【vue2第二十章】vuex使用 (state,mutations,actions,getters)
vuex是什么?
Vuex是一个用于Vue.js应用程序的状态管理模式。它允许您在应用程序中管理共享状态,并以可预测的方式进行状态更新。Vuex集成了Vue的响应式系统,使得状态的变化能够自动地更新视图。使用Vuex,您可以将应用程序的状态集中存储在一个地方,而不是分散在各个组件中。这样可以方便地跟踪、调试和管理应用程序中的状态,并且能够更好地处理复杂的应用程序逻辑和状态间的依赖关系。总之,Vuex可以帮助您更好地组织和管理Vue.js应用程序的状态。
用大白话来说就是,vuex是一个插件,可以帮助我们管理vue的通用数据(多组件共享数据)
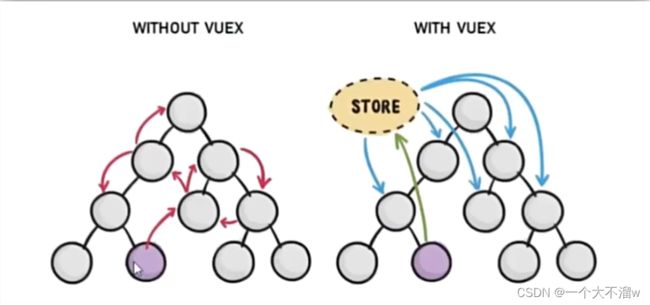
使用vuex就是很多个组件都可以使用一份数据,也可以对这同一份数据进行维护,不需要再使用组件之间的通讯方式,每个组件直接访问vuex里面的数据。如下图:
构建vuex(多组件数据共享)环境。
在创建项目时没有选择vuex时,需要手动安装,如果已经勾选则可以直接使用。接下来是手动安装步骤。
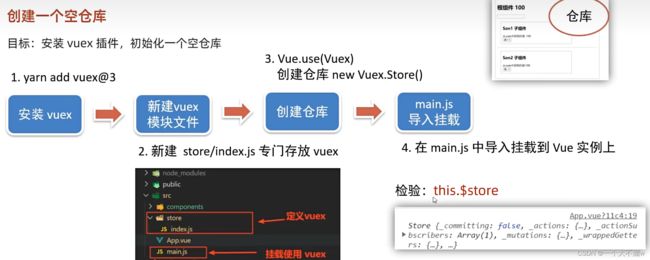
主要分为四步(这里使用的时npm):
- 在项目路径下打开终端输入
npm install [email protected] --save
- 在src目录下创建文件夹store,在其中创建index.js文件。
- 在index.js文件中引入vuex,创建仓库后导出。
import Vue from "vue";
import Vuex from "vuex";
Vue.use(Vuex);
const store =new Vuex.Store();
export default store;
- 在main.js文件中直接导入,然后挂载
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
import store from "@/store/index"
Vue.config.productionTip = false
new Vue({
render: h => h(App),
store
}).$mount('#app')
vuex如何提供数据和访问数据(state)。
vuex提供数据 核心概念state
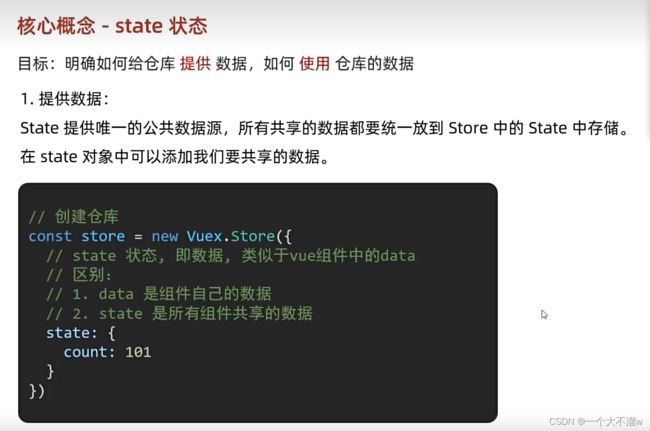
在创建仓库时,添加state对象,在state对象中添加数据。如下:
import Vue from "vue";
import Vuex from "vuex";
Vue.use(Vuex);
const store =new Vuex.Store({
state:{
count:0,
title:'大标题'
}
});
export default store;
vuex访问数据(直接访问 和 使用mapState辅助函数)
访问数据也就是如何使用数据。

在标签中直接使用模板语法{{ $store.state.数据名称}}即可访问数据。
在js代码中,使用this.$store.state.count访问数据。
<template>
<div id="app">
<div>{{ $store.state.title }}div>
<p>{{ $store.state.count }}p>
div>
template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'App',
created(){
console.log(this.$store.state.count)
}
}
script>
以上方法每次使用数据都需要写一大串,所以vuex也提供了简便方法,通过辅助函数。
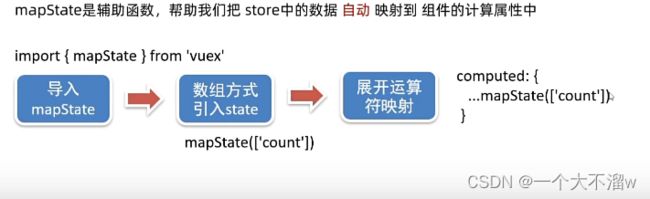
