PCL中点云特征描述与提取精通级实例解析
PCL中点云特征描述与提取精通级实例解析
- 1 3D对象识别的假设验证
- 2 隐式形状模型方法
-
- 2.1 隐式形状模型识别方法概述
- 2.2 实例解析
1 3D对象识别的假设验证
本教程将学习在高噪声和严重遮挡的场景中,如何通过模型假设验证,进行复杂场景下的3D目标识别。本教程实例先进行描述子匹配,然后运行之前教程介绍过的基于对应点聚类的识别算法,获取点对应的聚类,从而确定场景中目标模型假设的实例。在这些假设实例中本教程的核心部分是利用全局假设验证算法来减少错误的模型实例假设。所以说,本教程是前面教程基于对应点聚类的识别算法的延续。
全局假设验证方法的理论知识请参见:Aldoma A, Tombari F, Di Stefano L, et al. A global hypotheses verification method for 3D object recognition [M] //Computer Vision-ECCV 2012 . Springer Berlin Heidelberg , 2012 : 511-524.
首先创建一个工作空间global_hypothesis_verification,然后再在工作空间创建一个文件夹src用于存放源代码:
mkdir -p global_hypothesis_verification/src
接着,在global_hypothesis_verification/src路径下,创建一个文件并命名为global_hypothesis_verification.cpp,拷贝如下代码:
#include 【解释说明】
下面我们对上述源代码的关键语句进行解析,生成假设的源码已经在之前教程中讲解过,此处不再说明,下面主要分析如何进行假设验证。
首先为得到的假设实例,生成一个实例向量 instances 来保存假设实例对应的在场景中的点云数据,该假设实例的点云数据由模型本身和生成假设时得到的变换矩阵生成。
std::vector<pcl::PointCloud<PointType>::ConstPtr> instances;
for (size_t i = 0; i < rototranslations.size (); ++i)
{
pcl::PointCloud<PointType>::Ptr rotated_model (new pcl::PointCloud<PointType> ());
pcl::transformPointCloud (*model, *rotated_model, rototranslations[i]);
instances.push_back (rotated_model);
}
生成假设对应的变换矩阵误差较大,为了提高假设与场景的配准精度,应用ICP迭代,并且同时保存利用ICP迭代配准后的模型实例假设到 registered_instances 向量,用于后续的全局假设检验。
pcl::IterativeClosestPoint<PointType, PointType> icp;
icp.setMaximumIterations (icp_max_iter_);
icp.setMaxCorrespondenceDistance (icp_corr_distance_);
icp.setInputTarget (scene);
icp.setInputSource (instances[i]);
pcl::PointCloud<PointType>::Ptr registered (new pcl::PointCloud<PointType>);
icp.align (*registered);
registered_instances.push_back (registered);
类 GlobalHypothesesVerification 输入为配准后的假设实例和场景,其输出结果利用hypotheses_mask保存,这是一个bool数组,顺序与 registered_instances 中的实例假设对应,当registered_instances[i] 实例假设被验证为真时,hypotheses_mask[i] 也被设置为真,当其被验证为假时,hypotheses_mask[i] 也被设置为假,同时,该目标假设被剔除。
std::vector<bool> hypotheses_mask; // 用于保存检验假设的结果
pcl::GlobalHypothesesVerification<PointType, PointType> GoHv;
GoHv.setSceneCloud (scene); // 输入场景点云数据
GoHv.addModels (registered_instances, true); // 输入待被检验的模型实例
GoHv.setInlierThreshold (hv_inlier_th_);
GoHv.setOcclusionThreshold (hv_occlusion_th_);
GoHv.setRegularizer (hv_regularizer_);
GoHv.setRadiusClutter (hv_rad_clutter_);
GoHv.setClutterRegularizer (hv_clutter_reg_);
GoHv.setDetectClutter (hv_detect_clutter_);
GoHv.setRadiusNormals (hv_rad_normals_);
GoHv.verify ();
GoHv.getMask (hypotheses_mask);
最后进行可视化。
【编译和运行程序】
在工作空间根目录global_hypothesis_verification下,编写CMakeLists.txt文件如下:
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 2.6 FATAL_ERROR)
project(global_hypothesis_verification)
find_package(PCL 1.7 REQUIRED)
include_directories(${PCL_INCLUDE_DIRS})
link_directories(${PCL_LIBRARY_DIRS})
add_definitions(${PCL_DEFINITIONS})
add_executable (${PROJECT_NAME}_node src/global_hypothesis_verification.cpp)
target_link_libraries (${PROJECT_NAME}_node ${PCL_LIBRARIES})
在工作空间根目录global_hypothesis_verification下创建一个build文件夹,用于存放编译过程中产生的文件,然后执行编译:
mkdir build
cd build
cmake ..
