1.基本概念 进入Java的世界
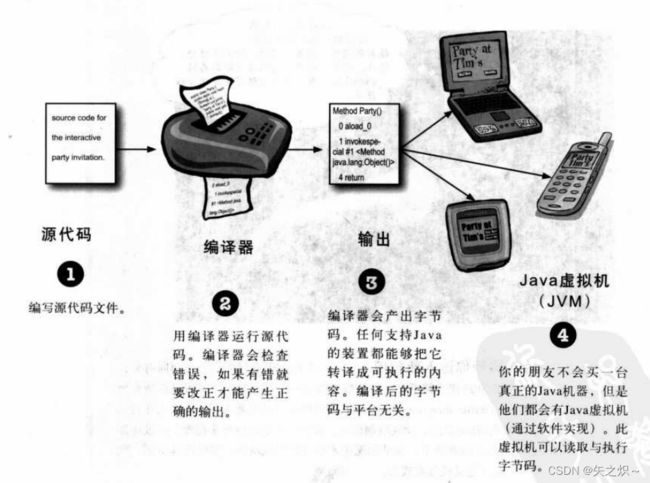
1.1 Java的工作方式
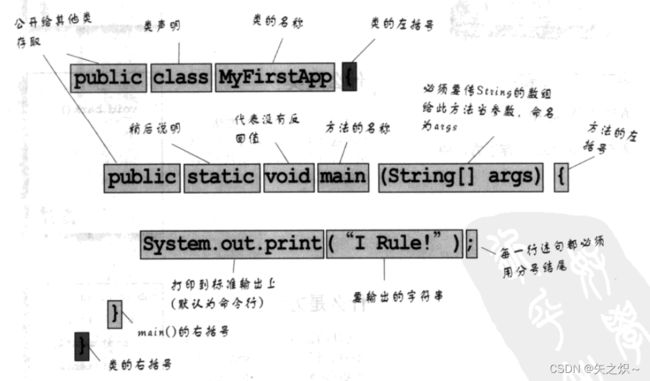
1.2 Java的程序结构
类存于源文件里面,方法存于类中,语句(statement)存于方法中
源文件(扩展名为.java)带有类的定义。类用来表示程序的一个组件,小程序或许只会有一个类。类的内容必须包在花括号里面。
类中带有一个或多个方法。在Dog这个类中,bark方法带有如何“汪汪“的指令。方法必须在类的内部声明。
在方法的花括号中编写方法 应该执行的指令。方法代码是由一组语句所组成,可以把方法想象成是一个函数或过程。
1.3 剖析类
当Java虚拟机启动执行时,它会寻找你在命令列所指定的类。然后锁定像下面这样一个特定的方法:
public static void mian (String[] args) {
//程序代码写在这里
}接着Java虚拟机就会执行main方法在花括号间的函数所有指令。每个Java程序最少都会有一个类以及一个main()。每个应用程序只有一个main()函数。
1.4 main()方法
在Java中的所有东西都会属于某个类。你会建立源文件(扩展名为.java),然后将它编译成新的类文件(扩展名为.class)。真正被执行的是类。
要执行程序就代表要命令Java虚拟机(JVM)去“加载Hello这个类,开始执行它的main(),然后一直运行到main的所有程序代码结束为止”。
main()就是程序的起点(不论程序有多大,有多少个类)。
public class MyFirstApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("I Rule!");
System.out.println("The World");
}
}
1.做某件事
声明、设定、调用方法等普通语句。
2.反复做某件事
for与while的循环(loop)
3.在适当条件下做某件事
if/else的条件分支测试
//为注释
其余与C语言语法基本一致
1.5 循环
同C语言
条件测试的结果是boolean值——boolean测试,true或false
1.6 条件分支
同C语言
System.out.print/println 后者会换行
1.7 设计程序
public class BeerSong {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int beerNum = 99;
String word = "bottles";
while (beerNum > 0) {
if (beerNum == 1) {
word = "bottle"; //单数的瓶子
}
System.out.println(beerNum + " " + word + " of beer on the wall");
System.out.println(beerNum + " " + word + " of beer.");
System.out.println("Take one down.");
System.out.println("Pass it around.");
beerNum = beerNum - 1;
if (beerNum > 0) {
System.out.println(beerNum + " " + word + " of beer on the wall");
} else {
System.out.println("No more bottles of beer on the wall");
}//else结束
}//while循环结束
}//main方法结束
}//class结束1.8 术语制造机
public class PhraseOMatic {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//你可以随意的加上其他术语
String[] wordListOne = {
"24/7","multi-Tier","30,000 foot","B-to-B","win-win","front-end","web-based","pervasive","smart","six-sigma","critical-path","dynamic"
};
String[] wordListTwo = {
"empowered","sticky","value-added","oriented","centric","distributed","clustered","branded","outside-the-box","positioned","networked","focused","leveraged","aligned","targeted","shared","cooperative","accelerated"
};
String[] wordListThree = {
"process","tipping-point","solution","architecture","core competency","strategy","mindshare","portal","space","vision","paradigm","mission"
};
//计算每一组有多少个名词术语
int oneLength = wordListOne.length;
int twoLength = wordListTwo.length;
int threeLength = wordListThree.length;
//产生随机数字
int rand1 = (int) (Math.random() * oneLength);
int rand2 = (int) (Math.random() * twoLength);
int rand3 = (int) (Math.random() * threeLength);
//组合出专家术语
String phrase = wordListOne[rand1] + " " + wordListTwo[rand2] + " " + wordListThree[rand3];
//输出
System.out.println("What we need is a " + phrase);
}
}