一文读懂spring的lookup-method的用法
背景:在spring中,我们通常创建的Bean是单例的。那么当我们使用存在一个这样bean,它自身是单例的,但是其需要通过调用某个原型bean的方法。在这种场景下,我们应该去怎么实现这个需求呢?
解决方案有如下几种,
一、该类型实现ApplicationContextAware接口,感知到应用上下文
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware;
public class CommandManager implements ApplicationContextAware {
private ApplicationContext applicationContext;
public Object process(Map commandState) {
// grab a new instance of the appropriate Command
Command command = createCommand();
// set the state on the (hopefully brand new) Command instance
command.setState(commandState);
return command.execute();
}
protected Command createCommand() {
// notice the Spring API dependency!
return this.applicationContext.getBean("command", Command.class);
}
public void setApplicationContext(
ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
this.applicationContext = applicationContext;
}
}
通过这种写法是可以实现我们的功能,但是一般来说不建议这样处理。因为我们的业务代码跟spring框架进行了深度耦合了。我们可以使用Lockup-method来处理
二、使用lookup-method进行解决
1、CommandManager 代码如下
public abstract class CommandManager {
public abstract Command createCommand();
public Object process(Map commandState) {
// grab a new instance of the appropriate Command
Command command = createCommand();
// set the state on the (hopefully brand new) Command instance
command.setState(commandState);
return command.execute();
}
} 2、 AsyncCommand的代码
public class AsyncCommand implements Command {
Map commandState = null;
@Override
public AsyncCommand execute() {
System.out.println("执行异步分命令方法");
return new AsyncCommand();
}
@Override
public void setState(Map commandState) {
this.commandState = commandState;
}
} 3、基于xml方法的配置:
测试类:
public class LookupMethodTest {
@Test
public void testLookupMethod() {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("lockup-method.xml");
CommandManager commandManager = applicationContext.getBean(CommandManager.class);
commandManager.process(new HashMap<>());
}
}运行测试代码后,发现能够获取到CommandManager类的实例,并且成功调用了Command的execute方法。
4、基于注解的解决方法如下:
CommandManager类的createCommand方法添加上@Lookup注解
@Component
public abstract class CommandManager {
@Lookup
public abstract Command createCommand();
public Object process(Map commandState) {
// grab a new instance of the appropriate Command
Command command = createCommand();
// set the state on the (hopefully brand new) Command instance
command.setState(commandState);
return command.execute();
}
}
Appconfig类
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(value = {"com.example.lockup.annotation"})
public class AppConfig {
@Bean
@Scope(value = ConfigurableBeanFactory.SCOPE_PROTOTYPE)
public Command myCommand(){
return new AsyncCommand();
}
}测试类:
public class LookupMethodTest {
@Test
public void testLookupMethod() {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
CommandManager commandManager = applicationContext.getBean(CommandManager.class);
commandManager.process(new HashMap<>());
}
}三、lookup-method 使用注意事项
1、CommandManager对象可以是非抽象类
其中CommandManager对象可以不一定需要是抽象,被lookup修饰的方法也不一定要求是抽象的,即如果将CommandManager修改为如下形式也是可以正常处理的!