make
此时,会在build文件夹下生成一个可执行文件global_hypothesis_verification_node,运行该可执行文件:
./global_hypothesis_verification_node milk.pcd milk_cartoon_all_small_clorox.pcd --algorithm GC -c -k
注意这里选择 GC 所谓对应点对聚类方法,-c 和 -k 设置启用关键点和对应点可视化。运行结果如下所示,其中绿色覆盖的实例是验证为真的假设实例,其他颜色蓝青色是验证为假的假设实例,所有假设实例用红色显示,关键点用粉红色显示。
2 隐式形状模型方法
2.1 隐式形状模型识别方法概述
基于隐式形状模型的目标识别方法把目标看成由许许多多的图片块或空间块(Patch)构成,下面将Patch简称为块元,这些块元可能对应目标的不同特征位置,具体的大小和位置由相关的算法确定。在训练阶段,主要任务是建立块字典(码本模型的空间共生分布模型 codebook),即为所有块元建立一个索引。之后需要该块元的相关信息时,如该块元与目标中心的距离等,只需查该字典便可。在检测阶段,先是检测兴趣点,提取兴趣点周围的块元,再从字典中找到匹配项,通过训练阶段记录的该项相对目标中心的信息,来对中心位置进行投票。那些获得最多投票超过一定阈值的中心点便被认作可能的检测结果,再经过自顶向下分割和验证步骤,得到最终分割结果。以上是基于隐式形状模型的识别检测方法概述,下面对PCL中实现的方法和使用进行详述。
我们将学习如何利用pcl::ism::ImplicitShapeMode 类,该类是一种隐式形状模型识别算法的实现。其将广义霍夫变换和 Bag of Features 方法相结合,基本就是输入一些训练集合,这些集合是已知类的不同对象的点云数据,然后通过离线学习训练集合得到一个形状模型,最后利用学习得到的形状模型预测物体中心,该物体可以不属于训练集合。
该算法分为两部分,第一个部分是训练,第二个部分是利用训练结果进行识别或检测。首先来看一下,训练阶段,该算法如何实施,主要分为如下六个步骤:
(1)首先进行关键点检测。在本实例中,通过下空间均匀采样的方法进行点云模型简化,将下采样后所有点作为关键点。
(2)对每一个关键点进行特征估计。在本例中,计算每一个关键点的FPFH特征,也可以是其他特征。
(3)所有的特征点利用K-means算法聚类而构建视觉词典(dictionary of visual words),获取的每个聚类代表一个视觉词(visual words),聚类中的每个特征是这个视觉词中的一个实例。
(4)对于在视觉词中每个单独的实例,计算获取该特征时的关键点空间位置到训练数据对象的质心的方向。
(5)对于每个视觉词,学习得到的统计权重利用下式计算。
w s t ( c i , v j ) = 1 n v w ( c i ) 1 n v o t ( v j ) n v o t ( c i , v j ) n f t r ( c i ) ∑ c k ϵ C n v o t ( c k , v j ) n f t r ( c k ) w_{st}\left ( c_{i}, v_{j} \right ) = \frac{1}{n_{vw}\left ( c_{i} \right )} \frac{1}{n_{vot}\left ( v_{j} \right )}\frac{\frac{n_{vot}\left ( c_{i},v_{j} \right )}{n_{ftr}\left ( c_{i} \right )}}{\sum_{c_{k}\epsilon C}^{}\frac{n_{vot}\left ( c_{k},v_{j} \right )}{n_{ftr}\left ( c_{k} \right )}} wst(ci,vj)=nvw(ci)1nvot(vj)1∑ckϵCnftr(ck)nvot(ck,vj)nftr(ci)nvot(ci,vj)
