工作流 Flowable 的使用
一、BPMN 业务流程建模与标注
通过 Status(状态) 字段维护流程状态,流程负责的审批人可能也是 Hard Code(硬编码)会出现以下问题:
1.流程健壮性差,但凡出现人员变动,或者组织结构调整,就需要修改代码,维护成本高。
2.流程无法复用,当组织出现新的工作流程,又要重新写一套代码,开发成本高。
3.流程和业务代码耦合,你中有我,我中有你(不符合单一职责和解耦的设计原则)。
1.1、BPMN 2.0 的核心:
流对象、数据、连接对象、泳道
1.1.1、流对象(Flow Objects):
事件、活动、网关
事件(Events):指的是在业务流程的运行过程中发生的事情,分为:
开始:表示一个流程的开始
中间:发生的开始和结束事件之间,影响处理的流程
结束:表示该过程结束
活动(Activities):
包括任务和子流程两类,
子流程在图形的下方中间外加一个小加号(+)来区分。
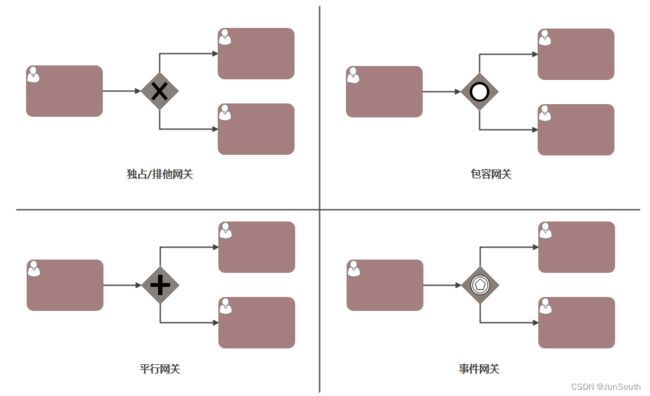
网关(Gateways):用于表示流程的分支与合并。
排他网关:只有一条路径会被选择
并行网关:所有路径会被同时选择
包容网关:可以同时执行多条线路,也可以在网关上设置条件。
事件网关:专门为中间捕获事件设置的,允许设置多个输出流指向多个不同的中间捕获事件。当流程执行到事件网关后,流程处于等待状态,需要等待抛出事件才能将等待状态转换为活动状态。
1.1.2、四种数据(Data)元素
数据对象(Data Objects)
数据输入(Data Inputs)
数据输出(Data Outputs)
数据存储(Data Stores)
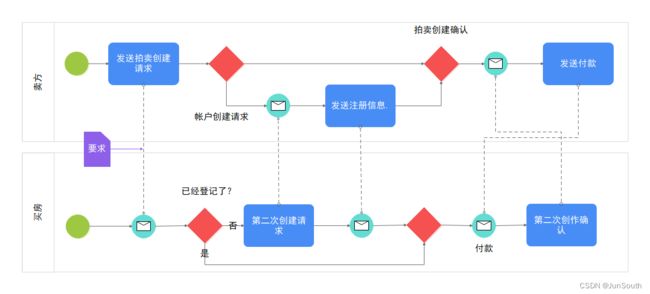
1.1.3、连接对象(Connecting Objects)
顺序流:用一个带实心箭头的实心线表示,用于指定活动执行的顺序。
信息流:用一条带箭头的虚线表示,用于描述两个独立的业务参与者(业务实体/业务角色)之间发送和接受的消息流动。
关联:用一根带有线箭头的点线表示,用于将相关的数据、文本和其他人工信息与流对象联系起来。用于展示活动的输入和输出。
1.1.4、泳道(Swimlanes)
对主要的建模元素进行分组,将活动划分到不同的可视化类别中来描述由不同的参与者的责任与职责。
1.2、Flowable常用配置项
# Core (Process) FlowableProperties
# 核心(流程)
flowable.check-process-definitions=true # 是否需要自动部署流程定义。
flowable.custom-mybatis-mappers= # 需要添加至引擎的自定义Mybatis映射的FQN。
flowable.custom-mybatis-x-m-l-mappers= # 需要添加至引擎的自定义Mybatis XML映射的路径。
flowable.database-schema= # 如果数据库返回的元数据不正确,可以在这里设置schema用于检测/生成表。
flowable.database-schema-update=true # 数据库schema更新策略。
flowable.db-history-used=true # 是否要使用db历史。
flowable.deployment-name=SpringBootAutoDeployment # 自动部署的名称。
flowable.history-level= # 要使用的历史级别。
flowable.process-definition-location-prefix=classpath*:/processes/ # 自动部署时查找流程的目录。
flowable.process-definition-location-suffixes=**.bpmn20.xml,**.bpmn # 'processDefinitionLocationPrefix'路径下需要部署的文件的后缀(扩展名)。
# Process FlowableProcessProperties
# 流程
flowable.process.definition-cache-limit=-1 # 流程定义缓存中保存流程定义的最大数量。默认值为-1(缓存所有流程定义)。
