Android ANR问题触发机制
1 Anr类型
Anr一般有四种类型。
1.1 input dispatching timeout
主要时按键或触摸屏事件在5s内没有响应。这个时间在ActivityManagerService中定义。
C:\Users\wangjie\AppData\Local\Android\Sdk\sources\android-32\com\android\server\am\ActivityManagerService.java
static final int KEY_DISPATCHING_TIMEOUT = 5*1000;
1.2 broadcast timeout
当onReceive执行超过阈值(前台10s,后台60s),将产生ANR。这个时间也是在ActivityManagerService中定义的。
C:\Users\wangjie\AppData\Local\Android\Sdk\sources\android-32\com\android\server\am\ActivityManagerService.java
static final int BROADCAST_FG_TIMEOUT = 10 * 1000 * Build.HW_TIMEOUT_MULTIPLIER;
static final int BROADCAST_BG_TIMEOUT = 60 * 1000 * Build.HW_TIMEOUT_MULTIPLIER;
这类超时没有提示弹窗。
1.3 service timeout
Service在规定的时间内无法完成任务,会报ANR。前台服务20s,后台服务200s。这个时间定义在ActivieServices中
C:\Users\wangjie\AppData\Local\Android\Sdk\sources\android-32\com\android\server\am\ActiveServices.java
// How long we wait for a service to finish executing.
static final int SERVICE_TIMEOUT = 20 * 1000 * Build.HW_TIMEOUT_MULTIPLIER;
// How long we wait for a service to finish executing.
static final int SERVICE_BACKGROUND_TIMEOUT = SERVICE_TIMEOUT * 10;
1.4 ContentProvider publish timeout
目标Provider的进程在启动过程中从attach到systerm_server进程开始到provider publish(发布)结束总耗时超过了10s。这个时间定义在ContentResolver中
public static final int CONTENT_PROVIDER_PUBLISH_TIMEOUT_MILLIS =
10 * 1000 * Build.HW_TIMEOUT_MULTIPLIER;
前三种ANR发生时都会由systerm_server进程在event log中输出发生ANR的reason、在data/anr目录下输出anr的trace文件,该文件会记录ANR reason、发生ANR的进程信息(pid,packageName),发生ANR的时间、发生ANR时内存占用情况,发生ANR进程各个线程的状态及堆栈调用情况,也会在main log中输出发生ANR前1分钟、5分钟、15分钟CPU的负载、各个进程CPU占用情况。
2 anr触发的机制
2.1 input分发超时anr触发原理
input 分发超时机制和Android系统中input事件分发处理流程有关。涉及到systerm_service进程的两个native线程的工作。
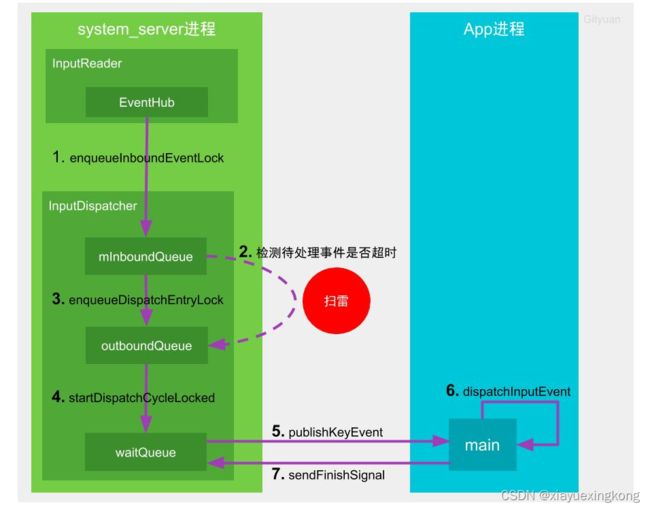
(1) InputReader线程通过EventHub监听底层上报的输入事件,一旦收到输入事件,就唤醒InputDispather线程,并将事件存放到mInboundQueue队列中。
(2) InputDispatcher先检测是否有正在处理的事件(mPendingEvent),如果没有则从mInboundQueue的头部取出一个事件元素,并将其赋值给mPendingEvent,且设置ANR超时;如果有正在处理的mPendingEvent,则不会从mInboundQueue中取出事件元素,也不会设置ANR超时,然后判断mWaitingQueue是否为空,如果不为空则判断上一个事件的处理是否超过5s,如果超过5s则触发ANR。如果当前没有处理的mPendingEvent,然后检查目标窗口是否就绪,如果窗口就绪则将mPendingEveng转移到mOutboundQueue中。
(3) 当mOutboundQueue不为空,且目标窗口进程的socket连接正常,将事件从mOutboundQueue中取出,放入到waitQueue中。
(4) InputDispatcher同时通过socket通信将事件分发给目标窗口进程,app接收到input事件后,主线程被唤醒,交给View Sesterm处理Input 事件。
(5) app处理完input事件后,通过socket通知systerm_server进程事件已处理,InputDisptacher将事件从waitQueue中移除。
综上,虽然app的主线程处理input事件的任务阻塞了主线程达到了5s,只要后续没有input事件,也不会触发ANR。
2.2 Service timeout ANR的触发原理
Service timeout分为前台服务和后台服务,前台服务超时时长是20s,后台服务超时是200s。服务是前台或后台是由启动服务的进程的调度组来决定的。当发起方进程的调度组不为ProcessList.SCHED_GROUP_BACKGROUND(后台进程组)的时候,启动的服务就是前台服务,否则为后台服务。
进程调度组大体可以分为TOP、前台、后台。进程调度组和进程的优先级Adi有关,其对应的关系可大致理解为ADJ等于0的进程属于Top调度组,ADJ等于100或者200的进程属于前台调度组,ADJ大于200的进程属于后台调度组。关于ADJ的含义见下表,简单来说是ADJ>200调度组的进程用户基本是无感知的。
以启动服务为例梳理服务超时anr的触发原理。
以下的源码基于 C:\Users\wangjie\AppData\Local\Android\Sdk\sources\android-32\
2.2.1 发送服务超时anr的延迟消息
2.2.1.1 Context#startService
public abstract ComponentName startService(Intent service);
2.2.1.2 ContextImpl#startService
@Override
public ComponentName startService(Intent service) {
warnIfCallingFromSystemProcess();
return startServiceCommon(service, false, mUser);
}
private ComponentName startServiceCommon(Intent service, boolean requireForeground,
UserHandle user) {
try {
validateServiceIntent(service);
service.prepareToLeaveProcess(this);
ComponentName cn = ActivityManager.getService().startService(
mMainThread.getApplicationThread(), service,
service.resolveTypeIfNeeded(getContentResolver()), requireForeground,
getOpPackageName(), getAttributionTag(), user.getIdentifier());
if (cn != null) {
if (cn.getPackageName().equals("!")) {
throw new SecurityException(
"Not allowed to start service " + service
+ " without permission " + cn.getClassName());
} else if (cn.getPackageName().equals("!!")) {
throw new SecurityException(
"Unable to start service " + service
+ ": " + cn.getClassName());
} else if (cn.getPackageName().equals("?")) {
throw ServiceStartNotAllowedException.newInstance(requireForeground,
"Not allowed to start service " + service + ": " + cn.getClassName());
}
}
// If we started a foreground service in the same package, remember the stack trace.
