彻底搞懂线程池原理以及创建方式
1. 为什么要使用线程池
在实际使用中,线程是很占用系统资源的,如果对线程管理不善很容易导致系统问题。因此,在大多数并发框架中都会使用线程池来管理线程,使用线程池管理线程主要有如下好处:
- 降低资源消耗。通过复用已存在的线程和降低线程关闭的次数来尽可能降低系统性能损耗;
- 提升系统响应速度。通过复用线程,省去创建线程的过程,因此整体上提升了系统的响应速度;
- 提高线程的可管理性。线程是稀缺资源,如果无限制的创建,不仅会消耗系统资源,还会降低系统的稳定性,因此,需要使用线程池来管理线程。
2. 线程池的工作原理
当一个并发任务提交给线程池,线程池分配线程去执行任务的过程如下图所示:
从图可以看出,线程池执行所提交的任务过程主要有这样几个阶段:
- 先判断线程池中核心线程池所有的线程是否都在执行任务。如果不是,则新创建一个线程执行刚提交的任务,否则,核心线程池中所有的线程都在执行任务,则进入第2步;
- 判断当前阻塞队列是否已满,如果未满,则将提交的任务放置在阻塞队列中;否则,则进入第3步;
- 判断线程池中所有的线程是否都在执行任务,如果没有,则创建一个新的线程来执行任务,否则,则交给饱和策略进行处理
3. 线程池的创建
创建线程池主要是ThreadPoolExecutor类来完成,ThreadPoolExecutor的有许多重载的构造方法,通过参数最多的构造方法来理解创建线程池有哪些需要配置的参数。ThreadPoolExecutor的构造方法为:
ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
int maximumPoolSize,
long keepAliveTime,
TimeUnit unit,
BlockingQueue workQueue,
ThreadFactory threadFactory,
RejectedExecutionHandler handler)
下面对参数进行说明:
- corePoolSize:表示核心线程池的大小。当提交一个任务时,如果当前核心线程池的线程个数没有达到corePoolSize,则会创建新的线程来执行所提交的任务,即使当前核心线程池有空闲的线程。如果当前核心线程池的线程个数已经达到了corePoolSize,则不再重新创建线程。如果调用了
prestartCoreThread()或者prestartAllCoreThreads(),线程池创建的时候所有的核心线程都会被创建并且启动。 - maximumPoolSize:表示线程池能创建线程的最大个数。如果当阻塞队列已满时,并且当前线程池线程个数没有超过maximumPoolSize的话,就会创建新的线程来执行任务。
- keepAliveTime:空闲线程存活时间。如果当前线程池的线程个数已经超过了corePoolSize,并且线程空闲时间超过了keepAliveTime的话,就会将这些空闲线程销毁,这样可以尽可能降低系统资源消耗。
- unit:时间单位。为keepAliveTime指定时间单位。
- workQueue:阻塞队列。用于保存任务的阻塞队列,关于阻塞队列可以看这篇文章。可以使用ArrayBlockingQueue, LinkedBlockingQueue, SynchronousQueue, PriorityBlockingQueue。
- threadFactory:创建线程的工程类。可以通过指定线程工厂为每个创建出来的线程设置更有意义的名字,如果出现并发问题,也方便查找问题原因。
- handler:饱和策略。当线程池的阻塞队列已满和指定的线程都已经开启,说明当前线程池已经处于饱和状态了,那么就需要采用一种策略来处理这种情况。采用的策略有这几种:
- AbortPolicy: 直接拒绝所提交的任务,并抛出RejectedExecutionException异常;
- CallerRunsPolicy:只用调用者所在的线程来执行任务;
- DiscardPolicy:不处理直接丢弃掉任务;
- DiscardOldestPolicy:丢弃掉阻塞队列中存放时间最久的任务,执行当前任务
线程池执行逻辑
通过ThreadPoolExecutor创建线程池后,提交任务后执行过程是怎样的,下面来通过源码来看一看。execute方法源码如下:
public void execute(Runnable command) {
if (command == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
int c = ctl.get();
