一、make编译逆向分析之prepare
在上一篇文章中分析Makefile文件依赖关系时采用自顶向下的方法,从顶层目标开始到最原始的依赖结束。
此处我们采用自下而上的方式,从最原始的依赖开始,一步一步的执行命令生成目标。
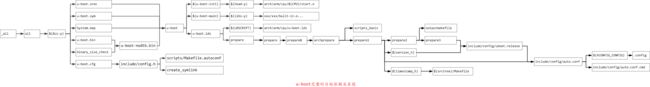
完整的prepare的目标依赖:
依次从最右边的依赖说起;
1.1 .config(配置阶段)
.config在执行make smdk2410_defconfig配置时生成,文件scripts/kconfig/Makefile中定义了所有匹配%_defconfig的目标:
%_defconfig: $(obj)/conf
$(Q)$< $(silent) --defconfig=arch/$(SRCARCH)/configs/$@ $(Kconfig)
展开为:
smdk2410_defconfig: scripts/kconfig/conf
$(Q)scripts/kconfig/conf --defconfig=arch/../configs/smdk2410_defconfig Kconfig
在配置阶段,scripts/kconfig/conf搜集所有默认的Kconfig配置,然后用指定的smdk2410_defconfig配置进行更新并输出到根目录的.config文件中:
1.2 include/config/auto.conf的规则
在编译阶段,scripts/kconfig/conf读取配置阶段生成的.config,并检查最新配置生成以下4个文件:
- include/generated/autoconf.h;
- include/config/auto.conf.cmd;
- include/config/tristate.conf;
- include/config/auto.conf;
在生成include/config/auto.conf的规则中:
# If .config is newer than include/config/auto.conf, someone tinkered
# with it and forgot to run make oldconfig.
# if auto.conf.cmd is missing then we are probably in a cleaned tree so
# we execute the config step to be sure to catch updated Kconfig files
include/config/%.conf: $(KCONFIG_CONFIG) include/config/auto.conf.cmd
$(Q)$(MAKE) -f $(srctree)/Makefile silentoldconfig
@# If the following part fails, include/config/auto.conf should be
@# deleted so "make silentoldconfig" will be re-run on the next build.
$(Q)$(MAKE) -f $(srctree)/scripts/Makefile.autoconf || \
{ rm -f include/config/auto.conf; false; }
@# include/config.h has been updated after "make silentoldconfig".
@# We need to touch include/config/auto.conf so it gets newer
@# than include/config.h.
@# Otherwise, 'make silentoldconfig' would be invoked twice.
$(Q)touch include/config/auto.conf
(1) 首先执行\$(MAKE) -f \$(srctree)/Makefile silentoldconfig外,即调用make -f ./Makefile silentoldconfig的最终结果是执行scripts/kconfig/Makefile中的规则:
silentoldconfig: $(obj)/conf
$(Q)mkdir -p include/config include/generated
$< $(silent) --$@ $(Kconfig)
这个规则展开为:
silentoldconfig: scripts/kconfig/conf
mkdir -p include/config include/generated
scripts/kconfig/conf --silentoldconfig Kconfig
(2) 然后执行\$(MAKE) -f \$(srctree)/scripts/Makefile.autoconf,在scripts/Makefile.autoconf的文件头部定义有:
