Redis缓存&分布式锁
缓存
- 一、缓存
-
- 1.缓存的使用
- 2.分布式缓存(Redis)
- 二、SpringBoot整合Redis
-
- Redis相关类
- 三、高并发下缓存失效问题(缓存`穿透、雪崩、击穿`)
-
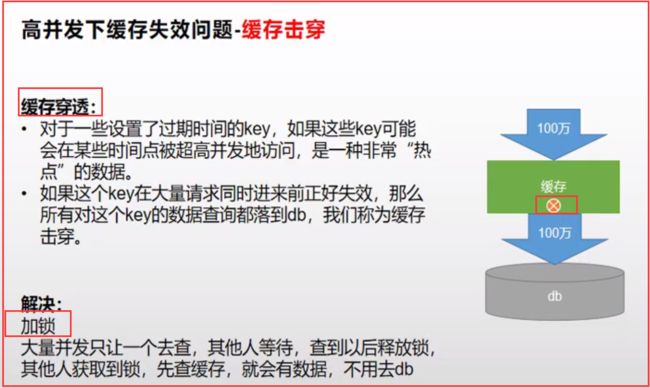
- 1.缓存`穿透`
- 2.缓存`雪崩`
- 3.缓存`击穿`
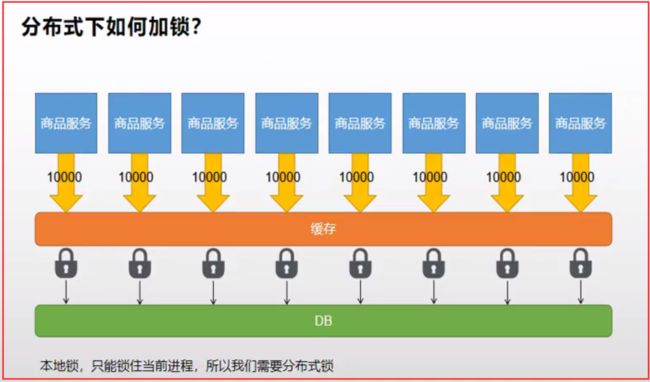
- 分布式下如何枷锁?
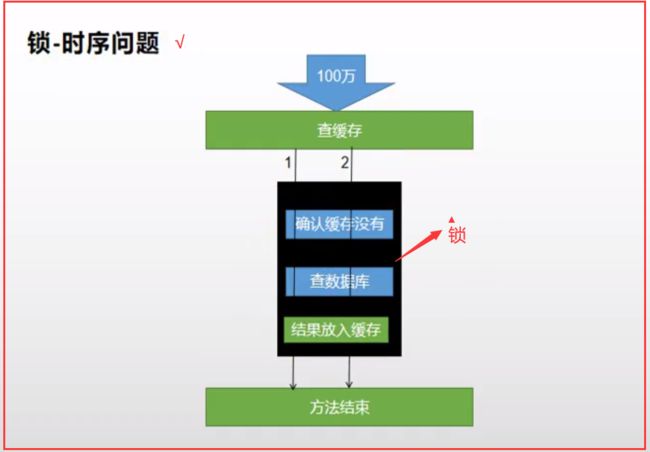
- 锁时序问题
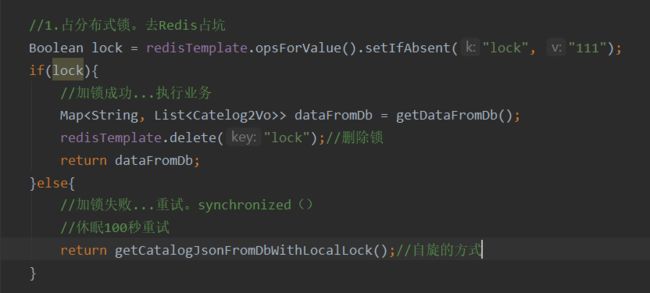
- 分布式锁演进
- 四、缓存分布式锁之Redisson
-
- 1.整合redisson作为分布式锁等功能框架
- 3.Redisson分布式锁之`可重入锁RLock`
- 4.Redisson分布式锁之`读写锁(ReadWriteLock)`
- 5.Redisson分布式锁之`信号量(Semaphore)`
- 6.Redisson分布式锁之`闭锁(CountDownLatch)`
- 五、缓存数据一致性(双写模式、失效模式)
- 六.Spring Cache
-
- 整合
- 相关配置类
- 十、常见问题bug
-
- 1.产生堆外内存溢出:OutOfDirectMemoryError
- 十一、Redis缓存过期淘汰策略
-
- 1.面试题
- 2.Redis内存满了怎么办
-
- 1.Redis默认内存多少?在哪里查看?如何设置?
-
- ①:查看Redis最大占用内存
- ②:Redis默认内存多少可以用?
- ③:一般生产上你如何配置?
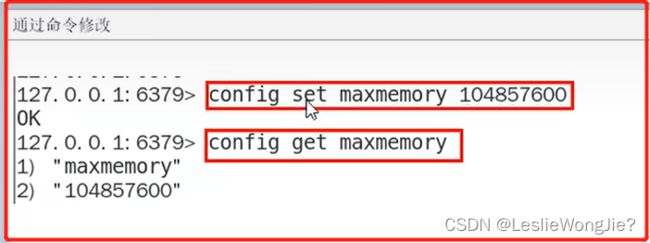
- ④:如何修改Redis内存设置
- ⑤:什么命令查看Redis内存使用情况?
- 2.真要打满了怎么样?如果Redis内存使用超出了设置的最大值会怎样?
- 3.Redis缓存淘汰策略
-
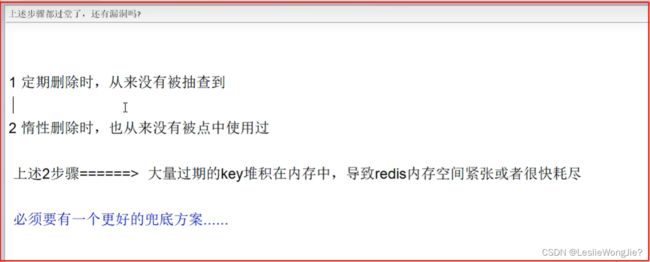
- 1.往redis里写的数据是怎么没了的
-
- ①:redis过期键的删除策略
- ②:三种不同的删除策略
-
- Ⅰ、定时删除
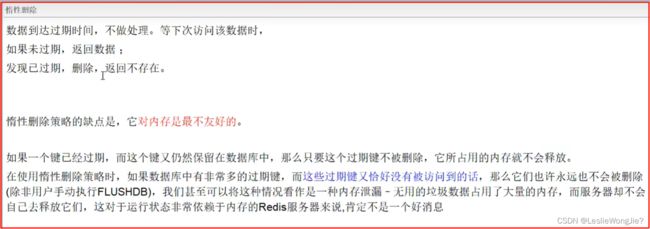
- Ⅱ、惰性删除
- Ⅲ、定期删除
- ③:上述步骤都过堂了,还有漏洞吗?
