在Spring Boot API Gateway中实现Sticky Session
文章目录
- 小结
- 问题
- 在API Gateway中实现Sticky Session
- 在同一个API Gateway中同时支持Sticky Session和RoundRobinLoadBalancer
- 参考
小结
在Kubernetes微服务的云环境中,如何在Spring Boot API Gateway中实现Sticky Session,当服务请求被某一个服务器处理后,所有后续的请求都被转发到被第一次进行处理的同一个服务器再进行处理,这里进行了尝试,取得了想要的结果。
问题
Spring Boot API Gateway中实现Sticky Session在Spring Boot官方文档并没有特别详细的描述,看来看去语焉不详,如下:
https://docs.spring.io/: 3.9. Request-based Sticky Session for LoadBalancer
解决这个问题不仅要自定义负载均衡策略和方法,并需要Spring Boot API Gateway能够用某种方法取得服务器实例的ID并将每一个收到的服务请求处理并转发到具有相应服务器实例ID的服务器。实际上在Github上已经有大神给出了解决方案,具体地址如下:
Github: tengcomplex/spring-cloud-gateway-lb-sticky-session
在API Gateway中实现Sticky Session
实现的环境为Kubernetes微服务的云环境,这里需要使用cookie,并使用Eureka服务发现模块。具体思路如下:
StickySessionLoadBalancer实现ReactorServiceInstanceLoadBalancer,相当于自定义了一个负载均衡策略- 当
Spring Boot API Gateway收到http服务请求,StickySessionLoadBalancer在cookie中找服务器实例ID: 自定义一个scg-instance-id为cookie的键值 - 如果
scg-instance-id为cookie被找到,而且是一个有效的服务器实例ID,那么这个服务请求就会被路由到这个具有服务器实例ID的服务器实例进行处理 - 反之,如果没有找到
scg-instance-id为cookie的键值,或者服务器实例ID无效(有可能服务器已经宕机),那么委托ReactorServiceInstanceLoadBalancer重新选择一个服务器,并将服务请求转发那个服务器 - 无论以上路由如何选择,
Spring Boot API Gateway会将服务器实例ID更新到cookie中去,scg-instance-id为的键值
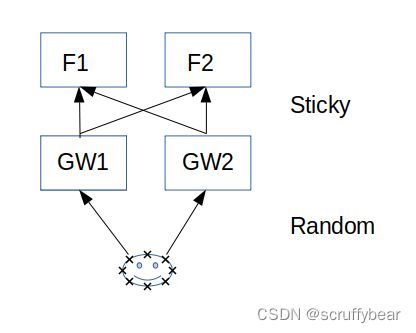
注:以上图片是Sticky Session的Spring Boot API Gateway路由示意图,来源于Github: Question: Sticky session in routes with load balancer #1176
首先,在Spring Boot API Gateway的模块中定义LoadBalancerClients :
@EnableEurekaClient
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableDiscoveryClient
@ComponentScan({"com.aa.bb.configuration"})
//
@LoadBalancerClients({
@LoadBalancerClient(value = "APPLICATION", configuration = com.aa.bb.configuration.StickySessionLoadBalancerConfiguration.class)})
这里StickySessionLoadBalancerConfiguration.class在有以下StickySessionLoadBalancer的Bean创建。
@Bean
@Lazy
public ReactorLoadBalancer<ServiceInstance> leastConnSticky(Environment environment,
LoadBalancerClientFactory loadBalancerClientFactory) {
String name = environment.getProperty(LoadBalancerClientFactory.PROPERTY_NAME);
L.debug("name: {}", name);
return new StickySessionLoadBalancer(loadBalancerClientFactory.getProvider(name, ServiceInstanceListSupplier.class),
name);
}
通常情况下Spring Boot API Gateway有关路由的配置是在application.yml,这里在Spring Boot API Gateway的模块中定义过滤器,并使用程序定义路由:
@Value("com.aa.bb.frontendUriAPPLICATION:lb://APPLICATION")
private String frontendUriAPPLICATION;
@Bean
public RouteLocator customRouteLocator(RouteLocatorBuilder builder) {
GatewayFilter gatewayFilter = customFilterSticky(clientFactory, properties);
return builder.routes()
.route("frontend",
r -> r.path("/application/**")
.filters(f -> f.filter(gatewayFilter))
.uri(frontendUri))
.build();
}
以上是由以下程序定义,此函数返回GatewayFilter,注意这里不是GlobalFilter, 否则无法在同一个API Gateway中同时支持Sticky Session和RoundRobinLoadBalancer:
@Bean
public GatewayFilter customFilterSticky(LoadBalancerClientFactory clientFactory, LoadBalancerProperties properties) {
return new ReactiveLoadBalancerStickySessionFilter(clientFactory, properties);
}
客户端服务请求被以上过滤器拦截后,交给了以下具体的由ReactiveLoadBalancerStickySessionFilter实现的过滤器方法filter处理 ,其中ReactiveLoadBalancerStickySessionFilter是GatewayFilter的实现:
@Override
public Mono<Void> filter(ServerWebExchange exchange, GatewayFilterChain chain) {
URI url = exchange.getAttribute(GATEWAY_REQUEST_URL_ATTR);
String schemePrefix = exchange.getAttribute(GATEWAY_SCHEME_PREFIX_ATTR);
L.debug("Filtering, url: {}, schemePrefix: {}", url, schemePrefix);