使用展开运算符的原因是,可以继续扩展组件需要的计算属性,不会因为一个mapState就把整个计算属性占满导致无法使用组件计算数据。
<template>
<div>
<p>{{ title }}p>
<p>{{ count }}p>
<button @click="changecount">新增button>
div>
template>
<script>
//1.导入mapState辅助函数
import { mapState } from 'vuex';
export default {
computed:{
//2.使用数组方式引入state,使用展开运算符自动映射到计算属性中
...mapState(['count','title'])
}
}
script>
vuex修改数据
修改数据很多人就会想到,既然可以直接拿,那么肯定可以直接改吧,就如下代码,直接写一个方法,直接在组件中修改vuex中的数据。 但是这样写是不规范的。
<template>
<div id="app">
<div>{{ $store.state.title }}div>
<p>{{ $store.state.count }}p>
<button @click="changecount">新增button>
div>
template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'App',
methods:{
changecount(){
//直接在组件中对vuex中的值进行修改,错误写法。
this.$store.state.count++
}
}
}
script>
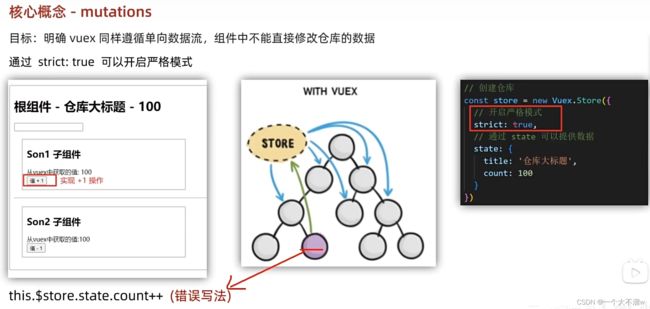
所以vuex提供了一个严格模式,只要在组件中进行修改vuex中的数据就会报错。
import Vue from "vue";
import Vuex from "vuex";
Vue.use(Vuex);
const store =new Vuex.Store({
//开启严格模式。
strict:true,
state:{
count:0,
title:'大标题'
}
});
export default store;
核心概念mutations
那么不可以直接修改,vuex肯定是提供了可以修改的方法,就是mutations。
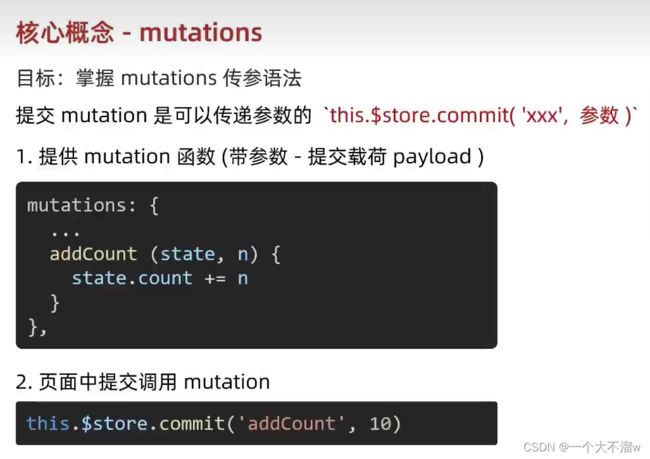
首先在仓库的index.js文件中新增一个mutations对象
import Vue from "vue";
import Vuex from "vuex";
Vue.use(Vuex);
const store =new Vuex.Store({
strict:true,
state:{
count:0,
title:'大标题'
},
mutations:{
//修改数据的逻辑
countadd(state,obj){
console.log(obj)
state.count = state.count + obj.num
}
}
});
export default store;
在组件中使用this.$store.commit('mutations中的方法名',参数)其中参数可以是对象,数据,基本数据类型等,但是只可以是一个,不可以传多个参数。
<template>
<div>
<p>{{ title }}p>
<p>{{ count }}p>
<button @click="changecount(1)">加1button>
<button @click="changecount(2)">加2button>
div>
template>
<script>
import { mapState } from 'vuex';
export default {
computed:{
...mapState(['count','title'])
},
methods:{
changecount(n){