- ④:内存淘汰策略登场
- 2.有那些(redis6.0.8版本)
- 3.你平时用哪一种
- 4.如何配置、修改
- 4.Redis的LRU算法简介
-
- 1.是什么
- 2.算法来源
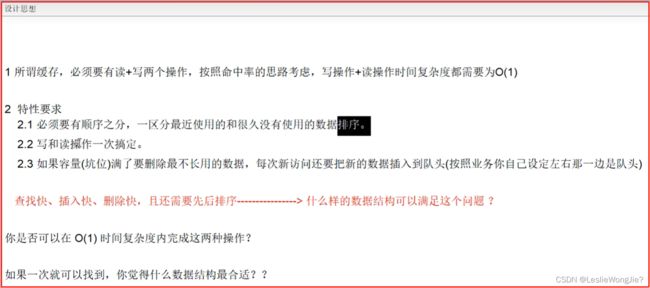
- 3.设计思想
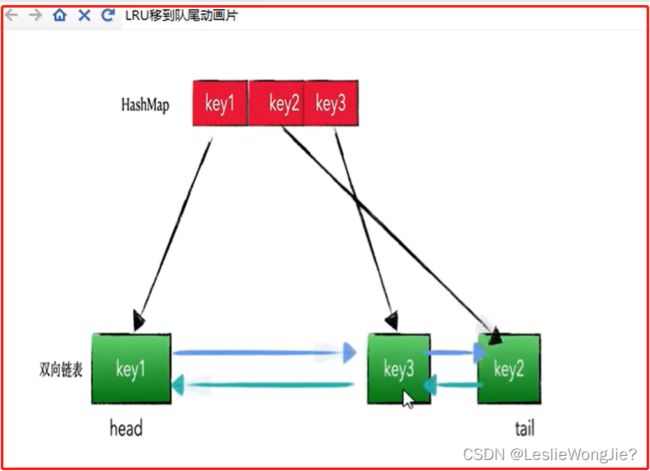
- 4.编码手写如何实现LRU
Redisson官方文档
一、缓存
1.缓存的使用
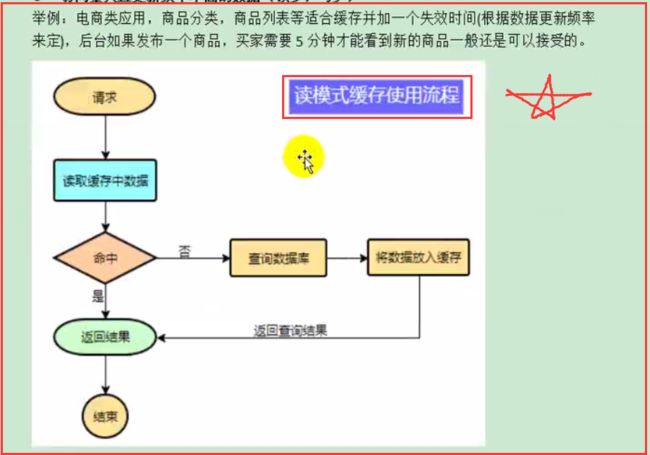
为了系统性能的提升,我们一般都会将部分数据放入缓存中,加速访问。而db承担数据落盘工作。
哪些数据适合放入缓存?
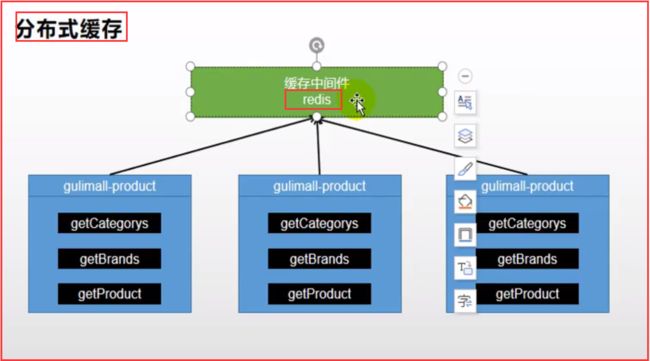
2.分布式缓存(Redis)
二、SpringBoot整合Redis
1.引入Redis场景启动器(starter)
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redisartifactId>
dependency>
2.配置Redis相关信息
# Redis相关配置
redis:
host: 192.168.10.22 # Redis主机地址
port: 6379 # Redis端口号
Redis相关类
Redis所有的相关属性配置类
RedisProperties
@ConfigurationProperties(
prefix = "spring.redis"
)
public class RedisProperties {
private int database = 0;
private String url;