if (cn != null && requireForeground) {
if (cn.getPackageName().equals(getOpPackageName())) {
Service.setStartForegroundServiceStackTrace(cn.getClassName(),
new StackTrace("Last startServiceCommon() call for this service was "
+ "made here"));
}
}
return cn;
} catch (RemoteException e) {
throw e.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
}
2.2.1.3 android.app.ActivityManager
@UnsupportedAppUsage
public static IActivityManager getService() {
return IActivityManagerSingleton.get();
}
@UnsupportedAppUsage
private static final Singleton<IActivityManager> IActivityManagerSingleton =
new Singleton<IActivityManager>() {
@Override
protected IActivityManager create() {
final IBinder b = ServiceManager.getService(Context.ACTIVITY_SERVICE);
final IActivityManager am = IActivityManager.Stub.asInterface(b);
return am;
}
};
这里获得的是ActivityManagerService,它继承于IActivityManager.Stub,实现了IActivityManager。通过Binder进程间通信调用Syserm_server进程的ActivityManagerService#startService方法。
2.2.1.4 android.server.am.ActivityManagerService
@Override
public ComponentName startService(IApplicationThread caller, Intent service,
String resolvedType, boolean requireForeground, String callingPackage,
String callingFeatureId, int userId)
throws TransactionTooLargeException {
enforceNotIsolatedCaller("startService");
// Refuse possible leaked file descriptors
if (service != null && service.hasFileDescriptors() == true) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("File descriptors passed in Intent");
}
if (callingPackage == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("callingPackage cannot be null");
}
if (DEBUG_SERVICE) Slog.v(TAG_SERVICE,
"*** startService: " + service + " type=" + resolvedType + " fg=" + requireForeground);
synchronized(this) {
final int callingPid = Binder.getCallingPid();
final int callingUid = Binder.getCallingUid();
final long origId = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
ComponentName res;
try {
// 1 调用了ActiveServices#startServiceLocked方法。
res = mServices.startServiceLocked(caller, service,
resolvedType, callingPid, callingUid,
requireForeground, callingPackage, callingFeatureId, userId);
} finally {
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(origId);
}
return res;
}
}
2.2.1.5 android.server.am.ActiveServices
ComponentName startServiceLocked(IApplicationThread caller, Intent service, String resolvedType,
int callingPid, int callingUid, boolean fgRequired, String callingPackage,
@Nullable String callingFeatureId, final int userId)
throws TransactionTooLargeException {
return startServiceLocked(caller, service, resolvedType, callingPid, callingUid, fgRequired,
callingPackage, callingFeatureId, userId, false, null);
}
ComponentName startServiceLocked(IApplicationThread caller, Intent service, String resolvedType,
int callingPid, int callingUid, boolean fgRequired,
String callingPackage, @Nullable String callingFeatureId, final int userId,
boolean allowBackgroundActivityStarts, @Nullable IBinder backgroundActivityStartsToken)
throws TransactionTooLargeException {
...
final boolean callerFg;
if (caller != null) {
final ProcessRecord callerApp = mAm.getRecordForAppLOSP(caller);
if (callerApp == null) {
throw new SecurityException(
"Unable to find app for caller " + caller
+ " (pid=" + callingPid
+ ") when starting service " + service);
}
// 1 判断启动服务的进程的调度组是否是后台调度组,如果不是后台调度组,那么启动服务的进程就是前台进程,对应的
// 服务是前台服务;否则启动服务的进程是后台进程,服务是后台服务。
callerFg = callerApp.mState.getSetSchedGroup() != ProcessList.SCHED_GROUP_BACKGROUND;
} else {
callerFg = true;
}
ServiceLookupResult res =
retrieveServiceLocked(service, null, resolvedType, callingPackage,
callingPid, callingUid, userId, true, callerFg, false, false);
...
ServiceRecord r = res.record;
...
return startServiceInnerLocked(r, service, callingUid, callingPid, fgRequired, callerFg,
allowBackgroundActivityStarts, backgroundActivityStartsToken);
}
private ComponentName startServiceInnerLocked(ServiceRecord r, Intent service,
int callingUid, int callingPid, boolean fgRequired, boolean callerFg,
boolean allowBackgroundActivityStarts, @Nullable IBinder backgroundActivityStartsToken)
throws TransactionTooLargeException {
...
r.lastActivity = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
r.startRequested = true;
r.delayedStop = false;
r.fgRequired = fgRequired;
r.pendingStarts.add(new ServiceRecord.StartItem(r, false, r.makeNextStartId(),
service, neededGrants, callingUid));
...
ComponentName cmp = startServiceInnerLocked(smap, service, r, callerFg, addToStarting);
return cmp;
}
ComponentName startServiceInnerLocked(ServiceMap smap, Intent service, ServiceRecord r,
boolean callerFg, boolean addToStarting) throws TransactionTooLargeException {
...
String error = bringUpServiceLocked(r, service.getFlags(), callerFg,
false /* whileRestarting */,
false /* permissionsReviewRequired */,
false /* packageFrozen */,
true /* enqueueOomAdj */);
...
return r.name;
}
private String bringUpServiceLocked(ServiceRecord r, int intentFlags, boolean execInFg,
boolean whileRestarting, boolean permissionsReviewRequired, boolean packageFrozen,
boolean enqueueOomAdj)
throws TransactionTooLargeException {
// 1
if (r.app != null && r.app.getThread() != null) {
sendServiceArgsLocked(r, execInFg, false);
return null;
}
...
final boolean isolated = (r.serviceInfo.flags&ServiceInfo.FLAG_ISOLATED_PROCESS) != 0;
final String procName = r.processName;
HostingRecord hostingRecord = new HostingRecord("service", r.instanceName);
ProcessRecord app;
if (!isolated) {
app = mAm.getProcessRecordLocked(procName, r.appInfo.uid);
if (DEBUG_MU) Slog.v(TAG_MU, "bringUpServiceLocked: appInfo.uid=" + r.appInfo.uid
+ " app=" + app);
// 2 如果Service所在的进程已存在
if (app != null) {
final IApplicationThread thread = app.getThread();
final int pid = app.getPid();
final UidRecord uidRecord = app.getUidRecord();
if (thread != null) {
try {
app.addPackage(r.appInfo.packageName, r.appInfo.longVersionCode,
mAm.mProcessStats);
// 3 启动服务
realStartServiceLocked(r, app, thread, pid, uidRecord, execInFg,
enqueueOomAdj);
return null;
} catch (TransactionTooLargeException e) {
throw e;
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Exception when starting service " + r.shortInstanceName, e);
}
// If a dead object exception was thrown -- fall through to
// restart the application.
