SpringBoot-17-异常处理
SpringBoot异常处理
在web开发中,会遇到一些异常,这通常需要一个统一的异常处理机制,保证客户端能接受到友好的提示。Spring Boot 中存在的异常处理机制有两种:默认异常处理机制和全局异常处理机制。
①默认异常处理机制
Spring Boot 默认提供了一套默认的异常处理机制,一旦程序出现了异常,Spring Boot 就会自动识别出客户端的类型(浏览器客户端或机器客户端),并根据客户端的不同,以不同的形式展示异常信息
- 对于浏览器客户端而言,Spring Boot会响应一个“whitelable”错误视图,以HTML格式显示错误信息
- 对于机器客户端而言,Spring Boot 将生成 JSON 响应,来展示异常消息。
{
"timestamp": "2021-07-12T07:05:29.885+00:00",
"status": 404,
"error": "Not Found",
"message": "No message available",
"path": "/m1ain.html"
}
Spring Boot 异常处理自动配置原理
Spring Boot 给我们的异常处理提供了自动配置类ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration,我们去spring.factories找到这个类。
- 我们先来看看这个自动配置类的注解
@Configuration(
proxyBeanMethods = false
)
//标明该类为一个配置类
@ConditionalOnWebApplication(
type = Type.SERVLET
)
//在web运行的条件是类型属于Servlet,才生效
@ConditionalOnClass({Servlet.class, DispatcherServlet.class})
//只有满足了在类路径上存在Servlet和DispatcherServlet这两个类,这个组件才生效
@AutoConfigureBefore({WebMvcAutoConfiguration.class})
//在自动配置之前需要WebMvcAutoConfiguration这个类
@EnableConfigurationProperties({ServerProperties.class, WebMvcProperties.class})
//让使用ConfigurationProperties注解的类生效,并加入到IOC容器中,交给IOC容器中统一管理,
//当前这个自动配置类,可以通过自动装配的形式,来获取ConfigurationProperties注解的类的对象
- 查看自动配置类里面的方法和对象
通过观察,我们可以知道:
-
这个ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration类通过构造函数初始化,以自动装配的方式加载了ServerProperties类。
-
该配置类向容器中添加的组件有:
| 组件 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| DefaultErrorAttributes | 用于在页面上共享异常信息 |
| BasicErrorController | 处理默认的“/error”请求 |
| ErrorPageCustomizer | 错误页面定制器,该组件在系统发生异常后,默认将组件请求到“/error”上 |
| PreserveErrorControllerTargetClassPostProcessor | 保存错误控制层目标类后处理器 |
| WhitelabelErrorViewConfiguration | 用来跳转到白板页面错误的视图配置类 |
| DefaultErrorViewResolverConfiguration | 默认的错误视图解析器配置,将异常信息解析到相应的错误视图中上。 |
- 我们来观察这些组件看看
ErrorPageCustomizer
它主要用于定制错误页面的响应规则,包含的参数有服务器属性对象和前端控制器路径对象
@Bean
public ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration.ErrorPageCustomizer errorPageCustomizer(DispatcherServletPath dispatcherServletPath) {
return new ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration.ErrorPageCustomizer(this.serverProperties, dispatcherServletPath);
}
static class ErrorPageCustomizer implements ErrorPageRegistrar, Ordered {
private final ServerProperties properties;
private final DispatcherServletPath dispatcherServletPath;
protected ErrorPageCustomizer(ServerProperties properties, DispatcherServletPath dispatcherServletPath) {
this.properties = properties;
this.dispatcherServletPath = dispatcherServletPath;
}
public void registerErrorPages(ErrorPageRegistry errorPageRegistry) {
//注册错误视图,只有当服务器属性对象有错误这个属性不为空条件下才生效
ErrorPage errorPage = new ErrorPage(this.dispatcherServletPath.getRelativePath(this.properties.getError().getPath()));
errorPageRegistry.addErrorPages(new ErrorPage[]{errorPage});
}
public int getOrder() {
return 0;
}
}
ErrorPageCustomizerr 通过 registerErrorPages() 方法来注册错误页面的响应规则。当系统中发生异常后,ErrorPageCustomizer 组件会自动生效,并将请求转发到 “/error”上
查看 registerErrorPages() 方法
public void registerErrorPages(ErrorPageRegistry errorPageRegistry) {
ErrorPage errorPage = new ErrorPage(this.dispatcherServletPath.getRelativePath(this.properties.getError().getPath()));