private String host = "localhost";
private String password;
private int port = 6379;
private boolean ssl;
private Duration timeout;
private String clientName;
private RedisProperties.Sentinel sentinel;
private RedisProperties.Cluster cluster;
private final RedisProperties.Jedis jedis = new RedisProperties.Jedis();
private final RedisProperties.Lettuce lettuce = new RedisProperties.Lettuce();
三、高并发下缓存失效问题(缓存穿透、雪崩、击穿)
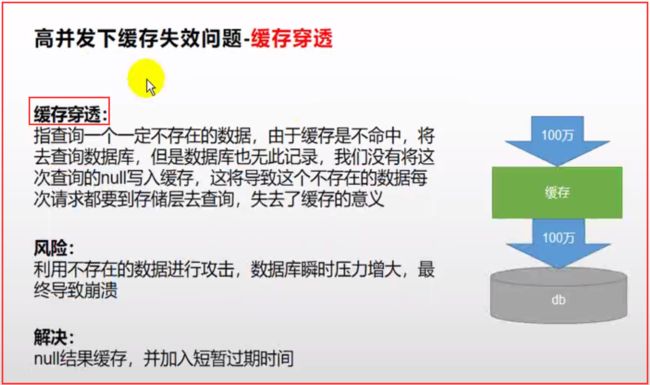
1.缓存穿透
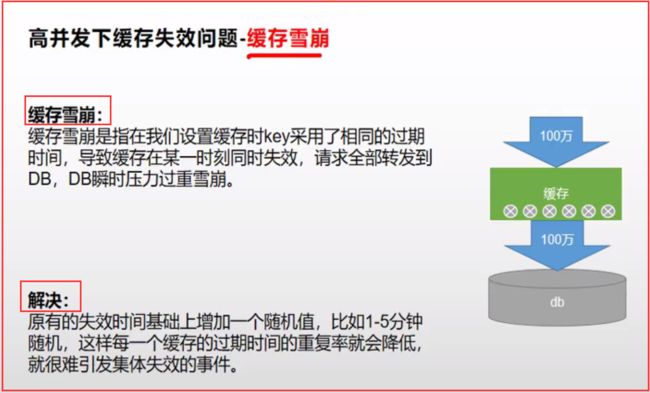
2.缓存雪崩
3.缓存击穿
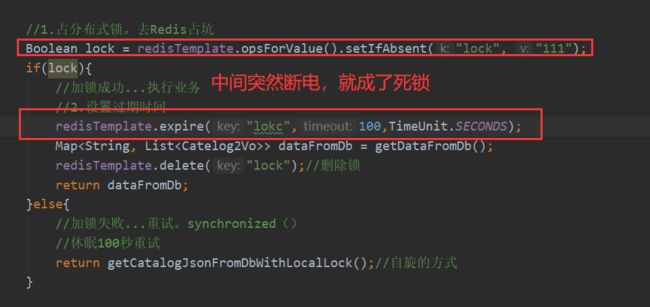
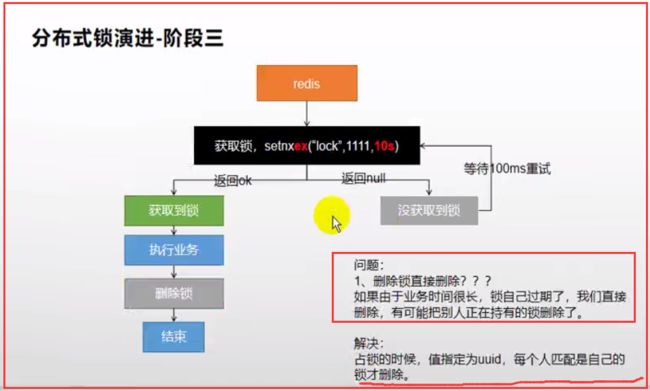
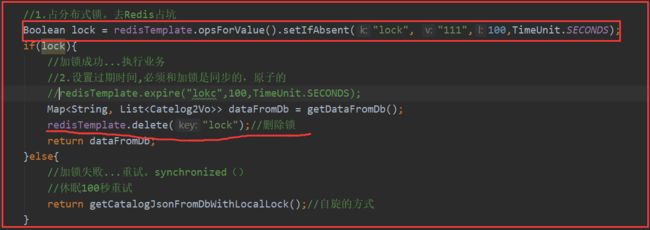
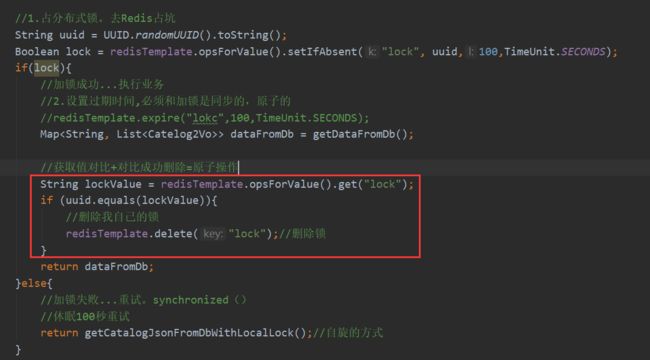
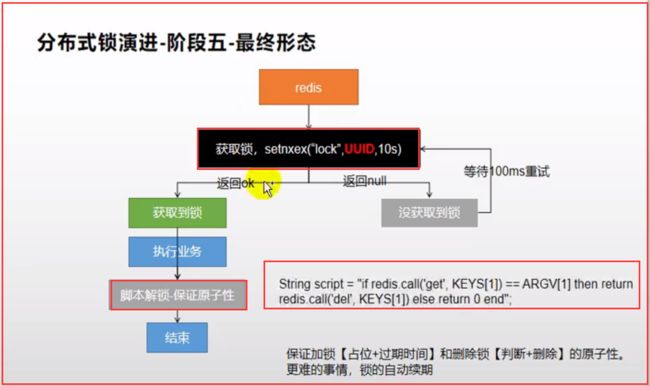
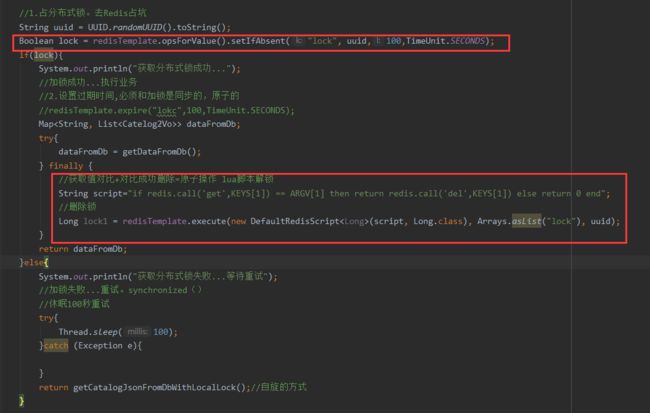
分布式下如何枷锁?