//如果线程池的线程个数少于corePoolSize则创建新线程执行当前任务
if (workerCountOf(c) < corePoolSize) {
if (addWorker(command, true))
return;
c = ctl.get();
}
//如果线程个数大于corePoolSize或者创建线程失败,则将任务存放在阻塞队列workQueue中
if (isRunning(c) && workQueue.offer(command)) {
int recheck = ctl.get();
if (! isRunning(recheck) && remove(command))
reject(command);
else if (workerCountOf(recheck) == 0)
addWorker(null, false);
}
//如果当前任务无法放进阻塞队列中,则创建新的线程来执行任务
else if (!addWorker(command, false))
reject(command);
}
ThreadPoolExecutor的execute方法执行逻辑请见注释。下图为ThreadPoolExecutor的execute方法的执行示意图:
execute方法执行逻辑有这样几种情况:
- 如果当前运行的线程少于corePoolSize,则会创建新的线程来执行新的任务;
- 如果运行的线程个数等于或者大于corePoolSize,则会将提交的任务存放到阻塞队列workQueue中;
- 如果当前workQueue队列已满的话,则会创建新的线程来执行任务;
- 如果线程个数已经超过了maximumPoolSize,则会使用饱和策略RejectedExecutionHandler来进行处理。
需要注意的是,线程池的设计思想就是使用了核心线程池corePoolSize,阻塞队列workQueue和线程池maximumPoolSize,这样的缓存策略来处理任务,实际上这样的设计思想在需要框架中都会使用。
4. 线程池的关闭
关闭线程池,可以通过shutdown和shutdownNow这两个方法。它们的原理都是遍历线程池中所有的线程,然后依次中断线程。shutdown和shutdownNow还是有不一样的地方:
shutdownNow首先将线程池的状态设置为STOP,然后尝试停止所有的正在执行和未执行任务的线程,并返回等待执行任务的列表;shutdown只是将线程池的状态设置为SHUTDOWN状态,然后中断所有没有正在执行任务的线程
可以看出shutdown方法会将正在执行的任务继续执行完,而shutdownNow会直接中断正在执行的任务。调用了这两个方法的任意一个,isShutdown方法都会返回true,当所有的线程都关闭成功,才表示线程池成功关闭,这时调用isTerminated方法才会返回true。
5. 如何合理配置线程池参数?
要想合理的配置线程池,就必须首先分析任务特性,可以从以下几个角度来进行分析:
- 任务的性质:CPU密集型任务,IO密集型任务和混合型任务。
- 任务的优先级:高,中和低。
- 任务的执行时间:长,中和短。
- 任务的依赖性:是否依赖其他系统资源,如数据库连接。
任务性质不同的任务可以用不同规模的线程池分开处理。CPU密集型任务配置尽可能少的线程数量,如配置Ncpu+1个线程的线程池。IO密集型任务则由于需要等待IO操作,线程并不是一直在执行任务,则配置尽可能多的线程,如2xNcpu。混合型的任务,如果可以拆分,则将其拆分成一个CPU密集型任务和一个IO密集型任务,只要这两个任务执行的时间相差不是太大,那么分解后执行的吞吐率要高于串行执行的吞吐率,如果这两个任务执行时间相差太大,则没必要进行分解。我们可以通过Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors()方法获得当前设备的CPU个数。
优先级不同的任务可以使用优先级队列PriorityBlockingQueue来处理。它可以让优先级高的任务先得到执行,需要注意的是如果一直有优先级高的任务提交到队列里,那么优先级低的任务可能永远不能执行。
执行时间不同的任务可以交给不同规模的线程池来处理,或者也可以使用优先级队列,让执行时间短的任务先执行。
依赖数据库连接池的任务,因为线程提交SQL后需要等待数据库返回结果,如果等待的时间越长CPU空闲时间就越长,那么线程数应该设置越大,这样才能更好的利用CPU。
并且,阻塞队列最好是使用有界队列,如果采用无界队列的话,一旦任务积压在阻塞队列中的话就会占用过多的内存资源,甚至会使得系统崩溃。
6.线程池的6种创建方式,你都清楚吗?
