DelayQueue 使用和延时功能源码分析
DelayQueue 延迟队列使用和延时功能源码分析,先看DelayQueue 的使用
目录
1、基本使用
2、延时功能源码分析
3、总结
1、基本使用
想要实现延时功能,需要实现 Delayed 接口,重写 getDelay 方法,在 getDelay 方法里返回延时时间
笔者定义一个 Order 类
在构造函数中传入延时的时间
package com.wsjzzcbq.java.queue;
import java.util.concurrent.Delayed;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/**
* Order
*
* @author wsjz
* @date 2023/09/22
*/
public class Order implements Delayed {
/**
* 延时时长
*/
private long time;
/**
* 延时开始时间
*/
private long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
public Order(long time) {
this.time = time;
}
public Order(long time, long start) {
this.time = time;
this.start = start;
}
@Override
public long getDelay(TimeUnit unit) {
return unit.convert((start + time) - System.currentTimeMillis(), TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Delayed o) {
Order order = (Order)o;
return (int) (this.getDelay(TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS) - order.getDelay(TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS));
}
}
延时队列使用
(1)、以现在时间为开始时间,延时获取
package com.wsjzzcbq.java.queue;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.util.concurrent.DelayQueue;
/**
* DelayQueueLearn
*
* @author wsjz
* @date 2023/09/22
*/
public class DelayQueueLearn {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
DelayQueue delayQueue = new DelayQueue<>();
Order order = new Order(5*1000);
System.out.println(LocalDateTime.now());
delayQueue.add(order);
Order order1 = delayQueue.take();
System.out.println(LocalDateTime.now());
System.out.println(order1);
}
}
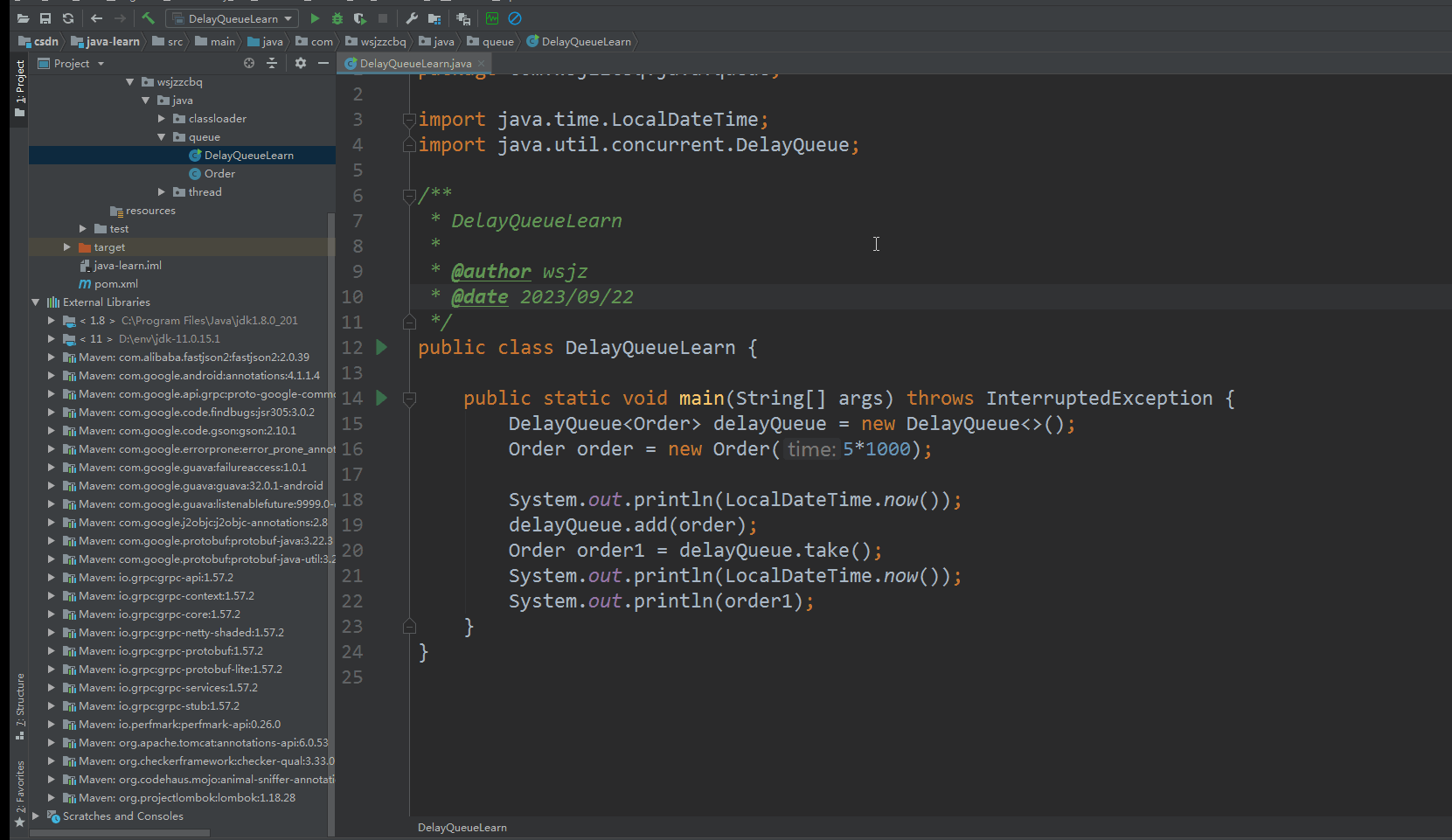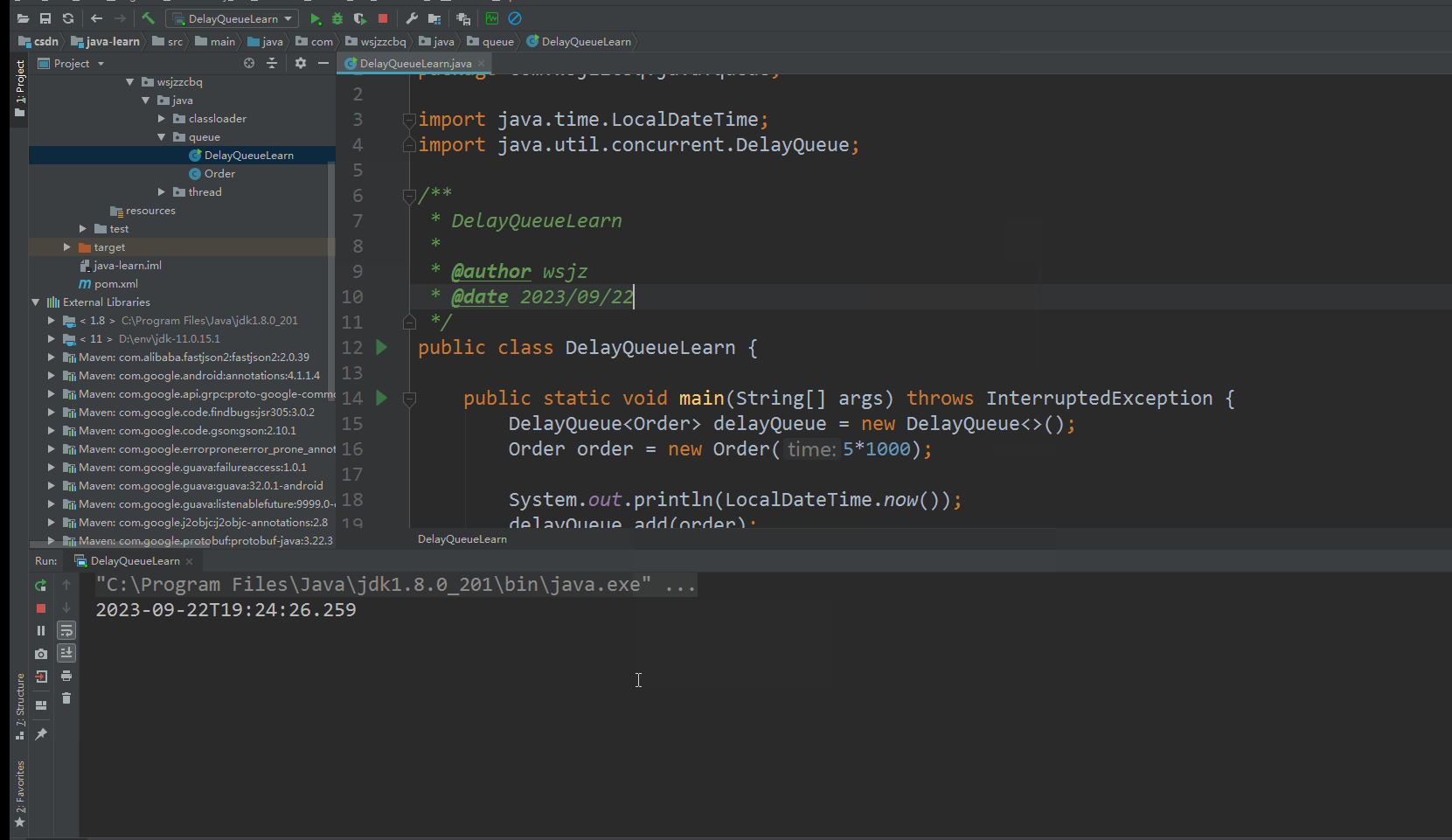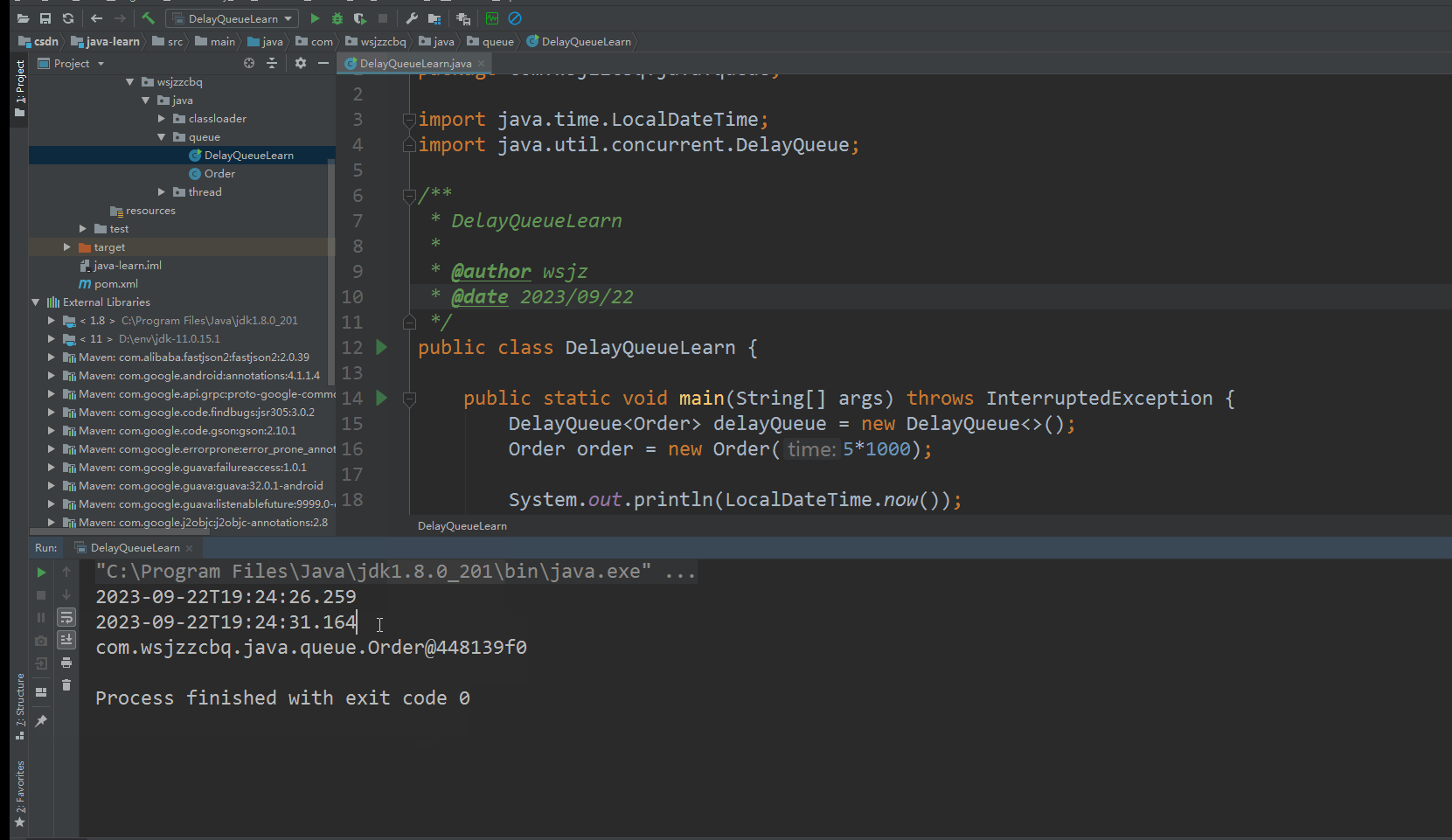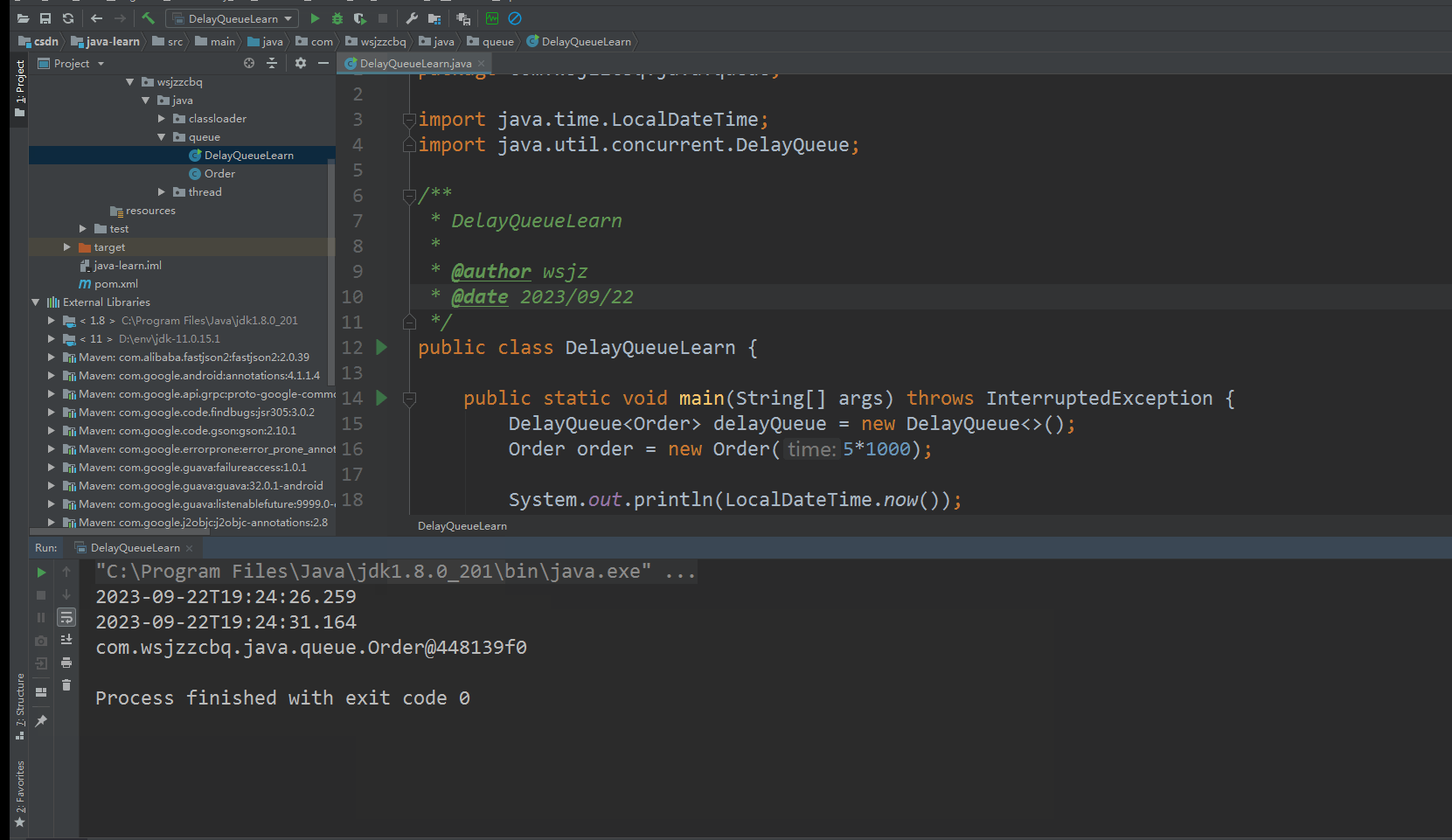
延时 5 秒钟才能获取
测试运行
添加到队列后5秒钟,获取数据
(2)、以指定时间为开始时间,延时获取
以当前时间加 5 秒为开始时间,延时 5 秒钟获取
package com.wsjzzcbq.java.queue;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.ZoneOffset;
import java.util.concurrent.DelayQueue;
/**
* DelayQueueLearn
*
* @author wsjz
* @date 2023/09/22
*/