# This helper makefile is used for creating
# - symbolic links (arch/$ARCH/include/asm/arch
# - include/autoconf.mk, {spl,tpl}/include/autoconf.mk
# - include/config.h
#
# When our migration to Kconfig is done
# (= When we move all CONFIGs from header files to Kconfig)
# this makefile can be deleted.
#
# SPDX-License-Identifier: GPL-2.0
#
__all: include/autoconf.mk include/autoconf.mk.dep
ifeq ($(shell grep -q '^CONFIG_SPL=y' include/config/auto.conf 2>/dev/null && echo y),y)
__all: spl/include/autoconf.mk
endif
ifeq ($(shell grep -q '^CONFIG_TPL=y' include/config/auto.conf 2>/dev/null && echo y),y)
__all: tpl/include/autoconf.mk
endif
此处没有设置CONFIG_SPL=y或CONFIG_TPL=y,所以整个makefile的__all的依赖有:
- include/autoconf.mk
- include/autoconf.mk.dep
然而include/autoconf.mk还要进一步依赖于config.h。
1.2.1 include/config.h的规则
所有的autoconf.mk都依赖于include/config.h:
include/autoconf.mk include/autoconf.mk.dep \
spl/include/autoconf.mk tpl/include/autoconf.mk: include/config.h
实际上include/config.h由宏filechk_config_h生成:
# include/config.h
# Prior to Kconfig, it was generated by mkconfig. Now it is created here.
define filechk_config_h
(echo "/* Automatically generated - do not edit */"; \
for i in $$(echo $(CONFIG_SYS_EXTRA_OPTIONS) | sed 's/,/ /g'); do \
echo \#define CONFIG_$$i \
| sed '/=/ {s/=/ /;q; } ; { s/$$/ 1/; }'; \
done; \
echo \#define CONFIG_BOARDDIR board/$(if $(VENDOR),$(VENDOR)/)$(BOARD);\
echo \#include \; \
echo \#include \; \
echo \#include \; \
echo \#include \; \
echo \#include \;)
endef
include/config.h: scripts/Makefile.autoconf create_symlink FORCE
$(call filechk,config_h)
最终生成的include/config.h也比较简单,不妨看看:
/* Automatically generated - do not edit */
#define CONFIG_BOARDDIR board/samsung/smdk2410
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
生成config.h之前,还要应用create_symlink生成相应的符号链接。
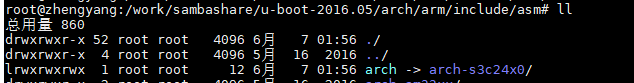
1.2.2 create_symlink的规则
# symbolic links
# If arch/$(ARCH)/mach-$(SOC)/include/mach exists,
# make a symbolic link to that directory.
# Otherwise, create a symbolic link to arch/$(ARCH)/include/asm/arch-$(SOC).
PHONY += create_symlink
create_symlink:
ifdef CONFIG_CREATE_ARCH_SYMLINK
ifneq ($(KBUILD_SRC),)
$(Q)mkdir -p include/asm
$(Q)if [ -d $(KBUILD_SRC)/arch/$(ARCH)/mach-$(SOC)/include/mach ]; then \
dest=arch/$(ARCH)/mach-$(SOC)/include/mach; \
else \
dest=arch/$(ARCH)/include/asm/arch-$(if $(SOC),$(SOC),$(CPU)); \
fi; \
ln -fsn $(KBUILD_SRC)/$$dest include/asm/arch
else
$(Q)if [ -d arch/$(ARCH)/mach-$(SOC)/include/mach ]; then \
dest=../../mach-$(SOC)/include/mach; \
else \
dest=arch-$(if $(SOC),$(SOC),$(CPU)); \
fi; \
ln -fsn $$dest arch/$(ARCH)/include/asm/arch
endif
endif
注释已经很好解释了create_symlink的行为:
- 如果arch/\$(ARCH)/mach-\$(SOC)/include/mach存在,则生成符号链接:
arch/$(ARCH)/include/asm/arch --> arch/$(ARCH)/mach-$(SOC)
- 否则生成符号链接:
arch/$(ARCH)/include/asm/arch -->arch/$(ARCH)/include/asm/arch-$(SOC)
对基于arm v9架构的s3c24x0芯片,arch/arm/mach-s3c2440文件夹不存在,所以生成链接:
arch/arm/include/asm/arch --> arch/arm/include/asm/arch-s3c24x0
简单说来,create_symlink就是将芯片arch/arm/include/asm/arch-s3c24x0链接到跟芯片名字无关的arch/arm/include/asm下。