其中: w s t ( c i , v j ) w_{st}\left ( c_{i}, v_{j} \right ) wst(ci,vj)是视觉词 v j v_{j} vj 投出的所有票对类 c i c_{i} ci 的统计权重, n v o t ( v j ) n_{vot}\left ( v_{j} \right ) nvot(vj) 是来自视觉词 v j v_{j} vj 的所有票数, n v o t ( c i , v j ) n_{vot}\left ( c_{i},v_{j} \right ) nvot(ci,vj) 是来自视觉词 v j v_{j} vj 的类 c i c_{i} ci 的票数, n v w ( c i ) n_{vw}\left ( c_{i} \right ) nvw(ci) 是投给类 c i c_{i} ci 视觉词的数量, n f t r ( c k ) n_{ftr}\left ( c_{k} \right ) nftr(ck) 是学习 c i c_{i} ci 时使用的特征点的数量, C C C 是所有类的集合,上述的类 c c c 都是指学习时输入的对象所属的类,与前面提到的聚类算法无关。
(6)对于每个特征点,学习得到的权重利用下式计算。
w l r n ( λ i j ) = f ( { e − d a ( λ i j ) 2 σ 2 ∣ a ϵ A } ) w_{lrn}\left ( \lambda _{ij} \right )= f\left ( \left \{ e^{-\frac{d_{a}\left ( \lambda _{ij} \right )^{2}}{\sigma ^{2}}} |a \epsilon A \right \} \right ) wlrn(λij)=f({e−σ2da(λij)2∣aϵA})
此处定义 w l r n ( λ i j ) w_{lrn}\left ( \lambda _{ij} \right ) wlrn(λij) 作为上述视觉词 v j v_{j} vj 中一实例为对应训练形状集中类 c i c_{i} ci 的一个投票, λ i j \lambda _{ij} λij 为视觉词 v j v_{j} vj 的一实例对应的特征点位置与该实例对应的训练形状中心之间的距离。 A A A 为视觉词 v j v_{j} vj 所有给类 c i c_{i} ci 形状投票的实例集合, σ \sigma σ 的推荐值为训练形状大小的10%,函数 f f f 是简单的中值函数, d a ( λ i j ) d_{a}\left ( \lambda _{ij} \right ) da(λij) 是投票得到的中心位置和实际的中心位置之间的欧氏距离。
训练过程完成后,训练获得对应的形状模型(即权重,方向等),利用该模型即可开始进行
行下述的物体识别,识别一共包括如下四个步骤:
(1)关键点检测。
(2)对点云数据中每个关键点进行特征估计.