线程池的创建⽅法总共有 7 种,但总体来说可分为 2 类:
- 通过
ThreadPoolExecutor创建的线程池; - 通过
Executors创建的线程池。
线程池的创建⽅式总共包含以下 7 种(其中 6 种是通过 Executors 创建的, 1 种是通过ThreadPoolExecutor 创建的):
Executors.newFixedThreadPool:创建⼀个固定⼤⼩的线程池,可控制并发的线程数,超出的线程会在队列中等待;Executors.newCachedThreadPool:创建⼀个可缓存的线程池,若线程数超过处理所需,缓存⼀段时间后会回收,若线程数不够,则新建线程;Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor:创建单个线程数的线程池,它可以保证先进先出的执⾏顺序;Executors.newScheduledThreadPool:创建⼀个可以执⾏延迟任务的线程池;Executors.newSingleThreadScheduledExecutor:创建⼀个单线程的可以执⾏延迟任务的线程池;Executors.newWorkStealingPool:创建⼀个抢占式执⾏的线程池(任务执⾏顺序不确定)【JDK1.8 添加】。ThreadPoolExecutor:最原始的创建线程池的⽅式,它包含了 7 个参数可供设置,后⾯会详细讲。
6.1.固定数目线程池
public class FixedNumberOfThreadPools {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
executorService.submit(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
});
executorService.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
});
}
}
输出结果:
pool-1-thread-1
pool-1-thread-26.1.1返回结果
public class FixedThreadPoolOfResult {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(1);
Future integerFuture = executorService.submit(new Callable() {
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
int num = new Random().nextInt(10);
System.out.println(num);
return num;
}
});
System.out.println("返回的结果:"+ integerFuture.get());
}
}
输出:
6
返回的结果:6 使用submit可以执行有返回值的任务或者是无返回值的任务;而execute只能执行不带返回值的任务。
6.1.2⾃定义线程池名称或优先级
public class FixedThreadPool {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
// 创建线程工厂
ThreadFactory threadFactory = new ThreadFactory() {
@Override
public Thread newThread(Runnable r) {
//要把任务Runnable设置给新创建的线程
Thread thread = new Thread(r);
//设置线程的命名规则
thread.setName("我的线程" + r.hashCode());
//设置线程的优先级
thread.setPriority(Thread.MAX_PRIORITY);
return thread;
}
};
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2,threadFactory);
//执行任务1
Future result = executorService.submit(new Callable() {
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
int num = new Random().nextInt(10);
System.out.println(num);
return num;
}
});
//打印线程池返回结果
System.out.println("返回结果:" + result.get());
}
} 提供的功能:
- 设置(线程池中)线程的命名规则。
- 设置线程的优先级。
- 设置线程分组。
- 设置线程类型(用户线程、守护线程)。
6.2. 带缓存的线程池
public class CachedThreadPool {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
int num = i;
executorService.submit(() -> {
System.out.println("i:" + num + "线程名字:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
});
}
}
}
输出结果:
i:0线程名字:pool-1-thread-1
i:3线程名字:pool-1-thread-4
i:2线程名字:pool-1-thread-3
i:1线程名字:pool-1-thread-2
i:4线程名字:pool-1-thread-5
i:6线程名字:pool-1-thread-7
i:5线程名字:pool-1-thread-6
i:8线程名字:pool-1-thread-9
i:9线程名字:pool-1-thread-10
i:7线程名字:pool-1-thread-8这种类型的线程池特点是:
- 工作线程的创建数量几乎没有限制(其实也有限制的,数目为Interger. MAX_VALUE), 这样可灵活的往线程池中添加线程。
- 如果长时间没有往线程池中提交任务,即如果工作线程空闲了指定的时间(默认为1分钟),则该工作线程将自动终止。终止后,如果你又提交了新的任务,则线程池重新创建一个工作线程。
- 在使用CachedThreadPool时,一定要注意控制任务的数量,否则,由于大量线程同时运行,很有会造成系统瘫痪。
6.3. 执⾏定时任务
6.3.1延迟执行(一次)
public class ScheduledThreadPool {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ScheduledExecutorService scheduledExecutorService = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(5);
System.out.println("添加任务时间:" + LocalDateTime.now());
// 执行定时任务(延迟3s执行)只执行一次
scheduledExecutorService.schedule(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("执行子任务时间:" + LocalDateTime.now());
}
},3, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
}
输出结果:
添加任务时间:2023-03-24T15:09:41.158
执行子任务时间:2023-03-24T15:09:44.1776.3.2固定频率执行
public class ScheduledThreadPool {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ScheduledExecutorService scheduledExecutorService = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(5);