1.2.3 include/autoconf.mk的规则
# We are migrating from board headers to Kconfig little by little.
# In the interim, we use both of
# - include/config/auto.conf (generated by Kconfig)
# - include/autoconf.mk (used in the U-Boot conventional configuration)
# The following rule creates autoconf.mk
# include/config/auto.conf is grepped in order to avoid duplication of the
# same CONFIG macros
quiet_cmd_autoconf = GEN $@
cmd_autoconf = \
$(CPP) $(c_flags) $2 -DDO_DEPS_ONLY -dM $(srctree)/include/common.h > [email protected] && { \
sed -n -f $(srctree)/tools/scripts/define2mk.sed [email protected] | \
while read line; do \
if [ -n "${KCONFIG_IGNORE_DUPLICATES}" ] || \
! grep -q "$${line%=*}=" include/config/auto.conf; then \
echo "$$line"; \
fi \
done > $@; \
rm [email protected]; \
} || { \
rm [email protected]; false; \
}
include/autoconf.mk: FORCE
$(call cmd,autoconf)
从cmd_autoconf来看,这里会根据include/common.h的依赖,然后调用tools/scripts/define2mk.sed,并合并之前生成的include/config/auto.conf生成最终的autoconf.mk。
1.2.4 include/autoconf.mk.dep的规则
quiet_cmd_autoconf_dep = GEN $@
cmd_autoconf_dep = $(CC) -x c -DDO_DEPS_ONLY -M -MP $(c_flags) \
-MQ include/config/auto.conf $(srctree)/include/common.h > $@ || { \
rm $@; false; \
}
include/autoconf.mk.dep: FORCE
$(call cmd,autoconf_dep)
这个规则比较简单,由于autoconf.mk由common.h和auto.conf而来,因此直接处理这两个文件的依赖并合并到autoconf.mk.dep中。
1.3 include/config/uboot.release
define filechk_uboot.release
echo "$(UBOOTVERSION)$$($(CONFIG_SHELL) $(srctree)/scripts/setlocalversion $(srctree))"
endef
# Store (new) UBOOTRELEASE string in include/config/uboot.release
include/config/uboot.release: include/config/auto.conf FORCE
$(call filechk,uboot.release)
命令$(call filechk,uboot.release)展开后就是调用宏filechk_uboot.release,最终将字符串2016.09写入include/config/uboot.release中。
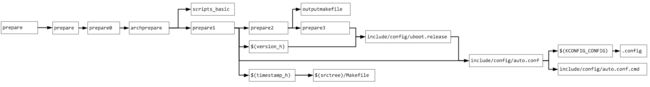
1.4 timestamp.h和version.h的规则
ersion_h := include/generated/version_autogenerated.h
timestamp_h := include/generated/timestamp_autogenerated.h
...
# Generate some files
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
define filechk_version.h
(echo \#define PLAIN_VERSION \"$(UBOOTRELEASE)\"; \
echo \#define U_BOOT_VERSION \"U-Boot \" PLAIN_VERSION; \
echo \#define CC_VERSION_STRING \"$$(LC_ALL=C $(CC) --version | head -n 1)\"; \
echo \#define LD_VERSION_STRING \"$$(LC_ALL=C $(LD) --version | head -n 1)\"; )
