【剑指offer刷题记录 java版】链表双指针
本系列文章记录labuladong的算法小抄中剑指offer题目
【剑指offer刷题记录 java版】链表双指针
- 剑指 Offer II 025. 链表中的两数相加
- 剑指 Offer 25. 合并两个排序的链表
- 剑指 Offer 52. 两个链表的第⼀个公共节点
- 剑指 Offer II 021. 删除链表的倒数第 n 个结点
- 剑指 Offer II 022. 链表中环的⼊⼝节点
- 剑指 Offer II 023. 两个链表的第⼀个重合节点
- 剑指 Offer II 078. 合并排序链表(困难)
- 剑指 Offer 49. 丑数
- 剑指 Offer 18. 删除链表的节点
- 剑指 Offer II 061. 和最⼩的 k 个数对
- 剑指 Offer II 027. 回⽂链表
- 总结
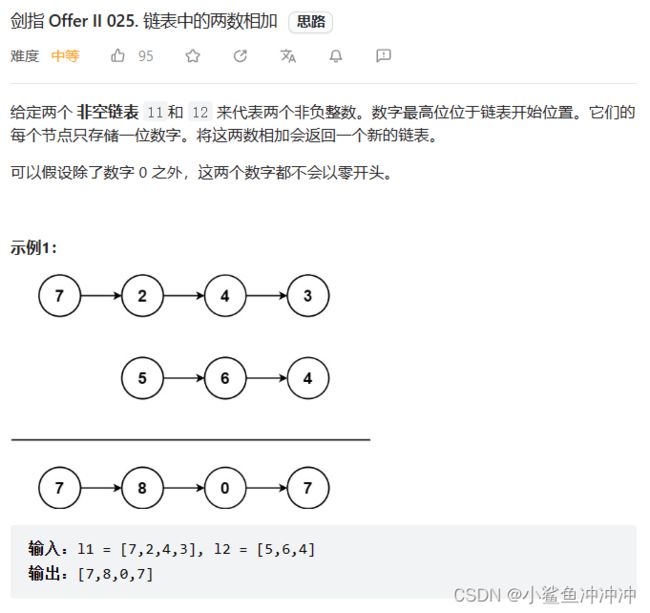
剑指 Offer II 025. 链表中的两数相加
题目链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/lMSNwu/
本题基础题:https://leetcode.cn/problems/add-two-numbers/ 基础题解法:
class Solution {
public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode p=l1,q=l2;//双指针
int temp = 0;//进位
ListNode res = new ListNode();//虚拟头节点(用于返回)
ListNode node = res;//结果指针
while(p!=null || q!=null || temp!=0){
int val = temp;//加上进位
if(p!=null){
val+=p.val;
p=p.next;
}
if(q!=null){
val+=q.val;
q=q.next;
}
temp=val/10;//记录本次进位
node.next=new ListNode();
node=node.next;
node.val=val%10;
}
return res.next;
}
}
class Solution {
public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
Deque<Integer> s1 = new LinkedList();
Deque<Integer> s2 = new LinkedList();
while(l1!=null){
s1.offerLast(l1.val);
l1=l1.next;
}
while(l2!=null){
s2.offerLast(l2.val);
l2=l2.next;
}
int temp=0;//记录进位
ListNode res = new ListNode();//结果指针
while(!s1.isEmpty() || !s2.isEmpty() || temp!=0){
int val = temp;
if(!s1.isEmpty()){
val += s1.pollLast();
}
if(!s2.isEmpty()){
val += s2.pollLast();
}
temp = val/10;
ListNode node = new ListNode(val%10);
node.next = res.next;
res.next = node;
}
return res.next;
}
}
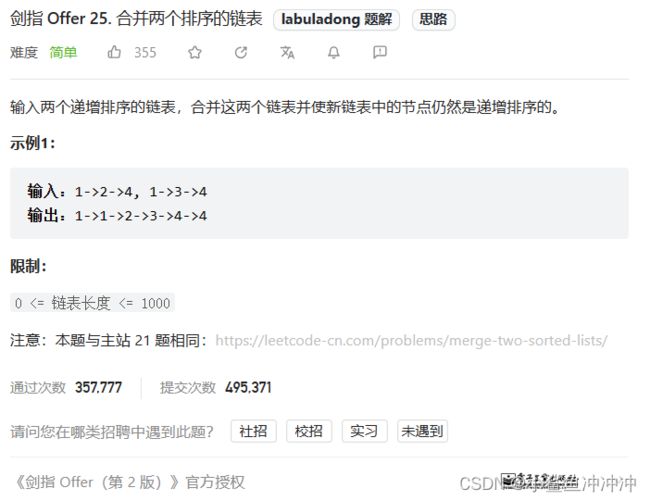
剑指 Offer 25. 合并两个排序的链表
题目链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/he-bing-liang-ge-pai-xu-de-lian-biao-lcof/