}
}
} else {
...
}
...
return null;
}
private void realStartServiceLocked(ServiceRecord r, ProcessRecord app,
IApplicationThread thread, int pid, UidRecord uidRecord, boolean execInFg,
boolean enqueueOomAdj) throws RemoteException {
if (thread == null) {
throw new RemoteException();
}
if (DEBUG_MU)
Slog.v(TAG_MU, "realStartServiceLocked, ServiceRecord.uid = " + r.appInfo.uid
+ ", ProcessRecord.uid = " + app.uid);
r.setProcess(app, thread, pid, uidRecord);
r.restartTime = r.lastActivity = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
final ProcessServiceRecord psr = app.mServices;
final boolean newService = psr.startService(r);
// 1 发送Service 超时ANR类型的延迟消息。
bumpServiceExecutingLocked(r, execInFg, "create", null /* oomAdjReason */);
mAm.updateLruProcessLocked(app, false, null);
updateServiceForegroundLocked(psr, /* oomAdj= */ false);
// Force an immediate oomAdjUpdate, so the client app could be in the correct process state
// before doing any service related transactions
mAm.enqueueOomAdjTargetLocked(app);
mAm.updateOomAdjLocked(app, OomAdjuster.OOM_ADJ_REASON_START_SERVICE);
boolean created = false;
try {
...
final int uid = r.appInfo.uid;
final String packageName = r.name.getPackageName();
final String serviceName = r.name.getClassName();
FrameworkStatsLog.write(FrameworkStatsLog.SERVICE_LAUNCH_REPORTED, uid, packageName,
serviceName);
mAm.mBatteryStatsService.noteServiceStartLaunch(uid, packageName, serviceName);
mAm.notifyPackageUse(r.serviceInfo.packageName,
PackageManager.NOTIFY_PACKAGE_USE_SERVICE);
// 2 调用客户端的ActivityThread.ApplicationThread#scheduleCreateService 执行Service的onCreate流程。
thread.scheduleCreateService(r, r.serviceInfo,
mAm.compatibilityInfoForPackage(r.serviceInfo.applicationInfo),
app.mState.getReportedProcState());
r.postNotification();
created = true;
} catch (DeadObjectException e) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Application dead when creating service " + r);
mAm.appDiedLocked(app, "Died when creating service");
throw e;
} finally {
...
}
if (r.allowlistManager) {
psr.mAllowlistManager = true;
}
// 3 调用客户端 ActivityThread.ApplicationThread#scheduleServiceArgs 执行Service的onStartCommand流程。
sendServiceArgsLocked(r, execInFg, true);
...
}
private boolean bumpServiceExecutingLocked(ServiceRecord r, boolean fg, String why,
@Nullable String oomAdjReason) {
...
long now = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
ProcessServiceRecord psr;
if (r.executeNesting == 0) {
r.executeFg = fg;
synchronized (mAm.mProcessStats.mLock) {
final ServiceState stracker = r.getTracker();
if (stracker != null) {
stracker.setExecuting(true, mAm.mProcessStats.getMemFactorLocked(), now);
}
}
if (r.app != null) {
psr = r.app.mServices;
psr.startExecutingService(r);
psr.setExecServicesFg(psr.shouldExecServicesFg() || fg);
if (timeoutNeeded && psr.numberOfExecutingServices() == 1) {
// 1发送 Service timeout anr的超时消息。
scheduleServiceTimeoutLocked(r.app);
}
}
} else if (r.app != null && fg) {
...
}
r.executeFg |= fg;
r.executeNesting++;
// 2 设置字段executingStart,本例讲述的是Service启动,所以这里可以理解为
// 设置服务启动开始时间;在后面处理超时消息的处理逻辑中有用到。
r.executingStart = now;
return oomAdjusted;
}
void scheduleServiceTimeoutLocked(ProcessRecord proc) {
if (proc.mServices.numberOfExecutingServices() == 0 || proc.getThread() == null) {
return;
}
Message msg = mAm.mHandler.obtainMessage(
ActivityManagerService.SERVICE_TIMEOUT_MSG);
msg.obj = proc;
mAm.mHandler.sendMessageDelayed(msg, proc.mServices.shouldExecServicesFg()
? SERVICE_TIMEOUT : SERVICE_BACKGROUND_TIMEOUT);
}
2.2.2 Service的onCreate流程
2.2.2.1 ActivityThread.ApplicationThread
public final void scheduleCreateService(IBinder token,
ServiceInfo info, CompatibilityInfo compatInfo, int processState) {
updateProcessState(processState, false);
CreateServiceData s = new CreateServiceData();
s.token = token;
s.info = info;
s.compatInfo = compatInfo;
sendMessage(H.CREATE_SERVICE, s);
}
2.2.2.2 ActivityThread
private void handleCreateService(CreateServiceData data) {
...
LoadedApk packageInfo = getPackageInfoNoCheck(
data.info.applicationInfo, data.compatInfo);
Service service = null;
try {
if (localLOGV) Slog.v(TAG, "Creating service " + data.info.name);
Application app = packageInfo.makeApplication(false, mInstrumentation);
final java.lang.ClassLoader cl;
if (data.info.splitName != null) {
cl = packageInfo.getSplitClassLoader(data.info.splitName);
} else {
cl = packageInfo.getClassLoader();
}
// 1 获取service对象。
service = packageInfo.getAppFactory()
.instantiateService(cl, data.info.name, data.intent);
ContextImpl context = ContextImpl.getImpl(service
.createServiceBaseContext(this, packageInfo));
if (data.info.splitName != null) {
context = (ContextImpl) context.createContextForSplit(data.info.splitName);
}
if (data.info.attributionTags != null && data.info.attributionTags.length > 0) {
final String attributionTag = data.info.attributionTags[0];
context = (ContextImpl) context.createAttributionContext(attributionTag);
}
// Service resources must be initialized with the same loaders as the application
// context.
context.getResources().addLoaders(
app.getResources().getLoaders().toArray(new ResourcesLoader[0]));
context.setOuterContext(service);
// 2 初始化Service的上下文
service.attach(context, this, data.info.name, data.token, app,
ActivityManager.getService());
// 3 调用onCreate方法。
service.onCreate();
...
try {
// 4 调用Systerm_server进程的ActivityManagerService组件的方法
ActivityManager.getService().serviceDoneExecuting(
data.token, SERVICE_DONE_EXECUTING_ANON, 0, 0);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
throw e.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
...
