Spring Boot事件机制浅析
1、概述
在设计模式中,观察者模式是一个比较常用的设计模式。维基百科解释如下:
观察者模式是软件设计模式的一种。在此种模式中,一个目标对象管理所有相依于它的观察者对象,并且在它本身的状态改变时主动发出通知。这通常透过呼叫各观察者所提供的方法来实现。
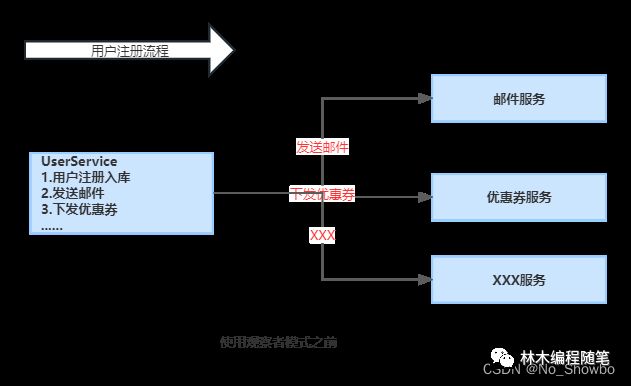
在我们日常业务开发中,观察者模式对我们很大的一个作用,在于实现业务的解耦、传参等。以用户注册的场景来举例子,假设在用户注册完成时,需要给该用户发送邮件、发送优惠劵等等操作,如下图所示:
-
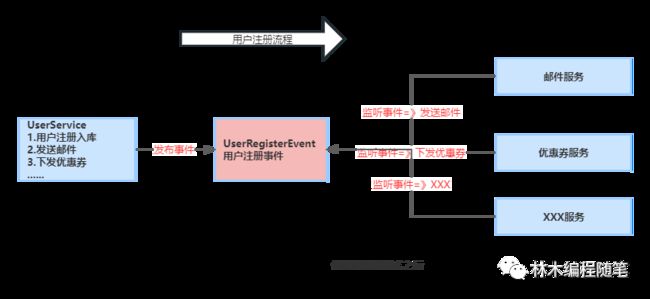
UserService 在完成自身的用户注册逻辑之后,仅仅只需要发布一个 UserRegisterEvent 事件,而无需关注其它拓展逻辑。
-
其它 Service 可以自己订阅UserRegisterEvent 事件,实现自定义的拓展逻辑。
注意:发布订阅模式属于广义上的观察者模式
在观察者模式中,观察者需要直接订阅目标事件;在目标发出内容改变的事件后,直接接收事件并作出响应
╭─────────────╮ Fire Event ╭──────────────╮
│ │─────────────>│ │
│ Subject │ │ Observer │
│ │<─────────────│ │
╰─────────────╯ Subscribe ╰──────────────╯
在发布订阅模式中,发布者和订阅者之间多了一个发布通道;一方面从发布者接收事件,另一方面向订阅者发布事件;订阅者需要从事件通道订阅事件,以此避免发布者和订阅者之间产生依赖关系
╭─────────────╮ ╭───────────────╮ Fire Event ╭──────────────╮
│ │ Publish Event │ │───────────────>│ │
│ Publisher │────────────────>│ Event Channel │ │ Subscriber │
│ │ │ │<───────────────│ │
╰─────────────╯ ╰───────────────╯ Subscribe ╰──────────────╯
简单来说,发布订阅模式属于广义上的观察者模式,在观察者模式的 Subject 和 Observer 的基础上,引入 Event Channel 这个中介,进一步解耦。
2、事件模式中的概念
-
事件源:事件的触发者,比如注册用户信息,入库,发布“用户XX注册成功”。
-
事件:描述发生了什么事情的对象,比如:XX注册成功的事件
-
事件监听器:监听到事件发生的时候,做一些处理,比如 注册成功后发送邮件、赠送积分、发优惠券…
3、spring事件使用步骤
-
定义事件
自定义事件,需要继承ApplicationEvent类,实现自定义事件。另外,通过它的
source属性可以获取事件源,timestamp属性可以获得发生时间。 -
定义监听器
自定义事件监听器,需要实现ApplicationListener接口,实现onApplicationEvent方法,处理感兴趣的事件
-
创建事件广播器
创建事件广播器实现ApplicationEventMulticaster接口,也可以使用spring定义好的SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster:
ApplicationEventMulticaster applicationEventMulticaster = new SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster(); -
向广播器中注册事件监听器
将事件监听器注册到广播器ApplicationEventMulticaster中,
applicationEventMulticaster.addApplicationListener(new SendEmailOnOrderCreaterListener()); -
通过广播器发布事件
广播事件,调用ApplicationEventMulticaster#multicastEvent方法广播事件,此时广播器中对这个事件感兴趣的监听器会处理这个事件。
applicationEventMulticaster.multicastEvent(new OrderCreateEvent(applicationEventMulticaster, 1L));
4、使用方式
4.1 面向接口的方式
案例:实现用户注册成功后发布事件,然后在监听器中发送邮件的功能。
用户注册事件:
创建 UserRegisterEvent事件类,继承 ApplicationEvent 类,用户注册事件。代码如下:
public class UserRegistryEvent extends ApplicationEvent {
private String userName;
public UserRegistryEvent(Object source, String userName) {
super(source);
this.userName = userName;
}
public String getUserName() {
return userName;
}
}
发送邮件监听器:
创建 SendEmailListener 类,邮箱 Service。代码如下:
@Component
public class SendEmailListener implements ApplicationListener {
Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(SendEmailListener.class);
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(UserRegistryEvent event) {
LOGGER.info("给用户{}发送注册成功邮件!", event.getUserName());
}
}
注意:
-
