JDBC详解(含Druid数据库连接池技术、JDBCTemplate)
文章目录
-
-
-
- JDBC编程六步
- SQL注入问题即解决办法
- Statement的使用场景
- 模糊查询
- JDBC事务
- JDBC工具类
- 锁
-
- 行级锁for update
- 数据库连接池
-
- 数据库连接池的具体实现技术
- JDBCTemplate
-
-
什么是JDBC?
Java DataBase Connectivity
在java语言中编写sql语句,对mysql数据库中的数据进行CRUD操作。
JDBC相关的类库在哪里?
java.sql.*;
JDBC本质上是一堆什么呢?
java.sql.*;这个包下都是JDBC的接口,SUN公司制定的。
JDBC是体现"接口作用”的非常经典的例子:JDBC降低了耦合度,提高了扩展力。对于java程序员来说,不需要关心数据库是哪个。只要面向JDBC接口编程就行。
JDBC整个程序的结构当中有三波人:
-
第一波:SUN公司, 负责制定JDBC接口。这些接口已经写好了,在java.sql.*;
-
第二波:java.sql.* 下面的所有接口都要有实现类,这些实现类是数据库厂家编写的。
我们连接的是mysql数据库,mysql数据库厂家的实现类在哪里呢?
mysql-connector-java-8.0.23.jar,jar包中很多.class字节码文件,这是mysql数据库厂家写的接口实现。
注意:如果连接的是oracle数据库,你需要从网上下载oracle的jar包。
mysql-connector-java-8.0.23.jar这个jar包有一个专业的术语——mysql 的驱动。如果是oracle的jar,被称为oracle的驱动。 -
第三波:Java程序员,面向JDBC接口编程。
JDBC开发之前的准备工作:
mysql的驱动jar包,需要配置到classpath当中吗?
mysql-connector-java-8.0.23. jar里是字节码,是class文件。
Java虛拟机的类加载器会去加载class文件,类加载器怎么能够找到这些class文件呢?
classpath没有配置的情况下,默认从当前路径下加载.class文件。
classpath如果配置死了,例如: classpath=D: \jar,则表示固定只从D:\jar目录下找.class文件
classpath=. ;E:\Lab project\Jar\mysql-connector-java-8.0.23\mysql-connector-java-8.0.23.jar;
.代表当前路径。
以上的classpath什么意思?
类加载器从当前路径下加载class,如果当前路径下没找到,则去E:\Lab project\Jar\mysql-connector-java-8.0.23\mysql-connector-java-8.0.23.jar 找.class文件。
jar包需要解压吗?
不需要解压,java虛拟机的类加载器有这个能力找到class文件。
JDBC编程六步
-
导入驱动 jar 包
在 src 同级目录下创建 libs 文件夹,将数据库驱动 jar 包复制粘贴到该文件夹中,并且右键点击 libs文件夹(或刚被导入的 jar包) 添加到classpath(Add as library)
-
注册驱动
通知java程序我们即将要连接的是哪个类型的数据库 -
获取数据库连接
java进程和mysql进程,两个进程之间的通道开启了(java进程可能在北京,mysql进程在上海) -
获取数据库操作对象
这个对象很重要,用这个对象执行SQL的 -
执行SQL语句
执行CRUD操作 -
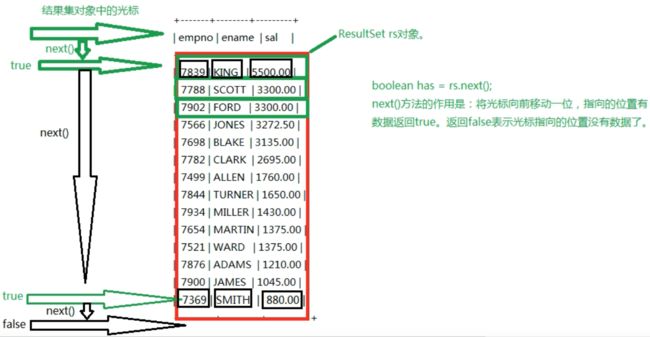
处理查询结果集
如果第四步是select语句,才有这个第五步 -
释放资源
关闭所有的资源(因为JDBC毕竟是进程之间的通信,占用很多资源的,需要关闭。
package jdbc;
import java.sql.*;
public class JDBC {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection connection = null;
Statement statement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
// 1.注册驱动
// 方式一:
/* com.mysql.jdbc.Driver是mysql数据库厂家写的,实现了java.sql.Driver接口
如果是 oracle数据库,类名是 oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver
Driver driver = new oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver */
// Driver driver = new com.mysql.jdbc.Driver();
// DriverManager.registerDriver(driver);
// 方式二: Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
try {
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 2.获取连接
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/joker";
String user = "root";