errorPageRegistry.addErrorPages(new ErrorPage[]{errorPage});
}
BasicErrorController
ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration还向容器注入了一个错误控制器组件BasicErrorController,代码如下。
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(value = ErrorController.class, search = SearchStrategy.CURRENT)
public BasicErrorController basicErrorController(ErrorAttributes errorAttributes,
ObjectProvider<ErrorViewResolver> errorViewResolvers) {
return new BasicErrorController(errorAttributes, this.serverProperties.getError(),
errorViewResolvers.orderedStream().collect(Collectors.toList()));
}
BasicErrorController在没有自定义的ErrorController类时生效。这个组件创建了一个BasicErrorController对象,我们点开这个对象查看。
//BasicErrorController用来处理“/error”请求
@Controller
@RequestMapping("${server.error.path:${error.path:/error}}")
//请求路径为服务器下的错误路径
public class BasicErrorController extends AbstractErrorController {
//获取ErrorProperties对象
private final ErrorProperties errorProperties;
/**
* Create a new {@link BasicErrorController} instance.
* @param errorAttributes the error attributes
* @param errorProperties configuration properties
*/
//自动装配的方式注入ErrorAttributes和ErrorProperties两个对象
public BasicErrorController(ErrorAttributes errorAttributes, ErrorProperties errorProperties) {
this(errorAttributes, errorProperties, Collections.emptyList());
}
/**
* Create a new {@link BasicErrorController} instance.
* @param errorAttributes the error attributes
* @param errorProperties configuration properties
* @param errorViewResolvers error view resolvers
*/
//构造函数,包含错误视图解析器
public BasicErrorController(ErrorAttributes errorAttributes, ErrorProperties errorProperties,
List<ErrorViewResolver> errorViewResolvers) {
super(errorAttributes, errorViewResolvers);
Assert.notNull(errorProperties, "ErrorProperties must not be null");
this.errorProperties = errorProperties;
}
/**
* 该方法用于处理浏览器客户端的请求发生的异常
* 生成 html 页面来展示异常信息
* @param request
* @param response
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping(produces = MediaType.TEXT_HTML_VALUE)
public ModelAndView errorHtml(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
//获取错误状态码
HttpStatus status = getStatus(request);
Map<String, Object> model = Collections
//getErrorAttributes根据错误信息来封装一些model数据,用来页面显示 .unmodifiableMap(getErrorAttributes(request, getErrorAttributeOptions(request, MediaType.TEXT_HTML)));
//为响应对象设置错误状态码
response.setStatus(status.value());
//调用resolverErrorView()方法,使用错误视图解析器生成ModelAndView对象(包含错误页面地址和页面内容)
ModelAndView modelAndView = resolveErrorView(request, response, status, model);
return (modelAndView != null) ? modelAndView : new ModelAndView("error", model);
}
/**
* 该方法用于处理机器客户端的请求发生的异常错误
* 产生 JSON 格式的数据展示错误信息
* @param request
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping
public ResponseEntity<Map<String, Object>> error(HttpServletRequest request) {
HttpStatus status = getStatus(request);
if (status == HttpStatus.NO_CONTENT) {
return new ResponseEntity<>(status);
}
Map<String, Object> body = getErrorAttributes(request, getErrorAttributeOptions(request, MediaType.ALL));
return new ResponseEntity<>(body, status);
}
protected ErrorAttributeOptions getErrorAttributeOptions(HttpServletRequest request, MediaType mediaType) {