flowable.process.enable-safe-xml=true # 在解析BPMN XML文件时进行额外检查。参见 https://www.flowable.org/docs/userguide/index.html#advanced.safe.bpmn.xml 。不幸的是,部分平台(JDK 6,JBoss)上无法使用这个功能,因此如果你所用的平台在XML解析时不支持StaxSource,需要禁用这个功能。
flowable.process.servlet.load-on-startup=-1 # 启动时加载Process servlet。
flowable.process.servlet.name=Flowable BPMN Rest API # Process servlet的名字。
flowable.process.servlet.path=/process-api # Process servelet的context path。
# Process Async Executor
# 流程异步执行器
flowable.process.async-executor-activate=true # 是否启用异步执行器。
flowable.process.async.executor.async-job-lock-time-in-millis=300000 # 异步作业在被异步执行器取走后的锁定时间(以毫秒计)。在这段时间内,其它异步执行器不会尝试获取及锁定这个任务。
flowable.process.async.executor.default-async-job-acquire-wait-time-in-millis=10000 # 异步作业获取线程在进行下次获取查询前的等待时间(以毫秒计)。只在当次没有取到新的异步作业,或者只取到很少的异步作业时生效。默认值 = 10秒。
flowable.process.async.executor.default-queue-size-full-wait-time-in-millis=0 # 异步作业(包括定时器作业与异步执行)获取线程在队列满时,等待执行下次查询的等待时间(以毫秒计)。默认值为0(以向后兼容)
flowable.process.async.executor.default-timer-job-acquire-wait-time-in-millis=10000 # 定时器作业获取线程在进行下次获取查询前的等待时间(以毫秒计)。只在当次没有取到新的定时器作业,或者只取到很少的定时器作业时生效。默认值 = 10秒。
flowable.process.async.executor.max-async-jobs-due-per-acquisition=1 # (译者补)单次查询的异步作业数量。默认值为1,以降低乐观锁异常的可能性。除非你知道自己在做什么,否则请不要修改这个值。
flowable.process.async.executor.retry-wait-time-in-millis=500 # ???(译者补不了了)
flowable.process.async.executor.timer-lock-time-in-millis=300000 # 定时器作业在被异步执行器取走后的锁定时间(以毫秒计)。在这段时间内,其它异步执行器不会尝试获取及锁定这个任务。
# CMMN FlowableCmmnProperties
flowable.cmmn.deploy-resources=true # 是否部署资源。默认值为'true'。
flowable.cmmn.deployment-name=SpringBootAutoDeployment # CMMN资源部署的名字。
flowable.cmmn.enable-safe-xml=true # 在解析CMMN XML文件时进行额外检查。参见 https://www.flowable.org/docs/userguide/index.html#advanced.safe.bpmn.xml 。不幸的是,部分平台(JDK 6,JBoss)上无法使用这个功能,因此如果你所用的平台在XML解析时不支持StaxSource,需要禁用这个功能。