String password = "root";
connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url,user,password);
/* System.out.println(connection);
输出连接对象的内存地址:com.mysql.cj.jdbc.ConnectionImpl@7ba18f1b
com.mysql.cj.jdbc.ConnectionImpl类实现了java.sql.Connection接口。
实际上后续开发不需要关心地城具体时哪个对象,因为面向接口编程 */
// 3.获取数据库操作对象
statement = connection.createStatement();
/* 通过一个连接对象connection可以创建多个Statement对象
Statement statement1 = connection.createStatement() */
// 4.执行SQL语句
// JDBC中的sql语句不需要以";"结尾
/* DML(insert delete update)
* Statement接口中的executeUpdate方法专门来执行DML语句,
* 该方法返回值为sql语句影响的数据库表中的总记录条数
String sql = "delete from t_user where id = 1";
System.out.println(statement.executeUpdate(sql)); */
/* DQL(select)
* Statement接口中executeQuery方法用于执行查询语句,
* 返回值为ResultSet查询结果集对象 */
String sql = "select empno,ename,sal from emp order by sal desc";
resultSet = statement.executeQuery(sql);
// 5.处理查询结果集
//把查询结果输出
while (resultSet.next()){
/* 根据下标来取值,并且都是以String类型取出
String empno = resultSet.getString(1);
String ename = resultSet.getString(2);
String sal = resultSet.getString(3);
System.out.println(empno+","+ename+","+sal); */
/* 根据下标来取值,以特定类型取出
int empno = resultSet.getInt(1);
String ename = resultSet.getString(2);
double sal = resultSet.getDouble(3);
System.out.println(empno+","+ename+","+(sal+100)); */
/* 根据查询结果的列名取值
以后这种方式是常用的、健壮 */
int empno = resultSet.getInt("empno");//empno并不是字段的名称,是查询结果的列名
String ename = resultSet.getString("ename");
double sal = resultSet.getDouble("sal");
System.out.println(empno+","+ename+","+(sal+100));
}
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// 6.释放资源
/* 先释放 ResultSet,再释放 Statement,最后释放 Connection
分别进行 try...catch...处理 */
if (resultSet!=null){
try {
resultSet.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (statement!=null){
try {
statement.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (connection!=null){
try {
connection.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
注册驱动的第二种方式:类加载注册原理
package com.mysql.jdbc;
import java.sql.SQLException;
public class Driver extends com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver {
public Driver() throws SQLException {
}
static {
System.err.println("Loading class `com.mysql.jdbc.Driver'. This is deprecated. The new driver class is `com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver'. The driver is automatically registered via the SPI and manual loading of the driver class is generally unnecessary.");
}
}
什么是URL?