锁时序问题
分布式锁演进
四、缓存分布式锁之Redisson
1.整合redisson作为分布式锁等功能框架
1)、引入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.redissongroupId>
<artifactId>redissonartifactId>
<version>3.12.0version>
dependency>
2)、配置redisson
/**
* @description <功能描述> 缓存分布式锁之Redisson配置
* @Author leslie
* @Date 2021/8/1
*/
@Configuration
public class MyRedissonConfig {
/**
* 所有对Redisson的使用都是通过RedissonClient对象
* @return
* @throws IOException
*/
@Bean(destroyMethod="shutdown")
public RedissonClient redisson() throws IOException {
// 1.创建配置
Config config = new Config();
// 单节点模式
// Redis url should start with redis:// or rediss:// (for SSL connection)
config.useSingleServer().setAddress("redis://192.168.10.22:6379");
// config.useClusterServers().addNodeAddress("127.0.0.1:7004", "127.0.0.1:7001");//Redis集群地址
// 2.根据config创建出RedissonClient实例
RedissonClient redissonClient = Redisson.create(config);
return redissonClient;
}
}
3.Redisson分布式锁之可重入锁RLock
@ResponseBody
@GetMapping("/hello")
public String hello(){
// 1.获取一把锁,只要锁的名字一样。就是同一把锁
RLock lock = redisson.getLock("my-lock");
// 2.加锁
//lock.lock();//阻塞是等待。默认加的锁都是30s时间。
//1)、锁的自动续期,如果业务超长,运行期间自动给锁续上新的30s。不用担心业务时间长,锁自动过期被删除
//2)、加锁的业务只要运行完成,就不会给当前锁续期,即使不手动解锁,锁默认在30s以后自动删除
lock.lock(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);// 10秒钟自动解锁,自动解锁时间一定要大于业务的执行时间
// 问题:lock.lock(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);在锁时间到了以后,不会自动续期
// 1.如果我们传递了锁的超时时间,就发送给redis执行脚本,进行占锁,默认超时就是我们指定的时间
// 2.如果我们未指定锁的超时时间,就使用30*1000【LockWatchdogTimeout看门狗的默认时间】;
// 只要占锁成功,就会启动一个定时任务【重新给锁设置过期时间,新的过期时间就是看门狗的默认时间】,每隔10s都会自动再次续期,续成30s
// internalLockLeaseTime【看门时间】/3,10s
// 最佳实战
// 1)、lock.lock(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);省掉整个续期操作。手动解锁
try{
System.out.println("加锁成功,执行业务..."+Thread.currentThread().getId());
Thread.sleep(30000);
}catch (Exception e){
}finally {
// 3.解锁 假设解锁代码没有运行,Redisson会不会出现死锁
System.out.println("释放锁"+Thread.currentThread().getId());
lock.unlock();
}
return "hello";
}
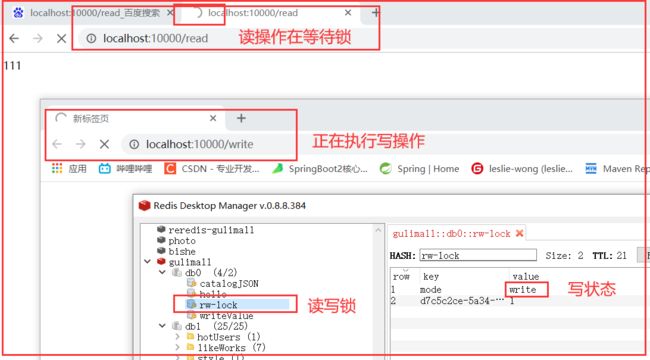
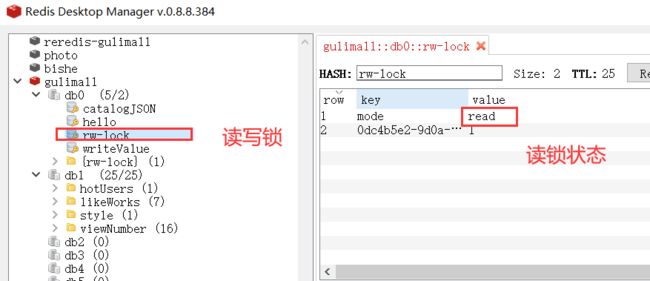
4.Redisson分布式锁之读写锁(ReadWriteLock)
保证一定能读到最新数据,修改期间,写锁是一个排他锁(互斥锁、独享锁)。读锁是一个共享锁。
写锁没释放读就必须等待
读 + 读:相当于无锁状态,并发读,只会在redis中记录好,所有当前的读锁。他们都会同时加锁成功写 + 读:读等待写锁释放写 + 写 :阻塞方式读 + 写:有读锁。写也需要等待- 只要有写的存在,都必须等待
// 保证一定能读到最新数据,修改期间,写锁是一个排他锁(互斥锁、独享锁)。读锁是一个共享锁。
// 写锁没释放读就必须等待
// 读 + 读:相当于无锁状态,并发读,只会在redis中记录好,所有当前的读锁。他们都会同时加锁成功
// 写 + 读:读等待写锁释放
// 写 + 写 :阻塞方式
// 读 + 写:有读锁。写也需要等待
// 只要有写的存在,都必须等待
@GetMapping("/write")
@ResponseBody
public String writeValue(){
RReadWriteLock lock = redisson.getReadWriteLock("rw-lock");
String s = "";
// 1. 改数据加写锁,读数据加读锁
RLock rLock = lock.writeLock();
rLock.lock();
try{
System.out.println("写锁加锁成功..."+Thread.currentThread().getId());
s = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
Thread.sleep(30000);
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("writeValue",s);
}catch (InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
rLock.unlock();
System.out.println("写锁释放..."+Thread.currentThread().getId());
}
return s;
}
@GetMapping("/read")
@ResponseBody
public String readValue(){
RReadWriteLock lock = redisson.getReadWriteLock("rw-lock");
String s = "";
// 加读锁
RLock rLock = lock.readLock();
rLock.lock();
try{
System.out.println("读锁加锁成功..."+Thread.currentThread().getId());
s = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("writeValue");
Thread.sleep(30000);
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
rLock.unlock();
System.out.println("读锁释放..."+Thread.currentThread().getId());
}
return s;
}
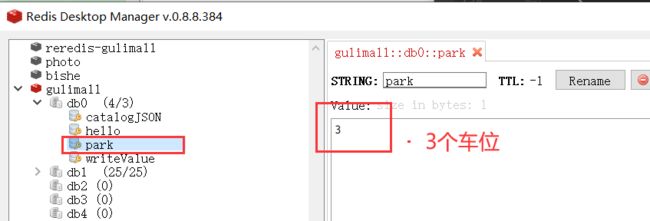
5.Redisson分布式锁之信号量(Semaphore)
/**
* 车库停车
* 3车位
* 信号量也可以用作分布式限流
*/
@GetMapping("/park")
@ResponseBody
public String park() throws InterruptedException {
RSemaphore park = redisson.getSemaphore("park");
//park.acquire();// 获取一个信号,获取一个值,一个车位
boolean b = park.tryAcquire();// 尝试获取
if(b){
// 执行业务
}else{
return "error";
}
return "ok"+b;
}
@GetMapping("/go")
@ResponseBody
public String go() throws InterruptedException {
RSemaphore park = redisson.getSemaphore("park");
park.release();// 释放一个车位
return "ok";
}
}
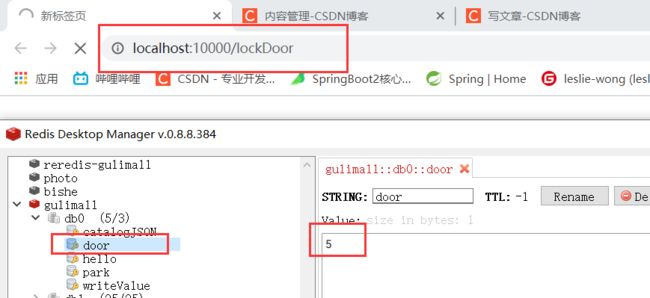
6.Redisson分布式锁之闭锁(CountDownLatch)
/**
* 放假,锁门
* 1班没人了 ,2班没人了
* 5个班全部走完,我们可以锁大门
*/
@GetMapping("/lockDoor")
@ResponseBody
public String lockDoor() throws InterruptedException {
RCountDownLatch door = redisson.getCountDownLatch("door");
door.trySetCount(5);
door.await();// 等待闭锁都完成
return "放假了";
}
@GetMapping("/gogogo/{id}")
@ResponseBody
public String gogogo(@PathVariable("id") Long id){
RCountDownLatch door = redisson.getCountDownLatch("door");
door.countDown();// 计数减1
return id+"班的人都走了";
}
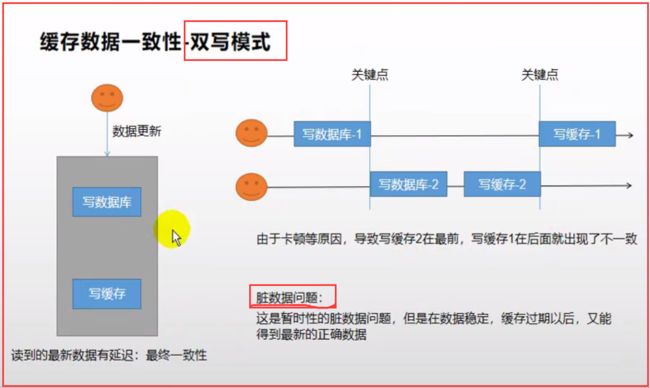
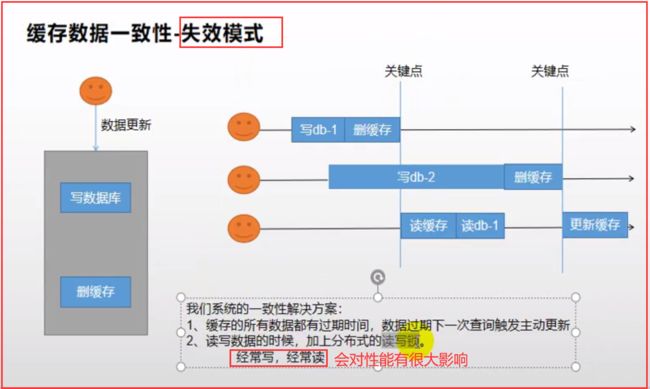
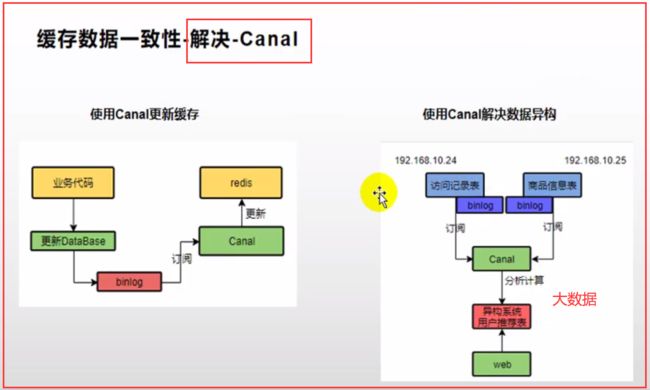
五、缓存数据一致性(双写模式、失效模式)
六.Spring Cache
整合
1.引入场景启动器
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-cacheartifactId>
dependency>
2.写配置
- 1)、自动配置了哪些
CacheAutoConfiguration会导入 RedisCacheConfiguration;
自动配置好了缓存管理器RedisCacheManager- 2)、配置使用Redis作为缓存
在application.properties配置
# 缓存类型 用Redis
spring.cache.type=redis
3.测试使用缓存
@Cacheable: Triggers cache population.:触发将数据保存到缓存的操作@CacheEvict: Triggers cache eviction.:触发将数据从缓存删除@CachePut: Updates the cache without interfering with the method execution.:不影响方法执行更新缓存@Caching: Regroups multiple cache operations to be applied on a method.:组合以上多个操作@CacheConfig: Shares some common cache-related settings at class-level.:在类级别共享缓存的相同配置
.