flowable.cmmn.enabled=true # 是否启用CMMN引擎。
flowable.cmmn.resource-location=classpath*:/cases/ # CMMN资源的路径。
flowable.cmmn.resource-suffixes=**.cmmn,**.cmmn11,**.cmmn.xml,**.cmmn11.xml # 需要扫描的资源后缀名。
flowable.cmmn.servlet.load-on-startup=-1 # 启动时加载CMMN servlet。
flowable.cmmn.servlet.name=Flowable CMMN Rest API # CMMN servlet的名字。
flowable.cmmn.servlet.path=/cmmn-api # CMMN servlet的context path。
# CMMN Async Executor
# CMMN异步执行器
flowable.cmmn.async-executor-activate=true # 是否启用异步执行器。
flowable.cmmn.async.executor.async-job-lock-time-in-millis=300000 # 异步作业在被异步执行器取走后的锁定时间(以毫秒计)。在这段时间内,其它异步执行器不会尝试获取及锁定这个任务。
flowable.cmmn.async.executor.default-async-job-acquire-wait-time-in-millis=10000 # 异步作业获取线程在进行下次获取查询前的等待时间(以毫秒计)。只在当次没有取到新的异步作业,或者只取到很少的异步作业时生效。默认值 = 10秒。
flowable.cmmn.async.executor.default-queue-size-full-wait-time-in-millis=0 # 异步作业(包括定时器作业与异步执行)获取线程在队列满时,等待执行下次查询的等待时间(以毫秒计)。默认值为0(以向后兼容)
flowable.cmmn.async.executor.default-timer-job-acquire-wait-time-in-millis=1000 # 定时器作业获取线程在进行下次获取查询前的等待时间(以毫秒计)。只在当次没有取到新的定时器作业,或者只取到很少的定时器作业时生效。默认值 = 10秒。
flowable.cmmn.async.executor.max-async-jobs-due-per-acquisition=1 # (译者补)单次查询的异步作业数量。默认值为1,以降低乐观锁异常的可能性。除非你知道自己在做什么,否则请不要修改这个值。
flowable.cmmn.async.executor.retry-wait-time-in-millis=500 #(译者补不了了)
flowable.cmmn.async.executor.timer-lock-time-in-millis=300000 # 定时器作业在被异步执行器取走后的锁定时间(以毫秒计)。在这段时间内,其它异步执行器不会尝试获取及锁定这个任务。
# Content FlowableContentProperties
flowable.content.enabled=true # 是否启动Content引擎。
flowable.content.servlet.load-on-startup=-1 # 启动时加载Content servlet。
flowable.content.servlet.name=Flowable Content Rest API # Content servlet的名字。
flowable.content.servlet.path=/content-api # Content servlet的context path。
flowable.content.storage.create-root=true # 如果根路径不存在,是否需要创建?
