并查集题目
并查集是一种十分常用并且好用的数据结构
并查集可以动态维护若干个不重叠的集合,支持合并与查询操作,是一种树形的数据结构
并查集的基础应用
村村通
对于这道题我们只需要求连通块的数量,然后将这几个联通快看成点,我们可以知道联通的n个点中最少有n-1边
#include
#include
using namespace std;
const int N = 1010;
int p[N], st[N];
int find(int x)
{
if(x == p[x]) return x;
return p[x] = find(p[x]);
}
int main()
{
// freopen("1.in", "r", stdin);
while(1)
{
memset(st, 0, sizeof st);
int n, ans = 0;
scanf("%d", &n);
if(n == 0) return 0;
else
{
int m; scanf("%d", &m);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++ i) p[i] = i;
for(int i = 0; i < m; ++ i)
{
int x, y; scanf("%d%d", &x, &y);
int a = find(x);
int b = find(y);
if(a != b) p[a] = b;
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++ i)
{
int x = find(i);
if(!st[x]) ans ++, st[x] = 1;;
}
cout << ans - 1 << endl;
}
}
}
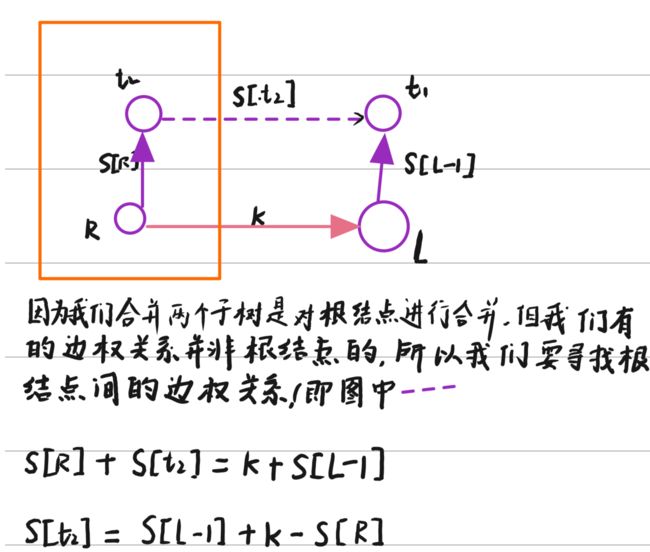
带权并查集
推导部分和
这道题的是带边权并查集的应用,比较难想到的是建图
对于每个区间l, r,k, 我们可以由前缀和s[r] - s[l - 1] = k,我们从r连一条l-1的边
#include
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
//p[N]数组用来做并查集
int p[N], n, m, q;
//s[N]数组是当前点到根结点的权值和,也是前缀和
LL s[N];
//并查集的查询操作(带路径压缩)
int find(int x)
{
if(x == p[x]) return x;
else
{
int t = find(p[x]);
s[x] += s[p[x]];
p[x] = t;
return t;
}
}
int main()
{
// freopen("1.in", "r", stdin);
cin >> n >> m >> q;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++ i) p[i] = i;
for(int i = 0; i < m; ++ i)
{
int l ,r;
LL k;
cin >> l >> r >> k;
int t1 = find(l - 1), t2 = find(r);
if(t1 != t2)
{
p[t2] = t1;
s[t2] = s[l - 1] - s[r] + k;
}
}
while(q --)
{
int l, r;cin >> l >> r;
int t1 = find(l - 1), t2 = find(r);
if(t1 != t2) puts("UNKNOWN");
else printf("%lld\n", s[r] - s[l - 1]);
}
return 0;
}
并查集的拓展域
例题团伙
#include
using namespace std;
const int N = 2010;
int p[N];
bool st[N];
int find(int x)
{
if(p[x] == x) return p[x];
return p[x] = find(p[x]);
}
void merge(int x, int y)
{
int px = find(x), py = find(y);
if(px != py) p[px] = py;
}
int main()
{
// freopen("1.in", "r", stdin);
int n, m;
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