}
}
2.2.3 移除服务超时ANR的消息
2.2.3.1 android.server.am.ActivityManagerService
public void serviceDoneExecuting(IBinder token, int type, int startId, int res) {
synchronized(this) {
if (!(token instanceof ServiceRecord)) {
Slog.e(TAG, "serviceDoneExecuting: Invalid service token=" + token);
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid service token");
}
mServices.serviceDoneExecutingLocked((ServiceRecord) token, type, startId, res, false);
}
}
2.2.3.2 android.server.am.ActiveServices
移除之前发出的Service timeout anr的消息
void serviceDoneExecutingLocked(ServiceRecord r, int type, int startId, int res,
boolean enqueueOomAdj) {
boolean inDestroying = mDestroyingServices.contains(r);
if (r != null) {
...
final long origId = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
serviceDoneExecutingLocked(r, inDestroying, inDestroying, enqueueOomAdj);
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(origId);
} else {
Slog.w(TAG, "Done executing unknown service from pid "
+ Binder.getCallingPid());
}
}
private void serviceDoneExecutingLocked(ServiceRecord r, boolean inDestroying,
boolean finishing, boolean enqueueOomAdj) {
...
r.executeNesting--;
if (r.executeNesting <= 0) {
if (r.app != null) {
final ProcessServiceRecord psr = r.app.mServices;
if (DEBUG_SERVICE) Slog.v(TAG_SERVICE,
"Nesting at 0 of " + r.shortInstanceName);
psr.setExecServicesFg(false);
psr.stopExecutingService(r);
// 1 移除之前发出的Service timeout anr的消息。
if (psr.numberOfExecutingServices() == 0) {
if (DEBUG_SERVICE || DEBUG_SERVICE_EXECUTING) Slog.v(TAG_SERVICE_EXECUTING,
"No more executingServices of " + r.shortInstanceName);
mAm.mHandler.removeMessages(ActivityManagerService.SERVICE_TIMEOUT_MSG, r.app);
} else if (r.executeFg) {
...
}
...
}
...
}
}
2.2.4 处理服务超时ANR消息,触发ANR
2.2.4.1 android.server.am.ActivityManagerService
处理Service超时ANR的消息,触发ANR。
final class MainHandler extends Handler {
public MainHandler(Looper looper) {
super(looper, null, true);
}
@Override
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
switch (msg.what) {
case GC_BACKGROUND_PROCESSES_MSG: {
synchronized (ActivityManagerService.this) {
mAppProfiler.performAppGcsIfAppropriateLocked();
}
} break;
case SERVICE_TIMEOUT_MSG: {
// 处理消息
mServices.serviceTimeout((ProcessRecord) msg.obj);
} break;
}
2.2.4.2 android.server.am.ActiveServices
void serviceTimeout(ProcessRecord proc) {
String anrMessage = null;
synchronized(mAm) {
final long now = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
final long maxTime = now -
(psr.shouldExecServicesFg() ? SERVICE_TIMEOUT : SERVICE_BACKGROUND_TIMEOUT);
ServiceRecord timeout = null;
long nextTime = 0;
for (int i = psr.numberOfExecutingServices() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
ServiceRecord sr = psr.getExecutingServiceAt(i);
// 1 本例讲解的是Service启动,所以可以理解为开始启动的时间如果早于maxTime,即
// 启动耗时超过了阈值。
if (sr.executingStart < maxTime) {
timeout = sr;
break;
}
if (sr.executingStart > nextTime) {
nextTime = sr.executingStart;
}
}
if (timeout != null && mAm.mProcessList.isInLruListLOSP(proc)) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Timeout executing service: " + timeout);
StringWriter sw = new StringWriter();
PrintWriter pw = new FastPrintWriter(sw, false, 1024);
pw.println(timeout);
timeout.dump(pw, " ");
pw.close();
mLastAnrDump = sw.toString();
mAm.mHandler.removeCallbacks(mLastAnrDumpClearer);
mAm.mHandler.postDelayed(mLastAnrDumpClearer, LAST_ANR_LIFETIME_DURATION_MSECS);
anrMessage = "executing service " + timeout.shortInstanceName;
} else {
Message msg = mAm.mHandler.obtainMessage(
ActivityManagerService.SERVICE_TIMEOUT_MSG);
msg.obj = proc;
mAm.mHandler.sendMessageAtTime(msg, psr.shouldExecServicesFg()
? (nextTime+SERVICE_TIMEOUT) : (nextTime + SERVICE_BACKGROUND_TIMEOUT));
}
}
if (anrMessage != null) {
// 2 触发了ANR
mAm.mAnrHelper.appNotResponding(proc, anrMessage);
}
}
2.3 Broadcast timeout ANR触发原理
静态注册的广播接收器处理的广播和动态注册的广播接收器处理的有序广播才会触发广播超时的ANR。详细见Android Broadcast的广播机制。
2.3.1 发送广播超时ANR的延迟消息
2.3.1.1 com.android.server.am.BroadcastQueue
final void processNextBroadcastLocked(boolean fromMsg, boolean skipOomAdj) {
BroadcastRecord r;
...
if (fromMsg) {
mBroadcastsScheduled = false;
}
// First, deliver any non-serialized broadcasts right away.
// 1 处理并行广播。
while (mParallelBroadcasts.size() > 0) {
r = mParallelBroadcasts.remove(0);
r.dispatchTime = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
r.dispatchClockTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
...
final int N = r.receivers.size();
...
for (int i=0; i<N; i++) {
Object target = r.receivers.get(i);
...
// 2 分发广播给动态注册的广播接收者。
deliverToRegisteredReceiverLocked(r,
(BroadcastFilter) target, false, i);
}
// 3 统计已经处理的广播。
addBroadcastToHistoryLocked(r);
}
...
boolean looped = false;
do {
final long now = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
// 4 从处理串行的广播集合中的头部取出一个元素
r = mDispatcher.getNextBroadcastLocked(now);
...
boolean forceReceive = false;
...
int numReceivers = (r.receivers != null) ? r.receivers.size() : 0;
if (mService.mProcessesReady && !r.timeoutExempt && r.dispatchTime > 0) {
if ((numReceivers > 0) &&
(now > r.dispatchTime + (2 * mConstants.TIMEOUT * numReceivers))) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Hung broadcast ["
+ mQueueName + "] discarded after timeout failure:"
+ " now=" + now
+ " dispatchTime=" + r.dispatchTime
+ " startTime=" + r.receiverTime
+ " intent=" + r.intent
+ " numReceivers=" + numReceivers
+ " nextReceiver=" + r.nextReceiver
+ " state=" + r.state);
// 5 当广播处理时间超时,则强制结束这条广播
broadcastTimeoutLocked(false); // forcibly finish this broadcast
forceReceive = true;
r.state = BroadcastRecord.IDLE;
}
}
...
// Is the current broadcast is done for any reason?
if (r.receivers == null || r.nextReceiver >= numReceivers
|| r.resultAbort || forceReceive) {
// 6 取消BROADCAST_TIMEOUT_MSG消息
cancelBroadcastTimeoutLocked();
...
}
...