开启缓存功能@EnableCaching
只需要使用注解就能完成缓存操作
/**
* 查出商品三级分类所有的1级分类
*
* 1.每一个需要缓存的数据我们都来指定要放到哪个名字的缓存。【缓存的分区(按照业务类型分)】
* 2.@Cacheable({"category"})
* 代表当前方法的结果需要缓存,如果缓存中有,方法不用调用。
* 如果缓存中没有,会调用方法,最后将方法的结果放入缓存
* 3.默认行为
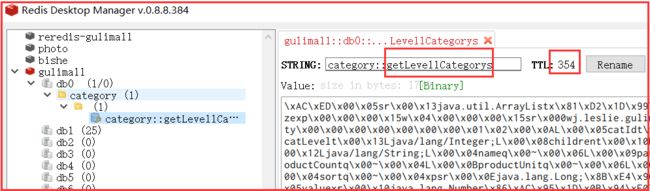
* 1)、如果缓存中有,方法不用调用。
* 2)、key默认生成;缓存的名字::SimpleKey [](自主生成的key值)
* 3)、缓存的value值。默认使用jdk序列化机制。将序列化后的数据缓存到Redis
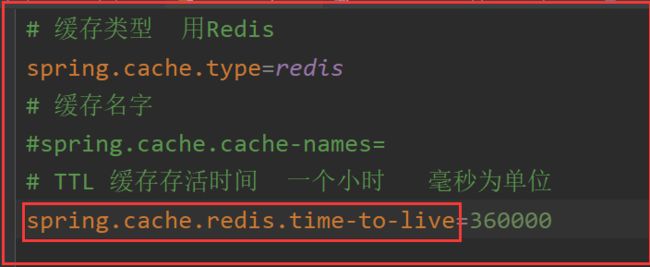
* 4)、默认TTL(过期时间) -1(永不过期);
*
*
* 自定义:
* 1)、指定生成的缓存使用的key: key属性指定。接收一个SpEL
* 2)、指定缓存的数据存活时间: 配置文件中修改TTL
* 3)、将数据保存为json格式
* 4.Sring-Cache的不足
* 1)、读模式:
* 缓存穿透:查询一个null数据。解决:缓存空数据;spring.cache.redis.cache-null-values=true
* 缓存击穿:大量并发进来同时查询一个正好过期的数据。解决:加锁;?默认是无加锁的;sync = true(加锁,解决击穿)
* 缓存雪崩:大量的key同时过期。解决:加随机时间。加上过期时间。:spring.cache.redis.time-to-live=360000
* 2)、写模式(缓存与数据一致)
* 1)、读写加锁。
* 2)、引入Canal,感知到MySQL的更新去更新数据库
* 3)、读多写多,直接去数据库查询就行
* 总结:
* 常规数据(读多写少,即时性、一致性要求不高的数据);完全可以使用Spring-Cache;写模式(只要缓存的数据有过期时间就够了)
* 特殊数据:特殊设计
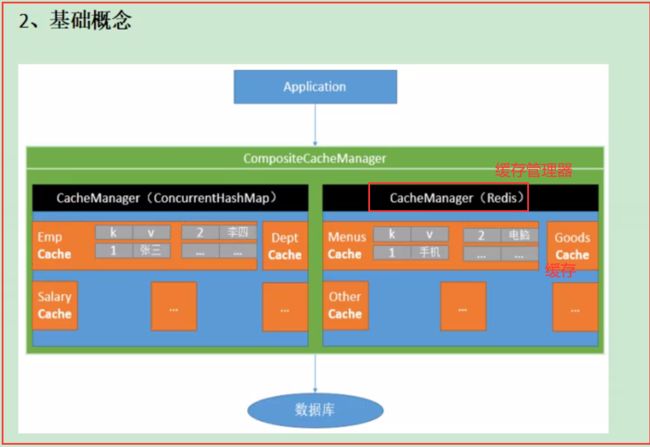
* 原理:
* CacheManager(RedisCacheManager)-->Cache(RedisCache)-->Cache负责缓存的读写
* @return
*/
@Cacheable(value = {"category"},key = "#root.method.name",sync = true)
@Override
public List<CategoryEntity> getLevel1Categorys() {
System.out.println("getLevel1Categorys...");
long l = System.currentTimeMillis();
List<CategoryEntity> categoryEntities = baseMapper.selectList(new QueryWrapper<CategoryEntity>().eq("parent_cid", 0));
return categoryEntities;
}
/**
* 级联更新所有关联的数据
* @CacheEvict:失效模式
* 1.组合多个操作,同时进行多种缓存操作 @Caching
* 2.指定删除某个分区下的所有数据 @CacheEvict(value = "category",allEntries = true)
* 3.存储统一类型的数据,都可以指定成同一分区。分区名默认就是缓存的前缀
* @param category
* key 常规字符串要加单引号
*/
//@Caching(evict = {
// @CacheEvict(value = {"category"},key ="'getLevel1Categorys'" ),
// @CacheEvict(value = {"category"},key ="'getCatalogJson'" )
//})
@CacheEvict(value = "category",allEntries = true)
@Transactional //添加事务
@Override
public void updateCascade(CategoryEntity category) {
//1.先更新自己表中的数据
this.updateById(category);
categoryBrandRelationService.updateCategory(category.getCatId(), category.getName());
}
4.自定义缓存配置类
/**
* @description 缓存配置类
* @Author leslie
* @Date 2021/8/6
*/
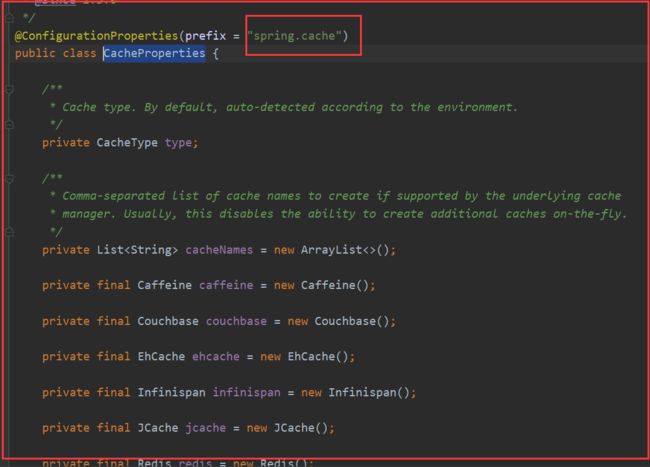
@EnableConfigurationProperties(CacheProperties.class)
@Configuration
@EnableCaching //开启缓存
public class MyCacheConfig {
// @Autowired
// CacheProperties cacheProperties;
/**
* 配置文件中的东西没有用上
*
* 1、原来和配置文件绑定的配置类是这样的
* @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.cache")
* public class CacheProperties {
* 2、要让他生效
* @EnableConfigurationProperties(CacheProperties.class)
* @return
*/
@Bean
RedisCacheConfiguration redisCacheConfiguration(CacheProperties cacheProperties){
RedisCacheConfiguration config = RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig();
// key的序列化机制
config = config.serializeKeysWith(
RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(new StringRedisSerializer()
));
// value的序列化机制
config = config.serializeValuesWith(
RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(new GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer())
);
CacheProperties.Redis redisProperties = cacheProperties.getRedis();
// 将配置文件中的所有配置都生效
if (redisProperties.getTimeToLive() != null) {
config = config.entryTtl(redisProperties.getTimeToLive());
}
if (redisProperties.getKeyPrefix() != null) {
config = config.prefixCacheNameWith(redisProperties.getKeyPrefix());
}
if (!redisProperties.isCacheNullValues()) {
config = config.disableCachingNullValues();
}
