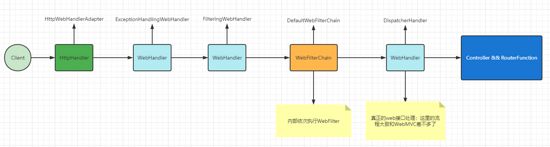
一文带你彻底理解Spring WebFlux的工作原理
1 、请求入口HttpHandler
自动配置
public class HttpHandlerAutoConfiguration {
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
public static class AnnotationConfig {
private final ApplicationContext applicationContext;
public AnnotationConfig(ApplicationContext applicationContext) {
this.applicationContext = applicationContext;
}
@Bean
public HttpHandler httpHandler(ObjectProvider propsProvider) {
HttpHandler httpHandler = WebHttpHandlerBuilder.applicationContext(this.applicationContext).build();
WebFluxProperties properties = propsProvider.getIfAvailable();
if (properties != null && StringUtils.hasText(properties.getBasePath())) {
Map handlersMap = Collections.singletonMap(properties.getBasePath(), httpHandler);
return new ContextPathCompositeHandler(handlersMap);
}
return httpHandler;
}
}
}
这个自动配置与DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration相对应;HttpHandler是WebFlux环境下的核心处理器类。
其中这里的WebHttpHandlerBuilder.applicationContext(this.applicationContext).build()代码就是用来构建HttpWebHandlerAdapter对象。
核心处理类 HttpWebHandlerAdapter。
public class HttpWebHandlerAdapter extends WebHandlerDecorator implements HttpHandler {
// 请求入口
public Mono handle(ServerHttpRequest request, ServerHttpResponse response) {
if (this.forwardedHeaderTransformer != null) {
try {
request = this.forwardedHeaderTransformer.apply(request);
} catch (Throwable ex) {
response.setStatusCode(HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST);
return response.setComplete();
}
}
ServerWebExchange exchange = createExchange(request, response);
// 获取委托类,最终是由委托的WebHandler进行处理
// 1.1
return getDelegate().handle(exchange)
.doOnSuccess(aVoid -> logResponse(exchange))
.onErrorResume(ex -> handleUnresolvedError(exchange, ex))
.then(Mono.defer(response::setComplete));
}
}
一个请求是如何通过上面的HttpWebHandlerAdapter执行调用处理的?
容器在启动执行refresh核心方法:
public abstract class AbstractApplicationContext {
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
// ...
// 执行子类方法
onRefresh();
// ...
}
}
public class ReactiveWebServerApplicationContext {
protected void onRefresh() {
// ...
createWebServer();
// ...
}
private void createWebServer() {
WebServerManager serverManager = this.serverManager;
if (serverManager == null) {
// ...
// this::getHttpHandler方法获取上面的HttpHandler对象
this.serverManager = new WebServerManager(this, webServerFactory, this::getHttpHandler, lazyInit);
// ...
}
initPropertySources();
}
protected HttpHandler getHttpHandler() {
String[] beanNames = getBeanFactory().getBeanNamesForType(HttpHandler.class);
// ...
return getBeanFactory().getBean(beanNames[0], HttpHandler.class);
}
}
(1) 请求处理委托类WebHandler
getDelegate方法返回的调用的是父类WebHandlerDecorator方法:
public class WebHandlerDecorator implements WebHandler {
private final WebHandler delegate;
public WebHandlerDecorator(WebHandler delegate) {\
this.delegate = delegate;
}
public WebHandler getDelegate() {
return this.delegate;
}
}
这里的delegate是谁?
(2) HttpWebHandlerAdapter创建
自动配置
public class HttpHandlerAutoConfiguration {
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
public static class AnnotationConfig {
private final ApplicationContext applicationContext;
public AnnotationConfig(ApplicationContext applicationContext) {
this.applicationContext = applicationContext;
}
@Bean
public HttpHandler httpHandler(ObjectProvider propsProvider) {
// 这里通过WebHttpHandlerBuilder对象创建HttpWebHandlerAdapter对象
HttpHandler httpHandler = WebHttpHandlerBuilder.applicationContext(this.applicationContext).build();
// ...
return httpHandler;
}
}
}
public final class WebHttpHandlerBuilder {
private final List filters = new ArrayList<>();
// 获取WebHttpHandlerBuilder对象
public static WebHttpHandlerBuilder applicationContext(ApplicationContext context) {
// 构造WebHttpHandlerBuilder对象,在参数上会获取
// 容器中的webHandler名称的WebHandler对象,
// 而这里获取的就是DispatcherHandler对象
// 这个对象是如何创建的?