} while (r == null);
// Get the next receiver...
// 7 获取下一个receiver。
int recIdx = r.nextReceiver++;
// Keep track of when this receiver started, and make sure there
// is a timeout message pending to kill it if need be.
r.receiverTime = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
...
// 8 发送BROADCAST_TIMEOUT_MSG延时消息,延迟时间根据是前台或后台广播分别为20s、200s。
if (! mPendingBroadcastTimeoutMessage) {
long timeoutTime = r.receiverTime + mConstants.TIMEOUT;
...
setBroadcastTimeoutLocked(timeoutTime);
}
final BroadcastOptions brOptions = r.options;
final Object nextReceiver = r.receivers.get(recIdx);
if (nextReceiver instanceof BroadcastFilter) {
// Simple case: this is a registered receiver who gets
// a direct call.
BroadcastFilter filter = (BroadcastFilter)nextReceiver;
...
// 9 分发广播给广播接收者。
deliverToRegisteredReceiverLocked(r, filter, r.ordered, recIdx);
...
return;
}
// Hard case: need to instantiate the receiver, possibly
// starting its application process to host it.
ResolveInfo info =
(ResolveInfo)nextReceiver;
ComponentName component = new ComponentName(
info.activityInfo.applicationInfo.packageName,
info.activityInfo.name);
boolean skip = false;
...
String targetProcess = info.activityInfo.processName;
ProcessRecord app = mService.getProcessRecordLocked(targetProcess,
info.activityInfo.applicationInfo.uid);
...
// Is this receiver's application already running?
if (app != null && app.getThread() != null && !app.isKilled()) {
try {
app.addPackage(info.activityInfo.packageName,
info.activityInfo.applicationInfo.longVersionCode, mService.mProcessStats);
maybeAddAllowBackgroundActivityStartsToken(app, r);
// 10 启动广播接收器所在的进程后,处理广播。
processCurBroadcastLocked(r, app);
return;
}
...
}
...
r.curApp = mService.startProcessLocked(targetProcess,
info.activityInfo.applicationInfo, true,
r.intent.getFlags() | Intent.FLAG_FROM_BACKGROUND,
new HostingRecord("broadcast", r.curComponent), isActivityCapable
? ZYGOTE_POLICY_FLAG_LATENCY_SENSITIVE : ZYGOTE_POLICY_FLAG_EMPTY,
(r.intent.getFlags() & Intent.FLAG_RECEIVER_BOOT_UPGRADE) != 0, false);
...
maybeAddAllowBackgroundActivityStartsToken(r.curApp, r);
mPendingBroadcast = r;
mPendingBroadcastRecvIndex = recIdx;
}
// 延迟的时间因前台或后台广播分别是10s和60s。
final void setBroadcastTimeoutLocked(long timeoutTime) {
if (! mPendingBroadcastTimeoutMessage) {
Message msg = mHandler.obtainMessage(BROADCAST_TIMEOUT_MSG, this);
mHandler.sendMessageAtTime(msg, timeoutTime);
mPendingBroadcastTimeoutMessage = true;
}
}
2.3.2 移除广播超时ANR的延迟消息
2.3.2.1 com.android.server.am.BroadcastQueue
final void cancelBroadcastTimeoutLocked() {
if (mPendingBroadcastTimeoutMessage) {
mHandler.removeMessages(BROADCAST_TIMEOUT_MSG, this);
mPendingBroadcastTimeoutMessage = false;
}
}
2.3.3 触发广播超时ANR
2.3.3.1 com.android.server.am.BroadcastQueue
final void broadcastTimeoutLocked(boolean fromMsg) {
if (fromMsg) {
mPendingBroadcastTimeoutMessage = false;
}
if (mDispatcher.isEmpty() || mDispatcher.getActiveBroadcastLocked() == null) {
return;
}
long now = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
BroadcastRecord r = mDispatcher.getActiveBroadcastLocked();
if (fromMsg) {
...
long timeoutTime = r.receiverTime + mConstants.TIMEOUT;
if (timeoutTime > now) {
...
setBroadcastTimeoutLocked(timeoutTime);
return;
}
}
...
final boolean debugging = (r.curApp != null && r.curApp.isDebugging());
r.receiverTime = now;
if (!debugging) {
r.anrCount++;
}
ProcessRecord app = null;
String anrMessage = null;
Object curReceiver;
...
if (curReceiver != null && curReceiver instanceof BroadcastFilter) {
BroadcastFilter bf = (BroadcastFilter)curReceiver;
if (bf.receiverList.pid != 0
&& bf.receiverList.pid != ActivityManagerService.MY_PID) {
synchronized (mService.mPidsSelfLocked) {
app = mService.mPidsSelfLocked.get(
bf.receiverList.pid);
}
}
} else {
app = r.curApp;
}
if (app != null) {
anrMessage = "Broadcast of " + r.intent.toString();
}
if (mPendingBroadcast == r) {
mPendingBroadcast = null;
}
// Move on to the next receiver.
// 1 继续第将广播调度 转发给下一个BroadcastReceiver。
finishReceiverLocked(r, r.resultCode, r.resultData,
r.resultExtras, r.resultAbort, false);
scheduleBroadcastsLocked();
if (!debugging && anrMessage != null) {
// 2 触发anr
mService.mAnrHelper.appNotResponding(app, anrMessage);
}
}
2.3.4 广播超时ANR触发机制小节
(1) 当发送无序广播,静态注册的广播接收者是串行处理;动态注册的广播接收者是并行处理。
(2) 当发送有序广播,静态注册和动态注册的广播接收者都是串行处理。
(3) 静态注册的广播接收者处理的广播和动态注册的广播接收者处理的有序广播才有处理超时的ANR的机制。
(4) 根据发送广播关联Intent是否添加了FLAG_RECEIVER_FOREGROUND,来使用ams的前台或后台广播队列,发送广播超时ANR的延迟消息延迟时间为10s或60s。
2.4 ContentProvider publish timeout ANR触发原理
2.4.1 发送Provider publish timeout ANR的延迟消息
目标Provider所在的进程启动阶段 进程关联syster_server进程阶段会发送Provider publish 超时的ANR的延迟消息,延迟时间是10s。
2.4.1.1 com.android.server.am.ActivityManagerService
@Override
public final void attachApplication(IApplicationThread thread, long startSeq) {
...
synchronized (this) {
int callingPid = Binder.getCallingPid();
final int callingUid = Binder.getCallingUid();
final long origId = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
attachApplicationLocked(thread, callingPid, callingUid, startSeq);
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(origId);
}
}
private boolean attachApplicationLocked(@NonNull IApplicationThread thread,
int pid, int callingUid, long startSeq) {
...
boolean normalMode = mProcessesReady || isAllowedWhileBooting(app.info);
// 1 由pms获取manifest文件配置的且过滤的ProviderInfo集合。
List<ProviderInfo> providers = normalMode
? mCpHelper.generateApplicationProvidersLocked(app)
: null;
// 1 如果目标Provider在待安装的Provider集合中,则发送Provider publish timeout anr的延迟消息
// 延迟时间使10s。
if (providers != null && mCpHelper.checkAppInLaunchingProvidersLocked(app)) {
Message msg = mHandler.obtainMessage(CONTENT_PROVIDER_PUBLISH_TIMEOUT_MSG);
msg.obj = app;
mHandler.sendMessageDelayed(msg,
ContentResolver.CONTENT_PROVIDER_PUBLISH_TIMEOUT_MILLIS);
}
...
