C++ STL之 string类用法
第二章 STL
string
ascll表
string所有方法列表
成员函数
迭代器
容量
元素访问
修饰符
字符串操作
非成员函数重载
成员常量
初始化
c_str
获取或改变长度和容量(length、size、capacity、resize、reserve)
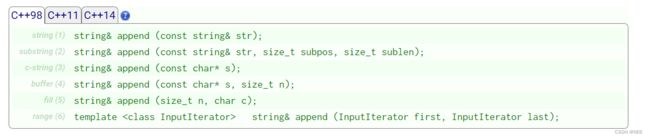
添加(append、push_back、+=)
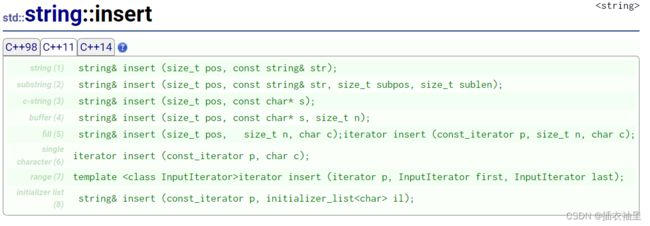
插入(insert)
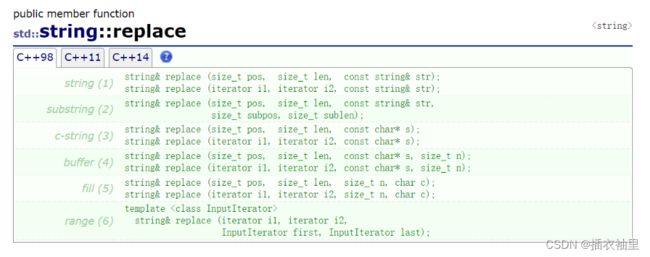
替换(replace)
删除和判空(erase、clear、empty)
遍历方式
加下标的形式
迭代器
加const的迭代器
范围for
c字符串的形式遍历
翻转字符串(reverse)
比较(compare)
裁剪(substr)
查找
find()方法从前往后
rfind()方法 从后往前
getline方法(刷题时常用)
string
string 是 basic_string模板 的一份实例,因为字符串多种多样,所以 string 也有各种各样的版本
string 其实就是 basic_string
string 常规字符串类,即每个字符占位 1byte
wstring 宽字符串类,用来处理较长字符串,Winows下占位 2byte,而 Linux下占位 4byte
u16string 匹配 UTF-16 编码标准,指定字符占位 2byte(C++11)
u32string 匹配 UTF-32 编码标准,规定字符占位 4byte(C++11)
ascll表
十进制 十六进制 字符 | 十进制 十六进制 字符 | 十进制 十六进制 字符 | 十进制 十六进制 字符
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
0 00 NUL | 32 20 | 64 40 @ | 96 60 `
1 01 SOH | 33 21 ! | 65 41 A | 97 61 a
2 02 STX | 34 22 " | 66 42 B | 98 62 b
3 03 ETX | 35 23 # | 67 43 C | 99 63 c
4 04 EOT | 36 24 $ | 68 44 D | 100 64 d
5 05 ENQ | 37 25 % | 69 45 E | 101 65 e
6 06 ACK | 38 26 & | 70 46 F | 102 66 f
7 07 BEL | 39 27 ' | 71 47 G | 103 67 g
8 08 BS | 40 28 ( | 72 48 H | 104 68 h
9 09 TAB | 41 29 ) | 73 49 I | 105 69 i
10 0A LF | 42 2A * | 74 4A J | 106 6A j
11 0B VT | 43 2B + | 75 4B K | 107 6B k
12 0C FF | 44 2C , | 76 4C L | 108 6C l
13 0D CR | 45 2D - | 77 4D M | 109 6D m
14 0E SO | 46 2E . | 78 4E N | 110 6E n
15 0F SI | 47 2F / | 79 4F O | 111 6F o
16 10 DLE | 48 30 0 | 80 50 P | 112 70 p
17 11 DC1 | 49 31 1 | 81 51 Q | 113 71 q
18 12 DC2 | 50 32 2 | 82 52 R | 114 72 r
19 13 DC3 | 51 33 3 | 83 53 S | 115 73 s
20 14 DC4 | 52 34 4 | 84 54 T | 116 74 t
21 15 NAK | 53 35 5 | 85 55 U | 117 75 u
22 16 SYN | 54 36 6 | 86 56 V | 118 76 v
23 17 ETB | 55 37 7 | 87 57 W | 119 77 w
24 18 CAN | 56 38 8 | 88 58 X | 120 78 x
25 19 EM | 57 39 9 | 89 59 Y | 121 79 y
26 1A SUB | 58 3A : | 90 5A Z | 122 7A z
27 1B ESC | 59 3B ; | 91 5B [ | 123 7B {
28 1C FS | 60 3C < | 92 5C \ | 124 7C |
29 1D GS | 61 3D = | 93 5D ] | 125 7D }
30 1E RS | 62 3E > | 94 5E ^ | 126 7E ~
31 1F US | 63 3F ? | 95 5F _ | 127 7F DEL
string所有方法列表
成员函数
构造函数 构造字符串对象(公共成员函数)
析构函数 字符串析构函数(公共成员函数)
operator= 字符串赋值(公共成员函数)
迭代器
