测试专项笔记(一): 通过算法能力接口返回的检测结果完成相关指标的计算(目标检测)
文章目录
- 一、任务描述
- 二、指标分析
-
- 2.1 TP/FP/FN/TN
- 2.2 精准率
- 2.3 召回率
- 三、接口处理
- 四、数据集处理
- 五、开始计算指标
- 五、实用工具
-
- 5.1 移动文件
- 5.2 可视化JSON标签
- 5.3 可视化TXT标签
一、任务描述
通过给定的算法接口,对算法的输出(置信度、检测框、告警、类别等)进行数据处理,结合原标签完成TP、FP、FN、TN、准确率、召回率的指标测试。
二、指标分析
2.1 TP/FP/FN/TN
TP(True Positives,真正例):表示模型正确预测为正类的样本数量,也就是将正例正确分类为正例的数量。
FP(False Positives,假正例):表示模型错误预测为正类的样本数量,也就是将负例错误分类为正例的数量。
FN(False Negatives,假负例):表示模型错误预测为负类的样本数量,也就是将正例错误分类为负例的数量。
TN(True Negatives,真负例):表示模型正确预测为负类的样本数量,也就是将负例正确分类为负例的数量。
2.2 精准率
精准率是指模型在所有被预测为正例的样本中,真正为正例的比例。它的计算公式是:Precision = TP / (TP + FP)。精准率衡量了模型的预测中有多少是真正的正例,是一个关于假正例的指标。
2.3 召回率
召回率是指模型在所有实际正例中,成功预测为正例的比例。它的计算公式是:Recall = TP / (TP + FN)。召回率衡量了模型对于所有正例的识别能力,是一个关于假负例的指标。
三、接口处理
import os, base64, json, time, requests
def get_all_file(path):
result_list = []
for root, dirs, files in os.walk(path):
for file in files:
if os.path.basename(file).__contains__(".jpg"):
result_list.append(os.path.join(root, file))
return result_list
def pic2base64(img_path):
if os.path.exists(img_path):
encoded_base64 = base64.b64encode(open(img_path, 'rb').read()).decode()
return encoded_base64
else:
os.error("图片不存在,请检查图片路径:{}".format(img_path))
def write_content_to_json(content, json_file_path):
with open(json_file_path, 'w+', encoding='utf-8') as f:
f.write(json.dumps(content, indent=4, ensure_ascii=False))
if __name__ == "__main__":
result = {}
fish_pic_path = r"D:\datasets\test_mission\fishing_test_data"
url_fish = "http://***.***.***.*:端口号/能力接口"
pic_list = get_all_file(fish_pic_path)
for pic in pic_list:
image_base64 = pic2base64(pic)
payload = {
"seqid": "test1",
"timestamp": int(time.time()),
"image": image_base64
# "image": rf';base64,{image_base64}\"alt=\"\">'
}
res = requests.post(url_fish, json=payload)
json_res = res.json()
print(json_res)
if 'code' in json_res and json_res['code'] == 6000:
result[os.path.basename(pic)] = json_res['data']
write_content_to_json(result, 'result/fish_result.json')
四、数据集处理
数据集如果是JSON格式,通过下面的代码转换为TXT格式
import os
import numpy as np
import json
from glob import glob
import cv2
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from shutil import copyfile
import argparse
obj_classes = []
# Labelme坐标到YOLO V5坐标的转换
def convert(size, box):
dw = 1. / (size[0])
dh = 1. / (size[1])
x = (box[0] + box[1]) / 2.0 - 1
y = (box[2] + box[3]) / 2.0 - 1
w = box[1] - box[0]
h = box[3] - box[2]
x = x * dw
w = w * dw
y = y * dh
h = h * dh
return (x, y, w, h)
def create(yolo_labels_dir):
if not os.path.exists(yolo_labels_dir):
os.makedirs(yolo_labels_dir)
# 样本转换
def convertToYolo5(fileList, output_dir, labelImg_path, unify_path):
# 创建指定样本的父目录
if not os.path.exists(output_dir):
os.makedirs(output_dir)
# 创建指定样本的images和labels子目录
yolo_images_dir = '{}/images/'.format(output_dir)
yolo_labels_dir = '{}/labels/'.format(output_dir)
create(yolo_images_dir)
create(yolo_labels_dir)
create(unify_path)
# 一个样本图片一个样本图片地转换
for num,json_file_ in enumerate(fileList):