flowable.content.storage.root-folder= # 存储content文件(如上传的任务附件,或表单文件)的根路径。
# DMN FlowableDmnProperties
flowable.dmn.deploy-resources=true # 是否部署资源。默认为'true'。
flowable.dmn.deployment-name=SpringBootAutoDeployment # DMN资源部署的名字。
flowable.dmn.enable-safe-xml=true # 在解析DMN XML文件时进行额外检查。参见 https://www.flowable.org/docs/userguide/index.html#advanced.safe.bpmn.xml 。不幸的是,部分平台(JDK 6,JBoss)上无法使用这个功能,因此如果你所用的平台在XML解析时不支持StaxSource,需要禁用这个功能。
flowable.dmn.enabled=true # 是否启用DMN引擎。
flowable.dmn.history-enabled=true # 是否启用DMN引擎的历史。
flowable.dmn.resource-location=classpath*:/dmn/ # DMN资源的路径。
flowable.dmn.resource-suffixes=**.dmn,**.dmn.xml,**.dmn11,**.dmn11.xml # 需要扫描的资源后缀名。
flowable.dmn.servlet.load-on-startup=-1 # 启动时加载DMN servlet。
flowable.dmn.servlet.name=Flowable DMN Rest API # DMN servlet的名字。
flowable.dmn.servlet.path=/dmn-api # DMN servlet的context path。
flowable.dmn.strict-mode=true # 如果希望避免抉择表命中策略检查导致失败,可以将本参数设置为false。如果检查发现了错误,会直接返回错误前一刻的中间结果。
# Form FlowableFormProperties
flowable.form.deploy-resources=true # 是否部署资源。默认为'true'。
flowable.form.deployment-name=SpringBootAutoDeployment # Form资源部署的名字。
flowable.form.enabled=true # 是否启用Form引擎。
flowable.form.resource-location=classpath*:/forms/ # Form资源的路径。
flowable.form.resource-suffixes=**.form # 需要扫描的资源后缀名。
flowable.form.servlet.load-on-startup=-1 # 启动时加载Form servlet。
flowable.form.servlet.name=Flowable Form Rest API # Form servlet的名字。
flowable.form.servlet.path=/form-api # Form servlet的context path。
# IDM FlowableIdmProperties
flowable.idm.enabled=true # 是否启用IDM引擎。
flowable.idm.password-encoder= # 使用的密码编码类型。
flowable.idm.servlet.load-on-startup=-1 # 启动时加载IDM servlet。
flowable.idm.servlet.name=Flowable IDM Rest API # IDM servlet的名字。
flowable.idm.servlet.path=/idm-api # IDM servlet的context path。
# IDM Ldap FlowableLdapProperties
flowable.idm.ldap.attribute.email= # 用户email的属性名。
flowable.idm.ldap.attribute.first-name= # 用户名字的属性名。
flowable.idm.ldap.attribute.group-id= # 用户组ID的属性名。
flowable.idm.ldap.attribute.group-name= # 用户组名的属性名。
flowable.idm.ldap.attribute.group-type= # 用户组类型的属性名。
flowable.idm.ldap.attribute.last-name= # 用户姓的属性名。
flowable.idm.ldap.attribute.user-id= # 用户ID的属性名。
flowable.idm.ldap.base-dn= # 查找用户与组的DN(标志名称 distinguished name)。
flowable.idm.ldap.cache.group-size=-1 # 设置{@link org.flowable.ldap.LDAPGroupCache}的大小。这是LRU缓存,用于缓存用户及组,以避免每次都查询LDAP系统。
flowable.idm.ldap.custom-connection-parameters= # 用于设置所有没有专用setter的LDAP连接参数。查看 http://docs.oracle.com/javase/tutorial/jndi/ldap/jndi.html 介绍的自定义参数。参数包括配置链接池,安全设置,等等。
flowable.idm.ldap.enabled=false # 是否启用LDAP IDM 服务。
flowable.idm.ldap.group-base-dn= # 组查找的DN。
flowable.idm.ldap.initial-context-factory=com.sun.jndi.ldap.LdapCtxFactory # 初始化上下文工厂的类名。