for(int i = 1; i <= 2 * n; ++ i) p[i] = i;
for(int i = 0; i < m; ++ i)
{
char op; int x, y;
cin >> op >> x >> y;
if(op == 'F')
{
merge(x, y);
// merge(x + n, y + n);
}
else
{
merge(x + n, y);
merge(x, y + n);
}
}
// for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++ i) cout << i << ' ' << find(i) << endl;
int cnt = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++ i)
if(!st[find(i)])
{
cnt ++;
st[find(i)] = 1;
}
cout << cnt << endl;
return 0;
}
这是一道并查集的拓展域的题目也可以用带权并查集去做
本题和普通的并查集不同,普通并查集维护的是不相交集合,是一种传递性的关系如亲戚的亲戚是亲戚
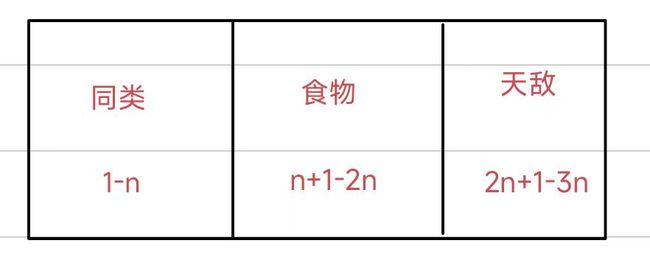
本题是天敌的天敌是食物,是一种环形的关系
我们如果用拓展域来解决这道题目的话可以用3个并查集来维护3种关系,第一种是同类关系,第二种是食物关系,第三种是天敌
就本题而言我们不用真开三个并查集,我们可以将三个并查集开到一个数组里,下标的范围代表不同的集合
#include
using namespace std;
const int N = 5e4 + 10;
int p[N * 3], ans, k, n;
//1--n代表x的同类,n + 1 -- 2n代表x的食物, 2n + 1 -- 3n代表x的天敌
int find(int x)
{
if(x == p[x]) return x;
return p[x] = find(p[x]);
}
void merge(int x, int y)
{
int px = find(x), py = find(y);
p[py] = px;
}
int main()
{
cin >> n >> k;
for(int i = 1; i <= 3 * n; ++ i) p[i] = i;
for(int i = 0; i < k; ++ i)
{
int d, x, y;scanf("%d%d%d", &d, &x, &y);
if(x > n || y > n) ans ++;
//x、y是同类
else if(d == 1)
{
//如果根据前面的信息,我们可以知道y在x的食物域,
//或者y在x的天敌域中,说明这句话是假话
if(find(x + n) == find(y) || find(x + n + n) == find(y)) ans ++;
//如果根据前面的信息,不能判断这句话是错误的,那么就讲这句话
//当成对的并且更新x的三个域
else
{
//y在x的同类域中
merge(x, y);
//y的食物和x的食物是同类
merge(x + n, y + n);
//y的天敌和x的天敌是同类
merge(x + n + n, y + n + n);
}
}
//如果x吃y
else
{
//若果y在x的同类域或者,y在x的天敌域说明这句话是假话
if(find(x) == find(y) || find(x + n + n) == find(y)) ans ++;
//这句话是真话就更新x的三个域
else
{
//y在x的食物域中
merge(x + n, y);
//y的食物是x的天敌
merge(x + n + n, y + n);
//y的天敌是x的同类
merge(x, y + n + n);
}
}
}
cout << ans << endl;
return 0;
}
牛客修棋盘
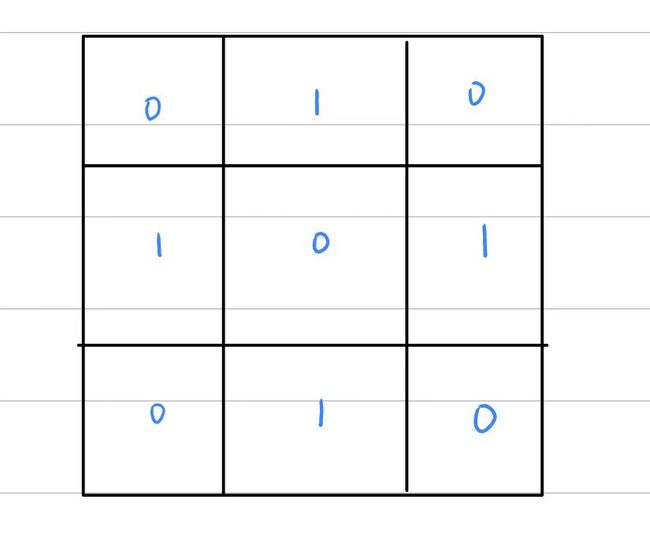
我们通过观察可以知道,走到每个点的奇偶性是确定的
同时我们的合法状态只有两种
如果我们对每个点都修改的话,我们能达到的状态如下:
所以我们每次修改次数最少的话应该是考虑我们每个点都修改的状态,当我们把每个点都修改的话就是互补的一个状态
#include
#include
#define x first