# print('fileList',fileList)
# 1. 生成YOLO样本图片
# 构建json图片文件的全路径名
imagePath = labelImg_path + '/' + json_file_ + ".jpg"
print('name',imagePath, json_file_)
# print('labelme_path', labelme_path)
# 构建Yolo图片文件的全路径名
yolo_image_file_path = yolo_images_dir + "{}.jpg".format(json_file_)
print('yolo_image_file_path', yolo_image_file_path)
# copy样本图片
copyfile(imagePath, yolo_image_file_path)
# 2. 生成YOLO样本标签
# 构建json标签文件的全路径名
labelme_path_ = labelImg_path.split('image')[0]
json_filename = labelme_path_ + 'json'+'\\' + json_file_ + ".json"
# 构建Yolo标签文件的全路径名
yolo_label_file_path = yolo_labels_dir + "{}.txt".format(json_file_)
txt_label_file_path = unify_path + "/{}.txt".format(json_file_)
# 创建新的Yolo标签文件
yolo_label_file = open(yolo_label_file_path, 'w')
txt_label_file = open(txt_label_file_path, 'w')
# 获取当前图片的Json标签文件
json_obj = json.load(open(json_filename, "r", encoding="utf-8"))
# 获取当前图片的长度、宽度信息
height = json_obj['imageHeight']
width = json_obj['imageWidth']
# 依次读取json文件中所有目标的shapes信息
for shape in json_obj["shapes"]:
# 获取shape中的物体分类信息
label = shape["label"]
if label not in ['car_red','car_orange','car_green','car_blue','car_black','car_white','car_purple','car_grey','car_silvery','car grey','car orange','car black','car','car blue','car purple','car white','car silvery','car green','car_yellow','car red']:
if label == 'Fengtain' or label == 'FengTain' or label == 'FengtTian' or label == 'Fengtian':
label = 'FengTian'
if (label not in obj_classes):
obj_classes.append(label)
# 获取shape中的物体坐标信息
if (shape["shape_type"] == 'rectangle'):
points = np.array(shape["points"])
xmin = min(points[:, 0]) if min(points[:, 0]) > 0 else 0
xmax = max(points[:, 0]) if max(points[:, 0]) > 0 else 0
ymin = min(points[:, 1]) if min(points[:, 1]) > 0 else 0
ymax = max(points[:, 1]) if max(points[:, 1]) > 0 else 0
# 对坐标信息进行合法性检查
if xmax <= xmin:
pass
elif ymax <= ymin:
pass
else:
# Labelme坐标转换成YOLO V5坐标
bbox_labelme_float = (float(xmin), float(xmax), float(ymin), float(ymax))
bbox_yolo_normalized = convert((width, height), bbox_labelme_float)
# 把分类标签转换成分类id
class_id = obj_classes.index(label)
# 生成YOLO V5的标签文件
yolo_label_file.write(str(class_id) + " " + " ".join([str(a) for a in bbox_yolo_normalized]) + '\n')
# 保存为统一的位置
txt_label_file.write(str(class_id) + " " + " ".join([str(a) for a in bbox_yolo_normalized]) + '\n')
yolo_label_file.close()
txt_label_file.close()
def check_output_directory(output=""):
# 创建保存输出图片的目录
save_path = output + '/'
is_exists = os.path.exists(save_path)
if is_exists:
print('Warning: path of %s already exist, please remove it firstly by manual' % save_path)
# shutil.rmtree(save_path) # 避免误删除已有的文件
return ""
# print('create output path %s' % save_path)
os.makedirs(save_path)
return save_path
def create_yolo_dataset_cfg(output_dir='', label_class=[]):
# 创建文件
data_cfg_file = open(output_dir + '/data.yaml', 'w')
# 创建文件内容
data_cfg_file.write('train: ../train/images\n')
data_cfg_file.write("val: ../valid/images\n")