endef
# The SOURCE_DATE_EPOCH mechanism requires a date that behaves like GNU date.
# The BSD date on the other hand behaves different and would produce errors
# with the misused '-d' switch. Respect that and search a working date with
# well known pre- and suffixes for the GNU variant of date.
define filechk_timestamp.h
(if test -n "$${SOURCE_DATE_EPOCH}"; then \
SOURCE_DATE="@$${SOURCE_DATE_EPOCH}"; \
DATE=""; \
for date in gdate date.gnu date; do \
$${date} -u -d "$${SOURCE_DATE}" >/dev/null 2>&1 && DATE="$${date}"; \
done; \
if test -n "$${DATE}"; then \
LC_ALL=C $${DATE} -u -d "$${SOURCE_DATE}" +'#define U_BOOT_DATE "%b %d %C%y"'; \
LC_ALL=C $${DATE} -u -d "$${SOURCE_DATE}" +'#define U_BOOT_TIME "%T"'; \
LC_ALL=C $${DATE} -u -d "$${SOURCE_DATE}" +'#define U_BOOT_TZ "%z"'; \
LC_ALL=C $${DATE} -u -d "$${SOURCE_DATE}" +'#define U_BOOT_DMI_DATE "%m/%d/%Y"'; \
else \
return 42; \
fi; \
else \
LC_ALL=C date +'#define U_BOOT_DATE "%b %d %C%y"'; \
LC_ALL=C date +'#define U_BOOT_TIME "%T"'; \
LC_ALL=C date +'#define U_BOOT_TZ "%z"'; \
LC_ALL=C date +'#define U_BOOT_DMI_DATE "%m/%d/%Y"'; \
fi)
endef
$(version_h): include/config/uboot.release FORCE
$(call filechk,version.h)
$(timestamp_h): $(srctree)/Makefile FORCE
$(call filechk,timestamp.h)
1.4.1 include/generated/version_autogenerated.h
根据include/config/uboot.release文件,规则调用filechk_version.h宏生成版本相关字符串文件include/generated/version_autogenerated.h,如下:
#define PLAIN_VERSION "2016.05"
#define U_BOOT_VERSION "U-Boot " PLAIN_VERSION
#define CC_VERSION_STRING "arm-none-linux-gnueabi-gcc (Sourcery G++ Lite 2008q3-72) 4.3.2"
#define LD_VERSION_STRING "GNU ld (Sourcery G++ Lite 2008q3-72) 2.18.50.20080215
1.4.2 include/generated/timestamp_autogenerated.h
调用宏filechk_timestamp.h生成编译的时间戳文件,如下:
#define U_BOOT_DATE "Jun 07 2021"
#define U_BOOT_TIME "01:58:59"
#define U_BOOT_TZ "+0800"
#define U_BOOT_DMI_DATE "06/07/2021"
1.5 outputmakfile的规则
PHONY += outputmakefile
# outputmakefile generates a Makefile in the output directory, if using a
# separate output directory. This allows convenient use of make in the
# output directory.
outputmakefile:
ifneq ($(KBUILD_SRC),)
$(Q)ln -fsn $(srctree) source
$(Q)$(CONFIG_SHELL) $(srctree)/scripts/mkmakefile \
$(srctree) $(objtree) $(VERSION) $(PATCHLEVEL)
endif
- 如果编译没有设置O,即输出和代码都在同一个目录下,则outputmakefile的规则什么都不做;
- 如果编译指定了输出目录O,则调用scripts/mkmakefile在O选项指定的目录下生成一个简单的makefile
1.6 scripts_basic的规则
# Basic helpers built in scripts/
PHONY += scripts_basic
scripts_basic:
$(Q)$(MAKE) $(build)=scripts/basic
$(Q)rm -f .tmp_quiet_recordmcount
scripts_basic的执行结果就是编译生成scripts/basic/fixdep工具,该工具是u-boot编译系统中最常用的工具,用于在编译过程中修正每一个生成文件的依赖关系。
1.7 parepare0的规则
prepare0: archprepare FORCE
$(Q)$(MAKE) $(build)=.
展开后为:
prepare0: archprepare FORCE
make -f ./scripts/Makefile.build obj=.
