Android SurfaceFlinger对VSync信号的处理过程分析
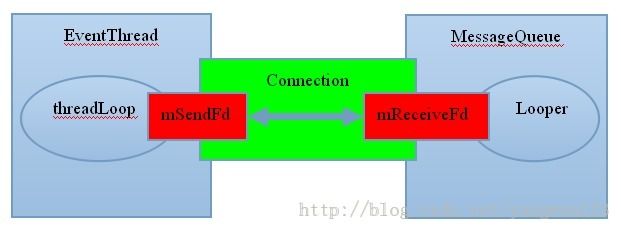
在Android SurfaceFlinger服务的消息循环过程源码分析中分析了SurfaceFlinger的消息循环过程,SurfaceFlinger通过维护一个消息队列来实现消息的异步处理。Android应用程序消息循环源码分析介绍了消息循环定义的Looper对象不仅可以处理Java层和C++层的消息,同时也可以监控用户添加的文件句柄。Android SurfaceFlinger服务的消息循环过程源码分析也介绍了SurfaceFlinger与EventThread线程间的VSync事件连接Connection的创建及注册到EventThread线程过程,同时将Connection中的Socket读端添加到SurfaceFlinger消息循环中监听。在Android VSync事件分发过程源码分析中介绍了EventThread线程负责分发VSync事件给已注册的Connection连接,下图就是SurfaceFlinger与EventThread之间的关系图:
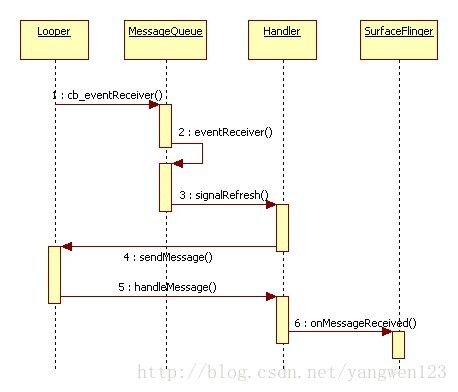
上图显示了EventThread线程是通过Socket方式与SurfaceFlinger的消息循环通信的,EventThread线程是Server,往Socket的发送端写入VSync事件信息,SurfaceFlinger是Client,从Socket的接收端读取到VSync事件信息,从而响应VSync中断信号。在将Socket的接收端添加到SurfaceFlinger的消息循环Looper对象中时,注册了Socket接收端数据读取时的回调函数:
void MessageQueue::setEventThread(const sp& eventThread)
{
mEventThread = eventThread;
mEvents = eventThread->createEventConnection();
mEventTube = mEvents->getDataChannel();
mLooper->addFd(mEventTube->getFd(), 0, ALOOPER_EVENT_INPUT,MessageQueue::cb_eventReceiver, this);
} createEventConnection()用于创建一个事件连接Connection,通过调用Connection的getDataChannel()函数返回一个BitTube对象,这是对Socket通信方式的封装类,描述了VSync事件信息的数据通道。调用BitTube对象的getFd()函数既可得到创建的Socket的发送端句柄,然后调用Looper类提供的addFd()函数将Socket发送端句柄添加到SurfaceFlinger的消息循环Looper对象中监听,同时注册回调函数MessageQueue::cb_eventReceiver。通过Looper添加了一个fd,这实际上就是Socket pair中的一端。然后Looper将这个fd与其callback函数(即MessageQueue::cb_eventReceiver)加入全局的mRequests进行管理。这个Vector会集中所有需要监测的fd,这样当Looper进行pollInner时,只要Socket接收端有数据可以读取时,SurfaceFlinger消息循环自动调用该函数来处理VSync事件,addFd()函数的最后一个参数this指向当前SurfaceFlinger的消息队列MessageQueue对象。
int MessageQueue::cb_eventReceiver(int fd, int events, void* data) {
MessageQueue* queue = reinterpret_cast(data);
return queue->eventReceiver(fd, events);
} 参数data即是上面addFd()函数的最后一个参数this指向的SurfaceFlinger的消息队列MessageQueue对象,这里进一步调用MessageQueue的eventReceiver()函数
int MessageQueue::eventReceiver(int fd, int events) {
ssize_t n;
DisplayEventReceiver::Event buffer[8];
while ((n = DisplayEventReceiver::getEvents(mEventTube, buffer, 8)) > 0) {
for (int i=0 ; isignalRefresh();
break;
}
}
}
return 1;
} 函数通过调用DisplayEventReceiver::getEvents()函数从Socket接收端读取VSync事件信息,Android VSync事件分发过程源码分析中介绍了,EventThread线程可以通过Socket发送端写入多个Event事件信息,在Socket接收端同样可以连续读取多个事件信息,当getEvents()函数从Socket接收端读取到多个事件信息时,接着就遍历这些事件,并且只对事件类型为DisplayEventReceiver::DISPLAY_EVENT_VSYNC的事件即VSync事件做处理,事件处理过程就是通过Handler向SurfaceFlinger的消息队列发送一个消息:
void MessageQueue::Handler::signalRefresh() {
if ((android_atomic_or(eventMaskRefresh, &mEventMask) & eventMaskRefresh) == 0) {
mQueue.mLooper->sendMessage(this, Message(MessageQueue::REFRESH));
}
}这里只是简单地向SurfaceFlinger的消息队列发送一个MessageQueue::REFRESH消息,关于消息的发送过程,请参考Android应用程序消息循环源码分析。SurfaceFlinger消息循环线程对该消息的处理过程如下:
void MessageQueue::Handler::handleMessage(const Message& message) {
switch (message.what) {
case INVALIDATE:
android_atomic_and(~eventMaskInvalidate, &mEventMask);
mQueue.mFlinger->onMessageReceived(message.what);
break;
case REFRESH:
android_atomic_and(~eventMaskRefresh, &mEventMask);
mQueue.mFlinger->onMessageReceived(message.what);
