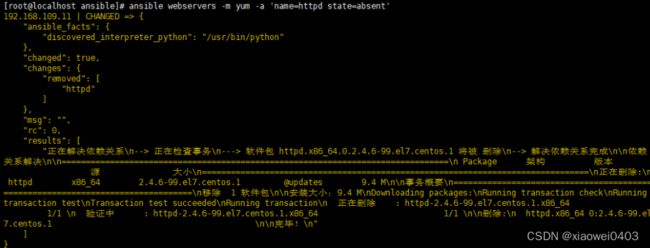
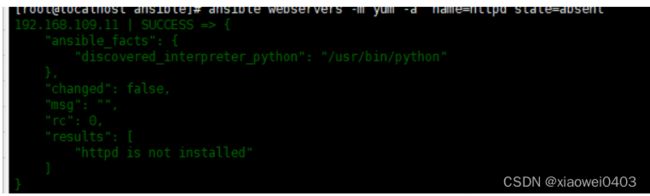
ansible webservers -m yum -a 'name=httpd state=absent' #卸载服务
12.script模块
//实现远程批量运行本地的 shell 脚本
ansible-doc -s script
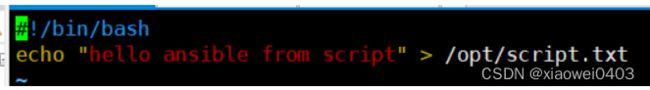
vim test.sh
#!/bin/bash
echo "hello ansible from script" > /opt/script.txt
chmod +x test.sh
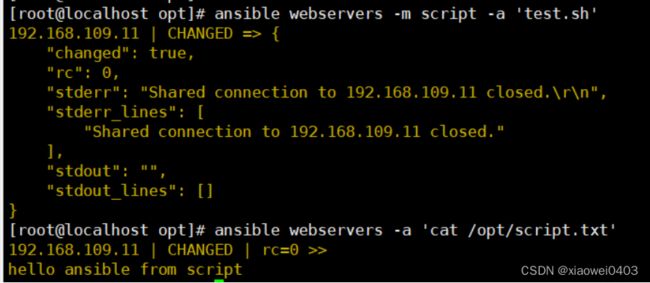
ansible webservers -m script -a 'test.sh'
ansible webservers -a 'cat /opt/script.txt'
13.setup模块
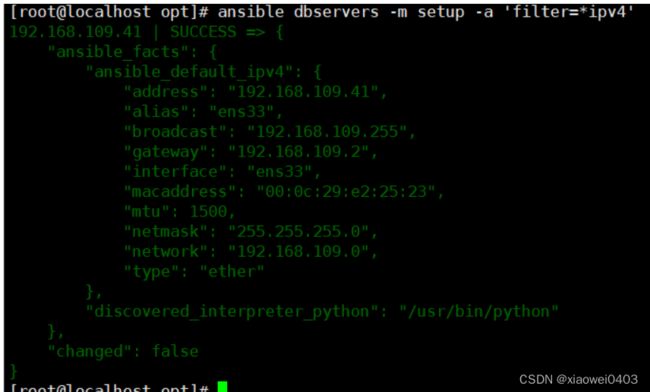
//facts组件是用来收集被管理节点信息的,使用setup模块可以获取这些信息
ansible-doc -s setup
ansible webservers -m setup #获取mysql组主机的facts信息
ansible dbservers -m setup -a 'filter=*ipv4' #使用filter可以筛选指定的facts信息