// 2 调用目标Provider进程的ActivityThread.ApplicationThread#bindApplication方法。
if (app.getIsolatedEntryPoint() != null) {
...
} else if (instr2 != null) {
thread.bindApplication(processName, appInfo, providerList,
instr2.mClass,
profilerInfo, instr2.mArguments,
instr2.mWatcher,
instr2.mUiAutomationConnection, testMode,
mBinderTransactionTrackingEnabled, enableTrackAllocation,
isRestrictedBackupMode || !normalMode, app.isPersistent(),
new Configuration(app.getWindowProcessController().getConfiguration()),
app.getCompat(), getCommonServicesLocked(app.isolated),
mCoreSettingsObserver.getCoreSettingsLocked(),
buildSerial, autofillOptions, contentCaptureOptions,
app.getDisabledCompatChanges(), serializedSystemFontMap);
} else {
thread.bindApplication(processName, appInfo, providerList, null, profilerInfo,
null, null, null, testMode,
mBinderTransactionTrackingEnabled, enableTrackAllocation,
isRestrictedBackupMode || !normalMode, app.isPersistent(),
new Configuration(app.getWindowProcessController().getConfiguration()),
app.getCompat(), getCommonServicesLocked(app.isolated),
mCoreSettingsObserver.getCoreSettingsLocked(),
buildSerial, autofillOptions, contentCaptureOptions,
app.getDisabledCompatChanges(), serializedSystemFontMap);
}
...
}
2.4.2 移除Provider publish timeout ANR的延迟消息
当目标Provider publish之后会移除Provider publish timeout ANR的延迟消息。
2.4.2.1 com.android.server.am.ContentProviderHelper
void publishContentProviders(IApplicationThread caller, List<ContentProviderHolder> providers) {
...
synchronized (mService) {
// 1 获取目标Provider进程
final ProcessRecord r = mService.getRecordForAppLOSP(caller);
...
final long origId = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
boolean providersPublished = false;
for (int i = 0, size = providers.size(); i < size; i++) {
ContentProviderHolder src = providers.get(i);
if (src == null || src.info == null || src.provider == null) {
continue;
}
ContentProviderRecord dst = r.mProviders.getProvider(src.info.name);
...
providersPublished = true;
ComponentName comp = new ComponentName(dst.info.packageName, dst.info.name);
// 2 将ContentProviderRecord存储到mProviderMap中。
mProviderMap.putProviderByClass(comp, dst);
String[] names = dst.info.authority.split(";");
for (int j = 0; j < names.length; j++) {
mProviderMap.putProviderByName(names[j], dst);
}
boolean wasInLaunchingProviders = false;
for (int j = 0, numLaunching = mLaunchingProviders.size(); j < numLaunching; j++) {
if (mLaunchingProviders.get(j) == dst) {
mLaunchingProviders.remove(j);
wasInLaunchingProviders = true;
j--;
numLaunching--;
}
}
if (wasInLaunchingProviders) {
// 3 移除WAIT_FOR_CONTENT_PROVIDER_TIMEOUT_MSG、CONTENT_PROVIDER_PUBLISH_TIMEOUT_MSG
// 的消息,解除触发ContentProvider publish超时的ANR。
mService.mHandler.removeMessages(
ActivityManagerService.WAIT_FOR_CONTENT_PROVIDER_TIMEOUT_MSG, dst);
mService.mHandler.removeMessages(
ActivityManagerService.CONTENT_PROVIDER_PUBLISH_TIMEOUT_MSG, r);
}
...
synchronized (dst) {
dst.provider = src.provider;
dst.setProcess(r);
// 4 唤醒使目标Provider操作进程的wait等待方法,见2.6。
dst.notifyAll();
// 5 唤醒使目标Provider操作进程的wait等待方法,见2.4。
dst.onProviderPublishStatusLocked(true);
}
dst.mRestartCount = 0;
}
...
}
}
2.4.3 触发Provider publish timeout的ANR
2.4.3.1 com.android.server.am.ActivityManagerService
case CONTENT_PROVIDER_PUBLISH_TIMEOUT_MSG: {
ProcessRecord app = (ProcessRecord) msg.obj;
synchronized (ActivityManagerService.this) {
mCpHelper.processContentProviderPublishTimedOutLocked(app);
}
} break;
2.4.3.2 com.android.server.am.ContentProviderHelper
void processContentProviderPublishTimedOutLocked(ProcessRecord app) {
// 1 清除内存中存储的有关目标Provider的各个元素,kill非用户感知的调用方进程。
cleanupAppInLaunchingProvidersLocked(app, true);
mService.mProcessList.removeProcessLocked(app, false, true,
ApplicationExitInfo.REASON_INITIALIZATION_FAILURE,
ApplicationExitInfo.SUBREASON_UNKNOWN,
"timeout publishing content providers");
}
boolean cleanupAppInLaunchingProvidersLocked(ProcessRecord app, boolean alwaysBad) {
...
boolean restart = false;
for (int i = mLaunchingProviders.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
ContentProviderRecord cpr = mLaunchingProviders.get(i);
if (cpr.launchingApp != app) {
continue;
}
if (++cpr.mRestartCount > ContentProviderRecord.MAX_RETRY_COUNT) {
// It's being launched but we've reached maximum attempts, mark it as bad
alwaysBad = true;
}
if (!alwaysBad && !app.mErrorState.isBad() && cpr.hasConnectionOrHandle()) {
restart = true;
} else {
// 调用removeDyingProviderLocked方法。
removeDyingProviderLocked(app, cpr, true);
}
}
return restart;
}
// 移除存储在各种集合中有关目标Provider的相关元素。kill目标Provider的进程。
boolean removeDyingProviderLocked(ProcessRecord proc, ContentProviderRecord cpr,
boolean always) {
boolean inLaunching = mLaunchingProviders.contains(cpr);
...
