源码阅读: expand 制表符展开程序
文章目录
-
- 1. 目的
- 2. 原始代码
- 3. 代码修改
- 4. expand用法:命令行参数
-
- 使用短横线加数字: `-数字`:
- 使用 `-t` 加数字
- 5. 逐字符处理输入
-
- 5.1 主体流程
- 5.2 while-switch-continue-default 理解
- 6. tab 字符的展开
-
- 6.1 展开 tab 的代码
- 6.2 最常见情况: 单个 tabstop
- 6.3 没指定tabstop: 默认tabstop等于8
- 6.3 多个 tabstop 情况
- 7. 简化版

1. 目的
阅读 netbsd 9.3 源码中 expand.c 程序, 理解其功能和实现思路。
expand.c 的作用是展开 tab 字符为空格, 其他字符则原样显示。用户输入需要被展开tab字符的文件名字,以及展开的tab字符宽度(叫做tabstop)。tabstop可以是单个数字也可以是多个数字。
2. 原始代码
https://github.com/NetBSD/src/blob/trunk/usr.bin/expand/expand.c
/* $NetBSD: expand.c,v 1.14 2016/09/05 00:40:28 sevan Exp $ */
/*
* Copyright (c) 1980, 1993
* The Regents of the University of California. All rights reserved.
*
* Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without
* modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions
* are met:
* 1. Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright
* notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer.
* 2. Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above copyright
* notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer in the
* documentation and/or other materials provided with the distribution.
* 3. Neither the name of the University nor the names of its contributors
* may be used to endorse or promote products derived from this software
* without specific prior written permission.
*
* THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE REGENTS AND CONTRIBUTORS ``AS IS'' AND
* ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE
* IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE
* ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE REGENTS OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE
* FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL
* DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS
* OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION)
* HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT
* LIABILITY, OR TORT (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY
* OUT OF THE USE OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF
* SUCH DAMAGE.
*/
#include 3. 代码修改
去除顶部 copyright 信息。
调整格式:使用 clang-format
BasedOnStyle: Microsoft
IndentWidth: 4
跨平台支持: getopt() 是 unistd.h 提供的, 是 POSIX 的一部分, MSVC 没提供这个函数, 不过微软确实实现过:
- getopt.c
- getopt.h
方便起见,只在 macosx 下编译, windows 自行使用上述 getopt 实现进行替换。
修改后的代码:
#include 4. expand用法:命令行参数
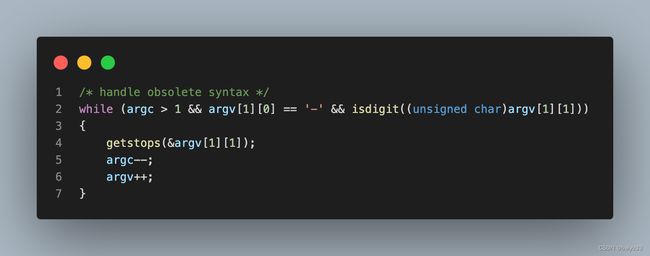
从使用者角度来说, netbsd 的 expand.c 实现,提供了两种风格的参数选项:
- 使用短横线开头,跟随数字
- 使用
-t开头,跟随数字
使用短横线加数字: -数字:
只指定一个tabstop
expand -4 test.txt
指定了两个tabstop
expand -4,8 test.txt
指定了两个 tabstop, 用空格间隔。需要用引号把它们包起来. 如果没有用引号包起来, 那么2和4是argv数组里的两个元素,4会被当作是文件名字。包起来的"2 4" 被当成 argv 数组的一个元素。
expand -"2 4" test.txt
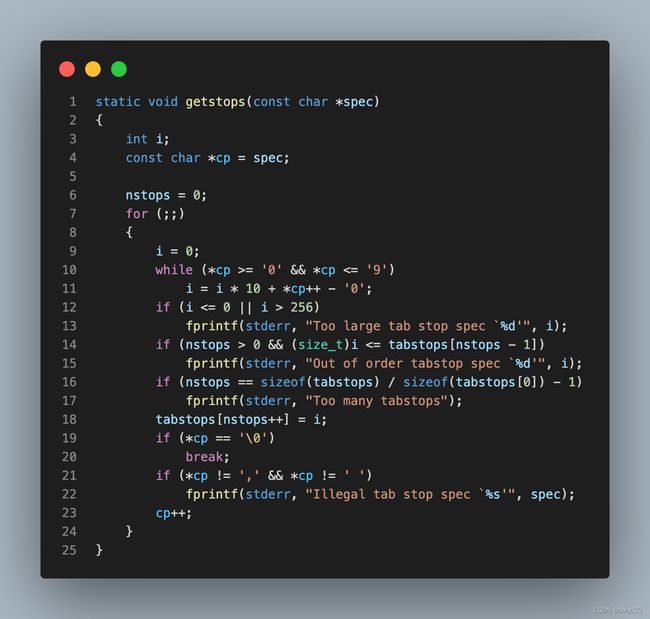
对应到源码中, 使用 getstops() 函数处理 - 开头的选项以及后续的数字:
getstops() 的实现:
使用 -t 加数字
指定单个数字,这是最常用的情况:
expand -t 4 test.txt
指定多个 tabstop 数值, 用逗号分隔:
expand -t 2,4 test.txt
指定多个 tabstop 数值,用空格分隔, 需要用双引号包起来, 把空格间隔的数字作为整体,作为 argv 的一个元素:
expand -t "2 4" test.txt
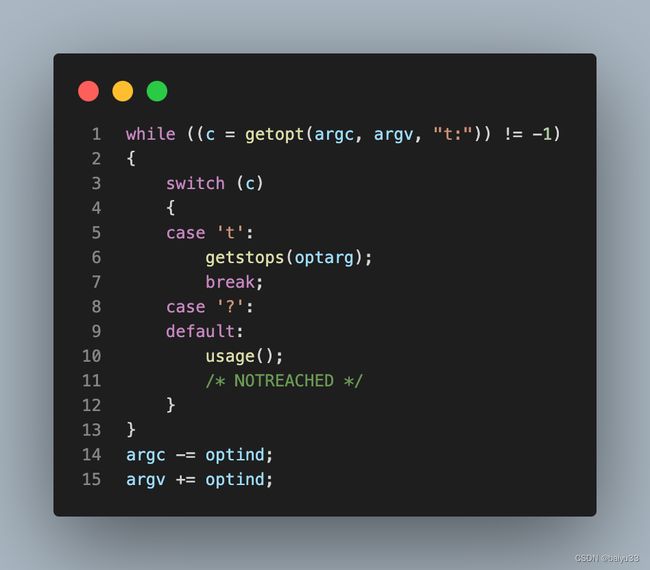
对应到代码中的实现, 外层调用 getopts(), 内层调用 getstops():
5. 逐字符处理输入
5.1 主体流程
do
{
if (argc > 0)
{
if (freopen(argv[0], "r", stdin) == NULL)
fprintf(stderr, "Cannot open `%s'", argv[0]);
argc--, argv++;
}
column = 0;
while ((c = getchar()) != EOF)
{
switch (c)
{
case '\t':
...
continue;
case '\b':
...
continue;
default:
...
continue;
case '\n':
...
continue;
}
}
可以看到处理了4种字符: \t 制表符, \b 回退字符, \n 换行符, default 处理其他字符。
这里的 switch case 写法和常见的不太一样,现在具体分析一下。
5.2 while-switch-continue-default 理解
continue
每一种字符处理的最后,都是执行 continue 而不是 break, 这和常见的 switch-case 有点不一样。此处的 continue 是和外部的 while 循环搭配使用, 因此编译可以通过, 相当于 break。如果没有外层的 while, 那这里的 continue 是非法的。
实际上这里的代码中, 可以用 break 替代 continue, 更好理解一些。如下两段代码可以自行编译运行,效果相同:
#include #include default可以不放最后吗?