break;
}
}从上面可以看出,函数调用SurfaceFlinger的onMessageReceived函数来处理MessageQueue::REFRESH消息
void SurfaceFlinger::onMessageReceived(int32_t what)
{
ATRACE_CALL();
switch (what) {
case MessageQueue::REFRESH: {
const uint32_t mask = eTransactionNeeded | eTraversalNeeded;
uint32_t transactionFlags = peekTransactionFlags(mask);
if (CC_UNLIKELY(transactionFlags)) {
handleTransaction(transactionFlags);
}
handlePageFlip();
handleRefresh();
const DisplayHardware& hw(graphicPlane(0).displayHardware());
if (CC_UNLIKELY(mHwWorkListDirty)) {
handleWorkList();
}
if (CC_LIKELY(hw.canDraw())) {
handleRepaint();
hw.compositionComplete();
postFramebuffer();
#if defined(LAYER_DUMP_BMP)
frame_count++;
#endif
} else {
hw.compositionComplete();
}
} break;
}
}1. handleTransaction
void SurfaceFlinger::handleTransaction(uint32_t transactionFlags)
{
ATRACE_CALL();
// here we keep a copy of the drawing state (that is the state that's
// going to be overwritten by handleTransactionLocked()) outside of
// mStateLock so that the side-effects of the State assignment
// don't happen with mStateLock held (which can cause deadlocks).
State drawingState(mDrawingState);
Mutex::Autolock _l(mStateLock);
const nsecs_t now = systemTime();
mDebugInTransaction = now;
//系统显示屏的属性发生了变化,eTransactionNeeded位就会等于1
//应用程序窗口的属性发生了变化,eTraversalNeeded位就会等于1
const uint32_t mask = eTransactionNeeded | eTraversalNeeded;
//检查系统显示屏或者应用程序窗口的属性是否发生了变化
transactionFlags = getTransactionFlags(mask);
handleTransactionLocked(transactionFlags);
mLastTransactionTime = systemTime() - now;
mDebugInTransaction = 0;
invalidateHwcGeometry();
// here the transaction has been committed
}void SurfaceFlinger::handleTransactionLocked(uint32_t transactionFlags)
{
//mCurrentState指向当前状态State对象,State对象的成员变量layersSortedByZ保存了SufaceFlinger服///务当前所需要渲染的应用程序窗口
const LayerVector& currentLayers(mCurrentState.layersSortedByZ);
const size_t count = currentLayers.size();
//应用程序窗口的属性发生了变化
const bool layersNeedTransaction = transactionFlags & eTraversalNeeded;
if (layersNeedTransaction) {
//循环检查每一个应用程序窗口的属性是否发生了变化
for (size_t i=0 ; i& layer = currentLayers[i];
uint32_t trFlags = layer->getTransactionFlags(eTransactionNeeded);
//应用程序窗口的属性被修改过
if (!trFlags) continue;
//处理应用程序窗口的属性变化
const uint32_t flags = layer->doTransaction(0);
//如果一个应用程序窗口发生的属性变化是可见区域发生了改变
if (flags & Layer::eVisibleRegion)
//要重新计算各个应用程序窗口的可见区域
mVisibleRegionsDirty = true;
}
}
//系统显示屏的属性发生了变化
if (transactionFlags & eTransactionNeeded) {
//mDrawingState用来描述SufaceFlinger服务的上一次渲染状态
//mCurrentState用来描述SufaceFlinger服务当前渲染状态
//判断系统显示屏的旋转方向是否发生变化
if (mCurrentState.orientation != mDrawingState.orientation) {
//重新设置系统显示屏的旋转方向
const int dpy = 0;
const int orientation = mCurrentState.orientation;
// Currently unused: const uint32_t flags = mCurrentState.orientationFlags;
GraphicPlane& plane(graphicPlane(dpy));
plane.setOrientation(orientation);
//同步更新的是mServerCblk中的信息,它是提供给各应用程序查询当前显示属性的,
//包括宽、高、格式、旋转角度、fps、密度等一系列数据。
// update the shared control block
const DisplayHardware& hw(plane.displayHardware());
