MySQL数据库入门学习(一)——创建数据库并Java实现JDBC连接数据库后添加数据
MySQL数据库入门学习(一)——创建数据库并Java实现JDBC连接数据库后添加数据
1.MySQL简介:
MySQL是一种DBMS,而且是一种一个小型的开源的关系型数据库管理系统。2008年1月16日MySQL AB被Sun公司收购。而2009年,SUN又被Oracle收购。就这样如同一个轮回,MySQL成为了Oracle公司的另一个数据库项目。
MySQL它在世界范围内得到了广泛的安装和使用,应该是使用人数最多的数据库软件了,因为它有着这样的特性:
成本——MySQL是开源软件,可以免费使用和修改。
性能——MySQL性能很好处理速度很快。
简单——MySQL很容易安装和使用,对新手友好。
MySQL数据库软件也是使用最常用的数据库管理语言:结构化查询语言(SQL)进行数据库管理和操作。
2.在MySQL数据库中创建表以及在Java中创建对应实体类
2.1创建数据库mysqldemo
create database if not exists mysqldemo;
2.2使用数据库mysqldemo:
use mysqldemo;
2.3创建表book:
create table if not exists book(id int primary key auto_increment,name varchar(20),price double,status tinyint(1),discount float,isBorrowed tinyint(2) default 0, createTime datetime default now());
为了尽可能演示MySQL中的数据类型和Java中类型的关系,这里将Book表的属性类型有int , varchar,doble,tinyint,float,tinyint,datetime。在这个表中isBorrowed 对应的实体类是一个Boolean类型,但是在MySQL中不支持Boolean类型的存储,但是可以通过tinyint来代替Boolean进行存储,在创建表的时候类型选择tinyint,长度*必须\为1,即tinyint(1).数据就保存0或者1,这样,在java后端取出数据的时候才会自动转化成true(数据库中的1)和false(数据库中的0)。
2.4创建book表对应的Java实体类
对应的实体类,在这个实体类中,类的属性和数据库表中的属性名一致方便之后的操作:
package entity;
import java.util.Date;
/**
* @author 陌意随影
* @create 2020-01-31 17:34
* @desc 书籍类
**/
public class Book {
//书籍的唯一主键,由数据库自动生成
private int id;
//书籍名称
private String name;
//价格
private double price;
//状态
private byte status;
/**状态正常*/
public final static byte STATUS_NORMAL=1;
/**状态异常*/
public final static byte STATUS_ERRO=0;
//折扣
private float discount;
//是否被借阅
boolean isBorrowed;
/**被借阅*/
public final static boolean isBorrowed_TRUE = true;
/**未被借阅*/
public final static boolean isBorrowed_FALSE = false;
//创建时间
private Date createTime;
public Book() {
}
@SuppressWarnings("javadoc")
public Book(int id, String name, double price,byte status, float discount, boolean isBorrowed, Date createTime) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.price = price;
this.status = status;
this.discount = discount;
this.isBorrowed = isBorrowed;
this.createTime = createTime;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public double getPrice() {
return price;
}
public byte getStatus() {
return status;
}
public float getDiscount() {
return discount;
}
public boolean isBorrowed() {
return isBorrowed;
}
public Date getCreateTime() {
return createTime;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void setPrice(double price) {
this.price = price;
}
public void setStatus(byte status) {
this.status = status;
}
public void setDiscount(float discount) {
this.discount = discount;
}
public void setBorrowed(boolean isBorrowed) {
this.isBorrowed = isBorrowed;
}
public void setCreateTime(Date createTime) {
this.createTime = createTime;
}
}
2.5向book表插入数据:
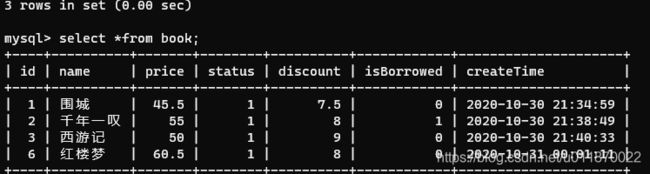