begin 将迭代器返回到开头(公共成员函数)
end 返回迭代器结束(公共成员函数)
rbegin 返回反向迭代器以反向开始(公共成员函数)
rend 返回反向迭代器到反向结束(公共成员函数)
cbegin 返回 const_iterator 到开头(公共成员函数)
cend 返回 const_iterator 结束(公共成员函数)
crbegin 返回 const_reverse_iterator 以反向开始(公共成员函数)
crend 返回 const_reverse_iterator 到反向结束(公共成员函数)
容量
size 返回字符串的长度(公共成员函数)
length 返回字符串的长度(公共成员函数)
max_size 返回字符串的容量的最大大小(公共成员函数)
resize 调整字符串大小(公共成员函数)
capacity 分配存储的返回大小(公共成员函数)
reserve 请求更改容量(公共成员函数)
clear 清除字符串(公共成员函数)
empty 测试字符串是否为空(公共成员函数)
shrink_to_fit 收缩以适应(公共成员函数)
元素访问
operator[] 获取字符串的字符(公共成员函数)
at 获取字符串中的字符(公共成员函数)
back 返回访问最后一个字符(公共成员函数)
front 访问第一个字符(公共成员函数)
修饰符
operator+= 添加到字符串(公共成员函数)
append 追加到字符串(公共成员函数)
push_back 追加字符到字符串(公共成员函数)
assign 给字符串赋值(公共成员函数)
insert 插入字符串(公共成员函数)
erase 从字符串中删除字符(公共成员函数)
replace 替换字符串的一部分(公共成员函数)
swap 交换字符串值(公共成员函数)
pop_back 删除最后一个字符(公共成员函数)
字符串操作
c_str 获取等效的 C 字符串(公共成员函数)
data 获取字符串数据(公共成员函数)
get_allocator 获取分配器(公共成员函数)
copy 从字符串中复制字符序列(公共成员函数)
find 在字符串中查找内容(公共成员函数)
rfind 查找字符串中最后一次出现的内容(公共成员函数)
find_first_of 在字符串中查找字符(公共成员函数)
find_last_of 从字符串末尾开始查找字符(公共成员函数)
find_first_not_of 查找字符串中不存在的字符(公共成员函数)
find_last_not_of 从字符串末尾查找不匹配的字符(公共成员函数)
substr 生成子串(公共成员函数)
compare 比较字符串(公共成员函数)
非成员函数重载
operator+ 连接字符串(函数)
关系运算符(relational operators) 字符串(函数)的关系运算符
包含 == != < <= > >=
swap 交换两个字符串的值(函数)
operater>> 从流中提取字符串(函数)
operater<< 将字符串插入流(函数)
getline 从流中获取行到字符串(函数)
成员常量
npos size_t 的最大值(公共静态成员常量)
源代码中
typedef unsigned int size_t;
static const size_t npos = -1; // 因为是无符号数,所以此时npos为此类型的最大值
初始化
string s1; // 为空
string s2("hello"); // hello
string s3("hello", 2); // he
string s4(s2); // hello
string s5(s2, 1, 2); // el // 这里是将字符串的第一个到第二个给s5
string s6(10, 'a'); // aaaaaaaaaa
string s7(s2, 1, string::npos);// ello 缺省参数 string::npos 无符号整数的最大值 ,可以不写
s1 = s6; // aaaaaaaaaa
string s8 = s2; // hello
char c[] = "hello";
string s9(c,5); // hello 这里是将字符数组c的前5个字符拷贝到str11中c_str
c_str本身和指向的值均不能改变,返回值是char*实际上返回的就是string类中的内容的地址,也就是字符串的地址。
获取或改变长度和容量(length、size、capacity、resize、reserve)
length()函数与size()函数均可获取字符串长度。但除了string,其他类型就只有size()。所以建议只用size() 方法
string s("12");
cout << s.size(); // 2cappacity 获取当前对象容量的大小
reserve 开空间,只改变空间(容量)大小
resize 即会改变空间也会改变数据
string s1("22");
cout << s1.capacity() << endl; // 15 // 按照两倍的规律开空间
//s1.reserve(100); // 开空间,只改变空间,开的空间大于100,涉及到内存对齐方面