data_cfg_file.write("test: ../test/images\n")
data_cfg_file.write("\n")
data_cfg_file.write("# Classes\n")
data_cfg_file.write("nc: %s\n" % len(label_class))
data_cfg_file.write('names: ')
i = 0
for label in label_class:
if (i == 0):
data_cfg_file.write("[")
else:
data_cfg_file.write(", ")
if (i % 10 == 0):
data_cfg_file.write("\n ")
i += 1
data_cfg_file.write("'" + label + "'")
data_cfg_file.write('] # class names')
data_cfg_file.close()
# 关闭文件
def labelImg2yolo(input='', output='', unify_path=""):
outputdir_root = output + '/'
labelImg_path = input
print(labelImg_path)
labelImg_path_imagepath = labelImg_path + '\\' + 'image'
print(labelImg_path_imagepath)
json_path = labelImg_path+'\\'+'json'
print(json_path)
print("*"*100)
# 1.获取input目录中所有的json标签文件全路径名
files = glob(json_path + "/*.json")
print(files)
# 2.获取所有标签文件的短文件名称
files = [i.replace("\\", "/").split("/")[-1].split(".json")[0] for i in files]
print(files)
# 3. 按比例随机切分数据集,获取训练集样本
train_files, valid_test_files = train_test_split(files, test_size=0.2, random_state=55)
# 4. 按比例随机切分数据集,获取验证集和测试集样本
valid_files, test_files = train_test_split(valid_test_files, test_size=0.1, random_state=55)
# 5. 构建YOLO数据集目录
train_path = outputdir_root + '/train'
valid_path = outputdir_root + '/valid'
test_path = outputdir_root + '/test'
# 6. 生成YOLO 训练、验证、测试数据集:图片+标签
convertToYolo5(train_files, train_path, labelImg_path_imagepath, unify_path)
convertToYolo5(valid_files, valid_path, labelImg_path_imagepath, unify_path)
convertToYolo5(test_files, test_path, labelImg_path_imagepath, unify_path)
print("*"*100)
# 7. 创建YOLO数据集配置文件
create_yolo_dataset_cfg(output, obj_classes)
labelme_path = input
print("Classes:", obj_classes)
print('Finished, output path =', outputdir_root)
return 0
def parse_opt():
# define argparse object
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
# input 包含两个文件夹, image和json,分别存放了对应的文件
parser.add_argument('--input', type=str, default=r'F:\python\mission\fish_power_test\data\test',help='The input LabelImg directory')
# output 存放保存的yolov5的训练数据,分为train、val、test三个文件,里面分别存放了对应的images和labels,在train目录下还存放了yolov5加载数据集的yaml文件(见data.yaml)
parser.add_argument('--output', type=str,default=r'F:\python\mission\fish_power_test\data\test/yolo_txt', help='The output YOLO V5 directory')
# 统一存放
parser.add_argument('--unify_path', type=str,default=r'F:\python\mission\fish_power_test\data\test/txt', help='The output txt directory')
# parse arges from command line
opt = parser.parse_args()
print("input =", opt.input)
print("output =", opt.output)
print("unify_path =", opt.unify_path)
# return opt
return opt
def main(opt):
labelImg2yolo(**vars(opt))
if __name__ == '__main__':
opt = parse_opt()
main(opt)
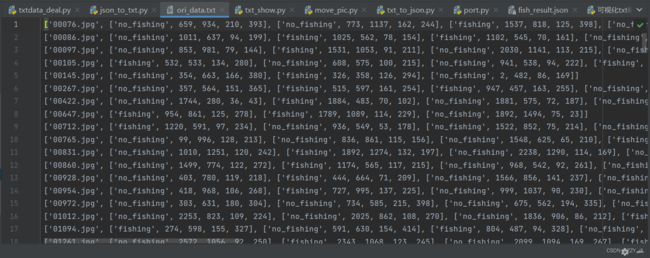
然后通过下面的代码将源标签的txt文档进行总结
# 将txt标签对应的原始的label和boxs写入到txt文档中
import cv2
import os
# 读取txt文件信息
def read_list(txt_path):
pos = []
with open(txt_path, 'r') as file_to_read:
while True:
lines = file_to_read.readline() # 整行读取数据
if not lines:
break
# 将整行数据分割处理,如果分割符是空格,括号里就不用传入参数,如果是逗号, 则传入‘,'字符。
p_tmp = [float(i) for i in lines.split(' ')]
pos.append(p_tmp) # 添加新读取的数据
pass
return pos
def draw_box_in_single_image(image_path, txt_path, image_name):
# 读取图像
image = cv2.imread(image_path)
pos = read_list(txt_path)
reses = []
reses.append(image_name)
for i in range(len(pos)):
label = classes[int(str(int(pos[i][0])))]
print('label is '+label)
# 将中心坐标、宽度和高度转换为 xywh 格式
x_center = int(pos[i][1] * image.shape[1])
y_center = int(pos[i][2] * image.shape[0])
width = int(pos[i][3] * image.shape[1])
height = int(pos[i][4] * image.shape[0])
x_min = x_center - width // 2
y_min = y_center - height // 2
# 绘制矩形框
cv2.rectangle(image, (x_min, y_min), (x_min + width, y_min + height), colores[int(str(int(pos[i][0])))], 2)
cv2.putText(image, label, (x_min, y_min - 2), 0, 1, colores[int(str(int(pos[i][0])))], thickness=2, lineType=cv2.LINE_AA)
res = [label, x_min, y_min, width, height]
reses.append(res)
# cv2.imshow("images", image)
# cv2.waitKey(0)
return reses
if __name__ == '__main__':
f = open('result/ori_data.txt', 'w+')
img_folder = "data/test/image"
img_list = [f for f in os.listdir(img_folder) if f.endswith('.jpg')]
img_list.sort()
label_folder = "data/test/txt"
label_list = [f for f in os.listdir(label_folder) if f.endswith('.txt')]
label_list.sort()
classes = {0: "fishing", 1: "no_fishing"}
colores = [(0, 0, 255), (255, 0, 255)]
for i in range(len(img_list)):
image_path = os.path.join(img_folder, img_list[i])
txt_path = os.path.join(label_folder, label_list[i])
reses = draw_box_in_single_image(image_path, txt_path, img_list[i])
print(reses)
f.write(str(reses))
f.write("\n")
f.close()
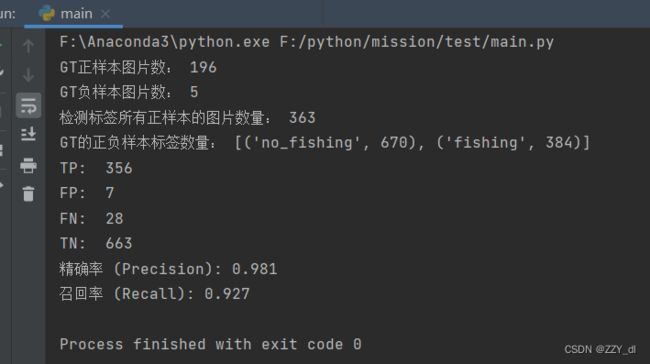
五、开始计算指标
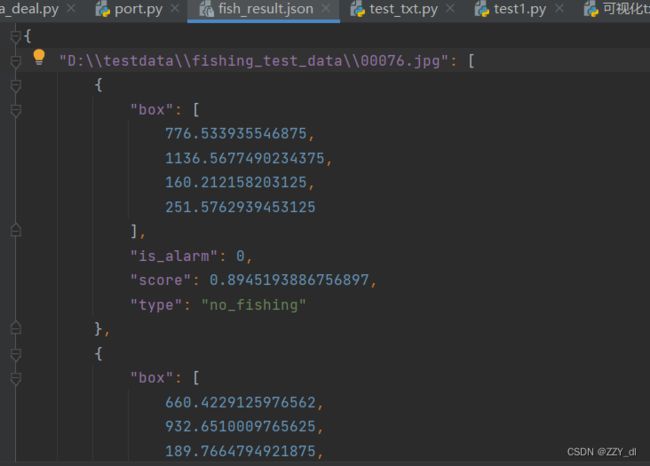
处理之后就可以得到检测后的fish_result.json和ori_data.txt。然后根据这两个文件来计算即可。
五、实用工具
5.1 移动文件
import os
import shutil
# 源文件夹和目标文件夹的路径
source_folder = 'fishing_test_data'
destination_folder = 'test/image'
# 确保目标文件夹存在,如果不存在就创建它
if not os.path.exists(destination_folder):
os.makedirs(destination_folder)
# 遍历源文件夹中的文件
for filename in os.listdir(source_folder):
# 检查文件扩展名是否为图片格式,可以根据需要添加其他格式
if filename.endswith(('.jpg', '.png', '.jpeg')):
# 构建源文件的完整路径和目标文件的完整路径
source_file_path = os.path.join(source_folder, filename)
destination_file_path = os.path.join(destination_folder, filename)
# 移动文件
shutil.move(source_file_path, destination_file_path)
print(f'Moved: {filename} to {destination_folder}')
5.2 可视化JSON标签
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import cv2
import os
import json
import shutil
import numpy as np
from pathlib import Path
from glob import glob
id2cls = {0: 'fishing', 1: "no_fishing"}
cls2id = {'fishing': 0, "no_fishing": 1}
id2color = {"fishing": (0, 255, 0), "no_fishing": (0, 255, 255)}
# 支持中文路径
def cv_imread(filePath):
cv_img = cv2.imdecode(np.fromfile(filePath, dtype=np.uint8), flags=cv2.IMREAD_COLOR)
return cv_img