实现 ApplicationListener 接口,通过
E泛型设置感兴趣的事件,如UserRegistryEvent; -
实现
#onApplicationEvent(E event)方法,针对监听的 UserRegisterEvent 事件,进行自定义处理。
用户注册服务:注册功能+发布用户注册事件
创建UserRegisterService 类,用户 Service。代码如下:
@Service
@Slf4j
public class UserRegisterService implements ApplicationEventPublisherAware {
private ApplicationEventPublisher applicationEventPublisher;
@Override
public void setApplicationEventPublisher(ApplicationEventPublisher applicationEventPublisher) {
this.applicationEventPublisher = applicationEventPublisher;
}
public void registryUser(String userName) {
// 用户注册(入库等)
log.info("用户{}注册成功", userName);
applicationEventPublisher.publishEvent(new UserRegistryEvent(this, userName));
//applicationEventPublisher.publishEvent(event);
}
}
注意:
-
上面实现了ApplicationEventPublisherAware接口,spring容器会通过setApplicationEventPublisher将ApplicationEventPublisher注入进来,然后我们就可以使用这个来发布事件了;
-
在执行完注册逻辑后,调用 ApplicationEventPublisher 的 [
#publishEvent(ApplicationEvent event)]方法,发布[UserRegisterEvent]事件
调用:
@RestController
public class SpringEventController {
@Autowired
private UserRegisterService userRegisterService;
@GetMapping("test-spring-event")
public Object test(String name){
LocalDateTime dateTime = LocalDateTime.now();
userRegisterService.registryUser(name);
return dateTime.toString() + ":spring";
}
}
运行 http://localhost:12000/server/test-spring-event?name=name1
输出:
用户name1注册成功
给用户name1发送注册成功邮件!
原理:
spring容器在创建bean的过程中,会判断bean是否为ApplicationListener类型,进而会将其作为监听器注册到AbstractApplicationContext#applicationEventMulticaster中,
AbstractApplicationContext.java -》ApplicationEventPublisher
@Override
public void addApplicationListener(ApplicationListener listener) {
Assert.notNull(listener, "ApplicationListener must not be null");
if (this.applicationEventMulticaster != null) {
this.applicationEventMulticaster.addApplicationListener(listener); // 广播器中添加监听器
}
this.applicationListeners.add(listener);
}
// 发布事件
protected void publishEvent(Object event, @Nullable ResolvableType eventType) {
Assert.notNull(event, "Event must not be null");
// Decorate event as an ApplicationEvent if necessary
ApplicationEvent applicationEvent;
if (event instanceof ApplicationEvent) {
applicationEvent = (ApplicationEvent) event;
}
else {
applicationEvent = new PayloadApplicationEvent<>(this, event);
if (eventType == null) {
eventType = ((PayloadApplicationEvent) applicationEvent).getResolvableType();
}
}
// Multicast right now if possible - or lazily once the multicaster is initialized
if (this.earlyApplicationEvents != null) {
this.earlyApplicationEvents.add(applicationEvent);
}
else {
getApplicationEventMulticaster().multicastEvent(applicationEvent, eventType);
}
// Publish event via parent context as well...