//cout << s1.capacity() << "\n";
//s1.resize(20); // 即会改变空间也会改变数据。当空间比20小会增容
s1.resize(20,'x'); // 填充字符x;添加(append、push_back、+=)
append 可以在字符串的末尾添加字符和字符串。
push_back 只适用于添加单个字符
string str = "hello world";
string str2 = "hard ";
string str3 = "it is so happy wow";
string str4 = "hello world"
//s.append(n,ch) 在当前字符串结尾添加n个字符c
str.append(4,'z'); // str = "hello worldzzzz"
//s.append(str) 把字符串str连接到当前字符串的结尾 // 最常用之一
str.append(str2); // str = "hello worldzzzzhard "
//s.append(str,pos,n) 把字符串str中从pos(数组下标)开始的n个字符连接到当前字符串的结尾
str.append(str3,6,9); // str = "hello worldzzzzso happy " // 注意最后的空格也算一个
//append(cstr,int n) 把字符数组cstr的前n个字符连接到当前字符串结尾
//此处不可将"it is so happy wow"替换为str3
str.append("it is so happy wow",6); // str = "hello worldit is "
// 建议这个
str4.push_back('h'); // str4 = "hello worldh" // 最常用之一
str4 += 'h'; // str4 = "hello worldhh"
st4 += "eeeee"; // str4 = "hello worldhheeeee" // 最常用之一插入(insert)
string s = "hello world";
string str3 = "it is so happy wow";
s.insert(s.begin(), '0'); // 头插 // 常用
//s.insert(pos,n,ch) 在字符串s的pos位置上面插入n个字符ch
//s.insert(pos,str) 在字符串s的pos位置插入字符串str // 常用
s.insert(2, "2");
//s.insert(pos,str,a,n) 在字符串s的pos位置插入字符串str中位置a到后面的n个字符
//s.insert(pos,cstr,n) 在字符串s的pos位置插入字符数组cstr从开始到后面的n个字符
//此处不可将"it is so happy wow"替换为str3
s.insert(6,"it is so happy wow",6); // str = "hello it is world"替换(replace)
string s = "hello world";
//s.replace(p0,n0,n,ch) 删除p0开始的n0个字符,然后在p0处插入n个字符ch
//s.replace(p0,n0,str) 删除从p0开始的n0个字符,然后在p0处插入字符串str
//s.replace(p0,n0,str,pos,n) 删除p0开始的n0个字符,然后在p0处插入字符串str中从pos开始的n个字符
//s.replace(p0,n0,cstr,n) 删除p0开始的n0个字符,然后在p0处插入字符数组cstr的前n个字符
删除和判空(erase、clear、empty)
string str = "hello";
//s.erase(pos,n) 把字符串s从pos开始的n个字符删除
str.erase(2,3); // str = "he"
str.clear(); // str = ""
str.empty(); // 返回trueclear()不会将空间capacity清除,只有个数size会改变
遍历方式
加下标的形式
string s1("hello");
s1 += " ";
s1 += "world";
// 推荐这个
for (size_t i = 0; i < s1.size(); i++)
{
s1[i] += 1;
}
for (size_t i = 0; i < s1.size(); i++)
{
cout << s1[i] <<" ";
}
cout << endl;
// i f m m p ! x p s m e 迭代器
底层是一个指针,但是类型不一定是 char*
string s1("hello");
s1 += " ";
s1 += "world";
// 迭代器
//string::iterator it = s1.begin();
auto it = s1.begin();
while (it != s1.end())
{
// 写
*it -= 1;
++it;
}
it = s1.begin();