if (!redisProperties.isUseKeyPrefix()) {
config = config.disableKeyPrefix();
}
return config;
}
}
相关配置类
CacheAutoConfiguration
十、常见问题bug
1.产生堆外内存溢出:OutOfDirectMemoryError
产生堆外内存溢出:OutOfDirectMemoryError
1)、SpringBoot2.0以后默认使用lettuce作为操作Redis的客户端。它使用netty进行网络通信
2)、lettuce的bug导致netty堆外内存溢出-Xmx300m;netty如果没有指定堆外内存,默认使用-Xmx300m可以通过-Dio.netty.maxDirectMemory进行设置
解决方案:不能使用-Dio.netty.maxDirectMemory只去调大堆外内存
1)、升级lettuce客户端。2)、切换使用jedis
redisTemplate:
lettuce、jedis操作redis的底层客户端。Spring再次封装redisTemplate
十一、Redis缓存过期淘汰策略
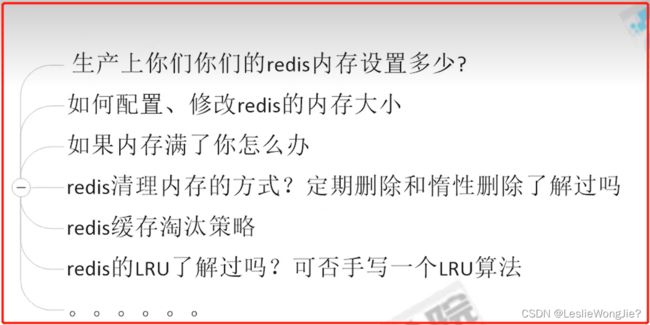
1.面试题
2.Redis内存满了怎么办
1.Redis默认内存多少?在哪里查看?如何设置?
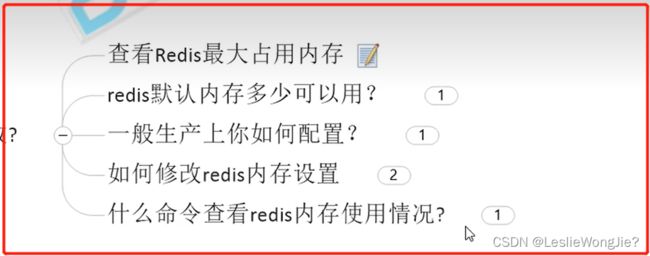
①:查看Redis最大占用内存
②:Redis默认内存多少可以用?
③:一般生产上你如何配置?
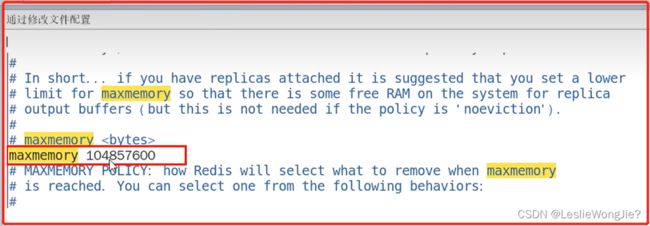
④:如何修改Redis内存设置
⑤:什么命令查看Redis内存使用情况?
2.真要打满了怎么样?如果Redis内存使用超出了设置的最大值会怎样?
3.Redis缓存淘汰策略
1.往redis里写的数据是怎么没了的
①:redis过期键的删除策略
②:三种不同的删除策略
Ⅰ、定时删除
Ⅱ、惰性删除
Ⅲ、定期删除
③:上述步骤都过堂了,还有漏洞吗?
④:内存淘汰策略登场
2.有那些(redis6.0.8版本)
3.你平时用哪一种
4.如何配置、修改
4.Redis的LRU算法简介
1.是什么
2.算法来源
3.设计思想
4.编码手写如何实现LRU
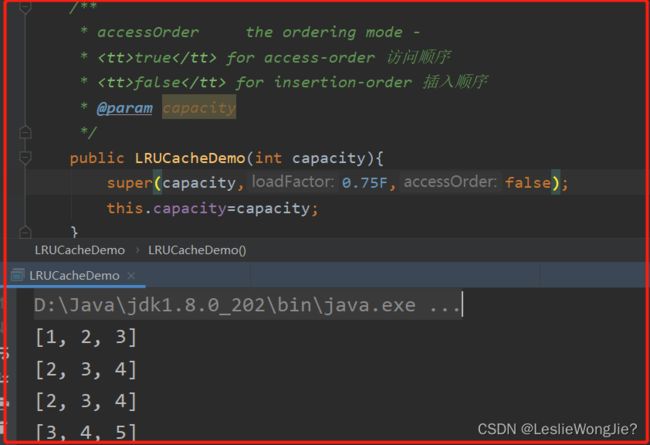
public class LRUCacheDemo<K,V> extends LinkedHashMap<K,V> {
private int capacity;//缓存坑位
/**
* accessOrder the ordering mode -
* true for access-order 访问顺序
* false for insertion-order 插入顺序
* @param capacity
*/
public LRUCacheDemo(int capacity){
super(capacity,0.75F,true);
this.capacity=capacity;
}
@Override
protected boolean removeEldestEntry(Map.Entry<K, V> eldest) {
return super.size()>capacity;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
LRUCacheDemo lruCacheDemo=new LRUCacheDemo(3);
lruCacheDemo.put(1,"a");
lruCacheDemo.put(2,"b");
lruCacheDemo.put(3,"c");
System.out.println(lruCacheDemo.keySet());
lruCacheDemo.put(4,"d");
System.out.println(lruCacheDemo.keySet());
lruCacheDemo.put(3,"c");
lruCacheDemo.put(3,"c");
lruCacheDemo.put(3,"c");
System.out.println(lruCacheDemo.keySet());
lruCacheDemo.put(5,"d");
System.out.println(lruCacheDemo.keySet());
}
}
[1, 2, 3]
[2, 3, 4]
[2, 4, 3]
[4, 3, 5]
public class LRUCacheDemo {
Map<Integer, Node<Integer, Integer>> map;
//map负责查找,构建一个虚拟的双向链表,它里面安装的就是一个个Node节点,作为数据载体
DoubleLinkedList<Integer, Integer> doubleLinkedList;
private int cacheSize;
public LRUCacheDemo(int cacheSize) {
this.cacheSize = cacheSize;//坑位
//map = new HashMap<>();//查找
map = new LinkedHashMap<>();
doubleLinkedList = new DoubleLinkedList<>();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
LRUCacheDemo lruCacheDemo = new LRUCacheDemo(3);
lruCacheDemo.put(1, 1);
lruCacheDemo.put(2, 2);
lruCacheDemo.put(3, 3);
System.out.println(lruCacheDemo.map.keySet());
lruCacheDemo.put(4, 4);
System.out.println(lruCacheDemo.map.keySet());
lruCacheDemo.put(4, 4);
System.out.println(lruCacheDemo.map.keySet());
lruCacheDemo.put(3, 3);
System.out.println(lruCacheDemo.map.keySet());
lruCacheDemo.put(5, 5);
System.out.println(lruCacheDemo.map.keySet());
}
public int get(int key) {
if (!map.containsKey(key)) {
return -1;
}
Node<Integer, Integer> node = map.get(key);
doubleLinkedList.removeNode(node);
doubleLinkedList.addHead(node);
return node.value;
}
//saveOrUpdate method
public void put(int key, int value) {
if (map.containsKey(key)) {//update
Node<Integer, Integer> node = map.get(key);
node.value = value;
//map.put(key, node);
map.remove(key);
doubleLinkedList.removeNode(node);
doubleLinkedList.addHead(node);
map.put(key, node);
} else {
if (map.size() == cacheSize) {//坑我满了
Node<Integer, Integer> lastNode = doubleLinkedList.getLast();
map.remove(lastNode.key);