flowable.idm.ldap.password= # 连接LDAP系统的密码。
flowable.idm.ldap.port=-1 # LDAP系统的端口。
flowable.idm.ldap.query.all-groups= # 查询所有组所用的语句。
flowable.idm.ldap.query.all-users= # 查询所有用户所用的语句。
flowable.idm.ldap.query.groups-for-user= # 按照指定用户查询所属组所用的语句
flowable.idm.ldap.query.user-by-full-name-like= # 按照给定全名查找用户所用的语句。
flowable.idm.ldap.query.user-by-id= # 按照userId查找用户所用的语句。
flowable.idm.ldap.search-time-limit=0 # 查询LDAP的超时时间(以毫秒计)。默认值为'0',即“一直等待”。
flowable.idm.ldap.security-authentication=simple # 连接LDAP系统所用的'java.naming.security.authentication'参数的值。
flowable.idm.ldap.server= # LDAP系统的主机名。如'ldap://localhost'。
flowable.idm.ldap.user= # 连接LDAP系统的用户ID。
flowable.idm.ldap.user-base-dn= # 查找用户的DN。
# Flowable Mail FlowableMailProperties
flowable.mail.server.default-from=flowable@localhost # 发送邮件时使用的默认发信人地址。
flowable.mail.server.host=localhost # 邮件服务器。
flowable.mail.server.password= # 邮件服务器的登录密码。
flowable.mail.server.port=1025 # 邮件服务器的端口号。
flowable.mail.server.use-ssl=false # 是否使用SSL/TLS加密SMTP传输连接(即SMTPS/POPS)。
flowable.mail.server.use-tls=false # 使用或禁用STARTTLS加密。
flowable.mail.server.username= # 邮件服务器的登录用户名。如果为空,则不需要登录。
# Actuator
management.endpoint.flowable.cache.time-to-live=0ms # 缓存响应的最大时间。
management.endpoint.flowable.enabled=true # 是否启用flowable端点。1.3、核心组件
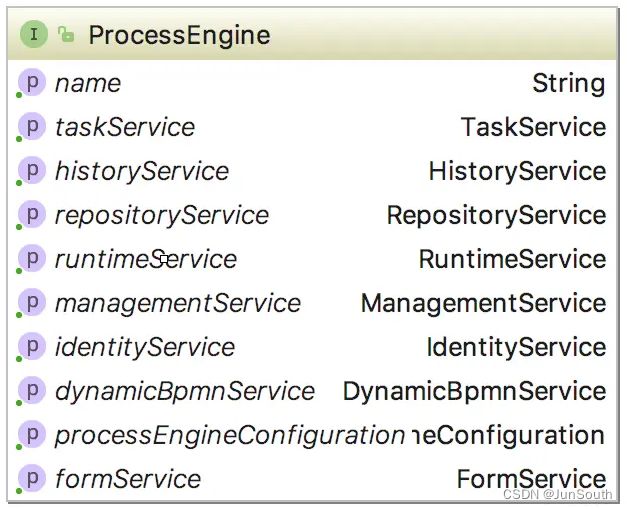
Flowable整体是通过ProcessEngine来操作的,操作流程要通过ProcessEngine类来处理。
1.3.1、FormService
表单数据的管理
formService.getStartFormKey() 获取表单key
formService.getRenderedStartForm()查询表单json(无数据)1.3.2、RepositoryService
提供了在编辑和发布审批流程的 api,模型管理、流程定义的业务 api。
1.提供了带条件的查询模型流程定义的api
repositoryService.createXXXQuery()
例:
repositoryService.createModelQuery().list() 模型查询
repositoryService.createProcessDefinitionQuery().list() 流程定义查询
repositoryService.createXXXXQuery().XXXKey(XXX) (查询该key是否存在)
2.提供一大波模型与流程定义的通用方法
模型相关(【本人亲测这里获取模型貌似不行,有知道的联系我】)
repositoryService.getModel() (获取模型)
repositoryService.saveModel() (保存模型)
repositoryService.deleteModel() (删除模型)
repositoryService.createDeployment().deploy(); (部署模型)
repositoryService.getModelEditorSource() (获得模型JSON数据的UTF8字符串)
repositoryService.getModelEditorSourceExtra() (获取PNG格式图像)
3.流程定义相关
repositoryService.getProcessDefinition(ProcessDefinitionId); 获取流程定义具体信息
repositoryService.activateProcessDefinitionById() 激活流程定义
repositoryService.suspendProcessDefinitionById() 挂起流程定义
repositoryService.deleteDeployment() 删除流程定义
repositoryService.getProcessDiagram()获取流程定义图片流
repositoryService.getResourceAsStream()获取流程定义xml流
repositoryService.getBpmnModel(pde.getId()) 获取bpmn对象(当前进行到的那个节点的流程图使用)
4.流程定义授权相关
repositoryService.getIdentityLinksForProcessDefinition() 流程定义授权列表