// 1.2.1
WebHttpHandlerBuilder builder = new WebHttpHandlerBuilder(
context.getBean(WEB_HANDLER_BEAN_NAME, WebHandler.class), context);
// 获取容器中所有的WebFilter类型的Bean对象
List webFilters = context
.getBeanProvider(WebFilter.class)
.orderedStream()
.collect(Collectors.toList());
// 添加到了filters集合中
builder.filters(filters -> filters.addAll(webFilters));
// 获取容器中所有的WebExceptionHandler类型的异常处理句柄
List exceptionHandlers = context
.getBeanProvider(WebExceptionHandler.class)
.orderedStream()
.collect(Collectors.toList());
builder.exceptionHandlers(handlers -> handlers.addAll(exceptionHandlers));
context.getBeanProvider(HttpHandlerDecoratorFactory.class)
.orderedStream()
.forEach(builder::httpHandlerDecorator);
try {
builder.sessionManager(
context.getBean(WEB_SESSION_MANAGER_BEAN_NAME, WebSessionManager.class));
}catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
}
try {
builder.codecConfigurer(
context.getBean(SERVER_CODEC_CONFIGURER_BEAN_NAME, ServerCodecConfigurer.class));
}catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
}
try {
builder.localeContextResolver(
context.getBean(LOCALE_CONTEXT_RESOLVER_BEAN_NAME, LocaleContextResolver.class));
} catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
}
try {
builder.forwardedHeaderTransformer(
context.getBean(FORWARDED_HEADER_TRANSFORMER_BEAN_NAME, ForwardedHeaderTransformer.class));
} catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
}
return builder;
}
public HttpHandler build() {
// 注意这里将webHandler = DispatcherHandler保存到了
// FilteringWebHandler对象中
WebHandler decorated = new FilteringWebHandler(this.webHandler, this.filters);
// 查看下面的类信息
decorated = new ExceptionHandlingWebHandler(decorated, this.exceptionHandlers);
HttpWebHandlerAdapter adapted = new HttpWebHandlerAdapter(decorated);
// ...
return (this.httpHandlerDecorator != null ? this.httpHandlerDecorator.apply(adapted) : adapted);
}
}
// --------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// 上面获取了WebHttpHandlerBuilder对象后调用build开始创建
// HttpWebHandlerAdapter对象
public class HttpWebHandlerAdapter extends WebHandlerDecorator implements HttpHandler {
public HttpWebHandlerAdapter(WebHandler delegate) {
super(delegate);
}
}
public class WebHandlerDecorator implements WebHandler {
// 通过上面的源码,知道了这个
// delegate = ExceptionHandlingWebHandler
private final WebHandler delegate;
public WebHandlerDecorator(WebHandler delegate) {
this.delegate = delegate;
}
public WebHandler getDelegate() {
return this.delegate;
}
}
// -------------------------------------------------------------------------------
public class FilteringWebHandler extends WebHandlerDecorator {
private final DefaultWebFilterChain chain;
// 这里传递过来的handler = DispatcherHandler
public FilteringWebHandler(WebHandler handler, List filters) {
super(handler);
// 创建了过滤器链
this.chain = new DefaultWebFilterChain(handler, filters);
}
}
public class ExceptionHandlingWebHandler extends WebHandlerDecorator {
private final List exceptionHandlers;
public ExceptionHandlingWebHandler(WebHandler delegate, List handlers) {
// 这里的delegate = FilteringWebHandler
super(delegate);
List handlersToUse = new ArrayList<>();
handlersToUse.add(new CheckpointInsertingHandler());
handlersToUse.addAll(handlers);
this.exceptionHandlers = Collections.unmodifiableList(handlersToUse);
}
}
通过上面的源码应该非常清楚HttpWebHandlerAdapter对象创建的过程及该对象都会写什么东西。
到此你应该清楚了,上面一开始说的getDelegate()方法返回的就是ExceptionHandlingWebHandler对象。
DispatcherHandler创建
public class WebFluxAutoConfiguration {
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@EnableConfigurationProperties(WebProperties.class)
public static class EnableWebFluxConfiguration extends DelegatingWebFluxConfiguration {
}
}
在这里的DelegatingWebFluxConfiguration的父类。
WebFluxConfigurationSupport中创建了webHandler名称的DispatcherHandler对象。
public class WebFluxConfigurationSupport implements ApplicationContextAware {
@Bean
public DispatcherHandler webHandler() {
return new DispatcherHandler();
}
}
到此HttpWebHandlerAdapter#handle中执行的getDelegate方法返回的是ExceptionHandlingWebHandler对象。
2、 委托类WebHandler执行
接下来就是执行ExceptionHandlingWebHandler的handle方法了。