(3)对于每个特征,在上述得到的视觉词典中检索最近的视觉词。
(4)对于第3步中检索得到的视觉词中,对于每个实例(包含了对被检测目标类的投票信息),利用公式,在对应方向上分别累计投票和用下式计算的票权重。
w ( λ i j ) = W s t ( v j , c i ) ∗ W l r n ( λ i j ) w\left ( \lambda _{ij} \right ) = W_{st}\left ( v_{j},c_{i} \right )* W_{lrn}\left ( \lambda _{ij} \right ) w(λij)=Wst(vj,ci)∗Wlrn(λij)
(5)第4步确定了一组指向估计中心的方向,以及每个票的权重(power for each vote)。为了获取对于中心的单个点,需要对这些票进行进一步分析。为了这个目的,采用非极大值抑制(Non-Maximum Supression)方法,用户只需输入感兴趣物体的半径,其他的将由 ISMVoteList::findStrongestPeaks ()方法自动完成。
2.2 实例解析
首先创建一个工作空间Implicit Shape Model,然后再在工作空间创建一个文件夹src用于存放源代码:
mkdir -p Implicit Shape Model/src
接着,在Implicit Shape Model/src路径下,创建两个文件,其中一个为训练阶段的代码,命名为implicit_shape_model_training.cpp,另一个为识别阶段的代码,命名为implicit_shape_model_classification.cpp,分别拷贝如下代码:
/* implicit_shape_model_training.cpp */
#include 【训练阶段代码解释】
下面我们对上述训练阶段的源代码中的关键语句进行解析。
for (unsigned int i_cloud = 0; i_cloud < number_of_training_clouds - 1; i_cloud++)
{
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr tr_cloud(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ> ());
if ( pcl::io::loadPCDFile <pcl::PointXYZ> (argv[i_cloud * 2 + 1], *tr_cloud) == -1 )
{
return (-1);
}
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::Normal>::Ptr tr_normals = (new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::Normal>)->makeShared ();
normal_estimator.setInputCloud (tr_cloud);
normal_estimator.compute (*tr_normals);
unsigned int tr_class = static_cast<unsigned int> (strtol (argv[i_cloud * 2 + 2], 0, 10));
training_clouds.push_back (tr_cloud);
training_normals.push_back (tr_normals);
training_classes.push_back (tr_class);
}
这几行代码用于载入训练所需的点云,计算法向量作为后续算法的输入。当循环完成后,所有的点云存储在training_clouds向量, training_normals 和 training_classes 存储对应对象的法向量和类标签。
pcl::FPFHEstimation<pcl::PointXYZ, pcl::Normal, pcl::Histogram<153> >::Ptr fpfh(new pcl::FPFHEstimation<pcl::PointXYZ, pcl::Normal, pcl::Histogram<153> >);
fpfh->setRadiusSearch (30.0);
pcl::Feature< pcl::PointXYZ, pcl::Histogram<153> >::Ptr feature_estimator(fpfh);
特征估计实例被创建,在本例中,采用FPFH,在其传递给ISM算法之前,特征描述子对应参数需要完整设置。
pcl::ism::ImplicitShapeModelEstimation<153, pcl::PointXYZ, pcl::Normal> ism;
该行创建pcl::ism::ImplicitShapeModelEstimation实例。该模板类,有以下三个参数,FeatureSize -计算的特征大小,该参数与选择的特征一致;PointT - 处理的点云类型;NormalT - 所使用的法向量类型。目前PCL默认只预编译了支持参数为<153, pcl::PointXYZ, pcl::Normal>,对于其他参数的需要包含.hpp文件,否则会出现链接错误。
ism.setFeatureEstimator(feature_estimator);
ism.setTrainingClouds (training_clouds);
ism.setTrainingNormals (training_normals);
ism.setTrainingClasses (training_classes);
ism.setSamplingSize (2.0f);
这个实例由提供特征估计对象和训练数据输入,最后一行提供采样大小,用于前面提到
的均匀下采样获取特征点。
pcl::ism::ImplicitShapeModelEstimation<153, pcl::PointXYZ, pcl::Normal>::ISMModelPtr model = boost::shared_ptr<pcl::features::ISMModel>(new pcl::features::ISMModel);
ism.trainISM (model);
以上两行实施训练进程。
std::string file ("trained_ism_model.txt");
model->saveModelToFile (file);