if (url == null || (!"lb".equals(url.getScheme()) && !"lb".equals(schemePrefix))) {
L.debug("Not choosing, go further in the chain");
return chain.filter(exchange);
}
// preserve the original url
addOriginalRequestUrl(exchange, url);
L.trace("{} url before: {}", ReactiveLoadBalancerStickySessionFilter.class.getSimpleName(), url);
return choose(exchange).doOnNext(response -> {
if (!response.hasServer()) {
throw NotFoundException.create(true, "Unable to find instance for " + url.getHost());
}
URI uri = exchange.getRequest().getURI();
// if the `lb:` mechanism was used, use `` as the default,
// if the loadbalancer doesn't provide one.
String overrideScheme = null;
if (schemePrefix != null) {
overrideScheme = url.getScheme();
}
DelegatingServiceInstance serviceInstance = new DelegatingServiceInstance(response.getServer(), overrideScheme);
URI requestUrl = reconstructURI(serviceInstance, uri);
L.debug("Url chosen: {}", requestUrl);
exchange.getAttributes().put(GATEWAY_REQUEST_URL_ATTR, requestUrl);
}).then(chain.filter(exchange));
}
接下来具体的choose(exchange)方法跳到以下进行处理:
private Mono<Response<ServiceInstance>> choose(ServerWebExchange exchange) {
URI uri = exchange.getAttribute(GATEWAY_REQUEST_URL_ATTR);
L.debug("We are choosing, uri: {}", uri);
ReactorLoadBalancer<ServiceInstance> loadBalancer = this.clientFactory.getInstance(uri.getHost(),
ReactorLoadBalancer.class, ServiceInstance.class);
if (loadBalancer == null) {
throw new NotFoundException("No loadbalancer available for " + uri.getHost());
}
L.debug("Using loadbalancer {}", loadBalancer.getClass().getSimpleName());
Mono<Response<ServiceInstance>> ret = loadBalancer.choose(createRequest(exchange));
ret.subscribe(r -> L.debug("We have {}", r.getServer().getUri()));
return ret;
}
以上loadBalancer.choose(createRequest(exchange)方法调用具体的定制化的StickySessionLoadBalancer的choose方法进行处理:
@SuppressWarnings("rawtypes")
@Override
public Mono<Response<ServiceInstance>> choose(Request request) {
ServiceInstanceListSupplier supplier = serviceInstanceListSupplierProvider
.getIfAvailable(NoopServiceInstanceListSupplier::new);
return supplier.get().next().flatMap(list -> getInstanceResponse(list, request));
}
那么,最后的重点,也就是核心的核心在Spring Boot API Gateway中实现Sticky Session的实现在这里,在此实现了服务请求拦截,选择Sticky Session决定的服务器,并更新cookie的操作:
@SuppressWarnings("rawtypes")
private Mono<Response<ServiceInstance>> getInstanceResponse(List<ServiceInstance> instances, Request request) {
if (instances.isEmpty()) {
L.warn("如果没有可用的服务: {}", this.serviceId);
return Mono.just(new EmptyResponse());
}
L.debug("request: {}, instances: {}", request.getClass().getSimpleName(), instances);
Object context = request.getContext();
L.debug("Context class name: {}", context.getClass().getSimpleName());
if (!(context instanceof ServerWebExchange)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("The context must be a ServerWebExchange");
}
ServerWebExchange exchange = (ServerWebExchange) context;
L.debug("exchange: {}", exchange);
// 检查 exchange 有一个 cookie 指向了一个可用的 ServiceInstance,这里使用`scg-instance-id`为`cookie`的键值
return serviceInstanceFromCookie(exchange, instances)
// 如果ServiceInstance存在, 那么路由到这个ServiceInstance
.map(instance -> Mono.just((Response<ServiceInstance>) new DefaultResponse(instance)))
// 否则使用ReactorServiceInstanceLoadBalancer委托选择一个服务器
.orElseGet(() -> delegate.choose(request))
// 无论如何,需要更新`cookie`键值为`scg-instance-id`的值