@Component
public class CommandManager {
@Lookup
public Command createCommand() {
return null;
}
public Object process(Map commandState) {
// grab a new instance of the appropriate Command
Command command = createCommand();
// set the state on the (hopefully brand new) Command instance
command.setState(commandState);
return command.execute();
}
} 2、CommandManager类及对应的方法均不能被final修饰,下面是不正确的示例:
@Component
public final class CommandManager {
@Lookup
public final Command createCommand() {
return null;
}
public Object process(Map commandState) {
// grab a new instance of the appropriate Command
Command command = createCommand();
// set the state on the (hopefully brand new) Command instance
command.setState(commandState);
return command.execute();
}
} 3、createCommand方法中不能包含有入参,其方法签名应该如下所示:
[abstract] theMethodName(no-arguments);
即方法一定要有返回值且方法中不能有参数
四、lookup的实现原理
1、原理实现的猜想
示例中CommandManager是一个抽象对象,那肯定是通过动态代理生成的代理对象。
2、猜想的快速验证
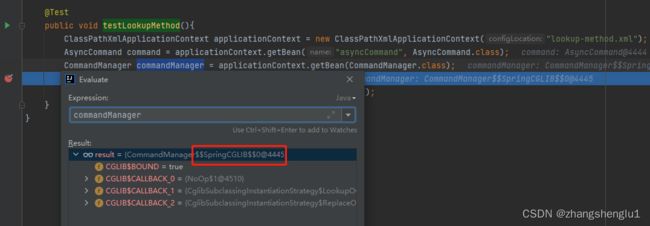
既然的CommandManager是一个代理类,那么我们可以通过applicationContext来获取到bean实例是否为一个代理对象。运行测试用例方法top.hdsw.ioc.lookup.xml.LookupMethodTest#testLookupMethod,可以看出这里的对象是一个Cglib的代理对象。说明我们的猜想是正确的
3、深入源码查找对应创建代码的逻辑
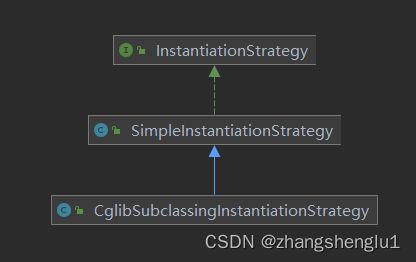
spring中都是通过InstantiationStrategy来进行创建的,目前已知的实现类有SimpleInstantiationStrategy、CglibSubclassingInstantiationStrategy。其类之间关系图如下:
创建的时候就是通过org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#instantiateBean方法来进行创建,其中getInstantiationStrategy()返回的均CglibSubclassingInstantiationStrategy对象。
protected BeanWrapper instantiateBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd) {
try {
Object beanInstance = getInstantiationStrategy().instantiate(mbd, beanName, this);
BeanWrapper bw = new BeanWrapperImpl(beanInstance);
initBeanWrapper(bw);
return bw;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, ex.getMessage(), ex);
}
}然后我们接下来查看CglibSubclassingInstantiationStrategy中的instantiate方法
@Override
public Object instantiate(RootBeanDefinition bd, @Nullable String beanName, BeanFactory owner) {
// Don't override the class with CGLIB if no overrides.
// 如果bean的定义没有通过lookup-method或者replace-method的来定义方法的重写时,就直接使用 BeanUtils.instantiateClass(constructorToUse)来实例化对象
if (!bd.hasMethodOverrides()) {
Constructor constructorToUse;
synchronized (bd.constructorArgumentLock) {
constructorToUse = (Constructor) bd.resolvedConstructorOrFactoryMethod;
if (constructorToUse == null) {
final Class clazz = bd.getBeanClass();
if (clazz.isInterface()) {
throw new BeanInstantiationException(clazz, "Specified class is an interface");
}
try {
constructorToUse = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor();
bd.resolvedConstructorOrFactoryMethod = constructorToUse;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanInstantiationException(clazz, "No default constructor found", ex);
}
}
}
return BeanUtils.instantiateClass(constructorToUse);
}
else {
// Must generate CGLIB subclass.
return instantiateWithMethodInjection(bd, beanName, owner);
}
}上面的源码中,通过判断bean的定义信息中是否包含的methodOverrides方法来确定是否生成代理对象。这里我们继续往下看org.springframework.beans.factory.support.CglibSubclassingInstantiationStrategy#instantiateWithMethodInjection其源码如下:
@Override
protected Object instantiateWithMethodInjection(RootBeanDefinition bd, @Nullable String beanName, BeanFactory owner,
@Nullable Constructor ctor, Object... args) {
return new CglibSubclassCreator(bd, owner).instantiate(ctor, args);
}至此我们可以看到代理对象真正是通过CglibSubclassCreator的instantiate方法进行创建