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode p1=l1,p2=l2;
ListNode res = new ListNode();
ListNode node = res;
while(p1!=null && p2!=null){
if(p1.val<p2.val){
node.next = p1;
p1=p1.next;
}else{
node.next = p2;
p2=p2.next;
}
node = node.next;
}
if(p1!=null){
node.next = p1;
}
if(p2!=null){
node.next = p2;
}
return res.next;
}
}
剑指 Offer 52. 两个链表的第⼀个公共节点
题目链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/liang-ge-lian-biao-de-di-yi-ge-gong-gong-jie-dian-lcof/

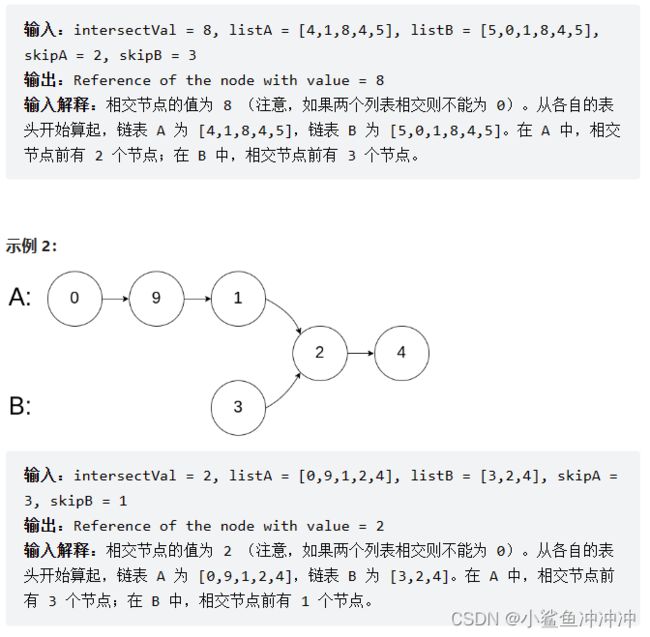

在逻辑上连接两个链表,使相交部分再其后半部分对齐。

class Solution {
ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
ListNode p1=headA, p2=headB;
while(p1!=p2){
if(p1==null){
p1=headB;
}else{
p1=p1.next;
}
if(p2==null){
p2=headA;
}else{
p2=p2.next;
}
}
return p1;
}
}
剑指 Offer II 021. 删除链表的倒数第 n 个结点
题目链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/SLwz0R/
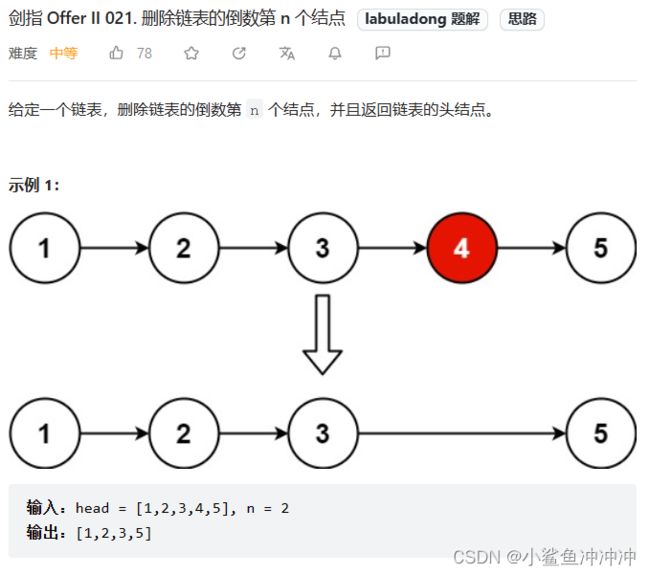
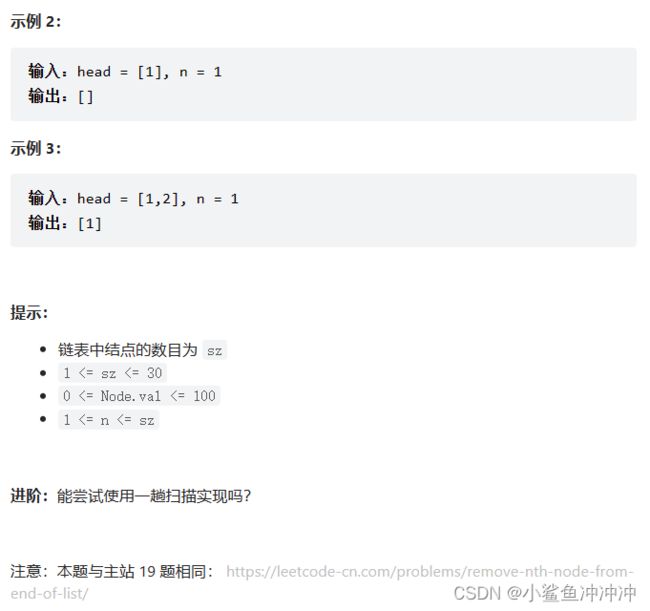
本题解法类似固定长度的滑动窗口。需要使用虚拟头节点避免空指针的状况。
class Solution {
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
// 虚拟头结点
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1);
dummy.next = head;
ListNode p1 = dummy;
//先走n+1步
for (int i = 0; i < n+1; i++) {
p1 = p1.next;
}
ListNode p2 = dummy;
while(p1!=null){
p1=p1.next;
p2=p2.next;
}
p2.next=p2.next.next;
return dummy.next;
}
}
剑指 Offer II 022. 链表中环的⼊⼝节点
基础题:https://leetcode.cn/problems/linked-list-cycle/ 链表找环解法:
public class Solution {
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
ListNode slow = head, fast = head;
while(fast!=null && fast.next!=null){
slow=slow.next;
fast=fast.next.next;
if(slow==fast){return true;}
}
return false;
}
}
题目链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/c32eOV/