//获取异常,错误消息,和请求路径
ErrorAttributeOptions options = ErrorAttributeOptions.defaults();
if (this.errorProperties.isIncludeException()) {
options = options.including(Include.EXCEPTION);
}
if (isIncludeStackTrace(request, mediaType)) {
options = options.including(Include.STACK_TRACE);
}
if (isIncludeMessage(request, mediaType)) {
options = options.including(Include.MESSAGE);
}
if (isIncludeBindingErrors(request, mediaType)) {
options = options.including(Include.BINDING_ERRORS);
}
return options;
}
Spring Boot通过BasicErrorController进行统一的错误处理(例如默认的"/error"请求)。Spring Boot会自动识别出请求的类型(浏览器客户端或机器客户端),并根据客户端类型,将请求分别交给errorHtml()和error()方法进行处理。
| 返回值类型 | 方法声明 | 客户端类型 |
|---|---|---|
| ModelAndView | errorHtml(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) | 浏览器客户端 |
| ResponseEntity |
error(HttpServlerRquest request)) | 机器客户端(例如安卓、IOS、Postman 等等 |
**要领:**当使用浏览器访问出现异常时,会进入 BasicErrorController 控制器中的 errorHtml() 方法进行处理,当使用安卓、IOS、Postman 等机器客户端访问出现异常时,就进入error() 方法处理。
errorHtml方法中会调用父类(AbstractErrorController)的resolveErrorView()方法,代码如下:
protected ModelAndView resolveErrorView(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, HttpStatus status,
Map<String, Object> model) {
//获取容器中的所有的错误视图解析器来处理该异常信息
for (ErrorViewResolver resolver : this.errorViewResolvers) {
//调用错误视图解析器的 resolveErrorView 解析到错误视图页面
ModelAndView modelAndView = resolver.resolveErrorView(request, status, model);
if (modelAndView != null) {
return modelAndView;
}
}
return null;
}
源码分析知,响应页面时,在AbstactErrorController的resolverErrorView方法中获取容器中所有的ErrorViewResolver对象(错误视图解析器,包括DefaultErrorViewResolver在内),一起来解析异常信息。
当发出请求的客户端为浏览器时,Spring Boot 会获取容器中所有的 ErrorViewResolver 对象(错误视图解析器),并分别调用它们的 resolveErrorView() 方法对异常信息进行解析,其中自然也包括 DefaultErrorViewResolver(默认错误信息解析器)
DefaultErrorViewResolver
ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration还向容器中注入了一个默认的错误视图解析器组件DefaultErrorViewResolver,代码如下。
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@EnableConfigurationProperties({ WebProperties.class, WebMvcProperties.class })
static class DefaultErrorViewResolverConfiguration {
//上下文内容
private final ApplicationContext applicationContext;
//资源
private final Resources resources;
//以自动装配的方式实现默认错误视图解析器配置类初始化
DefaultErrorViewResolverConfiguration(ApplicationContext applicationContext, WebProperties webProperties) {
this.applicationContext = applicationContext;
this.resources = webProperties.getResources();
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnBean(DispatcherServlet.class)
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(ErrorViewResolver.class)
DefaultErrorViewResolver conventionErrorViewResolver() {
return new DefaultErrorViewResolver(this.applicationContext, this.resources);
}
}
}
DefaultErrorResolver的代码解析
public class DefaultErrorViewResolver implements ErrorViewResolver, Ordered {
private static final Map<HttpStatus.Series, String> SERIES_VIEWS;
//得到视图序列
static {
Map<HttpStatus.Series, String> views = new EnumMap<>(HttpStatus.Series.class);
//客户端错误设置为4xx
views.put(Series.CLIENT_ERROR, "4xx");
//服务器错误设置5xx
views.put(Series.SERVER_ERROR, "5xx");
SERIES_VIEWS = Collections.unmodifiableMap(views);
//得到不可修改的视图Map
}
......