this.$store.commit('countadd',{
num:n,
text:"哈哈哈"
})
}
}
}
script>
成功修改效果:
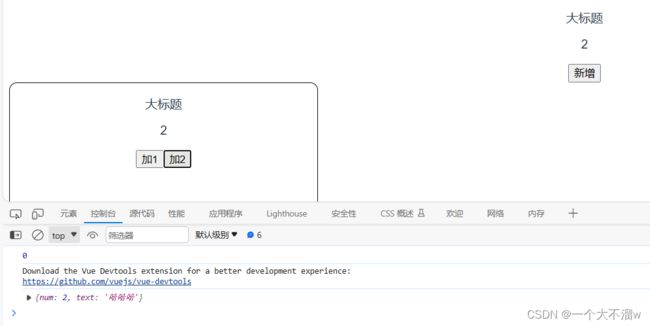
其中mutations也有对应的辅助函数mapMutations。

其中
methods:{
changecount(num){
this.$store.commit('countadd',num)
}
}
和
methods:{
...mapMutations(['countadd'])
}
是对等的。
使用mapMutations需要先导入mapMutations。
后续则可直接通过映射的方法名来调用。
<template>
<div>
<p>{{ title }}p>
<p>{{ count }}p>
<button @click="countadd(1)">加1button>
<button @click="countadd(2)">加2button>
div>
template>
<script>
//导入mapMutations
import { mapState,mapMutations } from 'vuex';
export default {
computed:{
...mapState(['count','title'])
},
methods:{
//映射方法 参数为数组,数组中的字符串为需要映射的方法名。
...mapMutations(['countadd'])
}
}
script>
核心概念actions
actions使用来处理一部操作的,为什么不使用mutations处理,因为mutations是同步的,因为mutations需要保准数据的精确性,所以使用actions来进行异步操作。
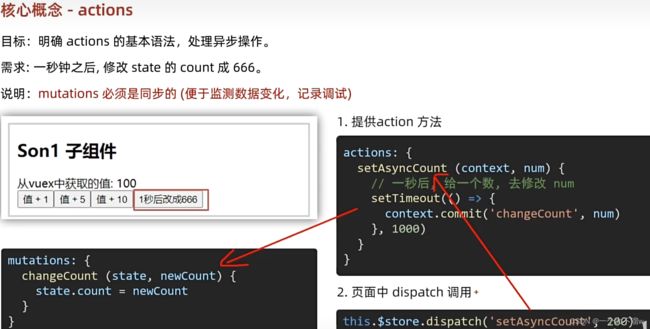
组件代码(使用actions时需要使用 this.$store.dispatch('方法名',参数)来提交数据):
<template>
<div>
<p>{{ title }}p>
<p>{{ count }}p>
<button @click="changecount(1)">加1button>
<button @click="changecount(2)">加2button>
<button @click="actionschangecount(1)">一秒钟后加1button>
<button @click="actionschangecount(2)">一秒钟后加2button>
div>
template>
<script>
import { mapState } from 'vuex';
export default {
computed:{
...mapState(['count','title'])
},
methods:{
changecount(num){
this.$store.commit('actionscountadd',num)
},
actionschangecount(num){
//需要使用dispatch来提交数据
this.$store.dispatch('actionscountadd',num)
}
}
}
script>
index.js新增actions对象新增代码逻辑,这里是使用了一个定时器来模拟发送了请求,在正式使用时就可以改为调用后台接口:
import Vue from "vue";
import Vuex from "vuex";
Vue.use(Vuex);
const store =new Vuex.Store({
strict:true,
state:{
count:0,
title:'大标题'
},
mutations:{
countadd(state,num){
state.count = state.count + num
}
},
//新增actions对象
actions:{
