Java JDBC连接数据库实现增删改查
Java JDBC连接数据库实现增删改查
- 前言
- 一、JDBC环境准备
- 二、基本操作
-
- 实现数据库的查询
- 实现数据库的删除
- 实现数据库的增添
- 实现数据库数据的修改
- 三(扩展)、整合增删改查的代码,封装为一个工具类
-
- 在util包下新建DBUtil类
- 在bean包下新建User类
- 在dao包下新建UserDao类
- 新建Test类
- 结语
前言
JDBC代表Java数据库连接。JDBC库中所包含的API通常与数据库使用于:连接到数据库创建SQL或MySQL语句,在数据库中执行SQL或MySQL,查看和修改数据库中的数据记录。
一、JDBC环境准备
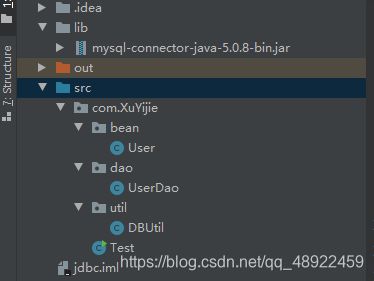
- 普通Java项目,在lib中粘贴此包(在官网上下),版本无所谓
jar包存放位置,项目根目录下的lib文件夹
![]()
- 如果是Maven或者Gradle或者Spring项目。不需要引入上面的jar包,直接在依赖里面写(Maven为例)
<dependency>
<groupId>mysqlgroupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-javaartifactId>
<version>8.0.31version>
dependency>
除上述环境配置外,还需要建立一个数据库,我使用的是SQLyog,假设创建一个数据库:wzsxy,在这个数据库上创建一张表:tb_user,并输入两条起始数据。如图![]()
二、基本操作
实现数据库的查询
新建Find类
import java.sql.*;
public class Find {
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException, ClassNotFoundException {
//1、加载驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
//2、创建连接
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/wzsxy","root","123456");
//3、写SQL语句
String sql="select * from tb_user";
//4、获得statement对象
PreparedStatement statement=connection.prepareStatement(sql);
//5、执行SQL语句 得到结果集
ResultSet resultSet = statement.executeQuery();
//6、处理结果集
while (resultSet.next()){
System.out.println(resultSet.getInt(1));
System.out.println(resultSet.getString(2));
System.out.println(resultSet.getString(3));
}
//7、关闭资源
resultSet.close();
statement.close();
connection.close();
}
}
![]()
实现数据库的删除
新建Delete类
import java.sql.*;
public class Delete {
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException, ClassNotFoundException {
//1、加载驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
//2、创建连接
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/wzsxy","root","123456");
//3、写SQL语句
String sql="delete from tb_user where id=2";
//4、获得statement对象
PreparedStatement statement=connection.prepareStatement(sql);
//5、执行SQL语句 得到结果集
statement.executeUpdate();
//6、处理结果集
//7、关闭资源
statement.close();
connection.close();
}
}
运行后在数据库中刷新表以后,发现id为“2”的用户被删除
![]()
![]()
实现数据库的增添
新建Add类,在SQL语句中输入要增加的信息
import java.sql.*;
public class Add {
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException, ClassNotFoundException {
//1、加载驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
//2、创建连接
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/wzsxy","root","123456");
//3、写SQL语句
String sql="INSERT INTO tb_user (username,PASSWORD) VALUES ('JinZiyi','123456')";
//4、获得statement对象
PreparedStatement statement=connection.prepareStatement(sql);
//5、执行SQL语句 得到结果集
statement.executeUpdate();
//6、处理结果集
//7、关闭资源
statement.close();
connection.close();
}
}
运行打开数据库刷新,发现数据增加成功
![]()
实现数据库数据的修改
新建Update类
import java.sql.*;
public class Update {
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException, ClassNotFoundException {
//1、加载驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
//2、创建连接
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/wzsxy","root","123456");
//3、写SQL语句
String sql="UPDATE tb_user SET username='JinZiyi',PASSWORD='000000' WHERE id=2";
//4、获得statement对象
PreparedStatement statement=connection.prepareStatement(sql);
//5、执行SQL语句 得到结果集
statement.executeUpdate();
//6、处理结果集
//7、关闭资源
statement.close();
connection.close();
}
}
刷新数据库后可见数据修改成功
![]()
三(扩展)、整合增删改查的代码,封装为一个工具类
在util包下新建DBUtil类
将JDBC的基本步骤的1、2、7步放入DBUtil类中,代码中使用了try…catch,也可以直接idea自动生成抛出异常
package com.XuYijie.util;
import java.sql.*;
public class DBUtil {
public static Connection getConnection(){
//1、加载驱动
try {
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//2、创建连接
Connection connection = null;
try {
connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/wzsxy","root","123456");
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("创建连接成功");
return connection;
}
//7、关闭资源
public static void closeAll(ResultSet resultSet, Statement statement,Connection connection) throws SQLException {
if (resultSet!=null){
resultSet.close();
}
if (resultSet!=null){
statement.close();
}
if (resultSet!=null){