repositoryService.addCandidateStarterGroup()新增组流程授权
repositoryService.addCandidateStarterUser()新增用户流程授权
repositoryService.deleteCandidateStarterGroup() 删除组流程授权
repositoryService.deleteCandidateStarterUser() 删除用户流程授权1.3.3、RuntimeService
处理正在运行的流程
runtimeService.createProcessInstanceBuilder().start() 发起流程
runtimeService.deleteProcessInstance() 删除正在运行的流程
runtimeService.suspendProcessInstanceById() 挂起流程定义
runtimeService.activateProcessInstanceById() 激活流程实例
runtimeService.getVariables(processInstanceId); 获取表单中填写的值
runtimeService.getActiveActivityIds(processInstanceId)获取以进行的流程图节点 (当前进行到的那个节点的流程图使用)
runtimeService.createChangeActivityStateBuilder().moveExecutionsToSingleActivityId(executionIds, endId).changeState(); 终止流程1.3.4、HistoryService
处理流程实例的 api,但是其中包括了已经完成的和未完成的流程实例。
historyService.createHistoricProcessInstanceQuery().list() 查询流程实例列表(历史流程,包括未完成的)
historyService.createHistoricProcessInstanceQuery().list().foreach().getValue() 可以获取历史中表单的信息
historyService.createHistoricProcessInstanceQuery().processInstanceId(processInstanceId).singleResult(); 根绝id查询流程实例
historyService.deleteHistoricProcessInstance() 删除历史流程
historyService.deleteHistoricTaskInstance(taskid); 删除任务实例
historyService.createHistoricActivityInstanceQuery().processInstanceId(processInstanceId).list() 流程实例节点列表 (当前进行到的那个节点的流程图使用)1.3.5、TaskService
对流程实例的各个节点的审批处理。
流转的节点审批
taskService.createTaskQuery().list() 待办任务列表
taskService.createTaskQuery().taskId(taskId).singleResult(); 待办任务详情
taskService.saveTask(task); 修改任务
taskService.setAssignee() 设置审批人
taskService.addComment() 设置审批备注
taskService.complete() 完成当前审批
taskService.getProcessInstanceComments(processInstanceId); 查看任务详情(也就是都经过哪些人的审批,意见是什么)
taskService.delegateTask(taskId, delegater); 委派任务
taskService.claim(taskId, userId);认领任务
taskService.unclaim(taskId); 取消认领
taskService.complete(taskId, completeVariables); 完成任务
任务授权
taskService.addGroupIdentityLink()新增组任务授权
taskService.addUserIdentityLink() 新增人员任务授权
taskService.deleteGroupIdentityLink() 删除组任务授权
taskService.deleteUserIdentityLink() 删除人员任务授权1.3.6、 ManagementService
主要是执行自定义命令
managementService.executeCommand(new classA()) 执行classA的内部方法,classA要实现Command,重写execute方法
在自定义的方法中可以使用以下方法获取 repositoryService。
ProcessEngineConfiguration processEngineConfiguration = CommandContextUtil.getProcessEngineConfiguration(commandContext);
RepositoryService repositoryService = processEngineConfiguration.getRepositoryService();
也可以获取流程定义方法集合
ProcessEngineConfigurationImpl processEngineConfiguration = CommandContextUtil.getProcessEngineConfiguration(commandContext);
ProcessDefinitionEntityManager processDefinitionEntityManager = processEngineConfiguration.getProcessDefinitionEntityManager();