@Override
//通过解析状态码和模型来获得错误视图
public ModelAndView resolveErrorView(HttpServletRequest request, HttpStatus status, Map<String, Object> model) {
//尝试以错误状态码作为错误页面名进行解析
ModelAndView modelAndView = resolve(String.valueOf(status.value()), model);
if (modelAndView == null && SERIES_VIEWS.containsKey(status.series())) {
//尝试以 4xx 或 5xx 作为错误页面页面进行解析
modelAndView = resolve(SERIES_VIEWS.get(status.series()), model);
}
return modelAndView;
}
//通过模板引擎找到errorName指定的视图,若模板引擎不能解析,则去静态资源文件夹下查找errorViewName对应的页面
private ModelAndView resolve(String viewName, Map<String, Object> model) {
//错误模板页面,例如 error/404、error/4xx、error/500、error/5xx
String errorViewName = "error/" + viewName;
//当模板引擎可以解析这些模板页面时,就用模板引擎解析
TemplateAvailabilityProvider provider = this.templateAvailabilityProviders.getProvider(errorViewName,
this.applicationContext);
if (provider != null) {
//在模板能够解析到模板页面的情况下,返回 errorViewName 指定的视图
return new ModelAndView(errorViewName, model);
}
//若模板引擎不能解析,则去静态资源文件夹下查找 errorViewName 对应的页面
return resolveResource(errorViewName, model);
}
//查找静态资源文件夹下的错误页面
private ModelAndView resolveResource(String viewName, Map<String, Object> model) {
//遍历所有静态资源文件夹
for (String location : this.resources.getStaticLocations()) {
try {
Resource resource = this.applicationContext.getResource(location);
//静态资源文件夹下的错误页面,例如error/404.html、error/4xx.html、error/500.html、error/5xx.html
resource = resource.createRelative(viewName + ".html");
//若静态资源文件夹下存在以上错误页面,则直接返回
if (resource.exists()) {
return new ModelAndView(new DefaultErrorViewResolver.HtmlResourceView(resource), model);
}
} catch (Exception ex) {
}
}
return null;
}
......
}
DefaultErrorViewResolver 解析异常信息的步骤如下:
- 根据错误状态码(例如 404、500、400 等),生成一个错误视图 error/status,例如 error/404、error/500、error/400。
- 尝试使用模板引擎解析 error/status 视图,即尝试从 classpath 类路径下的 templates 目录下,查找 error/status.html,例如 error/404.html、error/500.html、error/400.html。
- 若模板引擎能够解析到 error/status 视图,则将视图和数据封装成 ModelAndView 返回并结束整个解析流程,否则跳转到第 4 步。
- 依次从各个静态资源文件夹中查找 error/status.html,若在静态文件夹中找到了该错误页面,则返回并结束整个解析流程,否则跳转到第 5 步。
- 将错误状态码(例如 404、500、400 等)转换为 4xx 或 5xx,然后重复前 4 个步骤,若解析成功则返回并结束整个解析流程,否则跳转第 6 步。
- 处理默认的 “/error ”请求,使用 Spring Boot 默认的错误页面(Whitelabel Error Page)。
DefaultErrorAttributes
ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration 还向容器中注入了一个组件默认错误属性处理工具 DefaultErrorAttributes
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(value = ErrorAttributes.class, search = SearchStrategy.CURRENT)
public DefaultErrorAttributes errorAttributes() {
return new DefaultErrorAttributes();
}
DefaultErrorAttributes 是 Spring Boot 的默认错误属性处理工具,它可以从请求中获取异常或错误信息,并将其封装为一个 Map 对象返回。使用getErrorAttributes来获得错误异常和错误信息
public class DefaultErrorAttributes implements ErrorAttributes, HandlerExceptionResolver, Ordered {
......