编译时,命令make -f ./scripts/Makefile.build obj=.不会生成任何目标。
1.8 prepare系列目标总结
prepare阶段主要做了以下工作:
- scripts_basic规则生成fixdep工具,用于对整个系统生成目标文件相应依赖文件的更新;
- 配置阶段,scripts/kconfig/conf根据传入的指定配置文件在根目录下生成.config文件;
- 编译阶段,scripts/kconfig/conf读取配置阶段生成的.config,并检查最新配置生成以下文件:
- include/generated/autoconf.h
- include/config/auto.conf.cmd
- include/config/tristate.conf
- include/config/auto.conf
- 调用宏filechk_config_h生成include/config.h文件;
- 调用命令cmd_autoconf_dep生成autoconf.mk和autoconf.mk.cmd文件;
- 调用宏filechk_uboot.release生成include/config/uboot.release文件;
- 调用宏filechk_version.h生成include/generated/version_autogenerated.h文件;
- 调用宏filechk_timestamp.h生成include/generated/timestamp_autogenerated.h文件;
- 调用宏create_symlink就是将芯片arch/\$(ARCH)/include/asm/arch-\$(SOC)链接到跟芯片名字无关的arch/\$(ARCH)/include/asm下。
二、make编译逆向分析之u-boot
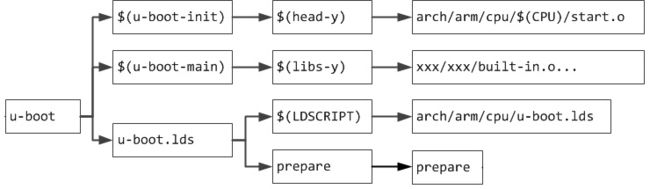
完整的u-boot的目标依赖:
从图上可见,除了prepare依赖外,u-boot还依赖于文件\$(head-y),\$(libs-y)和$(LDSCRIPT),即依赖于:
- 启动文件arch/arm/cpu/$(CPU)/start.o ;
- 各个目录下的build-in.o ;
- 链接脚本文件arch/arm/cpu/u-boot.lds;
2.1 启动文件start.o
$(head-y)在arch/arm/Makefile中被直接指定:
head-y := arch/arm/cpu/$(CPU)/start.o
在顶层makefile中被指定给变量u-boot-init:
u-boot-init := $(head-y)
2.2 各目录下的build-in.o
$(libs-y)在顶层的makefile中被指定为各个子目录下的build-in.o的集合:
libs-y += lib/
...
libs-y += fs/
libs-y += net/
libs-y += disk/
libs-y += drivers/
...
libs-y += $(if $(BOARDDIR),board/$(BOARDDIR)/)
libs-y := $(sort $(libs-y))
...
libs-y := $(patsubst %/, %/built-in.o, $(libs-y))
...
u-boot-main := $(libs-y)
以上脚本中,先将\$(libs-y)设置为各子目录的集合,最后调用patsubst函数将\$(libs-y)设置为这些目录下的built-in.o文件的集合,最后赋值给变量u-boot-main作为链接的主体文件。
各目录下的built-in.o是如何生成的呢?
以drivers/mmc/built-in.o为例,先查看生成的依赖文件drivers/mmc/.built-in.o.cmd:
cmd_drivers/mmc/built-in.o := rm -f drivers/mmc/built-in.o; arm-linux-ar rcs drivers/mmc/built-in.o
生成built-in.o的规则在scripts/Makefile.build中定义:
#
# Rule to compile a set of .o files into one .o file
#
ifdef builtin-target
quiet_cmd_link_o_target = LD $@
# If the list of objects to link is empty, just create an empty built-in.o
cmd_link_o_target = $(if $(strip $(obj-y)),\
$(LD) $(ld_flags) -r -o $@ $(filter $(obj-y), $^) \
$(cmd_secanalysis),\
rm -f $@; $(AR) rcs$(KBUILD_ARFLAGS) $@)
$(builtin-target): $(obj-y) FORCE
$(call if_changed,link_o_target)
targets += $(builtin-target)
endif # builtin-target
2.3 链接脚本u-boot.lds
链接脚本的规则如下:
quiet_cmd_cpp_lds = LDS $@
cmd_cpp_lds = $(CPP) -Wp,-MD,$(depfile) $(cpp_flags) $(LDPPFLAGS) \
-D__ASSEMBLY__ -x assembler-with-cpp -P -o $@ $<
u-boot.lds: $(LDSCRIPT) prepare FORCE
$(call if_changed_dep,cpp_lds)
2.4 生成u-boot规则
顶层Makefile中定义了生成u-boot文件的规则:
# Rule to link u-boot
# May be overridden by arch/$(ARCH)/config.mk
quiet_cmd_u-boot__ ?= LD $@
cmd_u-boot__ ?= $(LD) $(LDFLAGS) $(LDFLAGS_u-boot) -o $@ \
-T u-boot.lds $(u-boot-init) \
--start-group $(u-boot-main) --end-group \
$(PLATFORM_LIBS) -Map u-boot.map
...