统一资源定位符
任何一个URL都包括:协议+IP地址+端口号port+资源名
- 协议:是一个提前规定好的数据传输格式。通信协议有很多: http、https…在传送数据之前,提前先商量好数据传送的格式。这样对方接收到数据之后,就会按照这个格式去解析,拿到有价值的数据。
- IP地址:网络当中定位某台计算机的。
- PORT端口号:定位这台计算机上某个服务的。
- 资源名:这个服务下的某个资源。
jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/joker
jdbc:mysql://:java程序和 mysql 通信的协议。
localhost:本机的IP地址,本机的IP地址还可以写出:127.0.0.1
3306:mysql数据库的端口号
joker:mysql数据库的名称
如果是oracle数据库的话:
oracle:jdbc:thin:@localhost:1521:joker
oracle:jdbc:thin:@:java程序和 oracle 通信的协议
localhost:本机的IP地址
1521: oracle 默认端口
joker: oracle 中的数据库的名称
处理查询结果集
JDBC中所有的下标都是从1开始的。
读取配置文件
# mysql connectivity configuration
driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/joker
user=root
password=root
# oracle connectivity configuration
#driver=com.mysql.jdbc.OracleDriver
#url=jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:joker
#user=root
#password=root
package jdbc;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.ResourceBundle;
/*
* 将连接数据库的可变化的4条信息写到配置文件中。
* 以后想要连接其他数据库的时候,可以直接修改配置文件,不用修改java程序。
* 4个信息: driver url user password
* */
public class JDBCproperties {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 资源绑定器
ResourceBundle bundle = ResourceBundle.getBundle("resources/dataBase");
// 通过属性配置文件获取信息
String driver = bundle.getString("driver");
String url = bundle.getString("url");
String user = bundle.getString("user");
String password = bundle.getString("password");
Connection connection = null;
Statement statement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
try {
Class.forName(driver);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url,user,password);
statement = connection.createStatement();
String sql = "select empno,ename,sal from emp order by sal desc";
resultSet = statement.executeQuery(sql);
while (resultSet.next()){
int empno = resultSet.getInt("empno");
String ename = resultSet.getString("ename");
double sal = resultSet.getDouble("sal");
System.out.println(empno+","+ename+","+(sal+100));
}
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (resultSet!=null){
try {
resultSet.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (statement!=null){
try {
statement.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (connection!=null){
try {
connection.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
SQL注入问题即解决办法
“随意”输入一个用户名和密码,登录成功,这种现象被称为SQL注入现象。
导致SQL注入的根本原因是什么?
导致SQL注入的根本原因是:用户不是一般的用户,用户是懂得程序的。输入的用户名信息以及密码信息中含有SQL语句的关键字,这个SQL语句的关键字和底层的SQL语句进行“字符串拼接”,导致原SQL语句的含义被扭曲了。最主要的原因是:用户提供的信息参与了SQL语句的编译。
主要因素是:这个程序是先进行的字符串的拼接,然后再进行SQL语旬的编译,正好被注入。
怎么避免SQL注入?
SQL注入的根本原因是:先进行了字符串的拼接,然后再进行的编译。
java.sql.Statement接口的特点:先进行字符串的拼接,然后再进行sql语句的编译。
优点:使用Statement可以进行sql语句的拼接。
缺点:因为拼接的存在,导致可能给不法分子机会。导致SQL 注入。
java.sql.PreparedStatement接口的特点:先进行SQL语句的编译,然后再进行sql语句的传值。
优点:避免SQL注入。
缺点:没有办法进行sql语句的拼接,只能给sql语句传值。
PreparedStatement预编译的数据库操作对象。
package jdbc;
import java.sql.*;
public class CheckUsernameAndPassword {
public static void main(String[] args) {
}
public static boolean checkUsernameAndPassword(String username,String password){
boolean canLogin = false; //默认登录失败
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
// 1.注册驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
// 2.获取连接
connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/joker","root","root");
// 3.获取预编译的数据库操作对象
String sql = "select * from t_user where user_name = ? and password = ?";
// 注意:一个问号?是一个占位符,一个占位符只能接收一个“值/数据”
// 占位符?两边不能有单引号。'?'这样是错误的。
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql); //此时会发送 sql 给DBMS,进行 sql 语句的编译
// 给占位符?传值
// JDBC 中所有下标都是从1开始的
// 怎么解决SQL注入的:即使用户信息中有sql关键字,但是不参加编译就没事
preparedStatement.setString(1,username);//1代表第1个问号 ?
preparedStatement.setString(2,password);//2代表第2个问号 ?
// 4.执行SQL
resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery();
//这个方法不需要将sql语句传递进去,不能是这样 resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery(sql);
// 5.处理查询结果集
if (resultSet.next()) canLogin = true;
} catch (ClassNotFoundException | SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if (resultSet!=null){
try {
resultSet.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (preparedStatement!=null){
try {
preparedStatement.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (connection!=null){
try {
connection.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
return canLogin;
}
}
Statement的使用场景
需求:用户在控制台上输入desc则降序,输入asc则升序
思考一下:这个应该选择Statement还是PreparedStatement呢?