@Override
public Map<String, Object> getErrorAttributes(WebRequest webRequest, ErrorAttributeOptions options) {
Map<String, Object> errorAttributes = getErrorAttributes(webRequest, options.isIncluded(Include.STACK_TRACE));
if (!options.isIncluded(Include.EXCEPTION)) {
errorAttributes.remove("exception");
}
if (!options.isIncluded(Include.STACK_TRACE)) {
errorAttributes.remove("trace");
}
if (!options.isIncluded(Include.MESSAGE) && errorAttributes.get("message") != null) {
errorAttributes.remove("message");
}
if (!options.isIncluded(Include.BINDING_ERRORS)) {
errorAttributes.remove("errors");
}
return errorAttributes;
}
//返回一个Model数据
private Map<String, Object> getErrorAttributes(WebRequest webRequest, boolean includeStackTrace) {
Map<String, Object> errorAttributes = new LinkedHashMap<>();
//时间戳
errorAttributes.put("timestamp", new Date());
//状态码
addStatus(errorAttributes, webRequest);
//详细错误
addErrorDetails(errorAttributes, webRequest, includeStackTrace);
//错误路径
addPath(errorAttributes, webRequest);
return errorAttributes;
}
......
}
Spring Boot默认的Error控制器(BasicErrorController)处理错误时,会调用DefaultErrorAttributes的getErrorAttributes()方法获取错误信息或异常,封装为Model数据(Map对象),返回给页面或者JSON数据。
model包含以下属性:
timestamp:时间戳;
status:错误状态码
error:错误的提示
exception:导致请求处理失败的异常对象
message:错误/异常消息
trace: 错误/异常栈信息
path:错误/异常抛出时所请求的URL路径
②Spring Boot 全局异常处理
Spring Boot 提供了一套默认的异常处理机制,但是在实际业务场景中不一定适用,我们需要根据自己的需要对Spring Boot全局异常进行统一定制,例如:定制错误页面,定制错误数据。
定制错误页面
定制Spring Boot有三种方式:
- 自定义error.html
- 自定义动态错误页面
- 自定义静态页面
1.自定义error.html
在模板引擎下(/resources/templates)创建error.html,覆盖Spring Boot默认的错误视图页面(Whitelabel Error Page)
需要导入spring-boot-starter-web模块和thymeleaf模块
代码:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>自定义error.html</title>
</head>
<body>
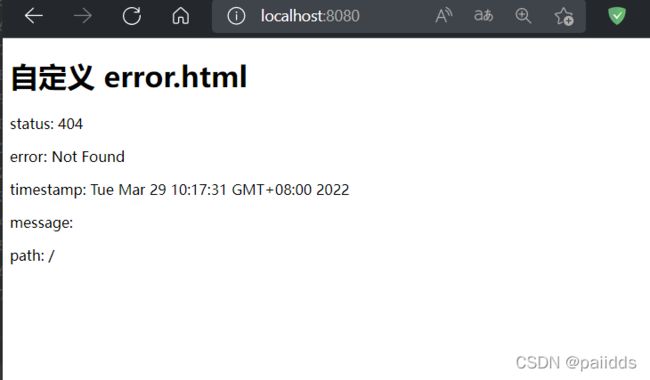
<h1>自定义 error.html</h1>
<p>status: <span th:text="${status}"></span></p>
<p>error: <span th:text="${error}"></span></p>
<p>timestamp: <span th:text="${timestamp}"></span></p>
<p>message: <span th:text="${message}"></span></p>
<p>path: <span th:text="${path}"></span></p>
</body>
</html>
运行结果
2.自定义动态错误页面
原理