trained_ism_model.txt为训练得到的模型,并保存到文件,以备后续分类识别使用。至此训练阶段的程序完成。
下面从文件中载入训练模型,同时设置输入点云数据、训练模型、点云数据法线和感兴趣类标签,并执行目标分类识别阶段,即在输入点云 testing_cloud中,寻找 testing_class类型的目标形状,算法可以使用用户传递的任何训练模型。当分类结束,返回中心投票列表,最终输出投票结果到ISMVoteList对象。
/* implicit_shape_model_classification.cpp */
#include model->loadModelFromfile (file); // 加载训练模型
unsigned int testing_class = static_cast<unsigned int> (strtol (argv[2], 0, 10));
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr testing_cloud (new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ> ());
if ( pcl::io::loadPCDFile <pcl::PointXYZ> (argv[1], *testing_cloud) == -1 )
{
return (-1);
}
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::Normal>::Ptr testing_normals = (new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::Normal>)->makeShared ();
normal_estimator.setInputCloud (testing_cloud);
normal_estimator.compute (*testing_normals);
boost::shared_ptr<pcl::features::ISMVoteList<pcl::PointXYZ> > vote_list = ism.findObjects (
model,
testing_cloud,
testing_normals,
testing_class);
ISMVoteList 类可以进行选票数据分析。下面行负责寻找投票结果中的最强峰值,该搜索基于非极大值抑制(Non-Maximum Suppression)思想,这就是为什么非极值搜索半径等于从训练模型中得到的待识别类对应的半径。剩下的代码相对简单,其负责可视化点云,并计算最强峰值,该峰值代表物体的估计中心,最后对估计的物体中心进行可视化。
double radius = model->sigmas_[testing_class] * 10.0;
double sigma = model->sigmas_[testing_class];
std::vector<pcl::ISMPeak, Eigen::aligned_allocator<pcl::ISMPeak> > strongest_peaks;
vote_list->findStrongestPeaks (strongest_peaks, testing_class, radius, sigma);
【编译和运行程序】
在工作空间根目录Implicit Shape Model下,编写CMakeLists.txt文件如下:
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 2.8 FATAL_ERROR)
project(implicit_shape_model)
find_package(PCL 1.5 REQUIRED)
set(CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE Release)
include_directories(${PCL_INCLUDE_DIRS})
link_directories(${PCL_LIBRARY_DIRS})
add_definitions(${PCL_DEFINITIONS})
add_executable (implicit_shape_model_training_node src/implicit_shape_model_training.cpp)
target_link_libraries (implicit_shape_model_training_node ${PCL_LIBRARIES})
add_executable (implicit_shape_model_classification_node src/implicit_shape_model_classification.cpp)
target_link_libraries (implicit_shape_model_classification_node ${PCL_LIBRARIES})
在工作空间根目录Implicit Shape Model下创建一个build文件夹,用于存放编译过程中产生的文件,然后执行编译:
mkdir build
cd build
cmake ..
make
此时,会在build文件夹下生成两个可执行文件implicit_shape_model_training_node和implicit_shape_model_classification_node ,首先运行下列命令进行学习训练:
./implicit_shape_model_training_node ism_train_cat.pcd 0 ism_train_horse.pcd 1 ism_train_lioness.pcd 2 ism_train_michael.pcd 3 ism_train_wolf.pcd 4
命令中,pcd和后面的数字为成对的训练数据集,包含数据和类标签,运行之后,在同文件夹下会生成trained_ism_model.txt文件,其就是训练得到的模型。下面利用该训练结果,运行如下命令行进行分类识别。
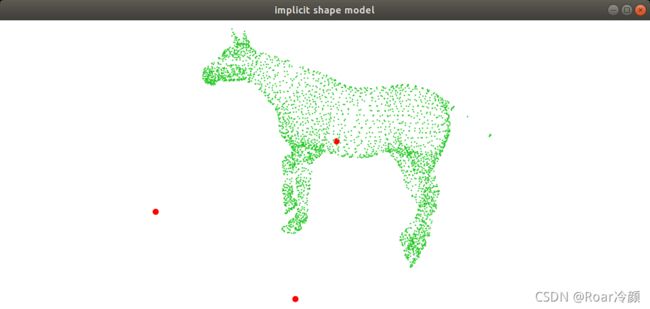
./implicit_shape_model_classification_node ism_train_horse.pcd 1
命令中的pcd文件为待识别的场景,数字为用户关心的类标签,可视化结果如下图所示,其中红色大点(图中着重显示的点云)为从数据中估计的中心点,很明显有错误的中心存在,因此一般识别流程中,还会加入验证步骤以达到最终正确的识别。