先快慢移动,相交后把一个放回起点,另一个再交点,这两个指针以相同速度移动,第二次相交位置即为环的起点。
public class Solution {
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
ListNode slow = head, fast = head;
while(fast!=null && fast.next!=null){
slow=slow.next;
fast=fast.next.next;
if(slow==fast){
slow=head;
while(slow!=fast){
slow=slow.next;
fast=fast.next;
}
return slow;
}
}
return null;
}
}
剑指 Offer II 023. 两个链表的第⼀个重合节点
题目链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/3u1WK4/



进阶:能否设计一个时间复杂度 O(n) 、仅用 O(1) 内存的解决方案?
【思路】两个指针分别遍历链表AB和链表BA,因为不同的元素数量一致,因此交点会在后半部分对齐。
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
ListNode p1=headA,p2=headB;
while(p2!=p1){
//遍历链表AB
if(p1==null){
p1=headB;
}else{
p1=p1.next;
}
//遍历链表AB
if(p2==null){
p2=headA;
}else{
p2=p2.next;
}
}
return p1;//如果没有交点,最后两个指针都为null
}
}
剑指 Offer II 078. 合并排序链表(困难)
题目链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/vvXgSW/


利用优先级队列,每次输出当前最小的节点
优先级队列基础知识
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists) {
if (lists.length == 0) return null;
// 虚拟头结点
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode p = dummy;
// 优先级队列,最小堆
PriorityQueue<ListNode> pq = new PriorityQueue<>(
lists.length, (a, b)->(a.val - b.val));
// 将 k 个链表的头结点加入最小堆
for (ListNode head : lists) {
if (head != null)
pq.add(head);
}
while (!pq.isEmpty()) {
// 获取最小节点,接到结果链表中
ListNode node = pq.poll();
p.next = node;
if (node.next != null) {
pq.add(node.next);
}
// p 指针不断前进
p = p.next;
}
return dummy.next;
}
}
剑指 Offer 49. 丑数
基础题:263. 丑数
基础题解法:
class Solution {
public boolean isUgly(int n) {
if (n <= 0) return false;
// 如果 n 是丑数,分解因子应该只有 2, 3, 5
while(n%2==0){n/=2;}//该数内部还有因数2时,除以2
while(n%3==0){n/=3;}//该数内部还有因数3时,除以3
while(n%5==0){n/=5;}//该数内部还有因数5时,除以5