if (this.parent != null) {
if (this.parent instanceof AbstractApplicationContext) {
((AbstractApplicationContext) this.parent).publishEvent(event, eventType);
}
else {
this.parent.publishEvent(event);
}
}
}
这块的源码在下面这个方法中,
org.springframework.context.support.ApplicationListenerDetector#postProcessAfterInitialization
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) {
if (bean instanceof ApplicationListener) {
// potentially not detected as a listener by getBeanNamesForType retrieval
Boolean flag = this.singletonNames.get(beanName);
if (Boolean.TRUE.equals(flag)) {
// singleton bean (top-level or inner): register on the fly
this.applicationContext.addApplicationListener((ApplicationListener) bean);
}
else if (Boolean.FALSE.equals(flag)) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled() && !this.applicationContext.containsBean(beanName)) {
// inner bean with other scope - can't reliably process events
logger.warn("Inner bean '" + beanName + "' implements ApplicationListener interface " +
"but is not reachable for event multicasting by its containing ApplicationContext " +
"because it does not have singleton scope. Only top-level listener beans are allowed " +
"to be of non-singleton scope.");
}
this.singletonNames.remove(beanName);
}
}
return bean;
}
4.2 面向@EventListener注解的方式
可以通过 condition 属性指定一个SpEL表达式,如果返回 “true”, “on”, “yes”, or “1” 中的任意一个,则事件会被处理,否则不会。
@EventListener(condition = "#userRegistryEvent.userName eq 'name2'")
public void getCustomEvent(UserRegistryEvent userRegistryEvent) {
LOGGER.info("EventListener 给用户{}发送注册邮件成功!", userRegistryEvent.getUserName());
}
运行http://localhost:12000/server/test-spring-event?name=name1
输出:
用户name1注册成功
给用户name1发送注册成功邮件!
运行http://localhost:12000/server/test-spring-event?name=name2
输出:
用户name2注册成功
给用户name2发送注册成功邮件!
EventListener 给用户name2发送注册邮件成功!
原理:
EventListenerMethodProcessor实现了SmartInitializingSingleton接口,SmartInitializingSingleton接口中的afterSingletonsInstantiated方法会在所有单例的bean创建完成之后被spring容器调用。spring中处理@EventListener注解源码位于下面的方法中
org.springframework.context.event.EventListenerMethodProcessor#afterSingletonsInstantiated
public class EventListenerMethodProcessor
implements SmartInitializingSingleton, ApplicationContextAware, BeanFactoryPostProcessor {
@Override
public void afterSingletonsInstantiated() {
...
...
...
try {
processBean(beanName, type); //bean
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanInitializationException("Failed to process @EventListener " +
"annotation on bean with name '" + beanName + "'", ex);
}
}
}
}
}
private void processBean(final String beanName, final Class targetType) {
if (!this.nonAnnotatedClasses.contains(targetType) &&
AnnotationUtils.isCandidateClass(targetType, EventListener.class) &&
!isSpringContainerClass(targetType)) {
Map annotatedMethods = null;
try {
annotatedMethods = MethodIntrospector.selectMethods(targetType,
(MethodIntrospector.MetadataLookup) method ->
AnnotatedElementUtils.findMergedAnnotation(method, EventListener.class));
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// An unresolvable type in a method signature, probably from a lazy bean - let's ignore it.
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Could not resolve methods for bean with name '" + beanName + "'", ex);
}
}
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(annotatedMethods)) {
this.nonAnnotatedClasses.add(targetType);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No @EventListener annotations found on bean class: " + targetType.getName());
}
}
else {
// Non-empty set of methods
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = this.applicationContext;
Assert.state(context != null, "No ApplicationContext set");
List factories = this.eventListenerFactories;
Assert.state(factories != null, "EventListenerFactory List not initialized");
for (Method method : annotatedMethods.keySet()) {
for (EventListenerFactory factory : factories) {
if (factory.supportsMethod(method)) { // 此处,针对所有EventListener注解的方法,均返回true,
Method methodToUse = AopUtils.selectInvocableMethod(method, context.getType(beanName));
ApplicationListener applicationListener =
factory.createApplicationListener(beanName, targetType, methodToUse);
if (applicationListener instanceof ApplicationListenerMethodAdapter) {
((ApplicationListenerMethodAdapter) applicationListener).init(context, this.evaluator);
}
context.addApplicationListener(applicationListener);// 往容器中注入监听器,同 接口方式
break;
}
}
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug(annotatedMethods.size() + " @EventListener methods processed on bean '" +
beanName + "': " + annotatedMethods);
}
}
}
}
}
4.3 监听器排序
如果某个事件有多个监听器,默认情况下,监听器执行顺序是无序的,不过我们可以为监听器指定顺序。
4.3.1 通过接口实现监听器:
三种方式指定监听器顺序:
-
实现org.springframework.core.Ordered接口#getOrder,返回值越小,顺序越高
-
实现org.springframework.core.PriorityOrdered接口#getOrder
-