微软的文档里说,switch-case 语句块种, default 可以不放最后,不影响结果。

https://learn.microsoft.com/zh-tw/cpp/c-language/switch-statement-c?view=msvc-170
小结
这 netbsd 9.3 的 expand.c 的代码也不怎么规范,看了让人更容易犯错。
6. tab 字符的展开
6.1 展开 tab 的代码
也就是 switch case 的第一部分。具体又划分为三部分:
- 用户没指定 tabstop
- 用户指定了单个 tabstop (最常见情况:指定为4)
- 用户指定了多个 tabstop
switch (c)
{
case '\t':
if (nstops == 0)
{
do
{
putchar(' ');
column++;
} while (column & 07);
continue;
}
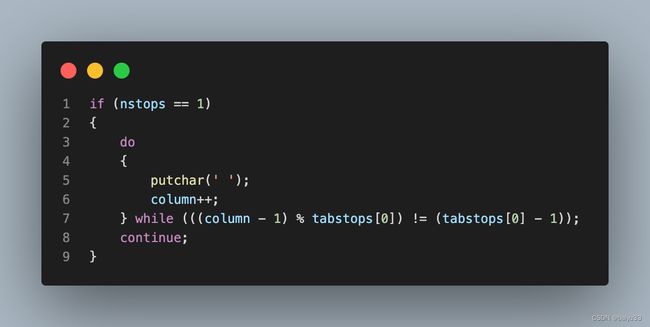
if (nstops == 1)
{
do
{
putchar(' ');
column++;
} while (((column - 1) % tabstops[0]) != (tabstops[0] - 1));
continue;
}
for (n = 0; n < nstops; n++)
if (tabstops[n] > column)
break;
//printf("[DEBUG] n = %d\n", n);
if (n == nstops)
{
putchar(' ');
column++;
continue;
}
while (column < tabstops[n])
{
putchar(' ');
column++;
}
continue;
...
}
6.2 最常见情况: 单个 tabstop
expand.c 核心功能是展开 tab 字符。最常见的情况是 tabstop 等于4,并且只有一个 tabstop。此时展开并不是说所有的 \t 都替换为4空格,而是说展开为若干空格,直到当前展开的空格缩在的列编号(从0开始计算的话),对4取余数后恰好等于3,则当前一次展开结束。
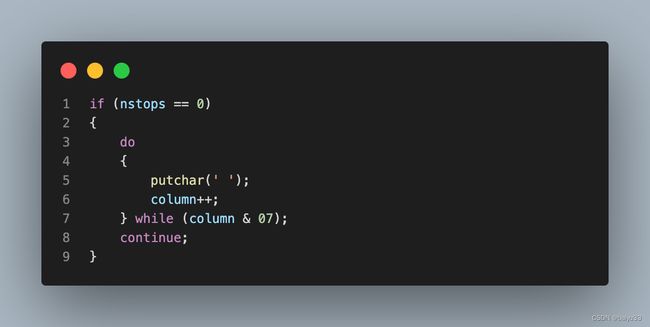
6.3 没指定tabstop: 默认tabstop等于8
while (column & 07) 是关键。 当 column 为 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 时, 会执行 do {...} 内的语句。当 column 等于8时不满足 while 条件,退出来了,完成一次 expand。
6.3 多个 tabstop 情况
首先是在命令行参数 argv 中, 如果指定了多次参数, 那么 tabstops 数组会被翻新:

在具体展开 tab 字符时, 会从 tabstops 里选出恰好大于 column 的那个 tabstops 元素,对应的索引为 n。 如果没找到, 那么n等于 nstops 也就是 tabstops 实际元素数量,会输出一个空格并结束展开; 如果找到了,那么持续输出空格, 直到 column 等于 tabstops[n].

7. 简化版
经过上面的分析发现, expand 处理的内容还是略多。如果我们从头实现,往往只关注最常用的功能, 对我而言就是 tabstop 为个位数字的情况。
于是删减改造得到一个精简版的 expand_simple.c:
#include 用法和效果:
gcc expand_simple.c
./a.out -t4 Makefile
all:
clang expand.c
clang echo.c -c -o echo
./a.out -t8 Makefile
all:
clang expand.c
clang echo.c -c -o echo