u-boot: $(u-boot-init) $(u-boot-main) u-boot.lds FORCE
$(call if_changed,u-boot__)
...
u-boot文件的生成很简单,调用ld命令,将\$(u-boot-init)和\$(u-boot-main)指定的一系列文件通过脚本u-boot.lds连接起来。
生成了u-boot文件后,后续就是针对u-boot文件的各种处理了。
三、make编译逆向分析之 顶层目标依赖
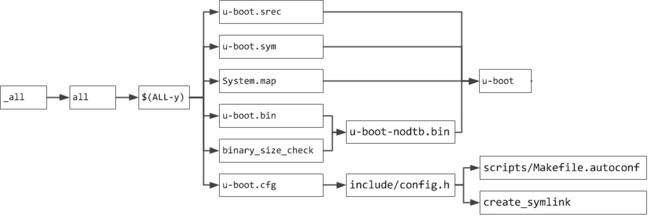
顶层目标依赖:
显然,在生成了u-boot的基础上,进一步生成所需要的各种目标文件:
3.1 u-boot.srec
# Normally we fill empty space with 0xff
quiet_cmd_objcopy = OBJCOPY $@
cmd_objcopy = $(OBJCOPY) --gap-fill=0xff $(OBJCOPYFLAGS) \
$(OBJCOPYFLAGS_$(@F)) $< $@
...
OBJCOPYFLAGS_u-boot.hex := -O ihex
OBJCOPYFLAGS_u-boot.srec := -O srec
u-boot.hex u-boot.srec: u-boot FORCE
$(call if_changed,objcopy)
调用objcopy命令,通过-O ihex或-O srec指定生成u-boot.hex或u-boot.srec格式文件。
3.2 u-boot.sym
quiet_cmd_sym ?= SYM $@
cmd_sym ?= $(OBJDUMP) -t $< > $@
u-boot.sym: u-boot FORCE
$(call if_changed,sym)
调用$(OBJDUMP)命令生成符号表文件u-boot.sym。
3.3 System.map
SYSTEM_MAP = \
$(NM) $1 | \
grep -v '\(compiled\)\|\(\.o$$\)\|\( [aUw] \)\|\(\.\.ng$$\)\|\(LASH[RL]DI\)' | \
LC_ALL=C sort
System.map: u-boot
@$(call SYSTEM_MAP,$<) > $@
调用$(NM)命令打印u-boot文件的符号表,并用grep -v处理后得到System.map文件,里面包含了最终使用到的各个符号的位置信息。
3.4 u-boot.bin和u-boot-nodtb.bin
PHONY += dtbs
dtbs: dts/dt.dtb
@:
dts/dt.dtb: checkdtc u-boot
$(Q)$(MAKE) $(build)=dts dtbs
quiet_cmd_copy = COPY $@
cmd_copy = cp $< $@
ifeq ($(CONFIG_OF_SEPARATE),y)
u-boot-dtb.bin: u-boot-nodtb.bin dts/dt.dtb FORCE
$(call if_changed,cat)
u-boot.bin: u-boot-dtb.bin FORCE
$(call if_changed,copy)
else
u-boot.bin: u-boot-nodtb.bin FORCE
$(call if_changed,copy)
endif
由于这里没有使用device tree设置,即编译没有定义CONFIG_OF_SEPARATE,因此u-boot.bin和u-boot-nodtb.bin是一样的。
至于生成u-boot-nodtb.bin的规则:
u-boot-nodtb.bin: u-boot FORCE
$(call if_changed,objcopy)
$(call DO_STATIC_RELA,$<,$@,$(CONFIG_SYS_TEXT_BASE))
$(BOARD_SIZE_CHECK)
显然,u-boot-nodtb.bin是u-boot文件通过objcopy得到。
3.5 u-boot.cfg
u-boot.cfg中包含了所有用到的宏定义,其生成规则如下:
# Create a file containing the configuration options the image was built with
quiet_cmd_cpp_cfg = CFG $@
cmd_cpp_cfg = $(CPP) -Wp,-MD,$(depfile) $(cpp_flags) $(LDPPFLAGS) -ansi \
-DDO_DEPS_ONLY -D__ASSEMBLY__ -x assembler-with-cpp -P -dM -E -o $@ $<
...