public class ExceptionHandlingWebHandler extends WebHandlerDecorator {
private final List exceptionHandlers;
public Mono handle(ServerWebExchange exchange) {
Mono completion;
try {
completion = super.handle(exchange);
} catch (Throwable ex) {
completion = Mono.error(ex);
}
for (WebExceptionHandler handler : this.exceptionHandlers) {
completion = completion.onErrorResume(ex -> handler.handle(exchange, ex));
}
return completion;
}
}
public class WebHandlerDecorator implements WebHandler {
// 通过在上面的build知道该deletgate = FilteringWebHandler
private final WebHandler delegate;
public Mono handle(ServerWebExchange exchange) {
return this.delegate.handle(exchange);
}
}
public class FilteringWebHandler extends WebHandlerDecorator {
private final DefaultWebFilterChain chain;
public FilteringWebHandler(WebHandler handler, List filters) {
// 这个handler = DispatcherHandler对象
super(handler);
this.chain = new DefaultWebFilterChain(handler, filters);
}
@Override
public Mono handle(ServerWebExchange exchange) {
// 执行所有的过滤器
return this.chain.filter(exchange);
}
}
public class DefaultWebFilterChain implements WebFilterChain {
private final List allFilters;
@Nullable
private final WebFilter currentFilter;
// handler = DispatcherHandler
private final WebHandler handler;
public DefaultWebFilterChain(WebHandler handler, List filters) {
Assert.notNull(handler, "WebHandler is required");
this.allFilters = Collections.unmodifiableList(filters);
this.handler = handler;
// 这里就是为了让所有的WebFilter串联起来,按照顺序执行
DefaultWebFilterChain chain = initChain(filters, handler);
this.currentFilter = chain.currentFilter;
this.chain = chain.chain;
}
private static DefaultWebFilterChain initChain(List filters, WebHandler handler) {
// 这里就相当于是最后执行的一个Chain了,因为第三个参数(currentFilter) = null
// 在羡慕的filter方法中执行的时候判断了currentFilter如果为空就执行DispatcherHandler#handle方法
// 这里大致的流程如下:
DefaultWebFilterChain chain = new DefaultWebFilterChain(filters, handler, null, null);
ListIterator iterator = filters.listIterator(filters.size());
while (iterator.hasPrevious()) {
chain = new DefaultWebFilterChain(filters, handler, iterator.previous(), chain);
}
return chain;
}
public Mono filter(ServerWebExchange exchange) {
return Mono.defer(() ->
this.currentFilter != null && this.chain != null ?
invokeFilter(this.currentFilter, this.chain, exchange) :
// 当过滤器都执行完了以后会执行DispatcherHandler调用
this.handler.handle(exchange));
}
private Mono invokeFilter(WebFilter current, DefaultWebFilterChain chain, ServerWebExchange exchange) {
String currentName = current.getClass().getName();
return current.filter(exchange, chain).checkpoint(currentName + " [DefaultWebFilterChain]");
}
}
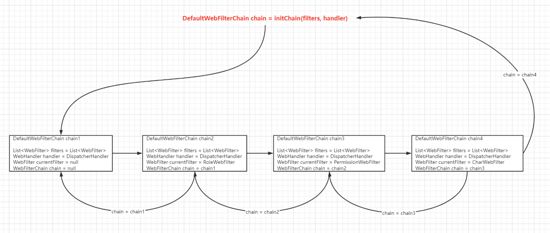
Webfilter: 1, 2, 3 三个WebFilter。
初始的chain: DefaultWebFilterChain chain = new DefaultWebFilterChain(filters, handler, null, null);
3: chain = DefaultWebFilterChain(filters,handler, 3,chain) 。
2: chain = DefaultWebFilterChain(filters,handler, 2,chain<3>) 。
1: chain = DefaultWebFilterChain(filters,handler, 1,chain<2>) 。
这样3个过滤器就串联在一起了。
WebFilter#filter实现: public Mono filter(ServerWebExchange exchange, WebFilterChain chain) { System.out.println("DemoFilter...") ; return chain.filter(exchange) ; } // 过滤器链执行过程: 1: chain.filter(exchange) ; => currentFilter.filter(exchange, chain) ;(执行的是当前WebFilter) 执行chain#filter,根据上面此时的chain = chain<2> 2: 依次类推。
3、 DispatcherHandler执行
public class DispatcherHandler implements WebHandler {
public Mono handle(ServerWebExchange exchange) {
if (this.handlerMappings == null) {
return createNotFoundError();
}
if (CorsUtils.isPreFlightRequest(exchange.getRequest())) {
return handlePreFlight(exchange);
}
return Flux.fromIterable(this.handlerMappings)
.concatMap(mapping -> mapping.getHandler(exchange))
.next()
.switchIfEmpty(createNotFoundError())
.flatMap(handler -> invokeHandler(exchange, handler))
.flatMap(result -> handleResult(exchange, result));
}
}
其实接下来的过程就和Spring WebMVC的执行大致相同。
- 查找HandlerMapping。
- 查找HandlerAdapter。
- 查找HandlerResultHandler。
通过HandlerAdapter调用处理程序的返回值被包装为HandlerResult,并传递给声称支持它的第一个HandlerResultHandler。下表显示了可用的HandlerResultHandler实现,所有这些实现都在WebFlux配置中声明:
4、 流程处理
+WebFlux