当程序发生异常是,Spring Boot的默认错误视图解析器(DefaultErrorViewResolver)就会解析模板引擎文件夹(resource/templates)下的error目录中的错误视图页面。
精确匹配
我们可以根据错误状态码(例如 404、500、400 等等)的不同,分别创建不同的动态错误页面(例如 404.html、500.html、400.html 等等),并将它们存放在模板引擎文件夹下的 error 目录中。当发生异常时,Spring Boot 会根据其错误状态码精确匹配到对应的错误页面上。
代码:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>自定义error.html</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>自定义 动态错误页面 404.html</h1>
<p>status: <span th:text="${status}"></span></p>
<p>error: <span th:text="${error}"></span></p>
<p>timestamp: <span th:text="${timestamp}"></span></p>
<p>message: <span th:text="${message}"></span></p>
<p>path: <span th:text="${path}"></span></p>
</body>
</html>
运行结果
模糊查询
我们可以使用 4xx.html 和 5xx.html 作为动态错误页面的文件名,并将它们存放在模板引擎文件夹下的 error 目录中,来模糊匹配对应类型的所有错误,例如 404、400 等错误状态码以“4”开头的所有异常,都会解析到动态错误页面 4xx.html 上。
代码
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title></title>
</head>
<body>
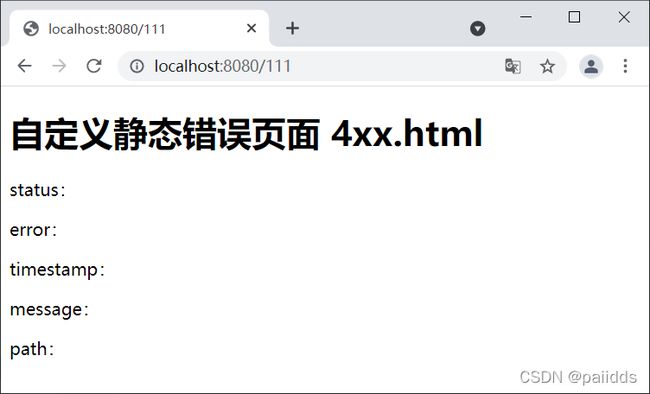
<h1>自定义动态错误页面 4xx.html</h1>
<p>status:<span th:text="${status}"></span></p>
<p>error:<span th:text="${error}"></span></p>
<p>timestamp:<span th:text="${timestamp}"></span></p>
<p>message:<span th:text="${message}"></span></p>
<p>path:<span th:text="${path}"></span></p>
</body>
</html>
运行结果
3.自定义静态错误页面
原理
与自定义动态错误页面类似,当程序发生异常时,如果在模板引擎下没有找到错误视图,则默认错误视图解析器去解析静态资源文件下的error目录中的错误页面。
分为精确匹配和模糊匹配,精确匹配是匹配到具体的错误状态码,而模糊匹配则是以错误状态码开头的字母进行匹配,匹配的结果是属于某一类异常的结果,例如 4xx包含404网页不存在,400客户端错误等
代码和自定义动态错误页面的基本一致,只是创建的地方不同,静态错误页面创建在静态资源(static,public)下的error目录中。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>自定义error.html</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>自定义 静态错误页面 404.html</h1>
<p>status: <span th:text="${status}"></span></p>
<p>error: <span th:text="${error}"></span></p>
<p>timestamp: <span th:text="${timestamp}"></span></p>
<p>message: <span th:text="${message}"></span></p>
<p>path: <span th:text="${path}"></span></p>
</body>
</html>
运行结果
错误页面优先级
定制 Spring Boot 错误页面优先级顺序为:
- 自定义动态错误页面(精确匹配)
- 自定义静态错误页面(精确匹配)
- 自定义动态错误页面(模糊匹配)
- 自定义静态错误页面(模糊匹配)-
- 自定义 error.html。
优先级依次降低,当遇到错误时,当遇到错误时,Spring Boot 会按照优先级由高到低,依次查找解析错误页,一旦找到可用的错误页面,则直接返回客户端展示。
定制错误数据
原理