选Statement,因为PreparedStatement只能传值,不能进行sql语句的拼接。
package jdbc;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class StatementUsing {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入desc或asc【desc表示降序,asc表示升序】:");
String orderKey = scanner.next();
Connection connection = null;
Statement statement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
// 1.注册驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
// 2.获取连接
connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/joker","root","root");
// 3.获取数据库操作对象
statement = connection.createStatement();
// 4.执行sql语句
String sql = "select ename,sal from emp order by sal "+orderKey;
resultSet = statement.executeQuery(sql);
// 5.处理查询结果集
while (resultSet.next()){
String ename = resultSet.getString("ename");
String sal = resultSet.getString("sal");
System.out.println(ename+","+sal);
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException|SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
// 6.关闭资源
if (resultSet!=null){
try {
resultSet.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (statement!=null){
try {
statement.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (connection!=null){
try {
connection.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
模糊查询
package jdbc;
import java.sql.*;
//使用PrepareStatement进行模糊查询
public class FuzzyQuery {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
// 1.注册驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
// 2.获取连接
connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/joker","root","root");
// 3.获取预编译的数据库操作对象(找出名字中含有o的)
//重点是占位符该怎么写
String sql = "select ename from emp where ename like ?";
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.setString(1,"%o%");
// 4.执行SQL语句
resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery();
while (resultSet.next()){
System.out.println(resultSet.getString("ename"));
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException | SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if (resultSet!=null){
try {
resultSet.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (preparedStatement!=null){
try {
preparedStatement.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (connection!=null){
try {
connection.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
也可以使用 PreparedStatement 完成数据库的增删改查(CRUD)。
JDBC事务
JDBC默认情况下支持自动提交:
什么叫做自动提交呢?
只要执行一条DML语句就自动提交一次。
在实际开发中必须将JDBC的自动提交机制关闭掉,改成手动提交。当一个完整的事务结束之后,再提交。
connection.setAutoCommit(false); 关闭自动提交机制
connection.commit(); 手动提交
connection.rollback; 手动回滚
package jdbc;
import java.sql.*;
/*
* JDBC默认情况下对事物是怎么处理的?
* 模拟一下银行账户转账操作,A账户向B账户转账10000元。
* 从A账户减去10000,向B账户加上10000,,
* 必须同时成功,或者同时失败。
* 转账需要执行两条update语句*/
public class JDBCTransaction {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
try {
// 1.注册驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
// 2.获取连接
connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/joker","root","root");
//开启事物:将自动提交机制关闭
connection.setAutoCommit(false);
// 3.获取预编译的数据库操作对象
//重点是占位符该怎么写
String sql = "update t_account set balance = ? where accountno = ?";
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
// 4.执行SQL语句
preparedStatement.setDouble(1,10000);
preparedStatement.setString(2,"A");
int count = preparedStatement.executeUpdate();//更新成功智慧表示更新1条,返回1
/*模拟异常
* String s = null;
* s.toString();
* */
preparedStatement.setDouble(1,10000);
preparedStatement.setString(2,"B");
count += preparedStatement.executeUpdate();//再次更新一条返回1
System.out.println(count==2?"转账成功":"转账失败");
//代码能够执行到此处,说明上面的代码没有出现任何异常,表示都成功了,手动提交事务结束。
connection.commit();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException | SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if (preparedStatement!=null){
//出现异常的话,为了保险起见,需要回滚。
try {
preparedStatement.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (connection!=null){
try {
connection.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
JDBC工具类
数据库工具类,便于JDBC的代码编写。
package jdbc;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.ResourceBundle;
//数据库工具类,便于JDBC的代码编写
public class JDBCUtil {
private JDBCUtil(){}
// 类加载时绑定属性资源文件
private static ResourceBundle bundle = ResourceBundle.getBundle("resources/dataBase");
// 注册驱动
static {
try {
Class.forName(bundle.getString("driver"));
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 获取数据库连接对象
* @return 连接对象
* @throws SQLException
*/
public static Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
String url = bundle.getString("url");
String user = bundle.getString("user");
String password = bundle.getString("password");
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url,user,password);
return connection;
}
/**
* 释放资源
* @param connection 连接对象
* @param statement 数据库操作对象
* @param resultSet 查询结果集
*/
public static void close(Connection connection, Statement statement, ResultSet resultSet){
if (resultSet != null){
try {
resultSet.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (statement!=null){
try {
statement.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (resultSet!=null){
try {
resultSet.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
工具类中的构造方法一般都是私有化的,为什么?
构造方法私有化是为了防止new对象,为什么要防止new对象?