u-boot.cfg: include/config.h FORCE
$(call if_changed,cpp_cfg)
因此,阅读源码时如果不确定某个宏的值,可以检查u-boot.cfg文件。
命令中的if_changed函数定义在scripts/Kbuild.include文件中:
if_changed = $(if $(strip $(any-prereq) $(arg-check)), \
@set -e; \
$(echo-cmd) $(cmd_$(1)); \
printf '%s\n' 'cmd_$@ := $(make-cmd)' > $(dot-target).cmd)
echo-cmd其定义如下:
echo-cmd = $(if $($(quiet)cmd_$(1)),\
echo ' $(call escsq,$($(quiet)cmd_$(1)))$(echo-why)';)
\$(echo-cmd) \$(cmd_$(1))有两个功能:
- echo 命令,即回显命令;
- 执行命令;
\$(echo-cmd) \$(cmd_\$(1))展开后会在控制台回显命令,然后执行命令,执行完之后,会生成u-boot.cfg文件:
arm-linux-gcc -E -Wp,-MD,
./.u-boot.cfg.d -D__KERNEL__ -D__UBOOT__ -D__ARM__ -marm -mno-thumb-interwork -mabi=aapcs-linux -mword-relocations -fno-pic -ffunction-sections -fdata-sections -fno-common -ffixed-r9 -msoft-float -pipe -march=armv4t
-Iinclude -I./arch/arm/include
-include ./include/linux/kconfig.h
-nostdinc -isystem /usr/local/arm/4.3.2/bin/../lib/gcc/arm-none-linux-gnueabi/4.3.2/include
-include ./include/u-boot/u-boot.lds.h
-DCPUDIR=arch/arm/cpu/arm920t
-ansi -DDO_DEPS_ONLY
-D__ASSEMBLY__ -x assembler-with-cpp -P -dM -E
-o u-boot.cfg include/config.h
这里指定了头文件主要是./include/linux/kconfig.h文件,这个文件引入了include/generated/autoconf.h,这个文件包含了各种宏定义:
#include
/*
*
* Automatically generated file; DO NOT EDIT.