insert into book(name,price,status,discount,isBorrowed,createTime) values("围城",45.5,1,7.5,false,now());
insert into book(name,price,status,discount,isBorrowed,createTime) values("千年一叹",55.0,1,8.0,true,now());
insert into book(name,price,status,discount,isBorrowed,createTime) values("西游记",50.0,1,9.0,false,now());
2.6使用select语句查询book表的数据
3.JDBC连接MySQL数据库
3.1JDBC简介
Java数据库连接,(Java Database Connectivity,简称JDBC)是Java语言中用来规范客户端程序如何来访问数据库的应用程序接口,提供了诸如查询和更新数据库中数据的方法。JDBC也是Sun Microsystems的商标。我们通常说的JDBC是面向关系型数据库的。
3.2连接MySQL数据库
jdbc连接数据库总体就是有五个步骤,简记为 “贾连预执释”:
“贾”:加载MySQL数据库驱动。
“连”:通过DriverManager.getConnection(url,user,password)获取连接对象Connection。其中url为需要连接的数据库名的地址,user为登录数据库的用户名,password为登录数据库的密码。
“预”:通过connection.createStatement();创建预处理对象。
“执”:执行SQL语句。
“释”:释放连接资源。
3.3Statement和PreparedStatement的异同
同:
1.PreparedStatement和Statement都是用来执行SQL查询语句的API之一。
2.PreparedStatement接口继承了Statement接口。
异:
- Statement不对sql语句作处理,直接交给数据库;而PreparedStatement支持预编译,会将编译好的sql语句放在数据库端,相当于缓存。对于多次重复执行的sql语句,使用PreparedStatement可以使得代码的执行效率更高。
- Statement的sql语句使用字符串拼接的方式,容易导致出错,且存在sql注入的风险;PreparedStatement使用“?”占位符提升代码的可读性和可维护性,并且这种绑定参数的方式,可以有效的防止sql注入。
3.4使用Statement来创建预处理对象执行SQL语句
/**
* @param book 需要保存的对象
* @return 保存成功返回1否则返回 0
*/
public int saveByStatement(Book book) {
//拼接需要执行的sql语句
String sql = "insert into book(name,price,status,discount,isBorrowed,createTime) values(\""+ book.getName()+"\",\""
+ book.getPrice()+"\",\""+book.getStatus()+"\",\""+book.getDiscount()+"\"," + book.isBorrowed()+",\"" + book.getCreateTime().toLocaleString()+"\");";
System.out.println(sql);
int result = 0;
try {
//1.加载驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
//2.获取创建连接
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mysqldemo?serverTimezone=UTC", "root", "root");
//3.创建预处理对象
Statement statement = connection.createStatement();
//4.执行sql语句并返回执行结果影响的行数
result = statement.executeUpdate(sql);
//5.释放资源,先开启的后释放
statement.close();
connection.close();
return result;
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
return result;
}
3.5使用PreparedStatement来创建预处理对象执行SQL语句
/**
* @param book 需要保存的对象
* @return 保存成功返回1否则返回 0
*/
public int saveByPrepareStatement(Book book) {
//拼接需要执行的sql语句
String sql = "insert into book(name,price,status,discount,isBorrowed,createTime) values(?,?,?,?,?,?)";
int result = 0;
try {
//加载驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
//获取创建连接
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mysqldemo?serverTimezone=UTC", "root", "root");
//创建预处理对象
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
//设置name占位符对应的值
preparedStatement.setString(1, book.getName());
//设置price占位符对应的值
preparedStatement.setDouble(2, book.getPrice());
//设置status占位符对应的值
preparedStatement.setByte(3, book.getStatus());
//设置discount占位符对应的值