因为工具类中的方法都是静态的,不需要new对象,直接使用“类名.方法名”的方式调用。
package jdbc;
import java.sql.*;
//使用PrepareStatement进行模糊查询
public class FuzzyQuery {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
// 1.注册驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
// 2.获取连接
connection = JDBCUtil.getConnection();
// 3.获取预编译的数据库操作对象(找出名字中含有o的)
//重点是占位符该怎么写
String sql = "select ename from emp where ename like ?";
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.setString(1,"%o%");
// 4.执行SQL语句
resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery();
while (resultSet.next()){
System.out.println(resultSet.getString("ename"));
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException | SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
// 6.释放资源
JDBCUtil.close(connection,preparedStatement,resultSet);
//如果没有结果集对象,调用这个方法的时候第三个参数传入null
//JDBCUtil.close(connection,preparedStatement,null);
}
}
}
锁
行级锁for update
关于DQL语句的悲观锁?
对于一个DQL语句来说,末尾是可以添加这样一个关键字的:for update
select ename,sal from emp where job = 'MANAGER' for update;
以上SQL语句的含义是:在本次事务的执行过程当中,job= ! MANAGER’的记录被查询,这些记录在我查询的过程中,任何人,任何事务都不能对这些记录进行修改操作。直到我当前事务结束。这种机制被称为:行级锁机制(又称悲观锁)。
在mysql中是这样的:
当使用select...where... for update...时,mysq进行row lock还是table lock只取决于是否能使用索引(例如主键,unique字段),能则为行锁,否则为表锁;未查到数据则无锁。而使用’<>’ , 'like’等操作时,索引会失效,自然进行的是table lock。
所以慎用for update
整个表锁住的时候会导致性能降低,谨慎使用。
使用for update的时候,最好是锁主键值,或者具有unique约束的字段,锁别的字段可能会导致整个表锁住。
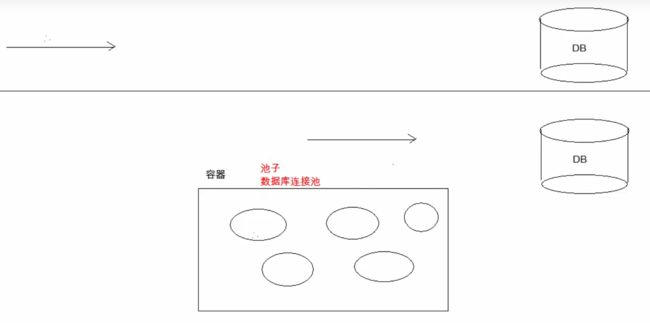
数据库连接池
概念:其实就是一个容器(集合),存放数据库连接的容器。
当系统初始化好后,容器被创建,容器中会申请一些连接对象,当用户来访问数据库时,从容器中获取连接对象,用户访问完之后,会将连接对象归还给容器。
好处:
- 节约资源
- 用户访问高效
实现:
-
标准接口:
DataSource javax.sql包下
方法:-
获取连接:
getConnection() -
归还连接:
Connection.close()如果连接对象Connection是从连接池中获取的,那么调用
Connection.close()方法,则不会再关闭连接
了,而是归还连接。
-
-
一般我们不去实现它,有数据库厂商来实现
- C3P0:数据库连接池技术
- Druid:数据库连接池实现技术(由阿里巴巴提供的)
数据库连接池的具体实现技术
C3P0
步骤:
-
导入jar包(两个) c3p0-0.9.5.2.jar mchange-commons-java-0.2.12.jar
不要忘记导入数据库驱动jar包
-
定义配置文件:
名称:c3p0.properties 或者 c3p0-config.xml
路径:直接将文件放在src目录下即可 -
创建核心对象数据库连接池对象
ComboPooledDataSource -
获取连接: getConnection
Druid
-
步骤:
- 导入jar包druid-1.0.9.jar
- 定义配置文件:
- 是properties形式的
- 可以叫任意名称,可以放在任意目录下
- 加载配置文件:Properties
- 获取数据库连接池对象:通过工厂来来获取
DruidDatasourceFactory - 获取连接:getConnection
driverClassName=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver #连接本机的路径时主机名和端口号可以不写 url=jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/joker username=root password=root #初始化连接数 initialSize=5 #最大连接数 maxActive=10 #最大等待时间(超时时间)单位(ms):若等待时间超过规定的时间,控制台会抛出异常 maxWait=3000若创建的为 JavaEE 项目需要将 properties文件存放在 resources文件夹下
public class DruidDemo { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { //1.导入jar包 //2.定义配置文件 //3.加载配置文件 Properties properties = new Properties(); InputStream resourceAsStream = DruidDemo.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("druid.properties"); properties.load(resourceAsStream); //4.获取连接池对象 DataSource dataSource = DruidDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(properties); //5.获取连接 Connection connection = dataSource.getConnection(); System.out.println(connection); } } -
定义工具类
- 定义一个类 JDBCUtils
- 提供静态代码块加载配置文件,初始化连接池对象
- 提供方法
- 获取连接方法:通过数据库连接池获取连接
- 释放资源
- 获取连接池的方法