volatile display_cblk_t* dcblk = mServerCblk->displays + dpy;
dcblk->orientation = orientation;
dcblk->w = plane.getWidth();
dcblk->h = plane.getHeight();
//需要重新计算各个应用程序窗口的可见区域
mVisibleRegionsDirty = true;
//需要重新绘制整个显示屏
mDirtyRegion.set(hw.bounds());
}
//判断是否增加了应用程序窗口
if (currentLayers.size() > mDrawingState.layersSortedByZ.size()) {
//需要重新计算各个应用程序窗口的可见区域
mVisibleRegionsDirty = true;
}
//判断是否移除了某些应用程序窗口
if (mLayersRemoved) {
mLayersRemoved = false;
//一旦图层被移除,意味着被它遮盖的区域就有可能重新显露出来
//所以需要重新计算各个应用程序窗口的可见区域
mVisibleRegionsDirty = true;
const LayerVector& previousLayers(mDrawingState.layersSortedByZ);
const size_t count = previousLayers.size();
//查找已经被移除的应用程序窗口
for (size_t i=0 ; i& layer(previousLayers[i]);
//在mCurrentState找不到了,就认为被移除了
if (currentLayers.indexOf( layer ) < 0) {
//需要将它所占用的区域增加到mDirtyRegionRemovedLayer所描述的一个区域去
mDirtyRegionRemovedLayer.orSelf(layer->visibleRegionScreen);
}
}
}
}
//系统显示屏以及各个应用程序窗口的属性变化已经处理完毕,把mCurrentState赋给mmDrawingState
commitTransaction();
} frameworks\native\services\surfaceflinger\Layer.cpp
uint32_t Layer::doTransaction(uint32_t flags)
{
ATRACE_CALL();
//每一个应用程序窗口在内部也分别使用两个类型为State的成员变量来描述前后状态
//mDrawingState描述上一次的渲染状态
const Layer::State& front(drawingState());
//mCurrentState描述当前渲染状态
const Layer::State& temp(currentState());
//判断窗口大小是否改变
const bool sizeChanged = (temp.requested.w != front.requested.w) ||
(temp.requested.h != front.requested.h);
//应用程序窗口的大小发生了变化
if (sizeChanged) {
// the size changed, we need to ask our client to request a new buffer
// record the new size, form this point on, when the client request
// a buffer, it'll get the new size.
mSurfaceTexture->setDefaultBufferSize(temp.requested.w, temp.requested.h);
}
//判断是否为固定大小模式
if (!isFixedSize()) {
const bool resizePending = (temp.requested.w != temp.active.w) ||
(temp.requested.h != temp.active.h);
if (resizePending) {
flags |= eDontUpdateGeometryState;
}
}
return LayerBase::doTransaction(flags);
}frameworks\native\services\surfaceflinger\LayerBase.cpp
uint32_t LayerBase::doTransaction(uint32_t flags)
{
const Layer::State& front(drawingState());
const Layer::State& temp(currentState());
// always set active to requested, unless we're asked not to
// this is used by Layer, which special cases resizes.
if (flags & eDontUpdateGeometryState) {
} else {
Layer::State& editTemp(currentState());
editTemp.active = temp.requested;
}
//窗口激活状态发生变化,需要重新计算可见区域
if (front.active != temp.active) {
// invalidate and recompute the visible regions if needed
flags |= Layer::eVisibleRegion;
}
//sequence用来描述一个应用程序窗口的其它属性是否发生过变化,当Layer的position、zorder、alpha
//matrix、transparent region、flags、crop等一系列属性发生变化,sequence的值就会比原来增加1。
//通过sequence收集属性的变化,而到了VSYNC信号产生时才做统一处理
if (temp.sequence != front.sequence) {
// invalidate and recompute the visible regions if needed
flags |= eVisibleRegion;
this->contentDirty = true;
// we may use linear filtering, if the matrix scales us
const uint8_t type = temp.transform.getType();
mNeedsFiltering = (!temp.transform.preserveRects() ||(type >= Transform::SCALE));
}
//应用程序窗口属性变化已经处理完毕,交换前后状态
commitTransaction();
return flags;
}