preparedStatement.setFloat(4, book.getDiscount());
//设置isBorrowed对应占位符的值
preparedStatement.setBoolean(5, book.isBorrowed());
//设置createTime占位符对应的值,需要将 java.Util.Date 转化为 java.sql.Date才可以
preparedStatement.setDate(6,new Date(book.getCreateTime().getTime()));
//开始执行,并返回影响的行数
result = preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
//释放资源,先开启的后释放
statement.close();
connection.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
return result;
}
connection.prepareStatement(sql)用来产生一个PreparedStatement预处理对象,此时需要插入到数据库的值使用“?”来代替,这个就叫占位符。此时SQL中的操作参数从左到右和每个占位符一一对应。比如String sql = “insert into book(name,price,status,discount,isBorrowed,createTime) values(?,?,?,?,?,?)”;中,name的对应占位符是第1个“?",price对应的占位符是第2个“?”,以此类推。注意,在preparedStatement.setXX(int parameterIndex, XX x)时,parameterIndex是从1开始的,而不是从0开始!并且preparedStatement.setXX(int parameterIndex, XX x)中setXX的类型要和真实值x一致。比如preparedStatement.setString(1, book.getName());中book.getName()的值就是preparedStatement.setString()中setXX的XX,也就是String类型,其它的依次类推。注意preparedStatement.setBoolean(5, book.isBorrowed());中这里设置的是Boolean类型,但是我们知道MySQL是没有Boolean类型的。而在之前我们说过在数据库中这个isBorrowed属性是tinyint(1),当Java在取值或者设置值时,会自动将true转换为1,将false转换为0,从而数据库达到相当于存储Boolean类型的情况。
//设置name占位符对应的值
preparedStatement.setString(1, book.getName());
//设置price占位符对应的值
preparedStatement.setDouble(2, book.getPrice());
//设置status占位符对应的值
preparedStatement.setByte(3, book.getStatus());
//设置discount占位符对应的值
preparedStatement.setFloat(4, book.getDiscount());
//设置isBorrowed对应占位符的值
preparedStatement.setBoolean(5, book.isBorrowed());
//设置createTime占位符对应的值,需要将 java.Util.Date 转化为 java.sql.Date才可以
preparedStatement.setDate(6,new Date(book.getCreateTime().getTime()));
通过使用真实值替换占位符,最终执行preparedStatement.executeUpdate()时的语句为:
insert into book(name,price,status,discount,isBorrowed,createTime) values("红楼梦","60.5","1","8.0",false,"2020-10-31 0:01:11");
3.6常用的Statement方法:
1,boolean execute 允许执行查询语句、更新语句、DDL语句
返回值为true时,表示执行的是查询语句,可以通过getResultSet方法获取结果;返回值为false时,执行的是更新语句或DDL语句。
2,getUpdateCount方法 获取更新的记录数量。
3,int executeUpdate(String sql)执行给定 SQL 语句
该语句可能为 INSERT、UPDATE 或 DELETE 语句,或者不返回任何内容的 SQL 语句(如 SQL DDL 语句)。
4,ResultSet executeQuery(String sql) 执行给定的 SQL 语句
该语句返回单个 ResultSet 对象。返回值是更新的记录数量。
4.使用JUnit测试
@Test
void testSaveBookByStament() {
Book book = new Book();
book.setName("红楼梦");
book.setBorrowed(Book.isBorrowed_FALSE);
book.setCreateTime(new Date());
book.setDiscount(8);
book.setPrice(60.5);
book.setStatus(Book.STATUS_NORMAL);
BookDao bookDao = new BookDao();
int result = bookDao.saveByStatement(book);
if(result == 1) {
System.out.println("添加新书成功!");
}else {
System.out.println("添加新书失败!");
}
}
5.实验环境
eclipse 2019, JDK1.8 ,MySQL8.0
6.本博客已经同步到个人博客并且源代码以及上传到个人服务器,如有需要请移步:
http://moyisuiying.com/index.php/javastudy/mysql/330.html