actionscountadd(context,num){
//在正式使用actions这里就可以改为调用后台接口获取数据
setTimeout(()=>{
context.commit ('countadd',num)
},1000)
}
}
});
export default store;
辅助函数mapActions和mapMutations同理。

首先需要导入mapActionsimport { mapActions } from 'vuex';
再通过...mapActions(['actionscountadd'])映射方法到methods,
最后直接调用。
<template>
<div>
<p>{{ title }}p>
<p>{{ count }}p>
<button @click="changecount(1)">加1button>
<button @click="changecount(2)">加2button>
<button @click="actionscountadd(1)">一秒钟后加1button>
<button @click="actionscountadd(2)">一秒钟后加2button>
div>
template>
<script>
//导入mapActions
import { mapState,mapActions } from 'vuex';
export default {
computed:{
...mapState(['count','title'])
},
methods:{
//使用mapActions映射需要使用的方法
...mapActions(['actionscountadd']),
changecount(num){
this.$store.commit('countadd',num)
}
}
}
script>
核心概念getters
除了state之外,有时我们还需要从state中派生出一些状态,这些状态是依赖state的,此时会用到getters,其实getters就类似于计算属性,而state就类似于data数据,getters需要从已知的state状态中计算出新的getters属性。
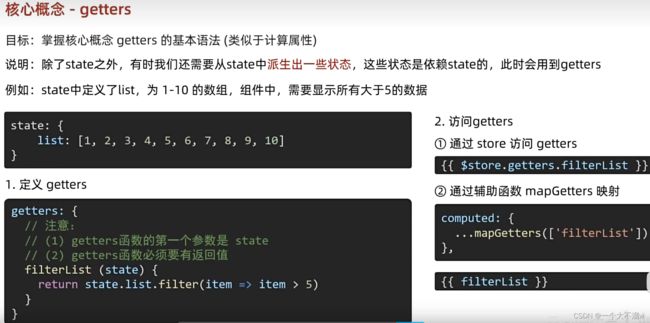
比如以下代码我需要把state中的list中的数字为奇数的过滤掉。只要偶数:
import Vue from "vue";
import Vuex from "vuex";
Vue.use(Vuex);
const store =new Vuex.Store({
strict:true,
state:{
count:0,
title:'大标题',
list:[1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10]
},
//新增getters对象
getters:{
filterList(state){
//需要返回一个数据
return state.list.filter(item => item % 2 == 0)
}
}
});
export default store;
通过import { mapState,mapGetters } from 'vuex'; 引入mapGetters ,使用filterList属性。
也可以直接通过模板语法{{ $store.getters.filterList }}使用getters属性
<template>
<div>
{{ $store.getters.filterList }}
{{ filterList }}
div>
template>
<script>
import { mapState,mapGetters } from 'vuex';
export default {
computed:{
...mapState(['count','title']),
...mapGetters(['filterList'])
}
}
script>