return n==1;
}
}
题目链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/chou-shu-lcof/
巧妙地合并三个链表,具体思路可以参考264. 丑数 II 中labuladong的可视化过程
class Solution {
public int nthUglyNumber(int n) {
// 可以理解为三个指向有序链表头结点的指针
int p2 = 1, p3 = 1, p5 = 1;
// 可以理解为三个有序链表的头节点的值
int product2 = 1, product3 = 1, product5 = 1;
// 可以理解为最终合并的有序链表(结果链表)
int[] ugly = new int[n + 1];
// 可以理解为结果链表上的指针
int p = 1;
// 开始合并三个有序链表
while (p <= n) {
// 取三个链表的最小结点
int min = Math.min(Math.min(product2, product3), product5);
// 接到结果链表上
ugly[p] = min;
p++;
// 前进对应有序链表上的指针
if (min == product2) {
product2 = 2 * ugly[p2];
p2++;
}
if (min == product3) {
product3 = 3 * ugly[p3];
p3++;
}
if (min == product5) {
product5 = 5 * ugly[p5];
p5++;
}
}
// 返回第 n 个丑数
return ugly[n];
}
}
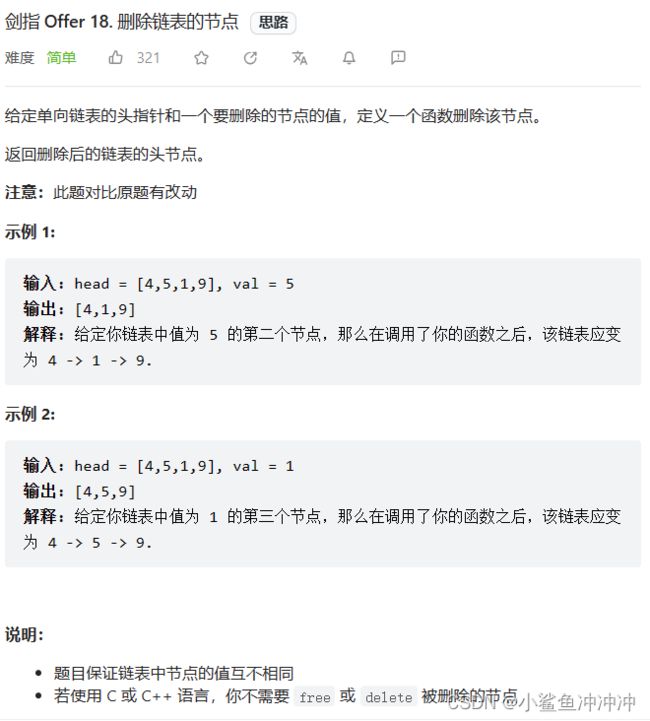
剑指 Offer 18. 删除链表的节点
题目链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/shan-chu-lian-biao-de-jie-dian-lcof/
class Solution {
public ListNode deleteNode(ListNode head, int val) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode();
dummy.next=head;
ListNode p = dummy;
while(p!=null && p.next!=null){
if(p.next.val==val){
p.next=p.next.next;
}
p=p.next;
}
return dummy.next;
}
}
剑指 Offer II 061. 和最⼩的 k 个数对
题目链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/qn8gGX/
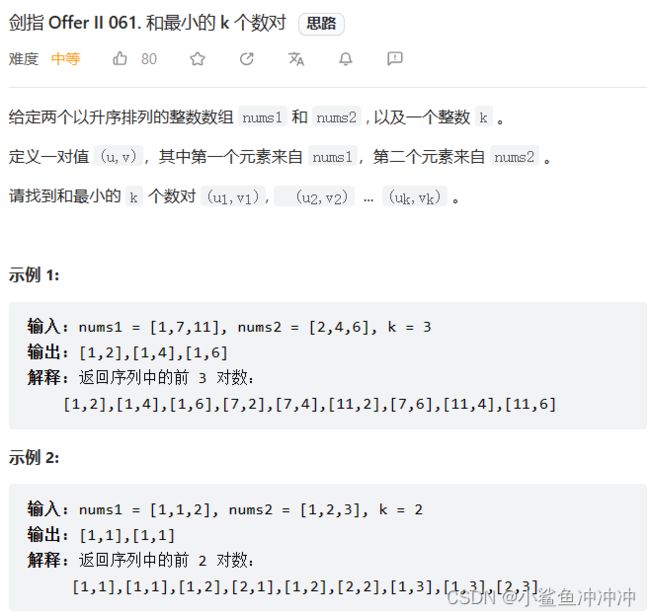
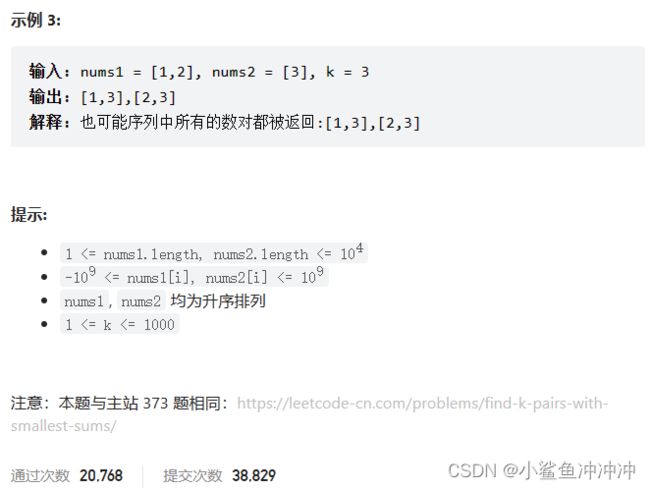
本质也是合并K个有序链表,可以用优先级队列处理。
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> kSmallestPairs(int[] nums1, int[] nums2, int k) {
// 存储三元组 (num1[i], nums2[i], i)
// i 记录 nums2 元素的索引位置,用于生成下一个节点
PriorityQueue<int[]> pq = new PriorityQueue<>((a, b) -> {
// 按照数对的元素和升序排序
return (a[0] + a[1]) - (b[0] + b[1]);
});
// 按照 23 题的逻辑初始化优先级队列(将每个链表的链表头加入优先级队列)
for (int i = 0; i < nums1.length; i++) {