doubleLinkedList.removeNode(lastNode);
}
//才是新增
Node<Integer, Integer> newNode = new Node<>(key, value);
map.put(key, newNode);
doubleLinkedList.addHead(newNode);
}
}
//1.构建一个Node节点,作为数据载体
class Node<K, V> {
K key;
V value;
Node<K, V> prev;
Node<K, V> next;
public Node() {
this.prev = this.next = null;
}
public Node(K key, V value) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.prev = this.next = null;
}
}
//2.构造一个双向队列,里面安装的就是我们的Node
class DoubleLinkedList<K, V> {
Node<K, V> head;
Node<K, V> tail;
//2.1构造方法
public DoubleLinkedList() {
head = new Node<>();
tail = new Node<>();
head.next = tail;
tail.prev = head;
}
//2.2添加头
public void addHead(Node<K, V> node) {
node.next = head.next;
node.prev = head;
head.next.prev = node;
head.next = node;
}
//2.3删除节点
public void removeNode(Node<K, V> node) {
node.next.prev = node.prev;
node.prev.next = node.next;
node.prev = null;
node.next = null;
}
//2.4获得最后一个节点
public Node getLast() {
return tail.prev;
}
}
}
[1, 2, 3]
[2, 3, 4]
[2, 3, 4]
[2, 4, 3]
[4, 3, 5]
public class LRUCacheDemo {
Map<Integer, Node<Integer, Integer>> map;
//map负责查找,构建一个虚拟的双向链表,它里面安装的就是一个个Node节点,作为数据载体
DoubleLinkedList<Integer, Integer> doubleLinkedList;
private int cacheSize;
public LRUCacheDemo(int cacheSize) {
this.cacheSize = cacheSize;//坑位
map = new HashMap<>();//查找
doubleLinkedList = new DoubleLinkedList<>();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
LRUCacheDemo lruCacheDemo = new LRUCacheDemo(3);
lruCacheDemo.put(1, 1);
lruCacheDemo.put(2, 2);
lruCacheDemo.put(3, 3);
System.out.println(lruCacheDemo.map.keySet());
lruCacheDemo.put(4, 4);
System.out.println(lruCacheDemo.map.keySet());
lruCacheDemo.put(4, 4);
System.out.println(lruCacheDemo.map.keySet());
lruCacheDemo.put(3, 3);
System.out.println(lruCacheDemo.map.keySet());
lruCacheDemo.put(5, 5);
System.out.println(lruCacheDemo.map.keySet());
}
public int get(int key) {
if (!map.containsKey(key)) {
return -1;
}
Node<Integer, Integer> node = map.get(key);
doubleLinkedList.removeNode(node);
doubleLinkedList.addHead(node);
return node.value;
}
//saveOrUpdate method
public void put(int key, int value) {
if (map.containsKey(key)) {//update
Node<Integer, Integer> node = map.get(key);
node.value = value;
map.put(key, node);
doubleLinkedList.removeNode(node);
doubleLinkedList.addHead(node);
} else {
if (map.size() == cacheSize) {//坑我满了
Node<Integer, Integer> lastNode = doubleLinkedList.getLast();
map.remove(lastNode.key);
doubleLinkedList.removeNode(lastNode);
}
//才是新增
Node<Integer, Integer> newNode = new Node<>(key, value);
map.put(key, newNode);
doubleLinkedList.addHead(newNode);
}
}
//1.构建一个Node节点,作为数据载体
class Node<K, V> {
K key;
V value;
Node<K, V> prev;
Node<K, V> next;
public Node() {
this.prev = this.next = null;
}
public Node(K key, V value) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.prev = this.next = null;
}
}
//2.构造一个双向队列,里面安装的就是我们的Node
class DoubleLinkedList<K, V> {
Node<K, V> head;
Node<K, V> tail;
//2.1构造方法
public DoubleLinkedList() {
head = new Node<>();
tail = new Node<>();
head.next = tail;
tail.prev = head;
}
//2.2添加头
public void addHead(Node<K, V> node) {
node.next = head.next;
node.prev = head;
head.next.prev = node;
head.next = node;
}
//2.3删除节点
public void removeNode(Node<K, V> node) {
node.next.prev = node.prev;
node.prev.next = node.next;
node.prev = null;
node.next = null;
}
//2.4获得最后一个节点
public Node getLast() {
return tail.prev;
}
}
}
[1, 2, 3]
[2, 3, 4]
[2, 3, 4]
[2, 3, 4]
[3, 4, 5]