.doOnNext(response -> setCookie(exchange, response));
}
以上是实现的全部过程,在控制台可以看到以下输出:
DEBUG 2023-09-19 11:47:28.008 [reactor-http-nio-6] - Mapping [Exchange: POST http://127.0.0.1:8080/application/Process] to Route{id='frontend', uri=com.aa.bb.frontendUri:lb://APPLICATION, order=0, predicate=Paths: [/application/**], match trailing slash: true, gatewayFilters=[com.aa.bb.configuration.ReactiveLoadBalancerStickySessionFilter@97002113], metadata={}}
在同一个API Gateway中同时支持Sticky Session和RoundRobinLoadBalancer
以上提到了在同一个API Gateway中同时支持Sticky Session和RoundRobinLoadBalancer, 需要使用GatewayFilter,而不是GlobalFilter。
例如这里需要同时支持RoundRobinLoadBalancer,那么,类似的可以自定义一个返回ReactorLoadBalancer的RoundRobinLoadBalancer,实际上是一个标准的实现,应该会有更好办法,为了简便,暂时使用:
@Bean
@Lazy
public ReactorLoadBalancer<ServiceInstance> leastConn(Environment environment,
LoadBalancerClientFactory loadBalancerClientFactory) {
String name = environment.getProperty(LoadBalancerClientFactory.PROPERTY_NAME);
L.debug("client name: {}", name);
return new RoundRobinLoadBalancer(loadBalancerClientFactory.getProvider(name, ServiceInstanceListSupplier.class),
name);
}
}
同前,再定义一个GatewayFilter, 不赘述。
同理,在Spring Boot API Gateway的模块中定义LoadBalancerClients :
@LoadBalancerClients({
@LoadBalancerClient(value = "APPLICATION_B", configuration = com.aa.bb.configuration.RoundRobinSessionLoadBalancerConfiguration.class)})
在Spring Boot API Gateway的主模块中如下操作:
@Value("com.aa.bb.frontendUriAPPLICATION_B:lb://APPLICATION_B")
private String frontendUriAPPLICATION_B;
@Bean
public RouteLocator customRouteLocatorSAMMSCP(RouteLocatorBuilder builder) {
GatewayFilter gatewayFilter = customFilter(clientFactory, properties);
return builder.routes()
.route("frontendapplicationb",
r -> r.path("/Application_B/**")
.filters(f -> f.filter(gatewayFilter))
.uri(frontendUriAPPLICATION_B))
.build();
}
@Bean
public GatewayFilter customFilter(LoadBalancerClientFactory clientFactory, LoadBalancerProperties properties) {
return new RoundRobinLoadBalancerFilter(clientFactory, properties);
}
与先前类似,使用RoundRobinLoadBalancerFilter实现的过滤器方法处理 ,其中RoundRobinLoadBalancerFilter是GatewayFilter的实现,在这里,RoundRobinLoadBalancerFilter不需要做任何处理,因为RoundRobinLoadBalancer已经由Spring Boot API Gateway标准包实现过了。
参考
Github: Question: Sticky session in routes with load balancer #1176
Github: LoadBalancer: Add Sticky LB implementation. #689
Github: tengcomplex/spring-cloud-gateway-lb-sticky-session
Github: POC for a session/cookie based sitcky load balancer implementation. #764
Saturn Cloud: Spring Cloud Gateway Route with Multiple Instances and Sticky Session
Stackoverflow: Sticky session loadbalancing in spring Microservices [closed]
Stackoverflow: How to use a Spring Cloud Gateway Custom Filter to filter every request?
Stackoverflow: No found for dependency: expected at least 1 bean which qualifies as autowire candidate for this dependency. Dependency annotations:
Stackoverflow: Sticky session loadbalancing in spring Microservices [closed]
Stackoverflow: Request-based Sticky Session configuration with Spring Cloud LoadBalancer
CSDN: 基于springcloud3.0.1版本Loadbalancer切换默认负载均衡策略
51 CTO: Spring Cloud LoadBalancer–自定义负载均衡策略–方法/实例
https://docs.spring.io/: 3.9. Request-based Sticky Session for LoadBalancer
https://docs.spring.io/: 3.2. Switching between the load-balancing algorithms3.2. Switching between the load-balancing algorithms
https://docs.spring.io/: 2.1. The @EnableDiscoveryClient Annotation