connection.close();
}
}
}
在bean包下新建User类
定义id、username、password,生成所有的get、set方法和构造方法,并重写toString
package com.XuYijie.bean;
public class User {
public User() {
}
private int id;
private String username;
private String password;
public User(int id, String username, String password) {
this.id = id;
this.username = username;
this.password = password;
}
public User(String username, String password) {
this.username = username;
this.password = password;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"id=" + id +
", username='" + username + '\'' +
", password='" + password + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
在dao包下新建UserDao类
package com.XuYijie.dao;
import com.XuYijie.bean.User;
import com.XuYijie.util.DBUtil;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class UserDao {
public List<User> findAll(){
Connection connection= null;
List<User> userList=new ArrayList<>();
PreparedStatement statement=null;
ResultSet resultSet =null;
try {
//2、创建连接
connection = DBUtil.getConnection();
//3.写sql语句
String sql="select * from tb_user";
//4.获得statement对象
statement=connection.prepareStatement(sql);
//5.执行sql 得到结果集
resultSet = statement.executeQuery();
//6.处理结果集
while (resultSet.next()){
User user=new User();
user.setId(resultSet.getInt(1));
user.setUsername(resultSet.getString(2));
user.setPassword(resultSet.getString(3));
userList.add(user);
}
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}finally {
//7.关闭资源
try {
DBUtil.closeAll(resultSet,statement,connection);
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
return userList;
}
public void deleteById(int id){
Connection connection= null;
PreparedStatement statement=null;
try {
//2、创建连接
connection = DBUtil.getConnection();
System.out.println("创建连接成功");
//3.写sql语句
String sql="delete from tb_user where id=5";
//4.获得statement对象
statement=connection.prepareStatement(sql);
//5.执行sql 得到结果集
statement.executeUpdate();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
DBUtil.closeAll(null,statement,connection);
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public void add(User user){
//2、创建连接
Connection connection= null;
PreparedStatement statement=null;
try {
connection = DBUtil.getConnection();
System.out.println("创建连接成功");
//3.写sql语句
String sql="INSERT INTO tb_user (username,PASSWORD) VALUES (?,?)";
//4.获得statement对象
statement=connection.prepareStatement(sql);
statement.setString(1,user.getUsername());
statement.setString(2,user.getPassword());
statement.executeUpdate();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
DBUtil.closeAll(null,statement,connection);
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public void update(User user){
//2、创建连接
Connection connection= null;
PreparedStatement statement=null;
try {
connection = DBUtil.getConnection();
System.out.println("创建连接成功");
//3.写sql语句
String sql="UPDATE tb_user SET username=?,PASSWORD=? WHERE id=?";
//4.获得statement对象
statement=connection.prepareStatement(sql);
statement.setString(1,user.getUsername());
statement.setString(2,user.getPassword());
statement.setInt(3,user.getId());
//5.执行sql 得到结果集
statement.executeUpdate();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
DBUtil.closeAll(null,statement,connection);
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
新建Test类
Test用来实现UserDao里面的方法
package com.XuYijie;
import com.XuYijie.bean.User;
import com.XuYijie.dao.UserDao;
import java.util.List;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
UserDao userDao = new UserDao();
//查询
List<User> userList = userDao.findAll();
System.out.println(userList);
//删除
userDao.deleteById(4);
//增添
User user = new User();
user.setUsername("HeGuanghui");
user.setPassword("123456");
userDao.add(user);
//修改
user.setUsername("HeGuanghui");
user.setPassword("654321");
userDao.update(user);
}
}
}
然后就可以自己运行试试啦
结语
JDBC在现在的正规项目中已经不使用了,但是初学者仍然要了解一些,另外JDBC可以在普通项目中作为临时连接数据库的方法使用,切换方便,非常灵活。
Spring和Maven操作数据的教程可以看我的传送门,可以在网页上展示数据,有源码,非常简单易懂
Maven工程实现前后端的数据展示与操作