SSAS 主动缓存的应用
Written By: Ray Barley
Problem
We have chosen MOLAP storage in order to maximize the query performance of our cubes. Since we have a number of cubes we are now focused on coming up with a strategy for keeping the cubes up to date as the data in our warehouse changes frequently. Can you give us the details on how we go about implementing the Proactive Caching feature in SQL Server Analysis Services 2005?
Solution
SSAS supports three storage modes:
- MOLAP - stores detailed data and aggregations in a compressed, proprietary format; i.e. a complete copy of the data is made but query performance is excellent
- HOLAP - stores aggregations same as MOLAP, detailed data is accessed as required from the relational data source
- ROLAP - accesses detailed data and aggregations from the relational data source
Note that with MOLAP or HOLAP storage, the cube becomes out of date as soon as the relational data source changes. Proactive Caching is a feature in SSAS that allows you to specify when to process a measure group partition or dimension as the data in the relational data source changes. When Proactive Caching is implemented, SSAS will handle keeping the cube up to date on its own, per the parameters you specify. The alternative to Proactive Caching is to develop an SSIS package that processes the dimensions and measure group partitions; you would execute the SSIS package periodically.
A typical scenario for Proactive Caching would be that you have a measure group partition where the latest data is added periodically then at some point the partition is merged with an existing partition. The data for the partition is often determined based on the transaction date. For instance you want the partition updated hourly during the day with new transactions, then at night you will merge the contents of the partition into a current week partition. This approach allows you to process the partition often, keeping it up to date with the relational data source, while minimizing the amount of data that needs to be processed each time. For additional details about measure group partitions, please refer to our earlier tip How To Define Measure Group Partitions in SQL Server Analysis Services (SSAS) 2005.
Proactive Caching supports three notification methods which inform SSAS that the relational data source has changed:
- SQL Server (2000 and later)
- Client Initiated
- Scheduled Polling
SQL Server notification can only be used if the relational data source is a SQL Server 2000 or later database. SQL Server raises trace events when data changes. In order to catch these trace events, SSAS must connect to the SQL Server with administrator rights. With SQL Server notifications, measure group partitions are always processed using Full Process which discards the contents of the partition and rebuilds it; dimensions are processed using Process Update which picks up inserts, updates, and deletes in the relational data source.
The client initiated notification is performed by sending a NotifyTableChange XMLA command to the SSAS server. For example an SSIS package that updates the data warehouse could use the Analysis Services Execute DDL Task to send the NotifyTableChange XMLA command to the SSAS server every time the data warehouse update processing is completed.
Scheduled polling simply queries the relational data source periodically to determine if the data has changed.
In this tip we will walk through the setup of Proactive Caching using the Adventure Works DW SSAS sample database that comes with SQL Server 2005.
Implementing Proactive Caching
To begin launch SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS) from the Microsoft SQL Server 2005 program group and connect to an Analysis Services server.
Step 1: Drill down to the partitions for the Internet Sales measure group in the Adventure Works cube:
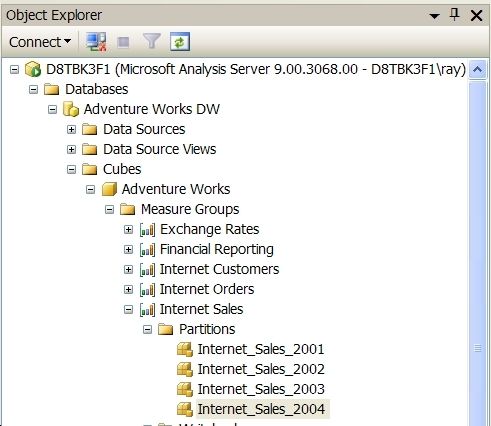
Step 2: Right click on the Internet_Sales_2004 partition and select properties from the context menu; click Proactive Caching in the Select a page list box to display the following dialog:
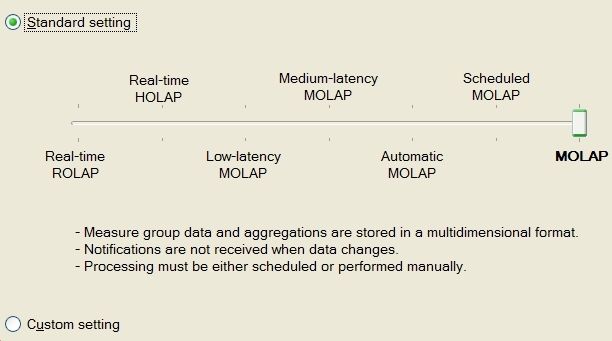
There are a number of predefined settings as shown above. The default setting is MOLAP with Proactive Caching disabled; i.e. SSAS does not automatically update the partition. You can move the slider to any one of the standard settings and go with it; you can also start with a standard setting then customize it by clicking the Options button at the bottom of the dialog (not shown above).