public class DelayQueueLearn {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
DelayQueue delayQueue = new DelayQueue<>();
//当前时间加5秒为开始时间
LocalDateTime localDateTime = LocalDateTime.now().plusSeconds(5);
long start = localDateTime.toInstant(ZoneOffset.of("+8")).toEpochMilli();
System.out.println(start);
Order order = new Order(5*1000, start);
System.out.println(LocalDateTime.now());
delayQueue.add(order);
Order order1 = delayQueue.take();
System.out.println(LocalDateTime.now());
System.out.println(order1);
}
}
测试运行
一共延时 10 秒钟
2、延时功能源码分析
DelayQueue 是基于 PriorityQueue(优先队列)实现的,PriorityQueue 默认是最小堆结构
我们先看 add 添加方法
/**
* Inserts the specified element into this delay queue.
*
* @param e the element to add
* @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Collection#add})
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified element is null
*/
public boolean add(E e) {
return offer(e);
}offer 方法
/**
* Inserts the specified element into this delay queue.
*
* @param e the element to add
* @return {@code true}
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified element is null
*/
public boolean offer(E e) {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
q.offer(e);
if (q.peek() == e) {
leader = null;
available.signal();
}
return true;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}先获取锁,然后调用 PriorityQueue 的 offer 方法,如果此时 PriorityQueue 的头部元素是新添加的元素,则 leader = null,并唤醒等待线程;否则直接返回 true
因为这里的 PriorityQueue 是最小堆结构,所以它能保证延时时间最小的元素最先出队(添加进去的元素 Order 对象实现了 compareTo 方法)
PriorityQueue 的 offer 方法
/**
* Inserts the specified element into this priority queue.
*
* @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Queue#offer})
* @throws ClassCastException if the specified element cannot be
* compared with elements currently in this priority queue
* according to the priority queue's ordering
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified element is null
*/
public boolean offer(E e) {
if (e == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
modCount++;
int i = size;
if (i >= queue.length)
grow(i + 1);
size = i + 1;
if (i == 0)
queue[0] = e;
else
siftUp(i, e);
return true;
}如果超出容量的话,调用 grow 方法扩容
如果是首次添加的话放在数组索引是0的首位
如果队列中有元素的话,调用 siftUp 方法添加
grow 方法
PriorityQueue 基于数组实现
/**
* Increases the capacity of the array.
*
* @param minCapacity the desired minimum capacity
*/
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
int oldCapacity = queue.length;
// Double size if small; else grow by 50%
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + ((oldCapacity < 64) ?
(oldCapacity + 2) :
(oldCapacity >> 1));
// overflow-conscious code
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
queue = Arrays.copyOf(queue, newCapacity);
}siftUp 方法
/**
* Inserts item x at position k, maintaining heap invariant by
* promoting x up the tree until it is greater than or equal to
* its parent, or is the root.
*
* To simplify and speed up coercions and comparisons. the
* Comparable and Comparator versions are separated into different
* methods that are otherwise identical. (Similarly for siftDown.)