def get_labelme_info(label_file):
anno = json.load(open(label_file, "r", encoding="utf-8"))
shapes = anno['shapes']
image_path = os.path.basename(anno['imagePath'])
labels = []
for s in shapes:
pts = s['points']
x1, y1 = pts[0]
x2, y2 = pts[1]
color = id2color[s["label"]]
labels.append([color, x1, y1, x2, y2])
return labels, image_path
def vis_labelme(labelme_label_dir, save_dir='res/'):
labelme_label_dir = str(Path(labelme_label_dir)) + '/'
save_dir = str(Path(save_dir)) + '/'
if not os.path.exists(save_dir):
os.makedirs(save_dir)
json_files = glob(labelme_label_dir + '*.json')
for ijf, jf in enumerate(json_files):
print(ijf + 1, '/', len(json_files), jf)
filename = os.path.basename(jf).rsplit('.', 1)[0]
labels, image_path = get_labelme_info(jf)
image = cv_imread(labelme_label_dir + image_path)
for label in labels:
color = label[0]
x1, y1, x2, y2 = label[1:]
x1, y1, x2, y2 = int(x1), int(y1), int(x2), int(y2)
cv2.rectangle(image, (x1, y1), (x2, y2), color, 3)
# 显示图片
# cv2.imshow(filename, image)
# cv2.waitKey(0)
# 支持中文路径,保存图片
cv2.imencode(os.path.splitext(image_path)[-1], image)[1].tofile(save_dir + image_path)
print('Completed!')
if __name__ == '__main__':
root_dir = r'D:\Python\money\data\test'
save_dir = r'D:\Python\money\data\test/t'
vis_labelme(root_dir, save_dir)
5.3 可视化TXT标签
import cv2
import os
# 读取txt文件信息
def read_list(txt_path):
pos = []
with open(txt_path, 'r') as file_to_read:
while True:
lines = file_to_read.readline() # 整行读取数据
if not lines:
break
# 将整行数据分割处理,如果分割符是空格,括号里就不用传入参数,如果是逗号, 则传入‘,'字符。
p_tmp = [float(i) for i in lines.split(' ')]
pos.append(p_tmp) # 添加新读取的数据
# Efield.append(E_tmp)
pass
return pos
# txt转换为box
def convert(size, box):
xmin = (box[1] - box[3] / 2.) * size[1]
xmax = (box[1] + box[3] / 2.) * size[1]
ymin = (box[2] - box[4] / 2.) * size[0]
ymax = (box[2] + box[4] / 2.) * size[0]
box = (int(xmin), int(ymin), int(xmax), int(ymax))
return box
def draw_box_in_single_image(image_path, txt_path):
# 读取图像
image = cv2.imread(image_path)
pos = read_list(txt_path)
for i in range(len(pos)):
label = classes[int(str(int(pos[i][0])))]
print('label is '+label)
box = convert(image.shape, pos[i])
image = cv2.rectangle(image,(box[0], box[1]),(box[2],box[3]),colores[int(str(int(pos[i][0])))],2)
cv2.putText(image, label,(box[0],box[1]-2), 0, 1, colores[int(str(int(pos[i][0])))], thickness=2, lineType=cv2.LINE_AA)
cv2.imshow("images", image)
cv2.waitKey(0)
if __name__ == '__main__':
img_folder = r"F:\python\mission\fish_power_test\data\test\yolo_txt\train\images"
img_list = os.listdir(img_folder)
img_list.sort()
label_folder = r"F:\python\mission\fish_power_test\data\test\yolo_txt\train/labels"
label_list = os.listdir(label_folder)
label_list.sort()
classes = {0: "fishing", 1: "no_fishing"}
colores = [(0,0,255),(255,0,255)]
for i in range(len(img_list)):
image_path = img_folder + "\\" + img_list[i]
txt_path = label_folder + "\\" + label_list[i]
draw_box_in_single_image(image_path, txt_path)