public class JDBCUtils { //1.定义成员变量 DataSource private static DataSource dataSource; static { try { //1.加载配置文件 Properties properties = new Properties(); properties.load(JDBCUtils.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("druid.properties")); //2.获取DataSource dataSource = DruidDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(properties); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } /** * 获取连接对象 * * @return 连接对象 * @throws SQLException */ public static Connection getConnection() throws SQLException { return dataSource.getConnection(); } public static void close(Statement statement, Connection connection) { if (statement != null) { try { statement.close(); } catch (SQLException throwables) { throwables.printStackTrace(); } } if (connection != null) { try { connection.close(); } catch (SQLException throwables) { throwables.printStackTrace(); } } } /** * 释放资源 * * @param resultSet 待关闭的数据查询结果集 * @param statement 待关闭的数据库执行对象 * @param connection 待归还的数据库连接对象 */ public static void close(ResultSet resultSet, Statement statement, Connection connection) { if (resultSet != null) { try { resultSet.close(); } catch (SQLException throwables) { throwables.printStackTrace(); } } close(statement, connection); } /** * 获取数据库连接池对象 * @return 数据库连接池对象 */ public static DataSource getDataSource(){ return dataSource; } }public class DruidUtilsTest { public static void main(String[] args){ Connection connection=null; PreparedStatement preparedStatement=null; try { //1.获取连接 connection = JDBCUtils.getConnection(); //2.定义sql String sql = "insert into sign_up_check values(?,?)"; //3.获取 PreparedStatement 对象 preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql); //4.给 ? 赋值 preparedStatement.setString(1,"Flow"); preparedStatement.setString(2,"Joker"); //5.执行sql int count = preparedStatement.executeUpdate(); System.out.println(count); }catch (SQLException throwables) { throwables.printStackTrace(); }finally { //6.释放资源 JDBCUtils.close(preparedStatement,connection); } } }测试数据库连接池最大连接数量和连接超时时间
public class JDBCUtils { public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException { for (int i = 0; i < 12; i++) { Connection connection = dataSource.getConnection(); System.out.println(i+":"+connection); if (i==5){ connection.close();//归还到连接池中 } } } //... }输出结果: 0:com.mysql.cj.jdbc.ConnectionImpl@1d548a08 ... 4:com.mysql.cj.jdbc.ConnectionImpl@50a7bc6e 5:com.mysql.cj.jdbc.ConnectionImpl@161b062a 6:com.mysql.cj.jdbc.ConnectionImpl@161b062a //归还后立即又被获取 7:com.mysql.cj.jdbc.ConnectionImpl@17c1bced ... 10:com.mysql.cj.jdbc.ConnectionImpl@e50a6f6超出最大连接数量时,当调用获取连接方法不能获取到对象且超过最大连接时间会抛出异常:
Exception in thread “main” com.alibaba.druid.pool.GetConnectionTimeoutException: wait millis 3001, active 10, maxActive 10, creating 0
JDBCTemplate
Spring JDBC
Spring框架对 JDBC 的简单封装。提供了一 个JDBCTemplate对象简化 JDBC 的开发。
步骤:
-
导入jar包
-
创建JdbcTemplate对象,依赖于数据源DataSource。
JdbcTemplate template = new JdbcTemplate(ds); -
调用 JdbcTemplate 的方 法来完成 CRUD 的操作
-
update():执行DML语句。增、删、改语句 -
queryForMap():查询结果将结果集封装为Map集合(将列名作为key、将值作为value、将这条记录封装为一个Map集合)注意:这个方法查询的结果集长度只能是1
-
queryForlist():查询结果将结果集封装为List集合注意:将每一条记录封装为一个Map集合,再将Map集合装载到List集合中
-
query(): 查询结果,将结果封装为JavaBean对象query的参数:
RowMapper接口
一般我们使用BeanPropertyRowMapper实现类。可以完成数据到JavaBean的自动封装。
new BeanPropertyRowMapper<类型> (类型.class) -
queryForobject:查询结果,将结果封装为对象一般用于聚合函数的查询
-
public class JDBCTemplateDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.导入jar包
//2.创建JDBCTemplate对象
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate = new JdbcTemplate(JDBCUtils.getDataSource());