- 发生异常时,将请求转发到“/error”,交由 BasicErrorController(Spring Boot 默认的 Error 控制器) 进行处理;
- BasicErrorController 根据客户端的不同,自动适配返回的响应形式,浏览器客户端返回错误页面,机器客户端返回 JSON 数据。
- BasicErrorController 处理异常时,会调用 DefaultErrorAttributes(默认的错误属性处理工具) 的 getErrorAttributes() 方法获取错误数据。
定制Spring Boot的错误数据,步骤如下:
-
自定义异常处理类,将请求转发到"/error"上,交由 Spring Boot 底层(BasicErrorController)进行处理,自动适配浏览器客户端和机器客户端。
-
. 通过继承 DefaultErrorAttributes 来定义一个错误属性处理工具,并在原来的基础上添加自定义的错误数据。
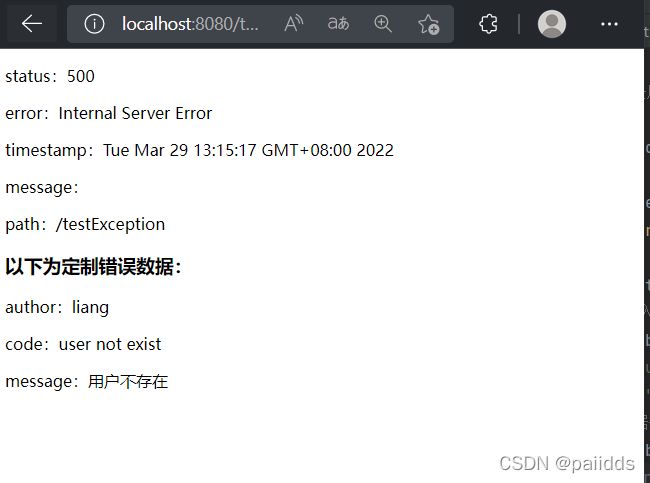
我们通过之前写的网页来测试全局异常处理
1. 自定义异常处理类UserNotExistException
在项目com.liang.component的包下创建一个异常处理类
public class UserNotExistException extends RuntimeException {
public UserNotExistException() {
super("用户不存在");
}
}
2.抛出该异常类出现的位置
在controller创建一个ErrorController来响应提交请求
@Controller
public class ErrorController {
@GetMapping("/testException")
public String textException(User user)
{
if(user.getUsername().equals("user"))
{
throw new UserNotExistException();
}
//跳转到登录
return "login";
}
}
3.全局处理这个异常类
在Controller层创建一个MyExceptHandler类,来处理错误数据完成转发“/errror”请求,使用@ControllerAdvice注解,里面使用@ExceptionHandler异常处理的注解,来给异常传入错误信息。
@ExceptionHandler(UserNotExistException.class)
public String handlerException(Exception e, HttpServletRequest request)
{
Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
//向request对象传入错误状态码
request.setAttribute("javax.servlet.error.status_code",500);
map.put("code","user not exist");
map.put("message",e.getMessage());
//将自定义的错误数据传入到request域中
request.setAttribute("ext",map);
//传入数据后转发到error请求中
return "forward:/error";
}
4. 通过继承DefaultErrorAttributes来定制数据
在conig文件下创建一个MyErrorAttributes的类,并标记为一个组件
代码如下
@Component
public class MyErrorAttributes extends DefaultErrorAttributes {
//重写getErrorAttributes的方法
@Override
public Map<String, Object> getErrorAttributes(WebRequest webRequest, ErrorAttributeOptions options) {
//得到spring Boot默认的错误数据
Map<String, Object> errorAttributes = super.getErrorAttributes(webRequest,options);
//添加自定义的错误数据
errorAttributes.put("author","liang");
// 得到请求域的错误数据 scope有两种: request为0,session为1
Map ext = (Map) webRequest.getAttribute("ext", 0);
errorAttributes.put("ext",ext);
return errorAttributes;
}
}
实现