while (it != s1.end())
{
// 读
cout << *it<< " ";
++it;
}
cout << endl;
//h e l l o w o r l d
// 倒着遍历
string::reverse_iterator rit = s1.rbegin();
while (rit != s1.rend())
{
cout << *rit << " ";
++rit;
}加const的迭代器
int string2int(const string& str) {
size_t val = 0;
// const 迭代器只能读不能写。
// 正向 // 12345
string::const_iterator it = str.begin();
while (it != str.end())
{
val *= 10;
val += (*it - '0');
++it;
}
val = 0;
// 反向 // 54321
//string::const_reverse_iterator rit = str.rbegin();
auto rit = str.rbegin();
while (rit != str.rend())
{
val *= 10;
val += (*rit - '0');
++rit;
}
return val;
}
void test3() {
string s1("12345");
cout << string2int(s1); // 将字符串转换为数字 范围for
// 范围for
// 原理被替换成迭代器
for (auto& i : s1)
{
cout << i << " ";
}
cout << endl;c字符串的形式遍历
// 获取字符数组首地址,用C字符串的形式遍历。
const char* str = s.c_str();
while (*str)
{
cout << *str << " ";
str++;
}
cout << endl;
cout << s << endl;
cout << s.c_str()<翻转字符串(reverse)
reverse(s.begin(),s.end());
比较(compare)
按ascll码值的大小比较
0 他们比较相等
<0 第一个不匹配的字符的值在被比较的字符串中较低,或者所有被比较的字符都匹配但被比较的字符串较短。
>0 比较字符串中第一个不匹配字符的值更大,或者所有比较字符都匹配但比较字符串更长。
//s.compare(str) 比较当前字符串s和str的大小
//s.compare(pos,n,str) 比较当前字符串s从pos开始的n个字符与str的大小
//s.compare(pos,n0,str,pos2,n) 比较当前字符串s从pos开始的n0个字符与str中pos2开始的n个字符组成的字符串的大小
//s.compare(pos,n0,cstr,n) 比较当前字符串s从pos开始的n0个字符与字符数组cstr中前n个字符的大小
裁剪(substr)
返回值是string
//s.substr(pos,n) 得到字符串s位置为pos后面的n个字符组成的串
//s.substr(pos) 得到字符串s从pos到结尾的串
常搭配find()使用
查找
返回值是下标,如果未找到匹配项,则该函数返回 string::npos。
find()方法从前往后
//s.find(str) 查找字符串str在当前字符串s中第一次出现的位置
//s.find(str,pos) 查找字符串str在当前字符串s的[pos,end]中第一次出现的位置
//s.find(cstr,pos,n) 查找字符数组cstr前n的字符在当前字符串s的[pos,end]中第一次出现的位置
//s.find(ch,pos) 查找字符ch在当前字符串s的[pos,end]中第一次出现的位置
rfind()方法 从后往前
//s.rfind(str) 查找字符串str在当前字符串s中最后一次出现的位置
//s.rfind(str,pos) 查找字符串str在当前字符串s的[0,pos+str.length()-1]中最后一次出现的位置
//s.rfind(cstr,pos,n) 查找字符数组cstr前n的字符在当前字符串s的[0,pos+n-1]中最后一次出现的位置
//s.rfind(ch.pos) 查找字符ch在当前字符串s的[0,pos]中最后一次出现的位置
substr 和 find 的应用
分割字符串
void split_url(const string& url) {
// 分离url 协议 域名 资源名称
// https://cplusplus.com/reference/string/string/substr/
size_t i1 = url.find(':'); // 5
if (i1 != string::npos)
{
cout << url.substr(0, i1)<getline方法(刷题时常用)
string s1;
//cin >> s1; // 换行或者空格结束。
//getline(cin, s); // 回车才结束 (会接收空格)
cout << s;