pq.offer(new int[]{nums1[i], nums2[0], 0});
}
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
// 执行合并多个有序链表的逻辑
while (!pq.isEmpty() && k > 0) {
int[] cur = pq.poll();
k--;
// 链表中的下一个节点加入优先级队列
int next_index = cur[2] + 1;
if (next_index < nums2.length) {
pq.add(new int[]{cur[0], nums2[next_index], next_index});
}
List<Integer> pair = new ArrayList<>();
pair.add(cur[0]);
pair.add(cur[1]);
res.add(pair);
}
return res;
}
}
剑指 Offer II 027. 回⽂链表
题目链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/aMhZSa/


方法一:时间复杂度 O(n) ,空间复杂度 O(n) ,将值复制到数组中后用双指针法
class Solution {
public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
List<Integer> vals = new ArrayList<Integer>();
// 将链表的值复制到数组中
ListNode currentNode = head;
while (currentNode != null) {
vals.add(currentNode.val);
currentNode = currentNode.next;
}
// 使用双指针判断是否回文
int front = 0;
int back = vals.size() - 1;
while (front < back) {
if (!vals.get(front).equals(vals.get(back))) {
return false;
}
front++;
back--;
}
return true;
}
}
方法二:时间复杂度 O(n) ,空间复杂度 O(1) ,双指针找到中间节点,反转链表然后对比
class Solution {
public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
ListNode slow=head,fast=head;
while(fast!=null && fast.next!=null){
slow=slow.next;
fast=fast.next.next;
}
if(fast!=null){
// 链表有奇数个节点
slow=slow.next;
}else{
// 链表有偶数个节点,什么都不做
}
// 从slow开始反转后半部分链表
ListNode pre = null;
ListNode cur = slow;
while(cur!=null){
ListNode next=cur.next;
cur.next=pre;
pre =cur;
cur = next;
}
//此时pre为反转后链表的头节点
while(pre!=null){
if(head.val!=pre.val){
return false;
}
head=head.next;
pre=pre.next;
}
return true;
}
}
总结
- 利用虚拟头节点可以简化链表的创建,创建时始终记得要有一个指针。
- 链表的增删改可以通过虚拟头节点来统一。
- 合并 k 个有序链表可以利用优先级队列来实现,流程是:先将所有链表的头节点传入优先级队列,没弹出一个就补上该链表的下一个元素,直至满足输出需求。