*
* @param k the position to fill
* @param x the item to insert
*/
private void siftUp(int k, E x) {
if (comparator != null)
siftUpUsingComparator(k, x);
else
siftUpComparable(k, x);
}默认 comparator 是 null,调用 siftUpComparable 方法
private void siftUpComparable(int k, E x) {
Comparable key = (Comparable) x;
while (k > 0) {
int parent = (k - 1) >>> 1;
Object e = queue[parent];
if (key.compareTo((E) e) >= 0)
break;
queue[k] = e;
k = parent;
}
queue[k] = key;
}siftUpComparable 方法会进行比较,保证延时时间最小的元素在最上面
然后我们直接看 take 方法
/**
* Retrieves and removes the head of this queue, waiting if necessary
* until an element with an expired delay is available on this queue.
*
* @return the head of this queue
* @throws InterruptedException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public E take() throws InterruptedException {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
for (;;) {
//队列头部元素
E first = q.peek();
if (first == null)
//如果头部元素是null 则让当前线程等待
available.await();
else {
//头部元素不为空,获取延时时间
long delay = first.getDelay(NANOSECONDS);
if (delay <= 0)
//延时时间小于等于0,出队返回
return q.poll();
first = null; // don't retain ref while waiting
if (leader != null)
available.await();
else {
Thread thisThread = Thread.currentThread();
leader = thisThread;
try {
//让线程等待延时时间
available.awaitNanos(delay);
} finally {
if (leader == thisThread)
leader = null;
}
}
}
}
} finally {
if (leader == null && q.peek() != null)
available.signal();
lock.unlock();
}
}相关说明在代码注释中,先看队列头部元素是不是null,如果是说明当前队列为空,让线程等待;如果不为空,看头部元素延时时间,如果延时时间小于等于0,则出队返回,leader 默认是null,因此线程等待延时时间的时长,等待时间到达后,重新开始循环,此时延时时间小于等于0,出队返回,达到延时效果
关于leader 的分析,leader 这里使用了 Leader-Follower 模式的变体
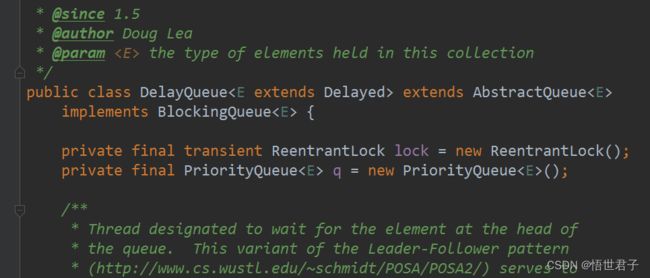
/**
* Thread designated to wait for the element at the head of
* the queue. This variant of the Leader-Follower pattern
* (http://www.cs.wustl.edu/~schmidt/POSA/POSA2/) serves to
* minimize unnecessary timed waiting. When a thread becomes
* the leader, it waits only for the next delay to elapse, but
* other threads await indefinitely. The leader thread must
* signal some other thread before returning from take() or
* poll(...), unless some other thread becomes leader in the
* interim. Whenever the head of the queue is replaced with
* an element with an earlier expiration time, the leader
* field is invalidated by being reset to null, and some
* waiting thread, but not necessarily the current leader, is
* signalled. So waiting threads must be prepared to acquire
* and lose leadership while waiting.
*/
private Thread leader = null;假设没有 leader,现在有2个线程,线程A 和线程B,线程A 和线程B 都会执行 available.awaitNanos(delay) 进行等待,等待时间结束后,线程A 和线程B中只有一个能拿到元素返回,另外一个将重新等待,对于没拿到元素的线程来说一开始等待,之后等待结束被唤醒,最后再次等待,是一种资源浪费,不如一开始就让它一直等待(如果它不是leader的话)
leader 更详细的分析:https://stackoverflow.com/questions/48493830/what-exactly-is-the-leader-used-for-in-delayqueue
3、总结
DelayQueue 内部基于优先队列 PriorityQueue(最小堆结构)实现延时时间小的元素总是先出队。延时功能是通过循环加线程等待的方式实现的,先判断 PriorityQueue 中延时时间最小的元素的延时时间是否小于等于0,如果是则直接出队返回;否则让线程等待延时的时长,等待结束后,开始新一轮循环,这时延时时间肯定是小于等于0的,出队返回,达到延时的效果
至此完