如findById/findLatestProcessDefinitionByKey/findLatestProcessDefinitionByKeyAndTenantId等。1.3.7、 IdentityService
用于身份信息获取和保存,这里主要是获取身份信息。
identityService.createUserQuery().userId(userId).singleResult(); 获取审批用户的具体信息
identityService.createGroupQuery().groupId(groupId).singleResult(); 获取审批组的具体信息1.4、核心数据库表
1.4.1 数据库
1、Flowable的所有数据库表都以ACT_开头。第二部分是说明表用途的两字符标示符。服务API的命名也大略符合这个规则。
2、ACT_RE_: 'RE’代表repository。带有这个前缀的表包含“静态”信息,例如流程定义与流程资源(图片、规则等)。
3、ACT_RU_: 'RU’代表runtime。这些表存储运行时信息,例如流程实例(process instance)、用户任务(user task)、变量(variable)、作业(job)等。Flowable只在流程实例运行中保存运行时数据,并在流程实例结束时删除记录。这样保证运行时表小和快。
4、ACT_HI_: 'HI’代表history。这些表存储历史数据,例如已完成的流程实例、变量、任务等。
5、ACT_GE_: 通用数据。在多处使用。
1.4.2 通用数据表(2个)
act_ge_bytearray:二进制数据表,如流程定义、流程模板、流程图的字节流文件;
act_ge_property:属性数据表(不常用);
1.4.3 历史表(8个,HistoryService接口操作的表)
act_hi_actinst:历史节点表,存放流程实例运转的各个节点信息(包含开始、结束等非任务节点);
act_hi_attachment:历史附件表,存放历史节点上传的附件信息(不常用);
act_hi_comment:历史意见表;
act_hi_detail:历史详情表,存储节点运转的一些信息(不常用);
act_hi_identitylink:历史流程人员表,存储流程各节点候选、办理人员信息,常用于查询某人或部门的已办任务;
act_hi_procinst:历史流程实例表,存储流程实例历史数据(包含正在运行的流程实例);
act_hi_taskinst:历史流程任务表,存储历史任务节点;
act_hi_varinst:流程历史变量表,存储流程历史节点的变量信息;
1.4.4 用户相关表(4个,IdentityService接口操作的表)
act_id_group:用户组信息表,对应节点选定候选组信息;
act_id_info:用户扩展信息表,存储用户扩展信息;
act_id_membership:用户与用户组关系表;
act_id_user:用户信息表,对应节点选定办理人或候选人信息;
1.4.5 流程定义、流程模板相关表(3个,RepositoryService接口操作的表)
act_re_deployment:部属信息表,存储流程定义、模板部署信息;
act_re_procdef:流程定义信息表,存储流程定义相关描述信息,但其真正内容存储在act_ge_bytearray表中,以字节形式存储;
act_re_model:流程模板信息表,存储流程模板相关描述信息,但其真正内容存储在act_ge_bytearray表中,以字节形式存储;
1.4.6 流程运行时表(6个,RuntimeService接口操作的表)
act_ru_task:运行时流程任务节点表,存储运行中流程的任务节点信息,重要,常用于查询人员或部门的待办任务时使用;
act_ru_event_subscr:监听信息表,不常用;
act_ru_execution:运行时流程执行实例表,记录运行中流程运行的各个分支信息(当没有子流程时,其数据与act_ru_task表数据是一一对应的);
act_ru_identitylink:运行时流程人员表,重要,常用于查询人员或部门的待办任务时使用;
act_ru_job:运行时定时任务数据表,存储流程的定时任务信息;
act_ru_variable:运行时流程变量数据表,存储运行中的流程各节点的变量信息;
二、flowable 简单使用
2.1、配置及依赖
1.依赖
org.flowable
flowable-spring-boot-starter
6.5.0
org.flowable
flowable-json-converter
6.5.0
2.BPMN流程图
Idea中的setting—plugins中直接搜索Activiti BPMN visualizer进行安装应用。
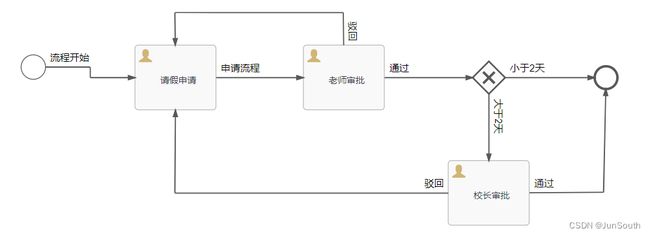
学生请假流程.bpmn20.xml 复制到项目resources/processes目录下(可以通过修改flowable.process-definition-location-prefix重新指定),Flowable会自动部署processes目录下的流程模型。
启动项目后通过RepositoryService查询已部署的模型,若查询结果不为空就代表模型部署成功了。
2}]]>
3.配置参数
server:
port: 9999
spring:
datasource:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/flowable?serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai&useUnicode=true&charcterEncoding=UTF-8&useSSL=false
username: root
password: root
flowable:
#关闭定时任务JOB
async-executor-activate: false