System.out.println("添加任务时间:" + LocalDateTime.now());
// 3s之后开始执行定时任务,定时任务每隔5s执行一次
scheduledExecutorService.scheduleAtFixedRate(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("执行子任务时间:" + LocalDateTime.now());
}
},3,5, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
}
输出结果:
添加任务时间:2023-03-24T15:13:57.609
执行子任务时间:2023-03-24T15:14:00.626
执行子任务时间:2023-03-24T15:14:05.624
执行子任务时间:2023-03-24T15:14:10.615
执行子任务时间:2023-03-24T15:14:15.622
执行子任务时间:2023-03-24T15:14:20.621
执行子任务时间:2023-03-24T15:14:25.620
执行子任务时间:2023-03-24T15:14:30.615
执行子任务时间:2023-03-24T15:14:35.615
执行子任务时间:2023-03-24T15:14:40.628
执行子任务时间:2023-03-24T15:14:45.6156.3.3scheduleAtFixedRate VS scheduleWithFixedDelay
public class ScheduledThreadPool {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ScheduledExecutorService scheduledExecutorService = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(5);
System.out.println("添加任务时间:" + LocalDateTime.now());
// 3s之后开始执行定时任务,定时任务每隔5s执行一次
scheduledExecutorService.scheduleWithFixedDelay(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("执行任务:" + LocalDateTime.now());
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}, 3, 5, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
}
输出结果:
添加任务时间:2023-03-24T15:16:42.195
执行任务:2023-03-24T15:16:45.206
执行任务:2023-03-24T15:16:51.225
执行任务:2023-03-24T15:16:57.226
执行任务:2023-03-24T15:17:03.235
执行任务:2023-03-24T15:17:09.254
执行任务:2023-03-24T15:17:15.266
执行任务:2023-03-24T15:17:21.281
执行任务:2023-03-24T15:17:27.304
执行任务:2023-03-24T15:17:33.309
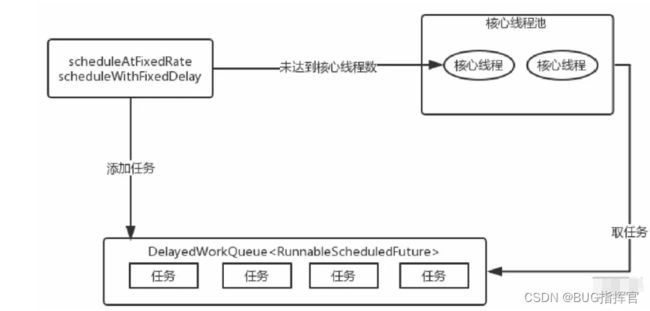
执行任务:2023-03-24T15:17:39.322- 当执行ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor的scheduleAtFixedRate或scheduleWithFixedDelay方法,会向DelayedWorkQueue添加一个实现RunnableScheduledFuture接口的任务包装类ScheduledFutureTask,并检查运行的线程是否达到核心线程数corePoolSize。
- 如果没有就新建线程,并启动。但并非立即执行任务,而是去DelayedWorkQueue中取任务包装类ScheduledFutureTask,然后再去执行任务;
- 如果运行的线程达到了corePoolSize,就把任务添加到任务队列DelayedWorkQueue中;DelayedWorkQueue会将任务排序,先执行的任务放在队列的前面。
- 任务执行完后,ScheduledFutureTask中的变量time改为下次要执行的时间,并放回到DelayedWorkQueue中。
6.4. 定时任务单线程
public class SingleThreadScheduledExecutor {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ScheduledExecutorService scheduledExecutorService = Executors.newSingleThreadScheduledExecutor();
System.out.println("添加任务时间:" + LocalDateTime.now());
scheduledExecutorService.schedule(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("添加子任务时间:" + LocalDateTime.now());
}
},3, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
}
输出:
添加任务时间:2023-03-24T15:24:36.459
添加子任务时间:2023-03-24T15:24:39.4736.5. 单线程线程池
public class SingleThreadScheduledExecutor {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService scheduledExecutorService = Executors.newSingleThreadScheduledExecutor();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
scheduledExecutorService.submit(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("线程名:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
});
}
}
}
线程名:pool-1-thread-1
线程名:pool-1-thread-1
线程名:pool-1-thread-1
线程名:pool-1-thread-1
线程名:pool-1-thread-1
线程名:pool-1-thread-1
线程名:pool-1-thread-1
线程名:pool-1-thread-1
线程名:pool-1-thread-1
线程名:pool-1-thread-1为什么不直接用线程?
单线程的线程池又什么意义?
- 复用线程。
- 单线程的线程池提供了任务队列和拒绝策略(当任务队列满了之后(Integer.MAX_VALUE),新来的任务就会拒绝策略)
6.6. 根据当前CPU⽣成线程池
public class WorkStealingPool {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newWorkStealingPool();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
executorService.submit(()->{
System.out.println("线程名:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
});
while (!executorService.isTerminated()){
}
}
}
}
输出:
线程名:ForkJoinPool-1-worker-9