* U-Boot 2016.05 Configuration
*
*/
#define CONFIG_CMD_BOOTM 1
#define CONFIG_CMD_USB 1
#define CONFIG_CMD_EDITENV 1
#define CONFIG_SYS_GENERIC_BOARD 1
#define CONFIG_CMD_CONSOLE 1
#define CONFIG_CMD_BOOTD 1
#define CONFIG_CMD_IMLS 1
#define CONFIG_BOOTSTAGE_STASH_ADDR 0x0
#define CONFIG_HAVE_PRIVATE_LIBGCC 1
#define CONFIG_CMD_BDI 1
#define CONFIG_ARM 1
#define CONFIG_CREATE_ARCH_SYMLINK 1
#define CONFIG_SYS_VENDOR "samsung"
#define CONFIG_CMD_PING 1
#define CONFIG_CMD_SAVEENV 1
#define CONFIG_CMD_MISC 1
#define CONFIG_SYS_CPU "arm920t"
#define CONFIG_BOOTSTAGE_USER_COUNT 0x20
#define CONFIG_CC_OPTIMIZE_FOR_SIZE 1
#define CONFIG_CMD_FLASH 1
#define CONFIG_REGEX 1
#define CONFIG_CMD_ENV_EXISTS 1
#define CONFIG_HAVE_GENERIC_BOARD 1
#define CONFIG_CMD_EXPORTENV 1
#define CONFIG_CMD_DHCP 1
#define CONFIG_SYS_EXTRA_OPTIONS ""
#define CONFIG_CMD_CRC32 1
#define CONFIG_SYS_BOARD "smdk2410"
#define CONFIG_SYS_CONFIG_NAME "smdk2410"
#define CONFIG_CMD_NFS 1
#define CONFIG_NET 1
#define CONFIG_TARGET_SMDK2410 1
#define CONFIG_CMD_GO 1
#define CONFIG_SYS_MALLOC_CLEAR_ON_INIT 1
#define CONFIG_CMD_IMI 1
#define CONFIG_SYS_HZ 1000
#define CONFIG_SUPPORT_OF_CONTROL 1
#define CONFIG_CMD_EXT2 1
#define CONFIG_LOCALVERSION ""
#define CONFIG_CMDLINE 1
#define CONFIG_CMD_LOADB 1
#define CONFIG_CMD_RUN 1
#define CONFIG_SYS_HUSH_PARSER 1
#define CONFIG_SYS_PROMPT "SMDK2410 # "
#define CONFIG_CMD_MEMORY 1
#define CONFIG_HUSH_PARSER 1
#define CONFIG_CMD_XIMG 1
#define CONFIG_CMD_ECHO 1
#define CONFIG_LOCALVERSION_AUTO 1
#define CONFIG_SYS_ARCH "arm"
#define CONFIG_EXPERT 1
#define CONFIG_SYS_SOC "s3c24x0"
#define CONFIG_CMD_ITEST 1
#define CONFIG_CMD_CACHE 1
#define CONFIG_BOOTSTAGE_STASH_SIZE 0x4096
#define CONFIG_CMD_LOADS 1
#define CONFIG_CMD_FAT 1
#define CONFIG_CMD_NET 1
#define CONFIG_CMD_FPGA 1
#define CONFIG_NET_TFTP_VARS 1
#define CONFIG_CPU_ARM920T 1
#define CONFIG_CMD_IMPORTENV 1
#define CONFIG_CMD_ELF 1
#define CONFIG_CMD_SOURCE 1
同时printf '%s\n' 'cmd_$@ := \$(make-cmd)' > \$(dot-target).cmd)会将如下信息输出到。u-boot.cfg.cmd文件中:
cmd_u-boot.cfg := arm-linux-gcc -E -Wp,-MD,./.u-boot.cfg.d -D__KERNEL__ -D__UBOOT__ -D__ARM__ -marm -mno-thumb-interwork -mabi=aapcs-linux -mword-relocations -fno-pic -ffunction-sections -fdata-sections -fno-common -ffixed-r9 -msoft-float -pipe -march=armv4t -Iinclude -I./arch/arm/include -include ./include/linux/kconfig.h -nostdinc -isystem /usr/local/arm/4.3.2/bin/../lib/gcc/arm-none-linux-gnueabi/4.3.2/include -include ./include/u-boot/u-boot.lds.h -DCPUDIR=arch/arm/cpu/arm920t -ansi -DDO_DEPS_ONLY -D__ASSEMBLY__ -x assembler-with-cpp -P -dM -E -o u-boot.cfg include/config.h
自此,生成了所有的目标文件,完成了整个编译过程的分析。
参考文章
[1]内核makefile echo-cmd表达式