#将databaseSchemaUpdate设置为true。当flowable发现库与数据库表结构不一致时,会自动将数据库表结构升级至新版本。
database-schema-update: true
#校验流程文件,默认校验resources下的processes文件夹里的流程文件
process-definition-location-prefix: classpath*:/processes/
process-definition-location-suffixes: "**.bpmn20.xml, **.bpmn"2.2、代码编写
1.查看是否成功加载流程图
import org.flowable.engine.RepositoryService;
import org.flowable.engine.repository.ProcessDefinition;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import java.util.List;
public class Test02 {
@Autowired
private RepositoryService repositoryService;
/**
* 查询流程定义列表, 涉及到 act_re_procdef 表,部署成功会新增记录
*/
public void testProcessDefinition() {
List processList = repositoryService.createProcessDefinitionQuery().list();
for(ProcessDefinition processDefinition : processList){
System.out.println("ProcessDefinition name = {},deploymentId = {}"+
processDefinition.getName()+ " "+
processDefinition.getDeploymentId());
}
}
} 2.审批流程Demo
import org.flowable.engine.HistoryService;
import org.flowable.engine.RuntimeService;
import org.flowable.engine.TaskService;
import org.flowable.engine.history.HistoricActivityInstance;
import org.flowable.engine.runtime.ProcessInstance;
import org.flowable.task.api.Task;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
public class Test01 {
@Autowired
private RuntimeService runtimeService;
@Autowired
private TaskService taskService;
@Autowired
private HistoryService historyService;
public void testFlow() {
// 发起请假
Map map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("day", 2);
map.put("studentUser", "小明");
ProcessInstance studentLeave = runtimeService.startProcessInstanceByKey("StudentLeave", map);
Task task = taskService.createTaskQuery().processInstanceId(studentLeave.getId()).singleResult();
taskService.complete(task.getId());
// 老师审批
List teacherTaskList = taskService.createTaskQuery().taskCandidateGroup("teacher").list();
Map teacherMap = new HashMap<>();
teacherMap.put("outcome", "通过");
for (Task teacherTask : teacherTaskList) {
taskService.complete(teacherTask.getId(), teacherMap);
}
// 校长审批
List principalTaskList = taskService.createTaskQuery().taskCandidateGroup("principal").list();
Map principalMap = new HashMap<>();
principalMap.put("outcome", "通过");
for (Task principalTask : principalTaskList) {
taskService.complete(principalTask.getId(), principalMap);
}
// 查看历史
List activities = historyService.createHistoricActivityInstanceQuery()
.processInstanceId(studentLeave.getId()).finished()
.orderByHistoricActivityInstanceEndTime().asc().list();
for (HistoricActivityInstance activity : activities) {
System.out.println(activity.getActivityName());
}
/*
开始
流程开始
请假申请
申请流程
老师审批
通过
判断是否大于2天
小于2天
结束
*/
}
}