#define y second
using namespace std;
typedef pairPII;
const int N = 1010;
int res, n, m;
char g[N][N];
bool st[N][N];
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++ i)
for(int j = 1; j <= m; ++ j)
{
char ch; cin >> ch;
int x = ch -'0';
if((i + j) % 2 == 0 && x == 1) res ++;
if((i + j) % 2 && x == 0) res ++;
}
if(res == m * n) puts("0");
else cout << res << endl;
return 0;
}
P5937 [CEOI1999] Parity Game
题目的具体思路如下:考虑一段连续区间的1个数的奇偶,可以转化为考虑考虑两个端点前缀和的奇偶性上,分为两种情况,如果[l, r]区间内1的个数为偶数,说明sum[r]和sum[l - 1]包含1的个数的奇偶性相同,反之若为奇数则两个包含1的个数的奇偶性相反,我们知道奇偶性具有传递性,这样我们就可以种类并查集来维护,注意n的范围比较大,但是实际的需要用到的点的个数是比较小的,这里我们需要离散化一下。
#include
#define LL long long
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e4 + 10;
int p[N * 2 + 10], n, m, k;
mapmp;
int b[N * 2];
struct wy
{
int l, r, op;
}q[N];
int find(int x)
{
if(x != p[x]) p[x] = find(p[x]);
return p[x];
}
void merge(int x, int y)
{
int px = find(x), py = find(y);
p[py] = px;
}
int query(int x)
{
return lower_bound(b + 1, b + 1 + k, x) - b;
}
void solve()
{
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
for(int i = 1; i <= m; ++ i)
{
int l, r, op;
char s[5];
scanf("%d%d%s", &l, &r, s);
if(s[0] == 'e') op = 1;
else op = 2;
q[i] = {--l, r, op};
b[++ k] = l;
b[++ k] = r;
}
sort(b + 1, b + 1 + k);
k = unique(b + 1, b + 1 + k) - (b + 1);
for(int i = 1; i <= 2 * k; ++ i) p[i] = i;
for(int i = 1; i <= m; ++ i)
{
int l = query(q[i].l), r = query(q[i].r), op = q[i].op;
if(op == 1)
{
if(find(l) == find(r + k) || find(r) == find(l + k))
{
printf("%d", i - 1);
return;
}
else
{
merge(l, r);
merge(l + k, r + k);
}
}
else
{
if(find(l) == find(r) || find(r + k) == find(l + k))
{
printf("%d", i - 1);
return;
}
else
{
merge(l, r + k);
merge(r, l + k);
}
}
}
printf("%d", m);
}
int main()
{
// freopen("1.in", "r", stdin);
solve();
return 0;
}
P1955 [NOI2015] 程序自动分析
这道题目是相等关系,相等关系也具有传递性,明显我们可以用并查集来维护。
我们可以先对处理相等,然后去查询不相等的是否在一个集合里面如果在一个集合里面则说明这样的点是不存在的。这道题目的数据的范围很大,但实际用到的很少,我们需要对数据进行离散化。
#include