Oracle中定义变量
关键字:declare
1、定义变量:
例如:declare i int :=1;
其中:=是赋值运算符
declare
i int :=0;
s int :=0;
begin
loop
i:=i+1;
s:=s+i;
exit when i=100; --这里不是赋值用“=”
end loop;
dbms_output.put_line(s);
end;
2、定义数组变量(长度不可变的):
declare
type type_array is varray(3) of int;
a type_array:=type_array(1,2,3); --此处不能是:a type_array
begin --然后如此: a:=(1,2,3) 先定义再赋值会报错
for i in 1..a.count
loop
dbms_output.put_line(a(i));
end loop;
end;
其中type_array可以随便取名
3、%type:
为了是一个变量的类型与另一个已经定义的变量的类型一致,Oracle提供了%type
-- 创建test2
CREATE TABLE TEST2
(
ID NUMBER(8) PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL,
NAME CHAR(8) NOT NULL,
AGE NUMBER(8) NULL,
SEX CHAR(2) NULL,
HOBBY VARCHAR2(200) NULL
);
INSERT INTO TEST2 VALUES (1,'齐天大圣',12,'男','打妖怪');
INSERT INTO TEST2 VALUES (2,'猪八戒',45,'男','吃货');
INSERT INTO TEST2 VALUES (5,'紫霞仙子',22,'女','至尊宝');
INSERT INTO TEST2 VALUES (6,'哇哈哈',34,'女','睡觉');
例如:
declare
a test2.name%type; -- a是定义的新的变量,类型与表test2的name列的类型一致
begin
select name into a from test2 where id=2;-- select 列名 into 变量名 from
dbms_output.put_line(a);
end;
4、%rowtype
如果一个表有较多的列,使用%ROWTYPE来定义一个表示表中一行记录的变量,比分别使用%TYPE来定义表示表中各个列的变量要简洁得多,并且不容易遗漏、出错。这样会增加程序的可维护性。
declare
a test2%rowtype;
begin
select * into a from test2 where id=2 ;--其中查询的是全部的列,否则会报错
dbms_output.put_line(a.id);
dbms_output.put_line(a.name);
dbms_output.put_line(a.age);
dbms_output.put_line(a.sex);
dbms_output.put_line(a.hobby);
end;
5、输出函数:
declare
a number(2) :=6;
begin
dbms_output.put_line(a);-- begin开始,end结束,注意加分号
end;
6、exception异常处理:
declare
a test2.age%type;
begin
select age into a from test2 where id=10;
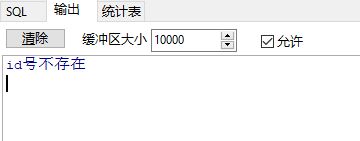
--这里没有id=10的数据,输出“id号不存在”字样
if a>100 then --满足条件就更新对应的值
update test2 set age=10 where id=10;
end if;
exception
when no_data_found then --when...then
dbms_output.put_line('id号不存在');
end;
declare
cursor a is select * from test2;
b a%rowtype;
begin
open a;--循环之前先打开游标
loop
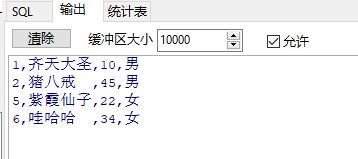
fetch a into b;--游标的值赋给定义的变量
exit when a%notfound;
dbms_output.put_line(b.id||','||b.name||','||b.age||','||b.sex);
end loop;
close a;--结束循环,关闭游标
end;
declare
a test2.name%type;
b test2.id%type;
c number(2);
begin
b:=&x;
select name into a from test2 where id=b;
if a='齐天大圣' then c:=1;
elsif a='猪八戒' then c:=3;--这里是elsif,不是elseif,或者else if
else c:=10;
end if;
update test2 set age=age+c where id=b;
exception
when no_data_found then
dbms_output.put_line('输入的id不存在');
end;
declare
a test2.name%type;
b test2.id%type;
c number(2);
begin
b:=&x;
select name into a from test2 where id=b;
case a
when '齐天大圣' then c:=1;
when '猪八戒' then c:=3;
else c:=10;
end case;
update test2 set age=age+c where id=b;
exception
when no_data_found then
dbms_output.put_line('输入的id不存在');
end;