if (!inLaunching || always) {
synchronized (cpr) {
cpr.launchingApp = null;
cpr.notifyAll();
cpr.onProviderPublishStatusLocked(false);
// 1 移除之前发送的有关等待目标Provider publish的延迟消息。
mService.mHandler.removeMessages(
ActivityManagerService.WAIT_FOR_CONTENT_PROVIDER_TIMEOUT_MSG, cpr);
}
final int userId = UserHandle.getUserId(cpr.uid);
// Don't remove from provider map if it doesn't match
// could be a new content provider is starting
if (mProviderMap.getProviderByClass(cpr.name, userId) == cpr) {
mProviderMap.removeProviderByClass(cpr.name, userId);
}
String[] names = cpr.info.authority.split(";");
for (int j = 0; j < names.length; j++) {
// Don't remove from provider map if it doesn't match
// could be a new content provider is starting
if (mProviderMap.getProviderByName(names[j], userId) == cpr) {
mProviderMap.removeProviderByName(names[j], userId);
}
}
}
for (int i = cpr.connections.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
ContentProviderConnection conn = cpr.connections.get(i);
if (conn.waiting) {
// If this connection is waiting for the provider, then we don't
// need to mess with its process unless we are always removing
// or for some reason the provider is not currently launching.
if (inLaunching && !always) {
continue;
}
}
ProcessRecord capp = conn.client;
final IApplicationThread thread = capp.getThread();
conn.dead = true;
if (conn.stableCount() > 0) {
final int pid = capp.getPid();
if (!capp.isPersistent() && thread != null
&& pid != 0 && pid != ActivityManagerService.MY_PID) {
// 2 如果调用方进程使用的是stable ContentProvider进程操作数据,当目标Provider进程触发
// ANR的时候,且调用方进程是非用户感知的进程,会kill 调用方进程。
capp.killLocked(
"depends on provider " + cpr.name.flattenToShortString()
+ " in dying proc " + (proc != null ? proc.processName : "??")
+ " (adj " + (proc != null ? proc.mState.getSetAdj() : "??") + ")",
ApplicationExitInfo.REASON_DEPENDENCY_DIED,
ApplicationExitInfo.SUBREASON_UNKNOWN,
true);
}
} else if (thread != null && conn.provider.provider != null) {
try {
thread.unstableProviderDied(conn.provider.provider.asBinder());
} catch (RemoteException e) {
}
// In the protocol here, we don't expect the client to correctly
// clean up this connection, we'll just remove it.
cpr.connections.remove(i);
...
}
}
if (inLaunching && always) {
mLaunchingProviders.remove(cpr);
cpr.mRestartCount = 0;
inLaunching = false;
}
return inLaunching;
}
如果调用目标Provider操作的进程,使用的使stable的ContentProvider则调用方进程依赖Provider进程,当Provider publish触发ANR的时候,会kill调用方进程。
2.4.3.3 com.android.server.am.ProcessList
boolean removeProcessLocked(ProcessRecord app, boolean callerWillRestart,
boolean allowRestart, int reasonCode, int subReason, String reason) {
final String name = app.processName;
final int uid = app.uid;
...
ProcessRecord old = mProcessNames.get(name, uid);
...
removeProcessNameLocked(name, uid);
mService.mAtmInternal.clearHeavyWeightProcessIfEquals(app.getWindowProcessController());
boolean needRestart = false;
final int pid = app.getPid();
if ((pid > 0 && pid != ActivityManagerService.MY_PID)
|| (pid == 0 && app.isPendingStart())) {
...
// 1 kill目标Provider的进程。
app.killLocked(reason, reasonCode, subReason, true);
mService.handleAppDiedLocked(app, pid, willRestart, allowRestart,
false /* fromBinderDied */);
if (willRestart) {
removeLruProcessLocked(app);
mService.addAppLocked(app.info, null, false, null /* ABI override */,
ZYGOTE_POLICY_FLAG_EMPTY);
}
} else {
mRemovedProcesses.add(app);
}
return needRestart;
}
2.4.4 Provider publish timeout ANR触发机制小节
(1) 只有目标Provider的进程启动阶段才会发送Provider publish timeout ANR的延迟消息,且延迟时间是10s。当目标Provider完成了publish会移除该消息,如果从目标Provider进程attach关联systerm_server进程开始到目标Provider 发布结束其耗时超过了10s,则会触发ANR。
(2) ContentProvider publish timeout ANR触发会kill目标Provider进程,如果client通过stable类型的IContentProvider操作数据库,且client进程的优先级是用户不可感知的,则会kill client的进程;而通过unstable类型的IContentProvider操作数据库并会kill client进程。
2.5 触发ANR后的处理流程
所有类型的ANR触发后都会调用AnrHelper的方法appNotResponding方法。
2.5.1 android.server.am.AnrHelper
void appNotResponding(ProcessRecord anrProcess, String annotation) {
appNotResponding(anrProcess, null /* activityShortComponentName */, null /* aInfo */,
null /* parentShortComponentName */, null /* parentProcess */,
false /* aboveSystem */, annotation);
}
void appNotResponding(ProcessRecord anrProcess, String activityShortComponentName,
ApplicationInfo aInfo, String parentShortComponentName,
WindowProcessController parentProcess, boolean aboveSystem, String annotation) {
synchronized (mAnrRecords) {
mAnrRecords.add(new AnrRecord(anrProcess, activityShortComponentName, aInfo,
parentShortComponentName, parentProcess, aboveSystem, annotation));
}
startAnrConsumerIfNeeded();
}
private void startAnrConsumerIfNeeded() {
if (mRunning.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
new AnrConsumerThread().start();
}
}
private class AnrConsumerThread extends Thread {
AnrConsumerThread() {
super("AnrConsumer");
}
private AnrRecord next() {
synchronized (mAnrRecords) {
return mAnrRecords.isEmpty() ? null : mAnrRecords.remove(0);
}
}
@Override
public void run() {
AnrRecord r;
while ((r = next()) != null) {
scheduleBinderHeavyHitterAutoSamplerIfNecessary();
final long startTime = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
// If there are many ANR at the same time, the latency may be larger. If the latency
// is too large, the stack trace might not be meaningful.
final long reportLatency = startTime - r.mTimestamp;
final boolean onlyDumpSelf = reportLatency > EXPIRED_REPORT_TIME_MS;
r.appNotResponding(onlyDumpSelf);
final long endTime = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
Slog.d(TAG, "Completed ANR of " + r.mApp.processName + " in "
+ (endTime - startTime) + "ms, latency " + reportLatency
+ (onlyDumpSelf ? "ms (expired, only dump ANR app)" : "ms"));
}
mRunning.set(false);
synchronized (mAnrRecords) {
// The race should be unlikely to happen. Just to make sure we don't miss.
if (!mAnrRecords.isEmpty()) {
startAnrConsumerIfNeeded();
}
}
}
}
private static class AnrRecord {
...
void appNotResponding(boolean onlyDumpSelf) {
mApp.mErrorState.appNotResponding(mActivityShortComponentName, mAppInfo,
mParentShortComponentName, mParentProcess, mAboveSystem, mAnnotation,
onlyDumpSelf);
}
}
2.5.2 android.server.am.ProcessErrorStateRecord
void appNotResponding(String activityShortComponentName, ApplicationInfo aInfo,
String parentShortComponentName, WindowProcessController parentProcess,
boolean aboveSystem, String annotation, boolean onlyDumpSelf) {
ArrayList<Integer> firstPids = new ArrayList<>(5);
SparseArray<Boolean> lastPids = new SparseArray<>(20);
mApp.getWindowProcessController().appEarlyNotResponding(annotation, () -> {
synchronized (mService) {
mApp.killLocked("anr", ApplicationExitInfo.REASON_ANR, true);
}
});
long anrTime = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
if (isMonitorCpuUsage()) {
mService.updateCpuStatsNow();
}
final boolean isSilentAnr;
final int pid = mApp.getPid();
final UUID errorId;
synchronized (mService) {
...