类上使用org.springframework.core.annotation.Order注解
4.3.2 通过@EventListener:
可以在标注@EventListener的方法上面使用@Order(顺序值)注解来标注顺序,
4.4 监听器异步模式
监听器最终通过ApplicationEventMulticaster内部的实现来调用,默认实现类SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster,这个类是支持监听器异步调用的。
@Override
public void multicastEvent(final ApplicationEvent event, @Nullable ResolvableType eventType) {
ResolvableType type = (eventType != null ? eventType : resolveDefaultEventType(event));
Executor executor = getTaskExecutor();
for (ApplicationListener listener : getApplicationListeners(event, type)) {
if (executor != null) {
executor.execute(() -> invokeListener(listener, event));
}
else {
invokeListener(listener, event);
}
}
}
上面的invokeListener方法内部就是调用监听器,从代码可以看出,如果当前executor不为空,监听器就会被异步调用,所以如果需要异步只需要让executor不为空就可以了,但是默认情况下executor是空的,此时需要我们来给其设置一个值,下面我们需要看容器中是如何创建广播器的,我们在那个地方去干预。
AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext -》 ServletWebServerApplicationContext -》 GenericWebApplicationContext -》 GenericApplicationContext -》 AbstractApplicationContext -》 ConfigurableApplicationContext -》 ApplicationContext -》 ApplicationEventPublisher
通常我们使用的容器是继承于AbstractApplicationContext类型的,在容器启动的时候会调用AbstractApplicationContext#initApplicationEventMulticaster,初始化广播器:
private ApplicationEventMulticaster applicationEventMulticaster;
public static final String APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME = "applicationEventMulticaster";
protected void initApplicationEventMulticaster() {
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory();
if (beanFactory.containsLocalBean(APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME)) { // 判断容器中是否有一个 applicationEventMulticaster bean,有的话直接拿到使用
this.applicationEventMulticaster =
beanFactory.getBean(APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME, ApplicationEventMulticaster.class);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Using ApplicationEventMulticaster [" + this.applicationEventMulticaster + "]");
}
}
else {
this.applicationEventMulticaster = new SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster(beanFactory);
beanFactory.registerSingleton(APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME, this.applicationEventMulticaster);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No '" + APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME + "' bean, using " +
"[" + this.applicationEventMulticaster.getClass().getSimpleName() + "]");
}
}
}
判断spring容器中是否有名称为applicationEventMulticaster的bean,如果有就将其作为事件广播器,否则创建一个SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster作为广播器,并将其注册到spring容器中。
自定义一个类型为SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster名称为applicationEventMulticaster的bean就可以了,顺便给executor设置一个值,就可以实现监听器异步执行了。
实现如下:
@Configuration
public class SyncListenerConfig {
@Bean
public ApplicationEventMulticaster applicationEventMulticaster() {
// 创建一个事件广播器
SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster result = new SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster();
// 给广播器提供一个线程池,通过这个线程池来调用事件监听器
ThreadPoolTool threadPoolTool = new ThreadPoolTool();
ThreadPoolExecutor executor = threadPoolTool.build();
// 设置异步执行器
result.setTaskExecutor(executor);
return result;
}
}
@Slf4j
//@Data
public class ThreadPoolTool {
private static int corePoolSize = Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors();
private static int maximumPoolSize = corePoolSize * 2;
private static long keepAliveTime = 10;
private static TimeUnit unit = TimeUnit.SECONDS;
private static BlockingQueue workQueue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(3);
private static ThreadFactory threadFactory = new NameTreadFactory();
private static RejectedExecutionHandler handler = new MyIgnorePolicy();
private ThreadPoolExecutor executor;
public ThreadPoolExecutor build() {
executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(corePoolSize, maximumPoolSize, keepAliveTime, unit,
workQueue, threadFactory, handler);
executor.prestartAllCoreThreads(); // 预启动所有核心线程
return executor;
}
}
@Slf4j
public class NameTreadFactory implements ThreadFactory {
private AtomicInteger mThreadNum = new AtomicInteger(1);
@Override
public Thread newThread(Runnable r) {
Thread thread = new Thread(r, "my-thread-" + mThreadNum.getAndIncrement());
log.info(thread.getName() + " has been created");
return thread;
}
}
运行后输出:
INFO []2023-02-15 14:58:49.182[org.im.eventtest.spring.UserRegisterService][31][http-nio-12000-exec-1][INFO]-用户name2注册成功
INFO []2023-02-15 14:58:49.184[org.im.eventtest.spring.SendEmailListener][24][my-thread-16][INFO]-给用户name2发送注册成功邮件!
INFO []2023-02-15 14:58:49.278[org.im.eventtest.spring.SendEmailListener][30][my-thread-15][INFO]-EventListener 给用户name2发送注册邮件成功!
5、使用建议
-
可以使用spring事件机制来传参、解耦等;
-
对于一些非主要的业务(失败后不影响主业务处理),可以使用异步的事件模式;
-
spring中事件无论是使用接口的方式还是使用注解的方式,都可以(最好团队内部统一使用一种方式)。