//3.调用方法
String sql = "update sign_up_check set password = 'Anonymous' where username = ?";
int count = jdbcTemplate.update(sql, "Flow");
System.out.println(count);
}
}
JDBCTemplate 内部封装的获取数据库连接对象、获取数据库操作对象、关闭数据库连接对象及数据库操作对象等操作。
相关方法的运用实例
public class Employee {/* 将属性的类型改变为 对象类型(例如:Integer、Double)对于数据库查询操作比较好
否则,可能出现数据库中元组中某些字段没有非空约束,字段值为NULL而不能转换为基本类型,
导致异常抛出 */
private int id;
private String name;
private double salary;
public Employee() {
}
public Employee(int id, String name, double salary) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.salary = salary;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public double getSalary() {
return salary;
}
public void setSalary(double salary) {
this.salary = salary;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Employee{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", salary=" + salary +
'}';
}
}
public class JDBCTemplateEmp {
//导入jar包
//获取JDBCTemplate对象
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate = new JdbcTemplate(JDBCUtils.getDataSource());
public static void main(String[] args) {
}
@Test//更新薪资
public void updateSalary(){
//定义sql
String sql = "update emp_salary set salary = 10000 where id = 1";
//执行sql
int count = jdbcTemplate.update(sql);
System.out.println(count);
}
@Test//添加成员信息
public void addEmp(){
String sql = "insert into emp_salary(id,name,salary) values(4,?,60000)";
int count = jdbcTemplate.update(sql,"Druid");
System.out.println(count);
}
@Test//删除成员信息
public void removeEmp(){
String sql = "delete from emp_salary where id = 3";
int count = jdbcTemplate.update(sql);
System.out.println(count);
}
@Test/* 查询记录,并将查询结果封装成Map集合
注意:这个方法查询的结果集长度只能是1 */
public void getMapByQuery(){
String sql = "select * from emp_salary where id = 1";
Map<String, Object> stringObjectMap = jdbcTemplate.queryForMap(sql);
System.out.println(stringObjectMap);//{id=1, name=Flow, salary=10000.00}
}
@Test//查询记录,并将查询结果封装成List集合
public void getListByQuery(){
String sql = "select * from emp_salary";
List<Map<String, Object>> maps = jdbcTemplate.queryForList(sql);
for (Map<String, Object> map: maps) {
System.out.println(map);
}
}
@Test//查询所有集合将其封装为Employee对象的List集合
public void getBeanMapByQuery(){
String sql = "select * from emp_salary";
/*List empList = jdbcTemplate.query(sql, new RowMapper() {//自己实现接口
@Override
public Employee mapRow(ResultSet resultSet, int i) throws SQLException {
int id = resultSet.getInt("id");
String name = resultSet.getString("name");
double salary = resultSet.getDouble("salary");
return new Employee(id, name, salary);
}
});*/
List<Employee> empList = jdbcTemplate.query(sql, new BeanPropertyRowMapper<>(Employee.class));
/* 这种方式,需要生成List集合的对象实现默认的构造方法,否则会抛出异常:
org.springframework.beans.BeanInstantiationException: Failed to instantiate [com.example.domain.Employee]:
No default constructor found; nested exception is java.lang.NoSuchMethodException: com.example.domain.Employee.() */
for (Employee emp:empList) {
System.out.println(emp);
}
}
@Test//查询总记录数
public void queryTotalRecordNum(){
String sql = "select count(id) from emp_salary";
Long total = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql,Long.class);
System.out.println(total);
}
}
数据库连接池学习笔记(一):原理介绍+常用连接池介绍
几种常用的数据库连接池的使用
(重点)MySQL(入门篇22)JDBC下载和驱动教程 ,第一个JDBC程序,驱动步骤的解析。
学JDBC,这一篇就够了
jdbctemplate jar包下载