Step 3: Move the slider in the Proactive Caching settings dialog to Scheduled MOLAP then click the Options button at the bottom of the dialog (not shown above); you will see the following Cache Settings on the General tab:
For the Scheduled MOLAP setting, we see that the Update the cache periodically option is the only one selected, with the rebuild interval set to 1 day. Thus the partition will be processed every day.
There are a number of other options on the Cache Settings dialog. As you move the slider to the various standard settings you will see these how options change. At this point let's describe these various options and settings:
- Silence interval is the amount of time to wait after an update notification is received before processing the partition. This allows for other updates before starting to process the partition.
- Silence override interval is the maximum time to wait after an update notification is received before processing the partition. Without the silence override interval you could conceivably have changes that keep occurring and the partition would never get processed.
- Latency is the maximum amount of time that you want to use the MOLAQP cache after changes have occurred in the relational data source and before/while the partition is processed. In other words you may continue to use the existing MOLAP cache for a period of time while it is being rebuilt. Once the latency is reached the MOLAP cached is dropped and queries can be satisfied by going back to the relational data source.
- Bring online immediately (when checked) will satisfy queries from the relational data source while the MOLAP cache is being rebuilt.
- Enable ROLAP aggregations (when checked) will create materialized views for aggregations in the relational data source.
Step 4: Click the Notifications tab to review the available options:
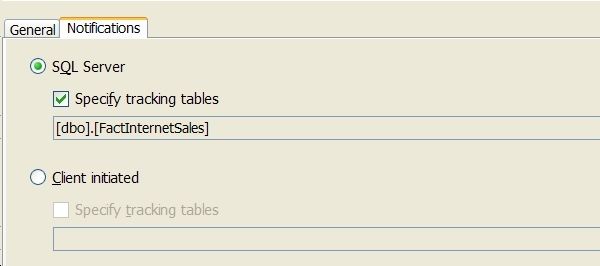
For both SQL Server and Client initiated notifications you must specify the table(s) to be tracked; i.e. which table(s) do you care about if they change.
For the Client initiated notification you could use the Analysis Services Execute DDL Task in an SSIS package and send XMLA like the following:
<Command>
<NotifyTableChange>
<Provider>SQLOLEDB</Provider>
<DataSource>localhost</DataSource>
<InitialCatalog>AdventureWorksDW</InitialCatalog>
<TableNotifications>
<TableNotification>
<DBTableName>FactInternetSales</DBTableName>
<DBSchemaName>dbo</DBSchemaName>
</TableNotification>
</TableNotifications>
</NotifyTableChange>
</Command> |
Step 5: Click the Scheduled polling radio button on the Notifications tab to review/setup this notification option:
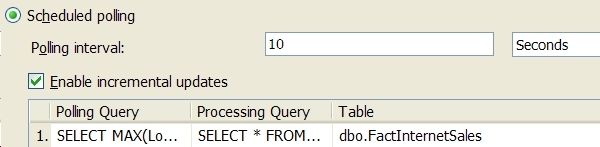
The Polling interval specifies how often to poll the relational data source for changes. The Polling Query is the query to be run to determine if there are any new rows. The query must return one row with a single column; e.g. the MAX of a datetime column like LoadedDate. SSAS maintains the value returned to determine when it changes, signifying that there is new data to load. Click Enable incremental updates to extract just the new rows from the relational data source. This requires entering the Processing Query which must properly identify the new rows using the single column returned in the Polling query. Sample queries are shown below (you can't see the entire query in the dialog):
-- Add LoadedDate column to table ALTER TABLE dbo.FactInternetSales ADD LoadedDate DATETIME NOT NULL DEFAULT GETDATE() -- Polling query SELECT MAX(LoadedDate) LoadedDate FROM dbo.FactInternetSales -- Processing query SELECT * FROM dbo.FactInternetSales WHERE LoadedDate > ? AND LoadedDate <= ? |
Since the FactInternetSales table didn't have a suitable column to use for the queries, a DATETIME column was added.
You can experiment with the remaining Standard settings on the Proactive Caching properties dialog to get an idea of the basic capabilities. In addition you can customize them to meet your specific requirements.
Next Steps
- If you don't already have the AdventureWorks SSAS sample projects and databases available, you can download them here to get the starting point for this tip. Click the AdventureWorksBICI.msi link. Also click on the Release Notes link for the details on attaching the relational database. The default install location for the project is C:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\90\Tools\Samples\AdventureWorks Analysis Services Project; you will see Enterprise and Standard folders. We used the project in the Enterprise folder.
- While Proactive Caching is a very interesting feature, you should consider carefully whether it's the right solution versus creating an SSIS package to process your dimensions and measure group partitions.