// In case we come through here for the same app before completing
// this one, mark as anring now so we will bail out.
synchronized (mProcLock) {
setNotResponding(true);
}
// Log the ANR to the event log.
// 1 在event log中输出ANR, 关键字为am_anr
EventLog.writeEvent(EventLogTags.AM_ANR, mApp.userId, pid, mApp.processName,
mApp.info.flags, annotation);
...
// Dump thread traces as quickly as we can, starting with "interesting" processes.
firstPids.add(pid);
// Don't dump other PIDs if it's a background ANR or is requested to only dump self.
isSilentAnr = isSilentAnr();
...
}
// Log the ANR to the main log.
// 2 在main log中输出 ANR日志,关键字为ANR in
StringBuilder info = new StringBuilder();
info.setLength(0);
info.append("ANR in ").append(mApp.processName);
if (activityShortComponentName != null) {
info.append(" (").append(activityShortComponentName).append(")");
}
info.append("\n");
info.append("PID: ").append(pid).append("\n");
if (annotation != null) {
info.append("Reason: ").append(annotation).append("\n");
}
if (parentShortComponentName != null
&& parentShortComponentName.equals(activityShortComponentName)) {
info.append("Parent: ").append(parentShortComponentName).append("\n");
}
if (errorId != null) {
info.append("ErrorId: ").append(errorId.toString()).append("\n");
}
info.append("Frozen: ").append(mApp.mOptRecord.isFrozen()).append("\n");
...
StringBuilder report = new StringBuilder();
report.append(MemoryPressureUtil.currentPsiState());
// 3 创建CPU tracker对象。
ProcessCpuTracker processCpuTracker = new ProcessCpuTracker(true);
...
StringWriter tracesFileException = new StringWriter();
// To hold the start and end offset to the ANR trace file respectively.
final long[] offsets = new long[2];
// 4 在/data/anr 目录输出anr的trace文件。
File tracesFile = ActivityManagerService.dumpStackTraces(firstPids,
isSilentAnr ? null : processCpuTracker, isSilentAnr ? null : lastPids,
nativePids, tracesFileException, offsets, annotation);
if (isMonitorCpuUsage()) {
mService.updateCpuStatsNow();
mService.mAppProfiler.printCurrentCpuState(report, anrTime);
info.append(processCpuTracker.printCurrentLoad());
info.append(report);
}
report.append(tracesFileException.getBuffer());
info.append(processCpuTracker.printCurrentState(anrTime));
Slog.e(TAG, info.toString());
...
// Check if package is still being loaded
...
// 5 将traces文件 和 CPU使用率信息保存到dropbox,即data/system/dropbox目录
final ProcessRecord parentPr = parentProcess != null
? (ProcessRecord) parentProcess.mOwner : null;
mService.addErrorToDropBox("anr", mApp, mApp.processName, activityShortComponentName,
parentShortComponentName, parentPr, null, report.toString(), tracesFile,
null, new Float(loadingProgress), incrementalMetrics, errorId);
if (mApp.getWindowProcessController().appNotResponding(info.toString(),
() -> {
synchronized (mService) {
mApp.killLocked("anr", ApplicationExitInfo.REASON_ANR, true);
}
},
() -> {
synchronized (mService) {
mService.mServices.scheduleServiceTimeoutLocked(mApp);
}
})) {
return;
}
synchronized (mService) {
// mBatteryStatsService can be null if the AMS is constructed with injector only. This
// will only happen in tests.
if (mService.mBatteryStatsService != null) {
mService.mBatteryStatsService.noteProcessAnr(mApp.processName, mApp.uid);
}
// 6 杀死后台 anr 的进程
if (isSilentAnr() && !mApp.isDebugging()) {
mApp.killLocked("bg anr", ApplicationExitInfo.REASON_ANR, true);
return;
}
synchronized (mProcLock) {
// Set the app's notResponding state, and look up the errorReportReceiver
makeAppNotRespondingLSP(activityShortComponentName,
annotation != null ? "ANR " + annotation : "ANR", info.toString());
mDialogController.setAnrController(anrController);
}
// mUiHandler can be null if the AMS is constructed with injector only. This will only
// happen in tests.
if (mService.mUiHandler != null) {
// Bring up the infamous App Not Responding dialog
Message msg = Message.obtain();
msg.what = ActivityManagerService.SHOW_NOT_RESPONDING_UI_MSG;
msg.obj = new AppNotRespondingDialog.Data(mApp, aInfo, aboveSystem);
// 7 // 发送 anr 弹窗信息
mService.mUiHandler.sendMessageDelayed(msg, anrDialogDelayMs);
}
}
}
2.5.3 小节
当发生ANR时,会按顺序依次执行:
(1) 输入ANR Reason到 event log中,打印event log的ANR日志的时间时最接近进程发生ANR的。
(2) 收集并输出各个重要进程中各个线程的堆栈信息,以trace文件形式输出。
(3) 输出发生ANR的Reason,进程id,组件name,各个进程的CPU使用情况及CPU负载情况。
(4) 将trace文件和CPU使用情况信息保存到dropbox,即/data/systerm/dropbox目录。
3 触发ANR的影响因素
触发ANR的影响因素分为两类:一类时系统负载正常,但是应用内部其他线程占用资源过多,或者主线程处理消息过多或耗时严重或者;另一类则是系统负载过高或应用内部其他线程负载过高,应用主线程调度被严重抢占。
如果应用进程内部或者系统进程负载很大,如高CPU、高IO、低内存等,导致应用ANR。针对这种情况具体到主线程消息调度来看,就是很多消息耗时比较多,而且每次消息调度统计的Wall Duration(绝对时间:包括正常调度和等待、休眠时间)和CPU Duration(绝对时间:只包括CPU执行时间)相差很大。如果这种情况我们则认为系统负载或应用负载过高。
参考文章
1教你如何分析Android ANR问题
2Android ANR 经验汇总一 —— ANR介绍
3深入理解 Android ANR 触发原理以及信息收集过程
4startService启动过程分析
5今日头条 ANR 优化实践系列分享 - 实例剖析集锦
6Android线程的状态
7理解Android ANR的触发原理
8[ANR的原理分析和简单总结]